Embed presentation
Downloaded 71 times




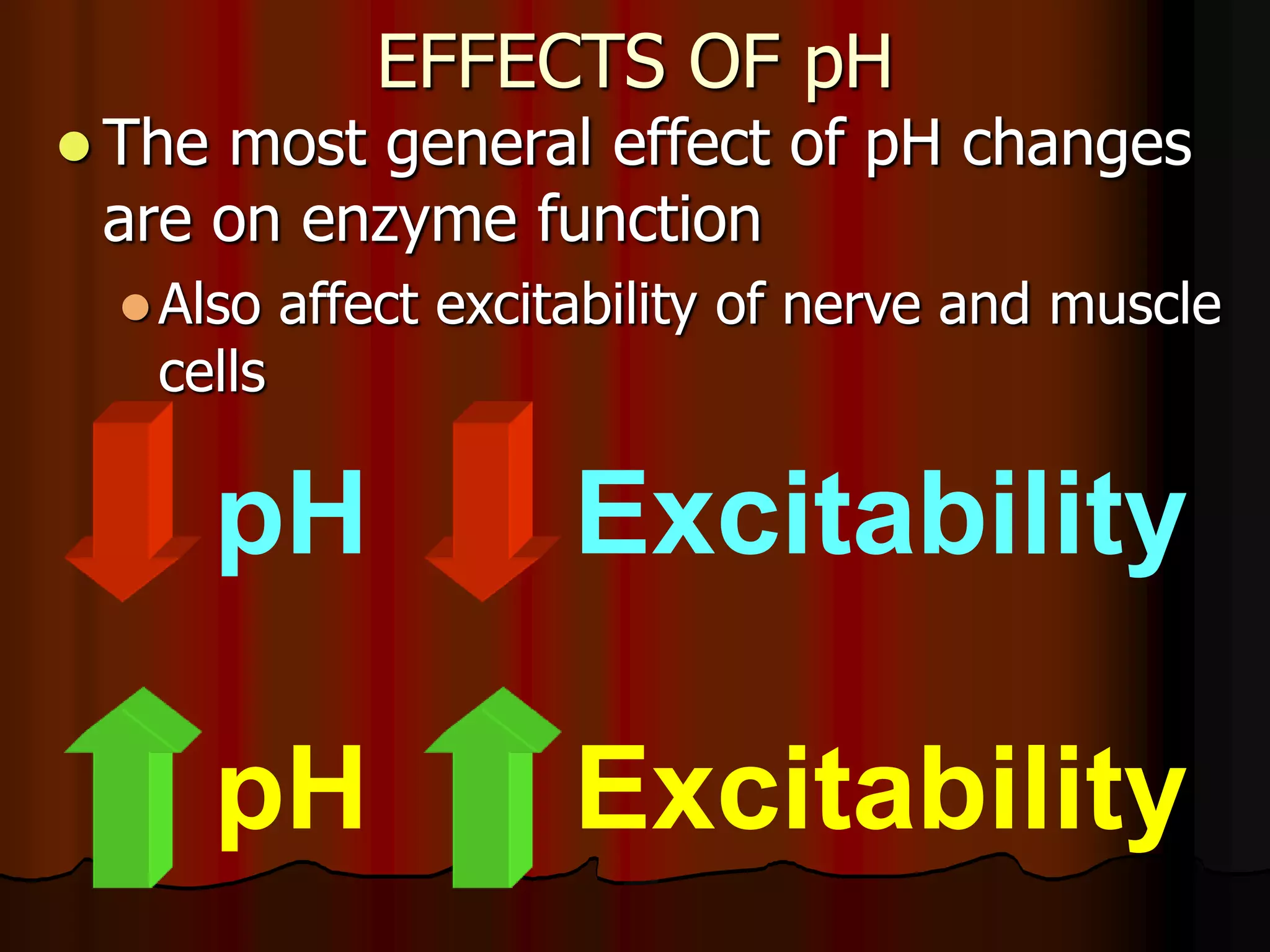

