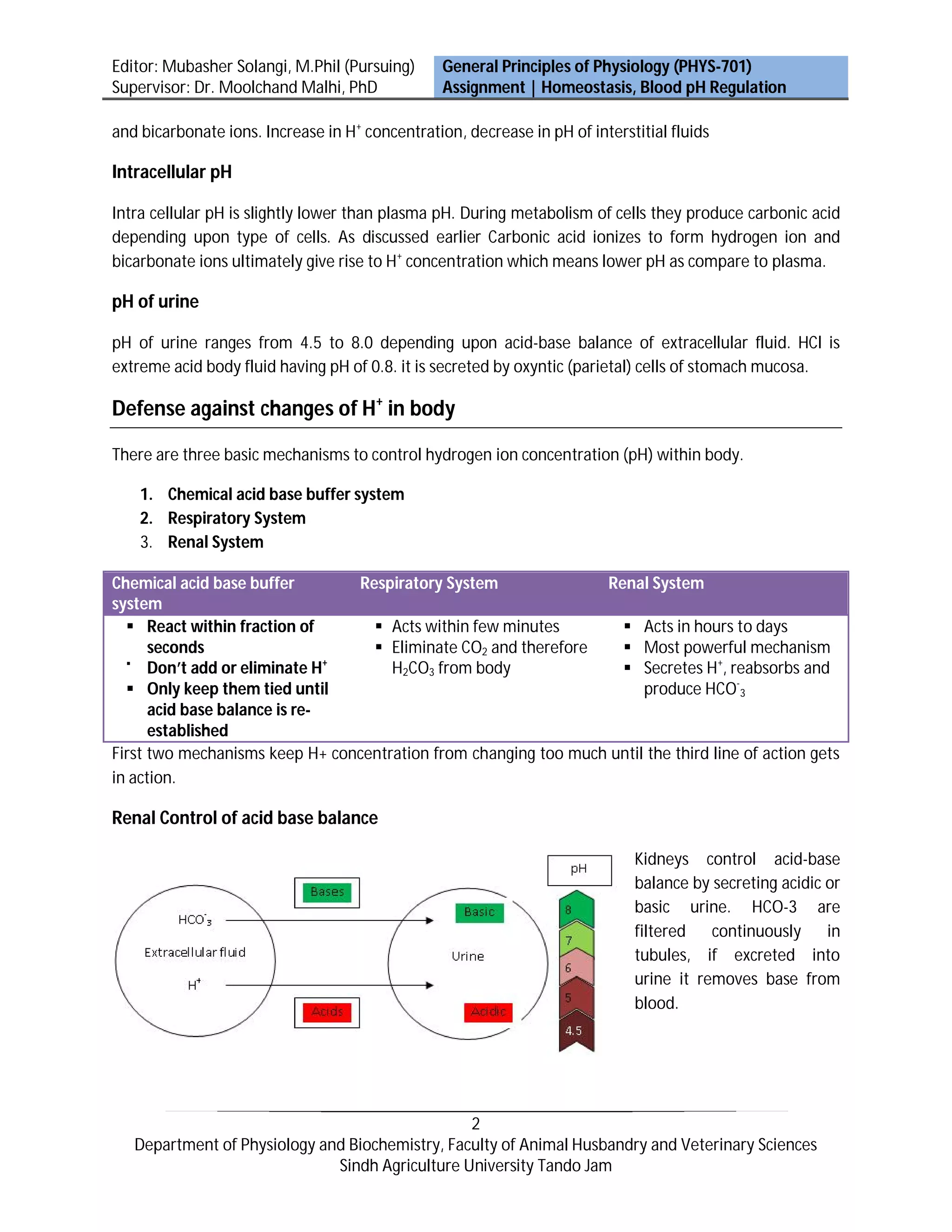
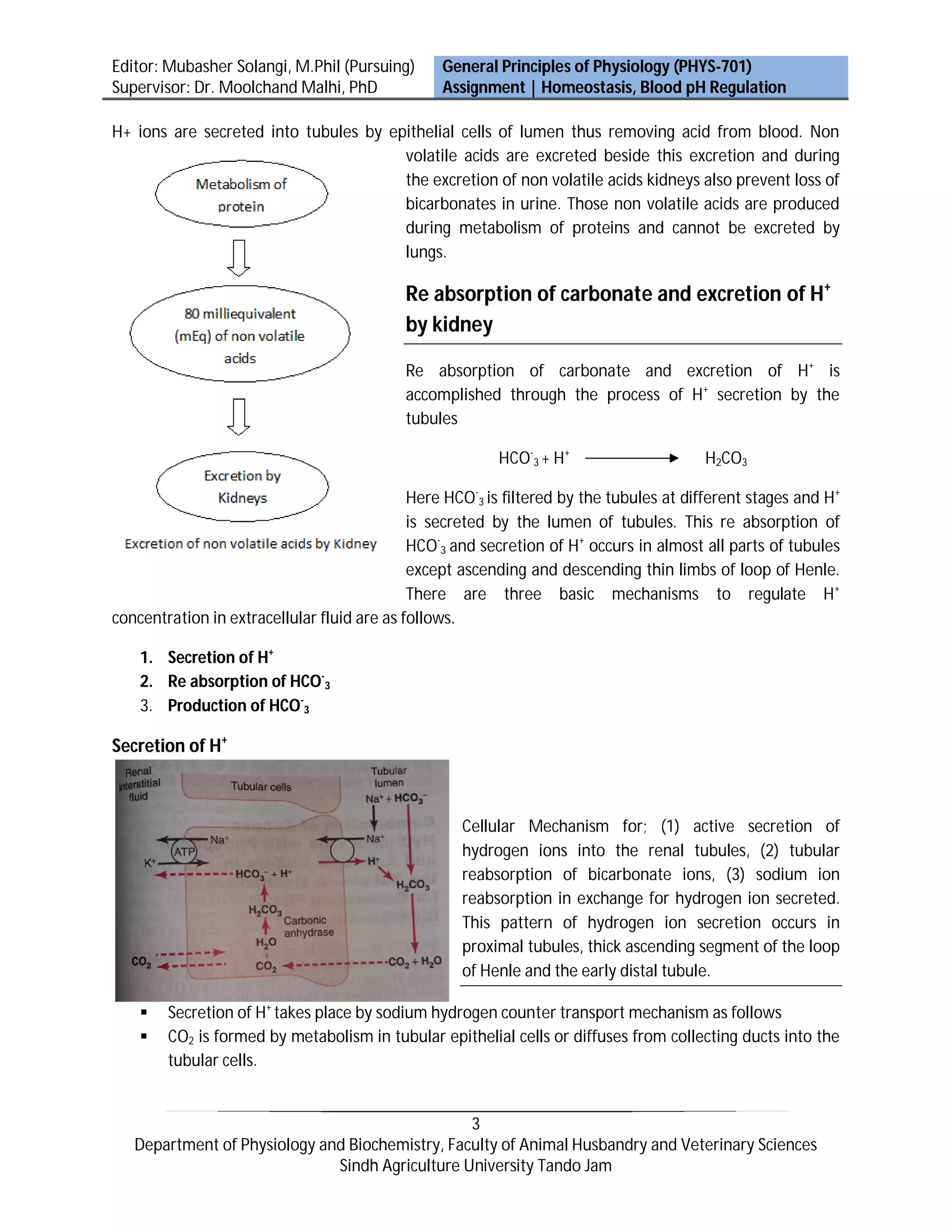
Activities of almost all enzyme systems within the body are influenced by hydrogen ion (H+) concentration. Substances that release H+ are acids and substances that tend to receive H+ are bases. The kidneys control acid-base balance by secreting acidic or basic urine. HCO-3 is continuously filtered in tubules - if excreted into urine, it removes base from the blood. There are three main mechanisms to regulate H+ concentration in the body: chemical buffers, the respiratory system, and the renal system. The kidneys play the most important role by secreting H+ into tubules, reabsorbing HCO-3, and producing new HCO-3.