This document discusses water, electrolyte, and pH balance in the human body. It contains the following key points:
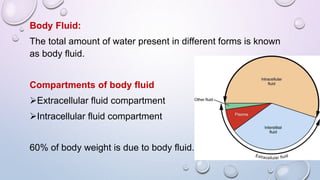
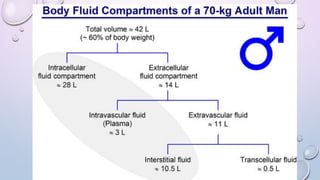
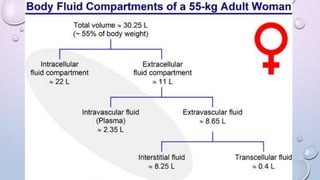
- 60% of body weight is composed of body fluid, which is divided into intracellular and extracellular compartments. Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and chloride are important components of body fluids.
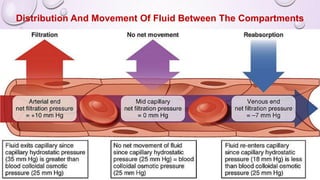
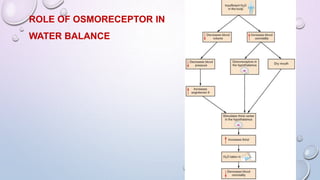
- The body maintains water and electrolyte balance through mechanisms like osmoreception, thirst, ADH release, and kidney regulation of reabsorption and excretion.
- The body also maintains acid-base balance through buffer systems like bicarbonate, phosphate, and proteins. Chemical buffers, the lungs, and kidneys all work to regulate pH levels and compensate for acidosis or alk