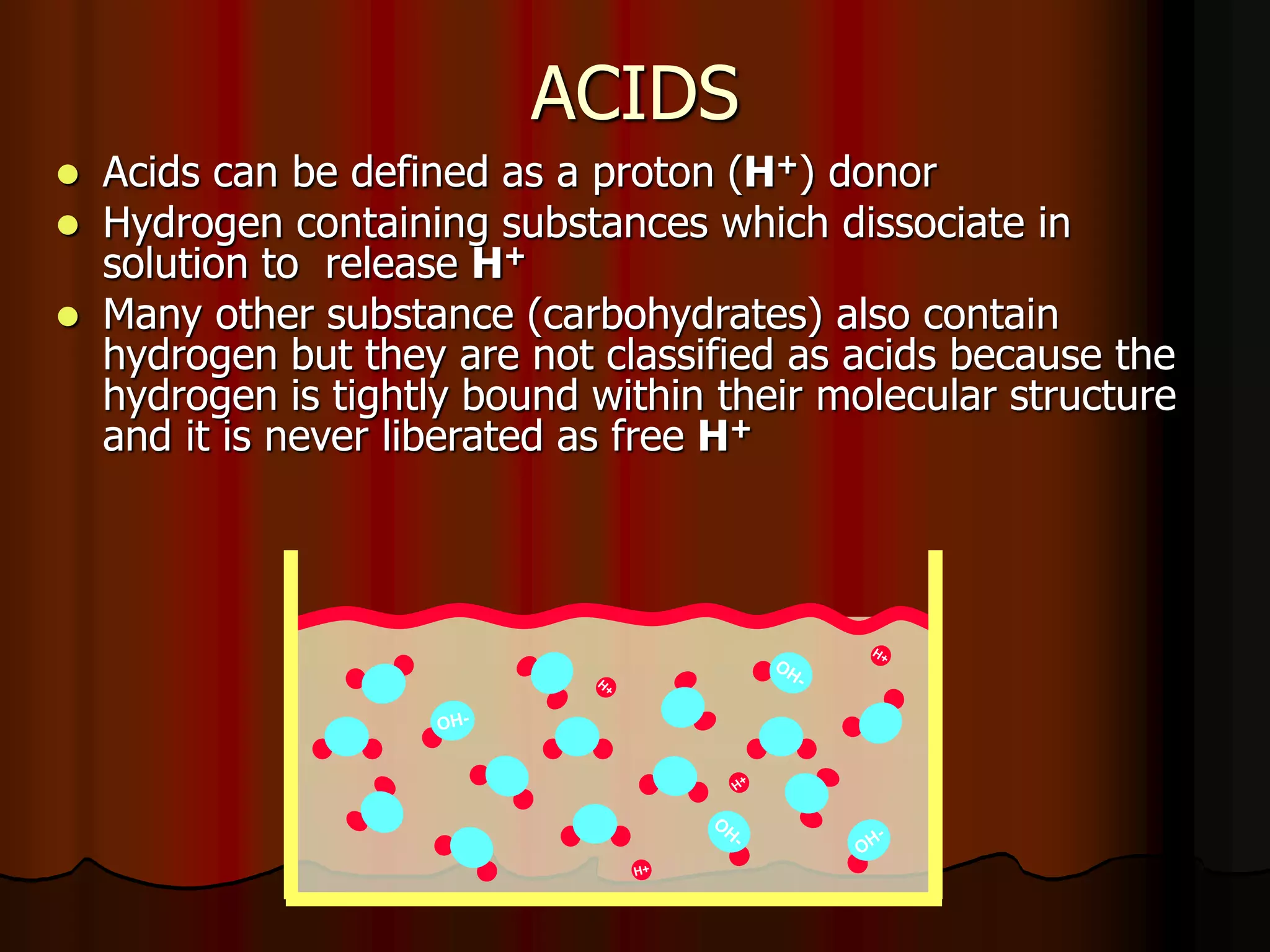
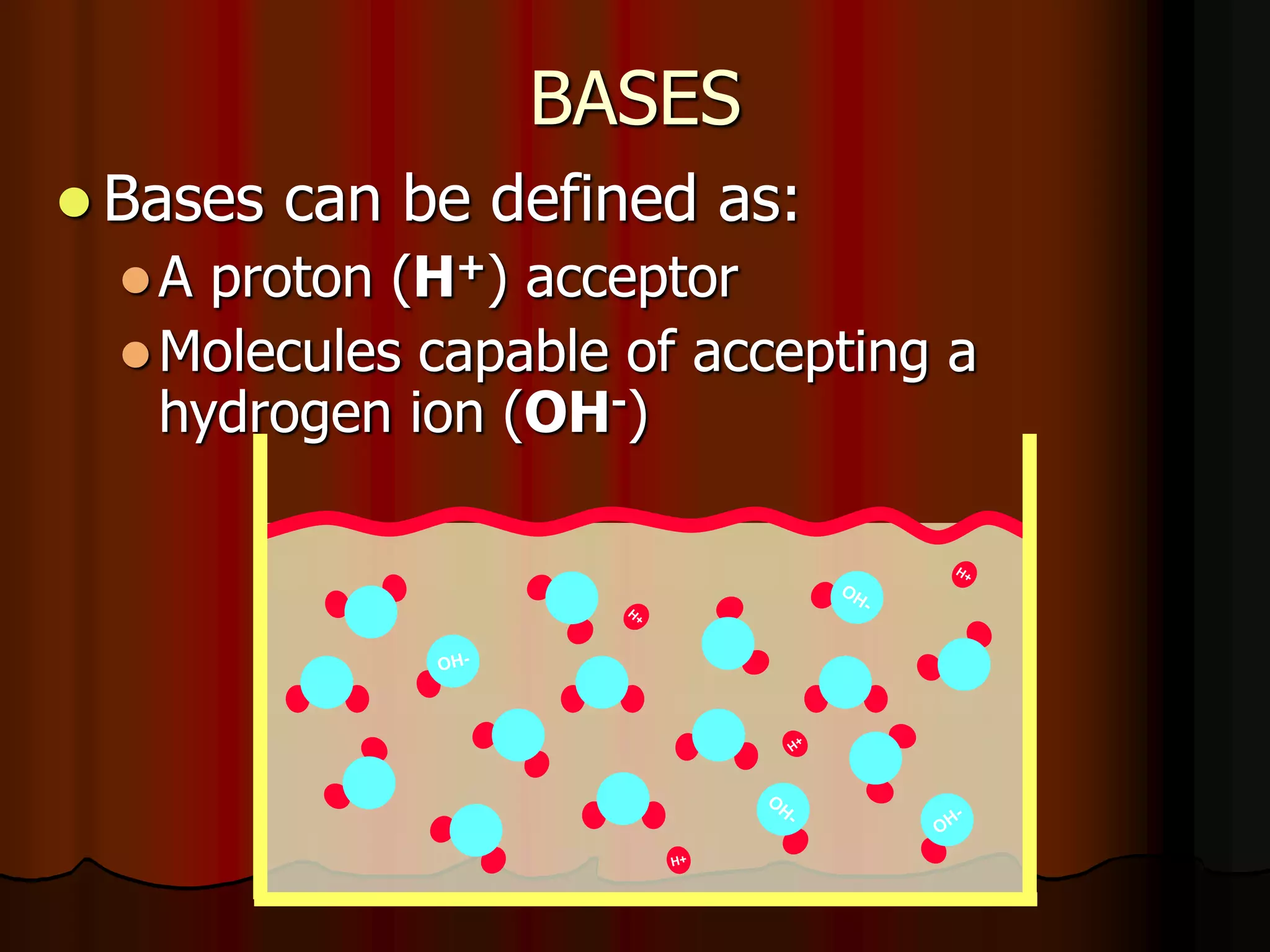
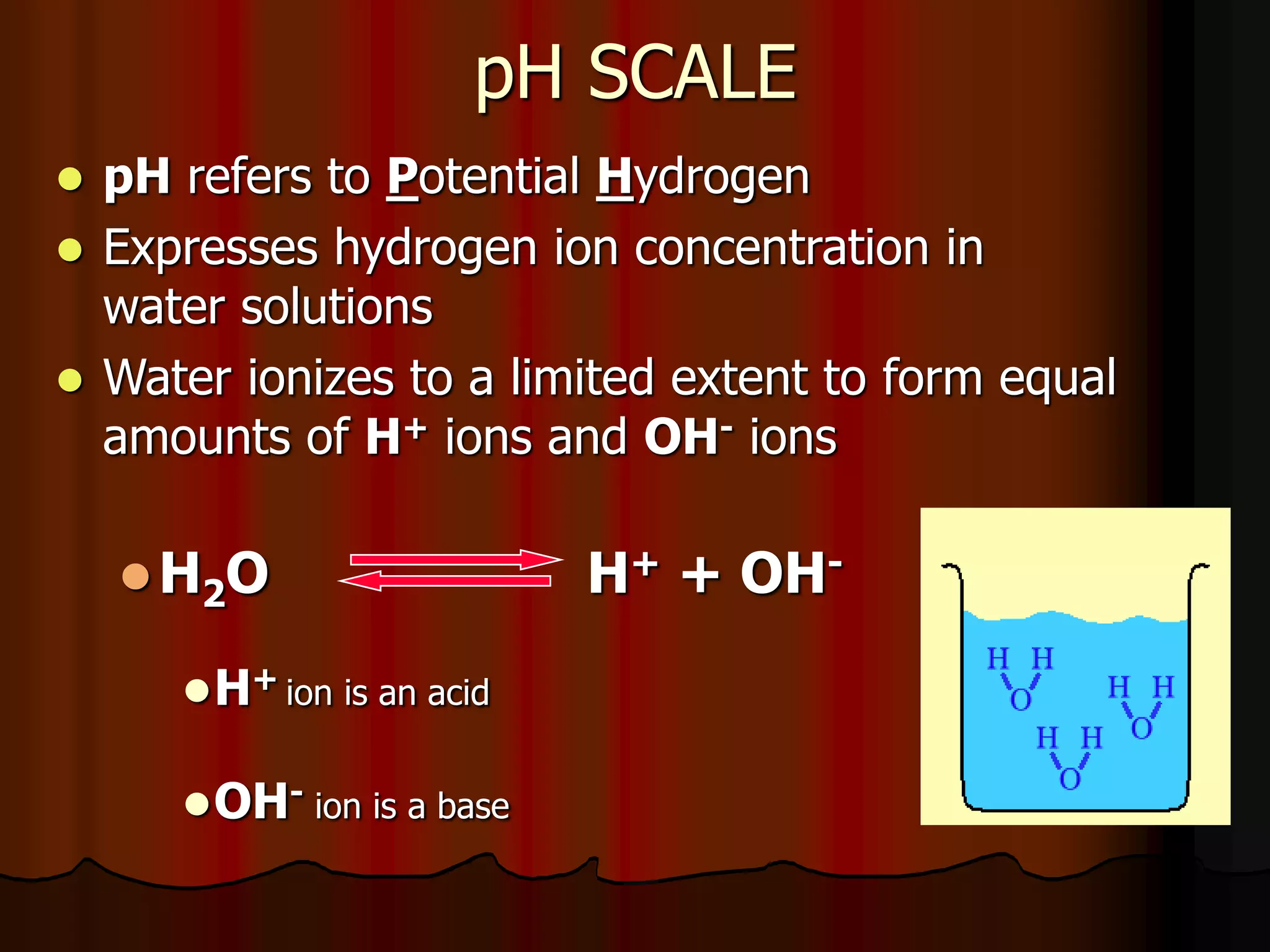


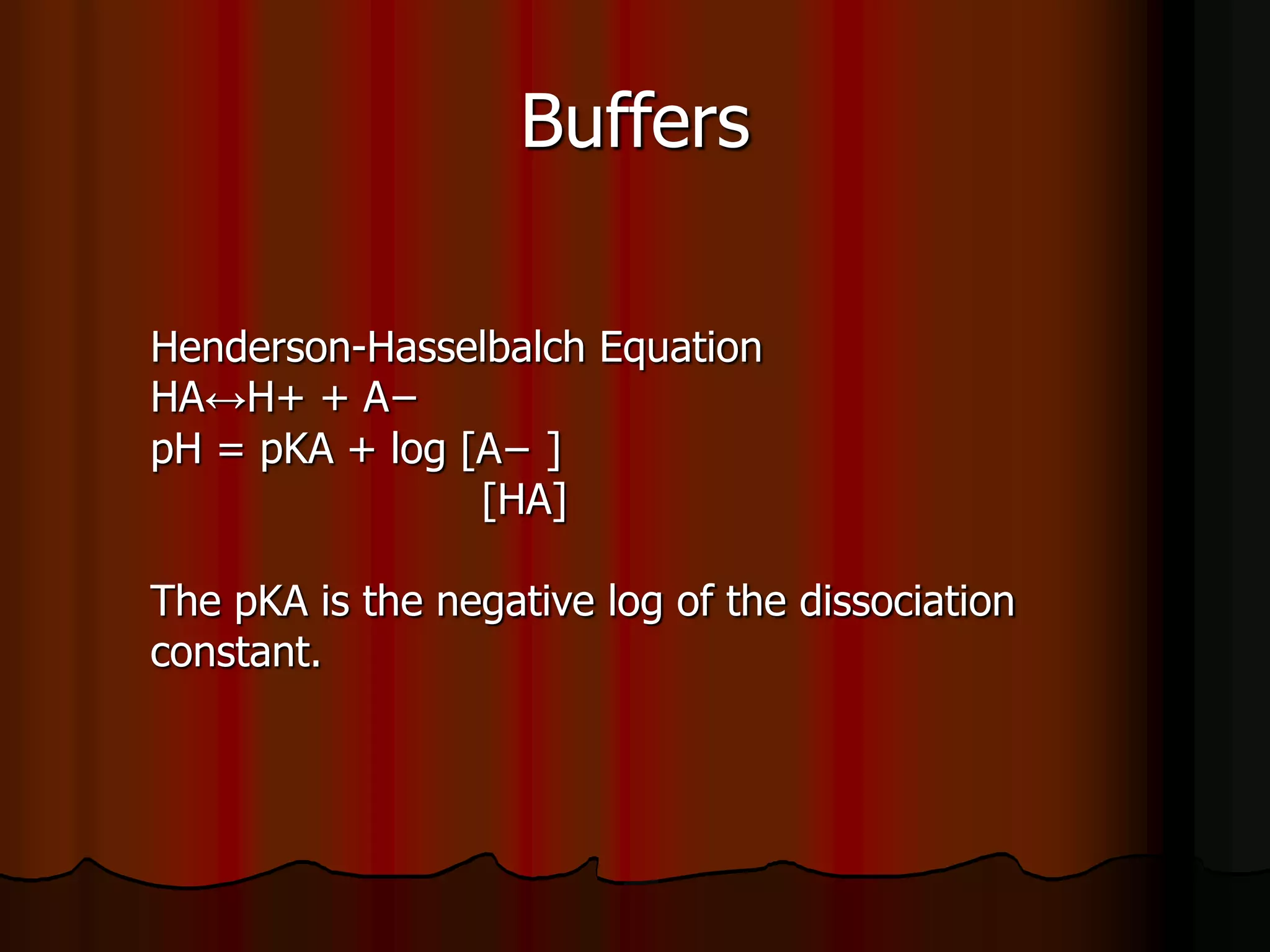


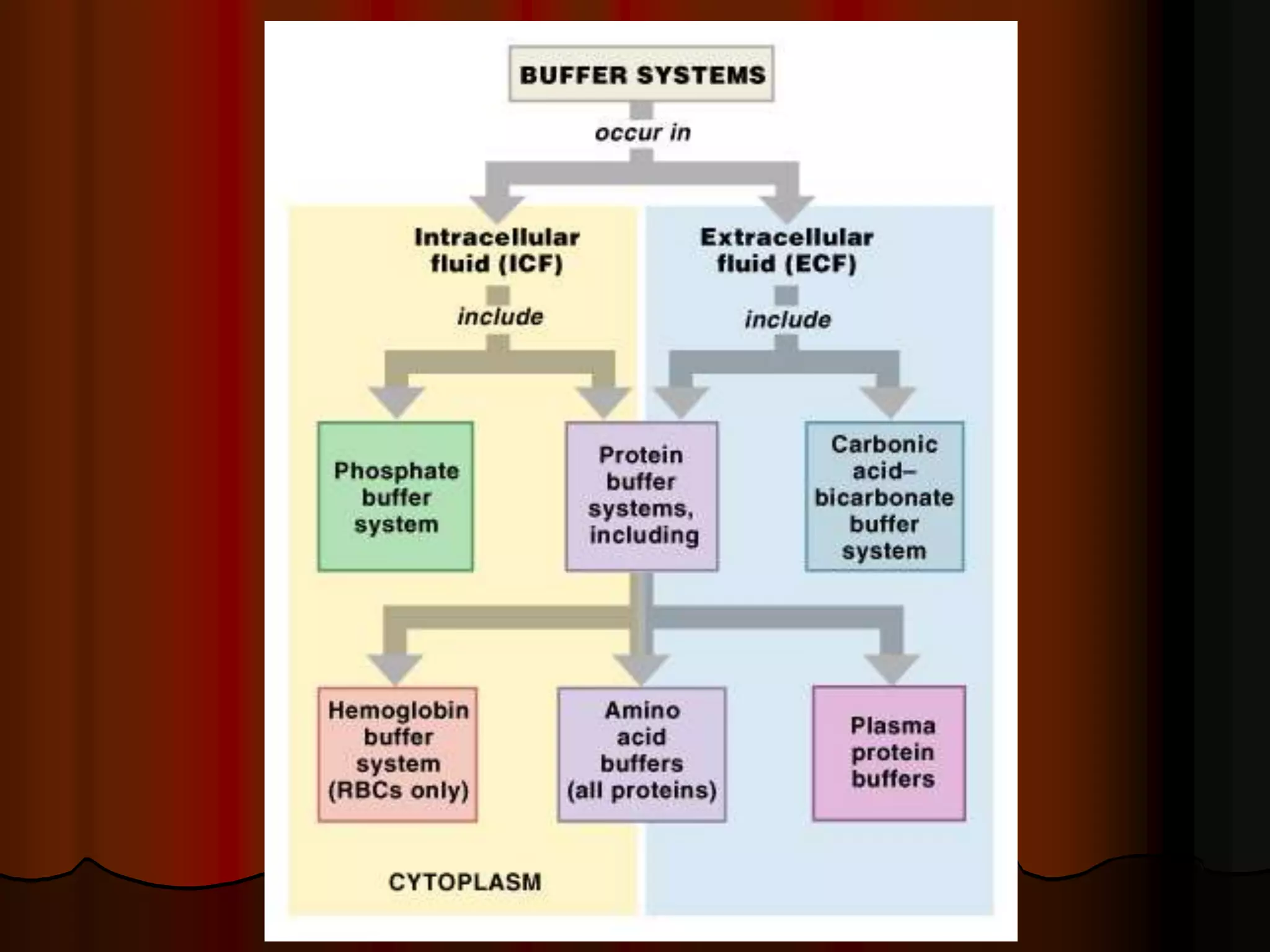
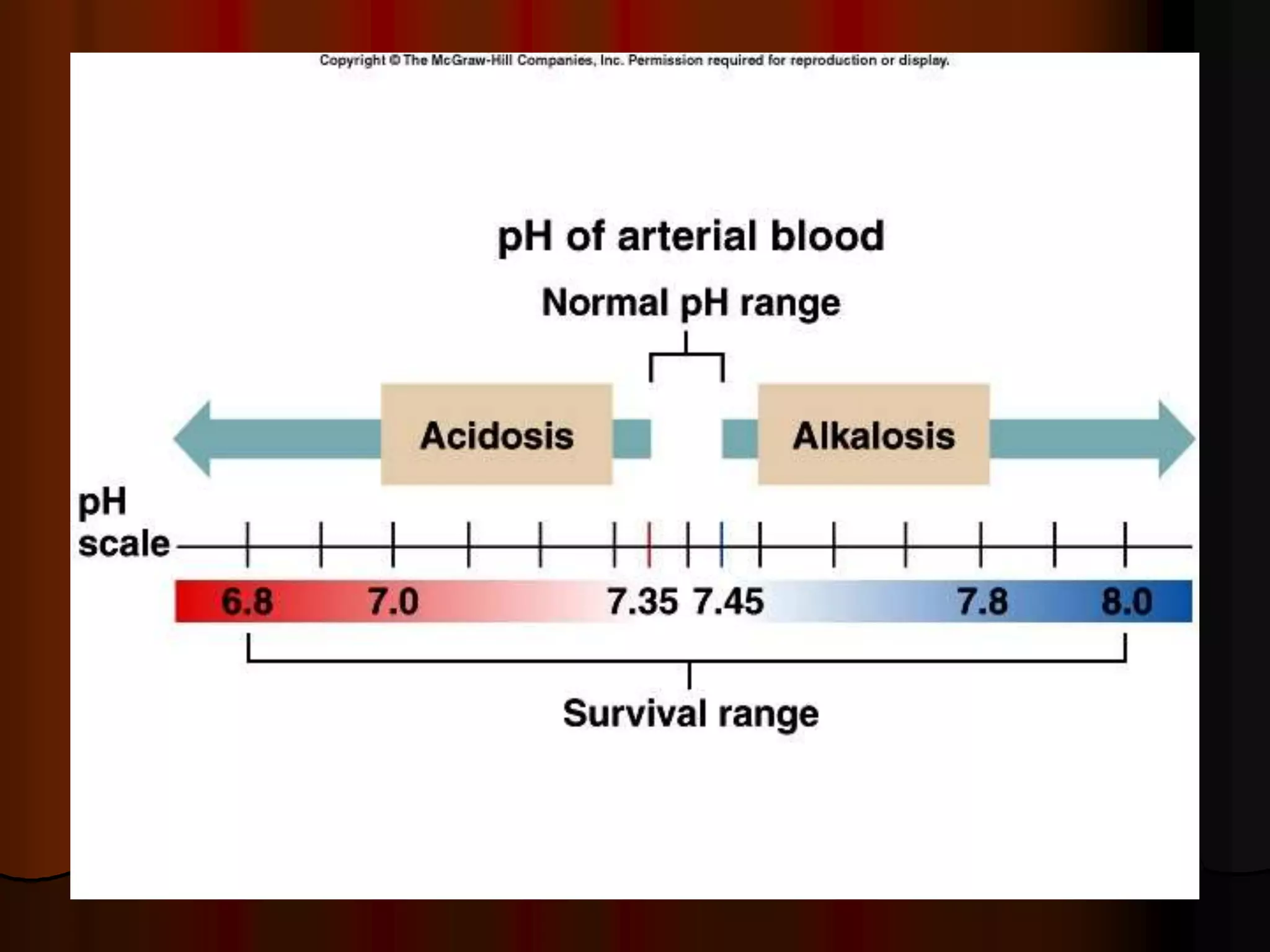
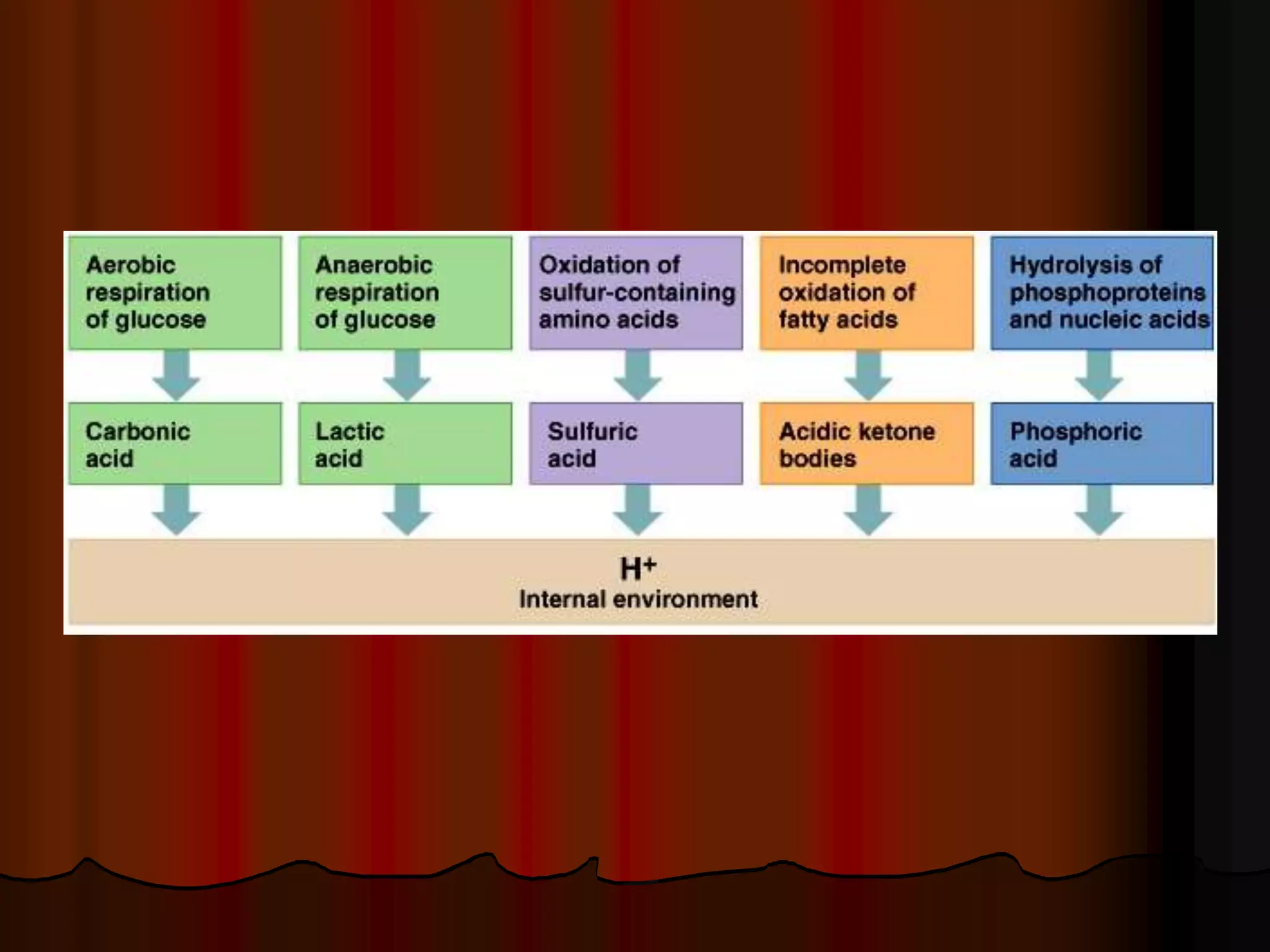
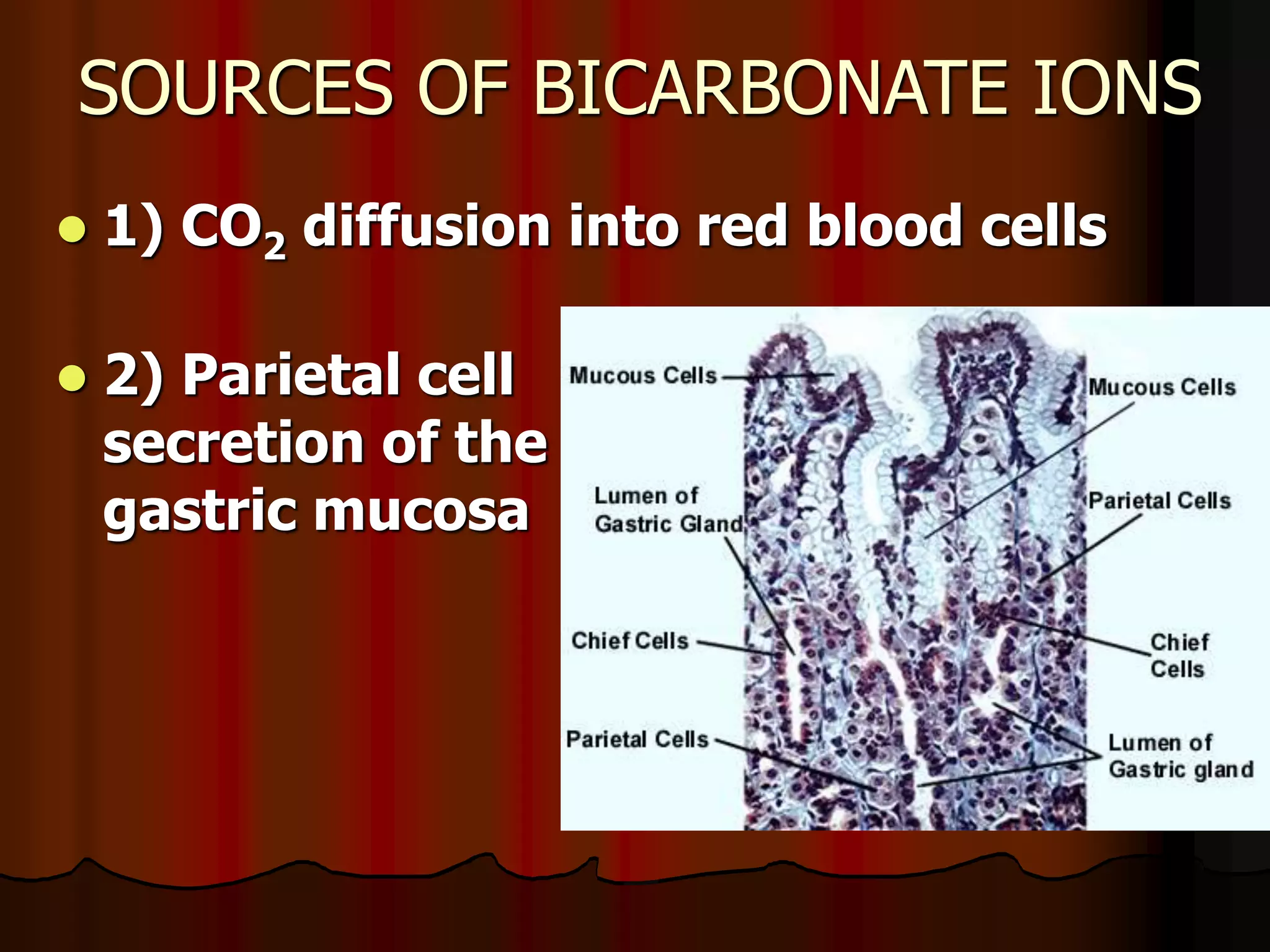
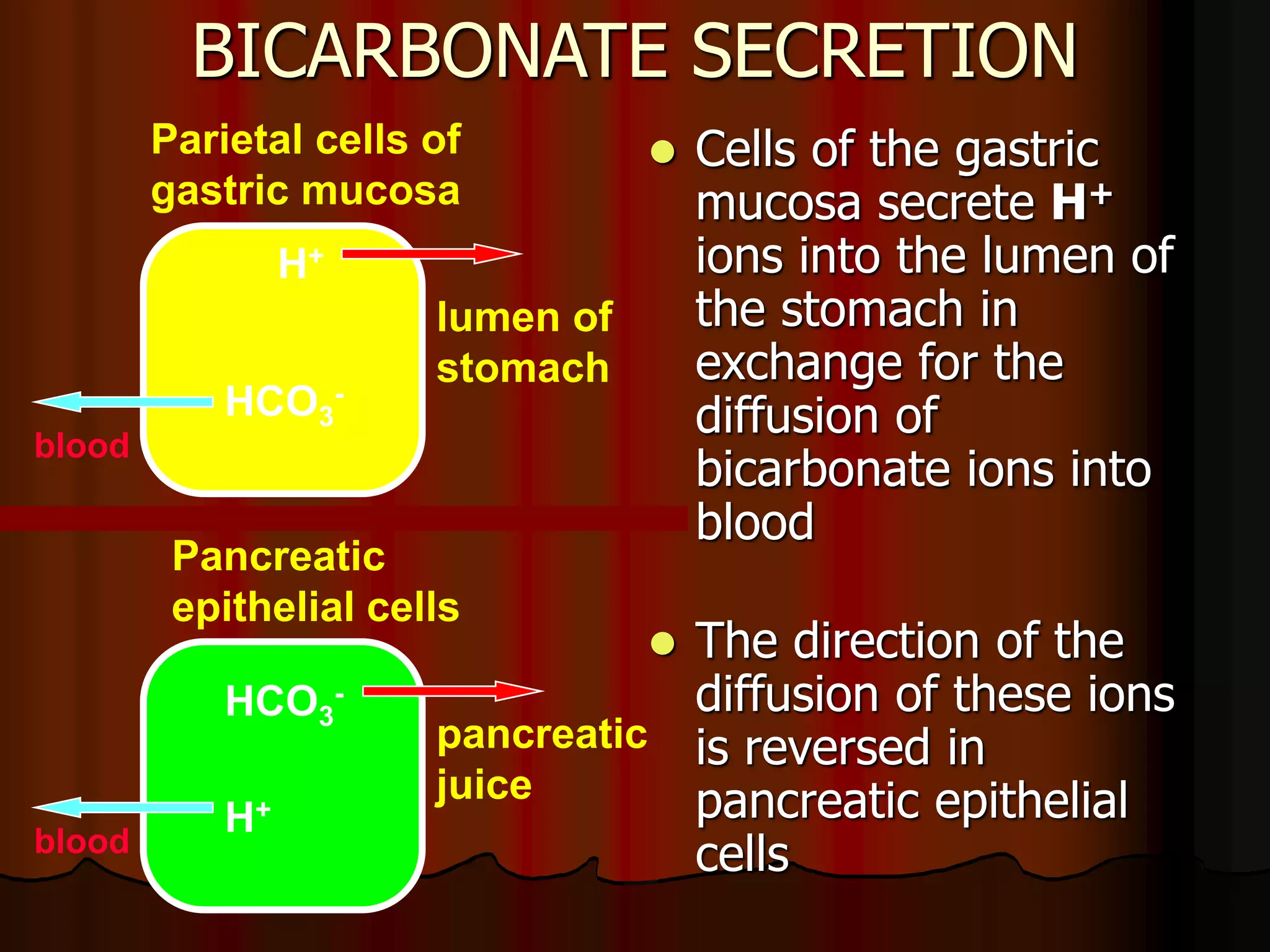

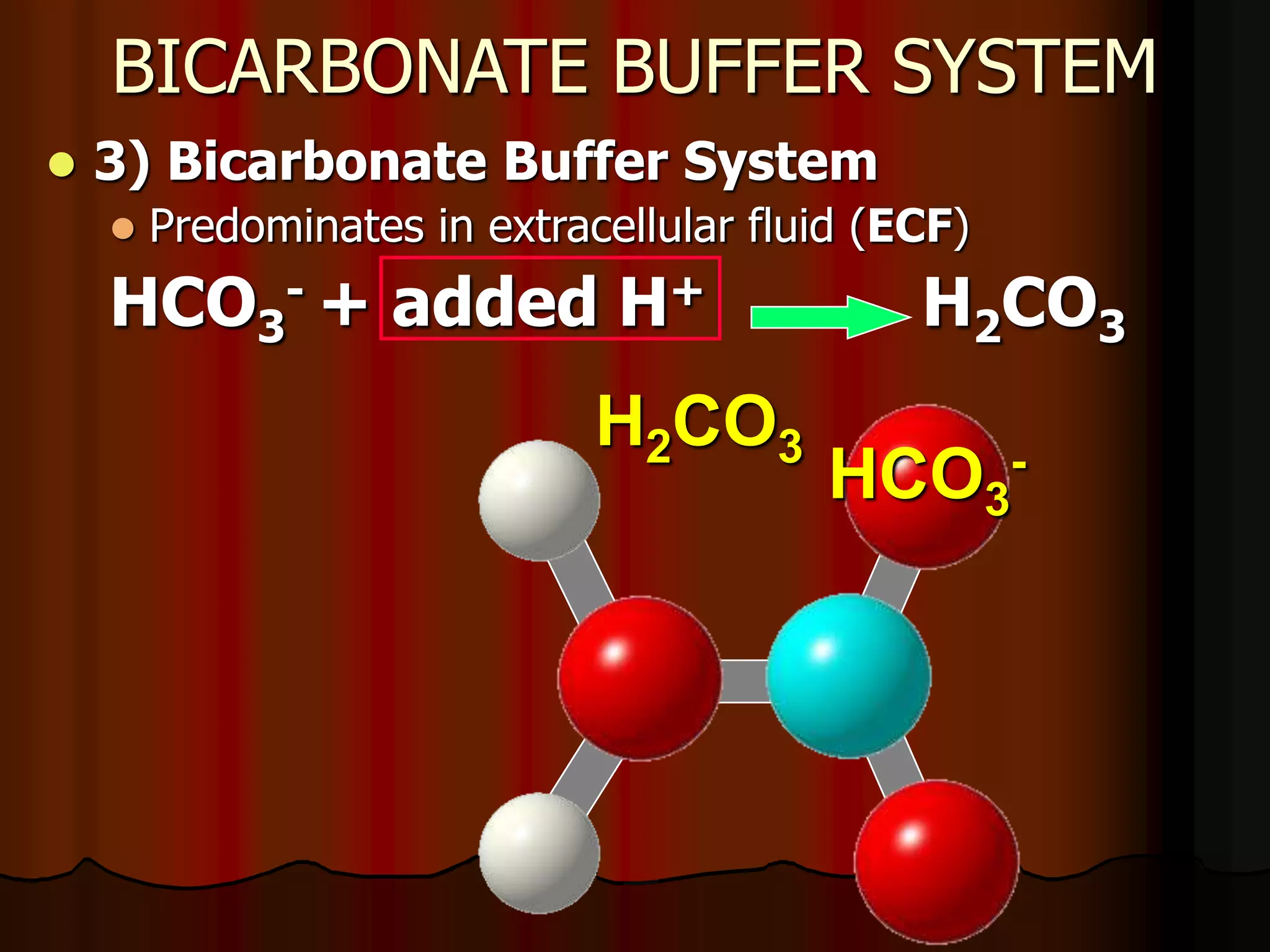





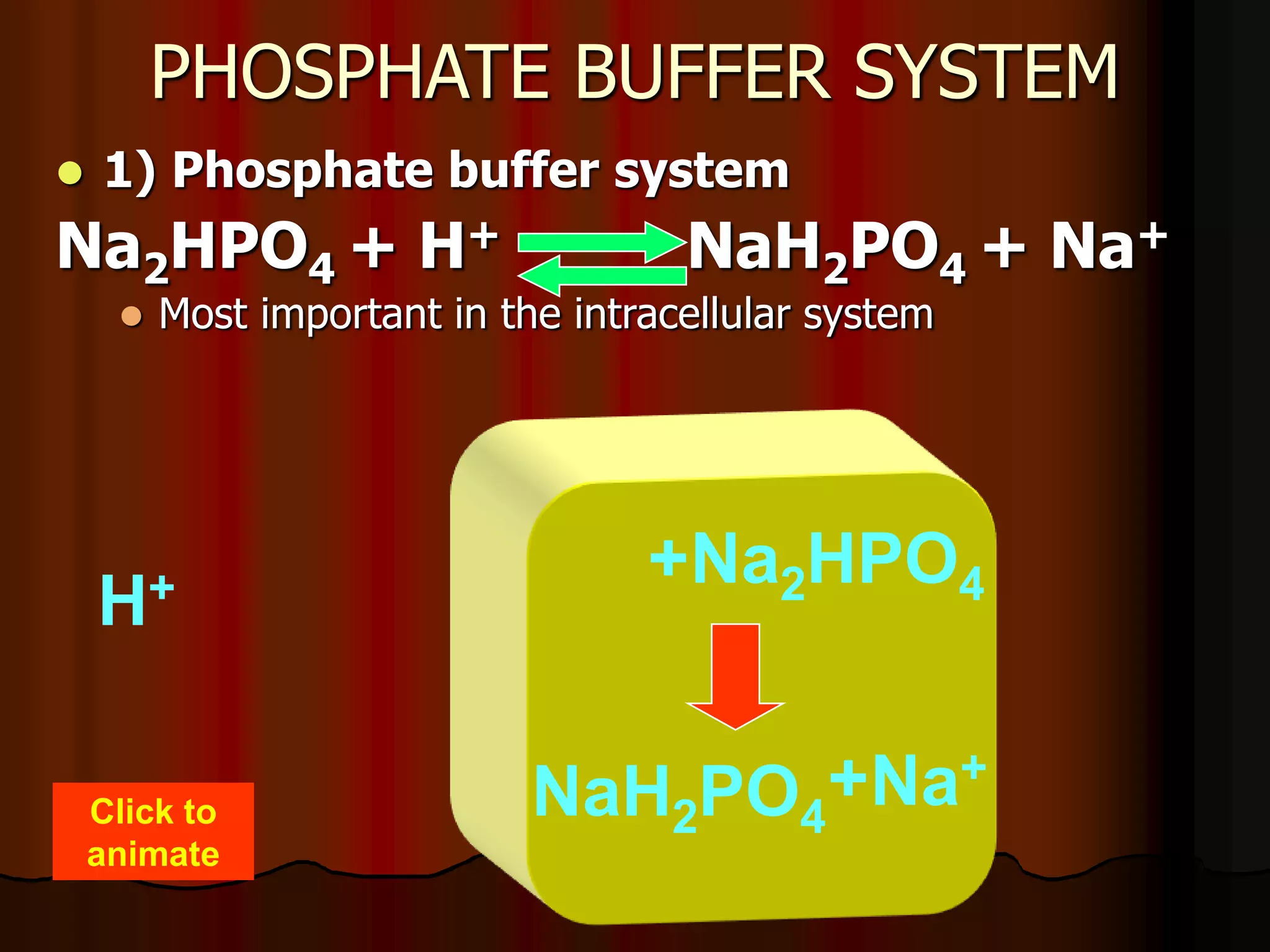
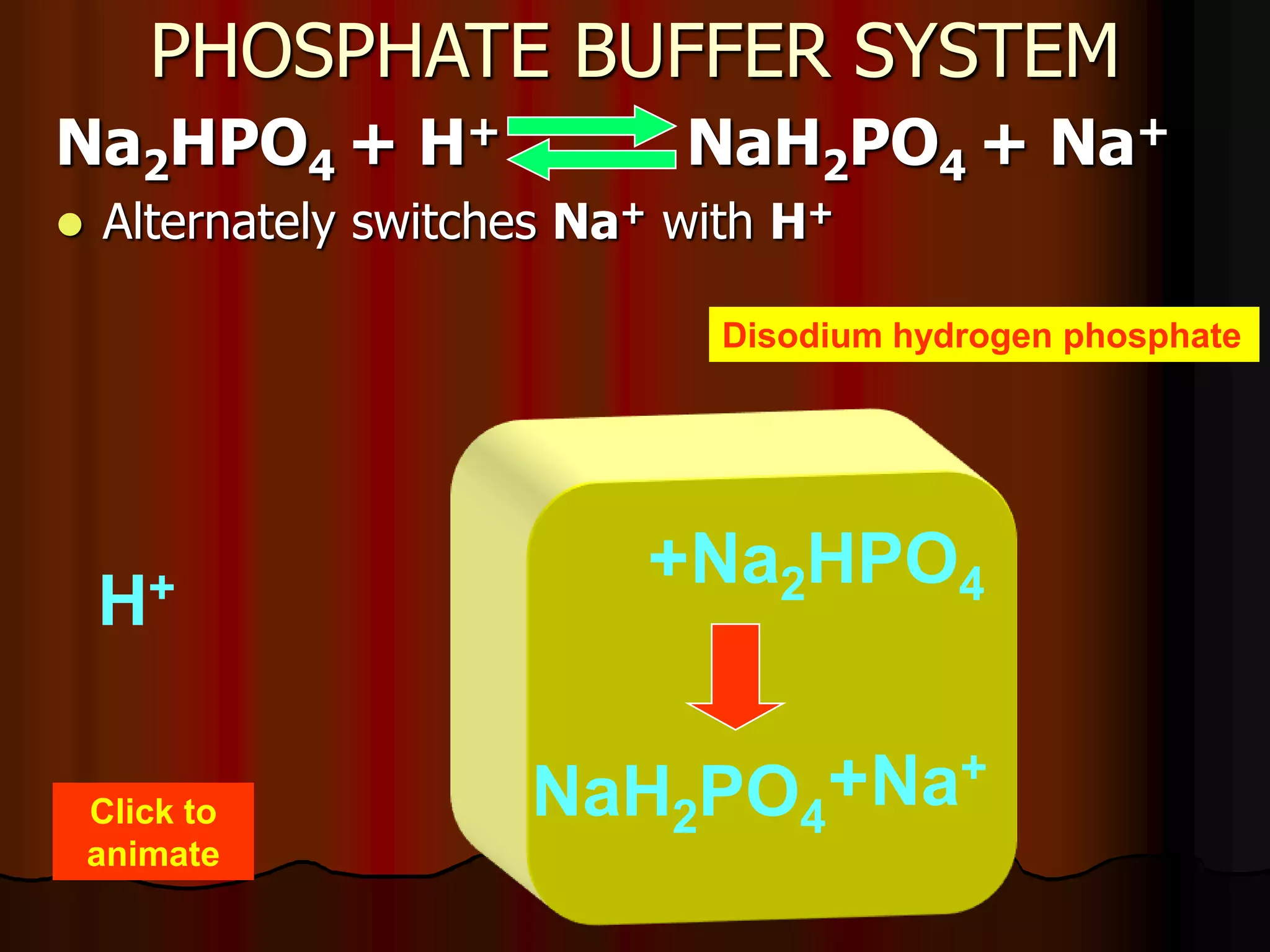
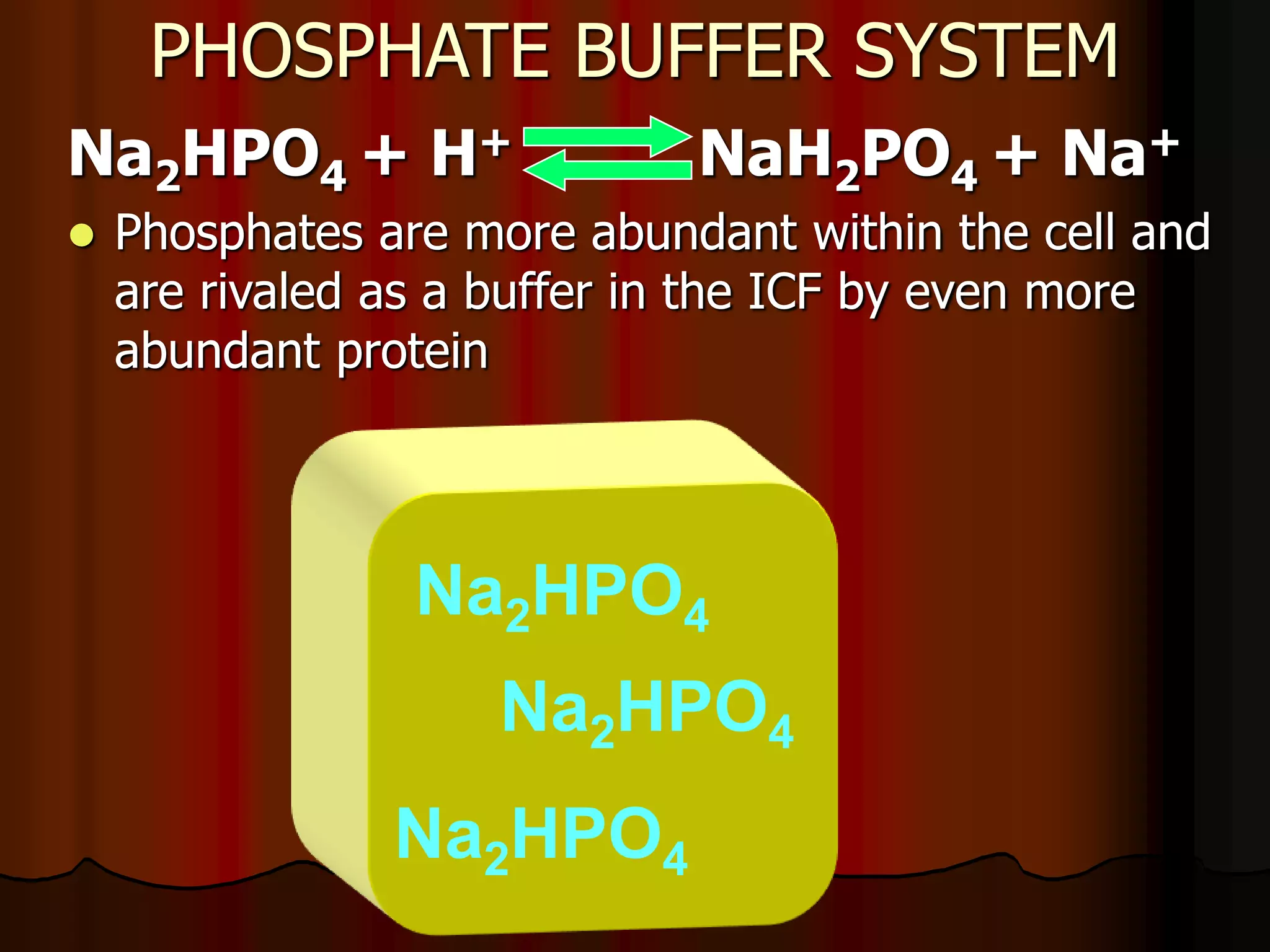

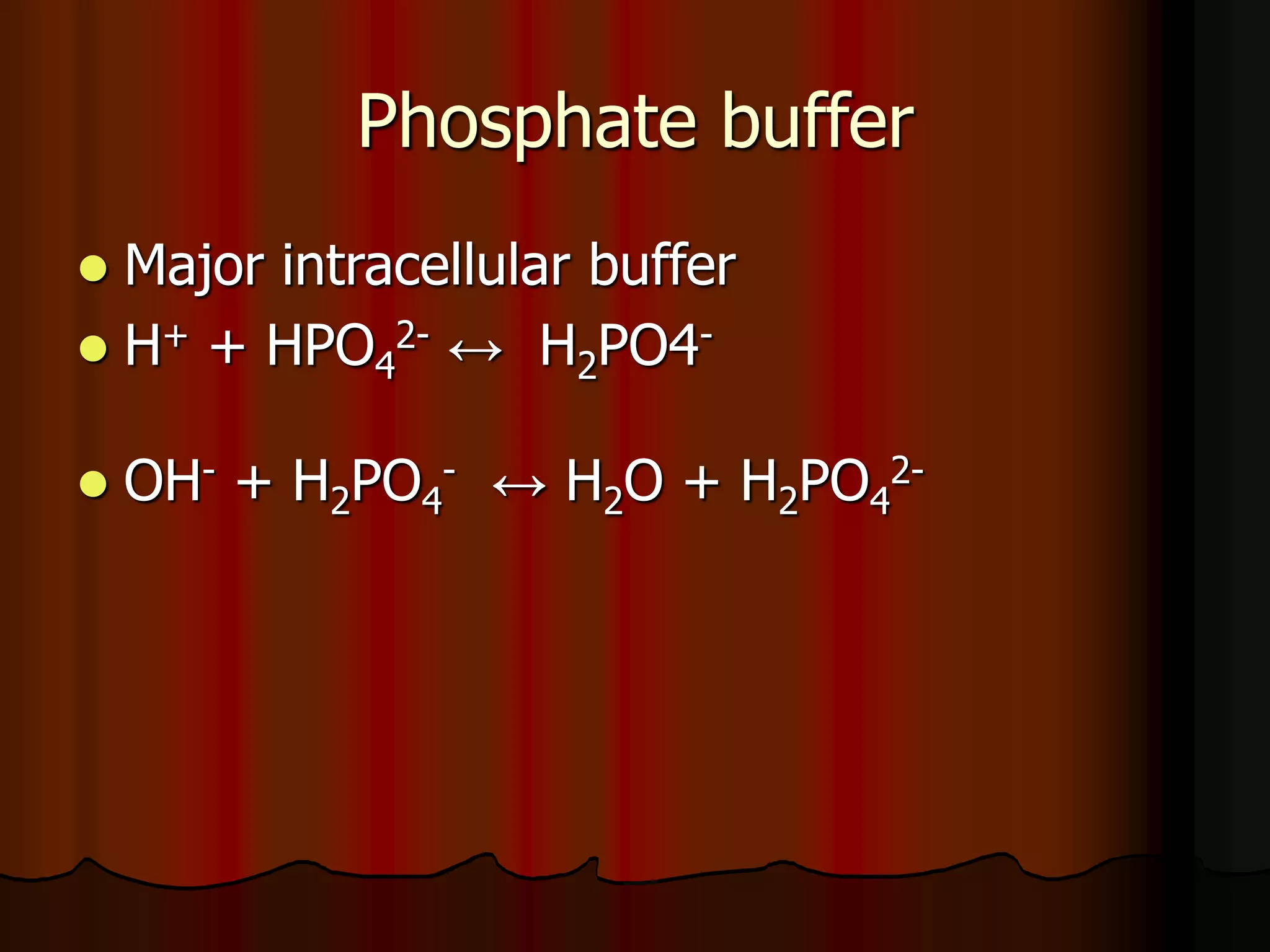


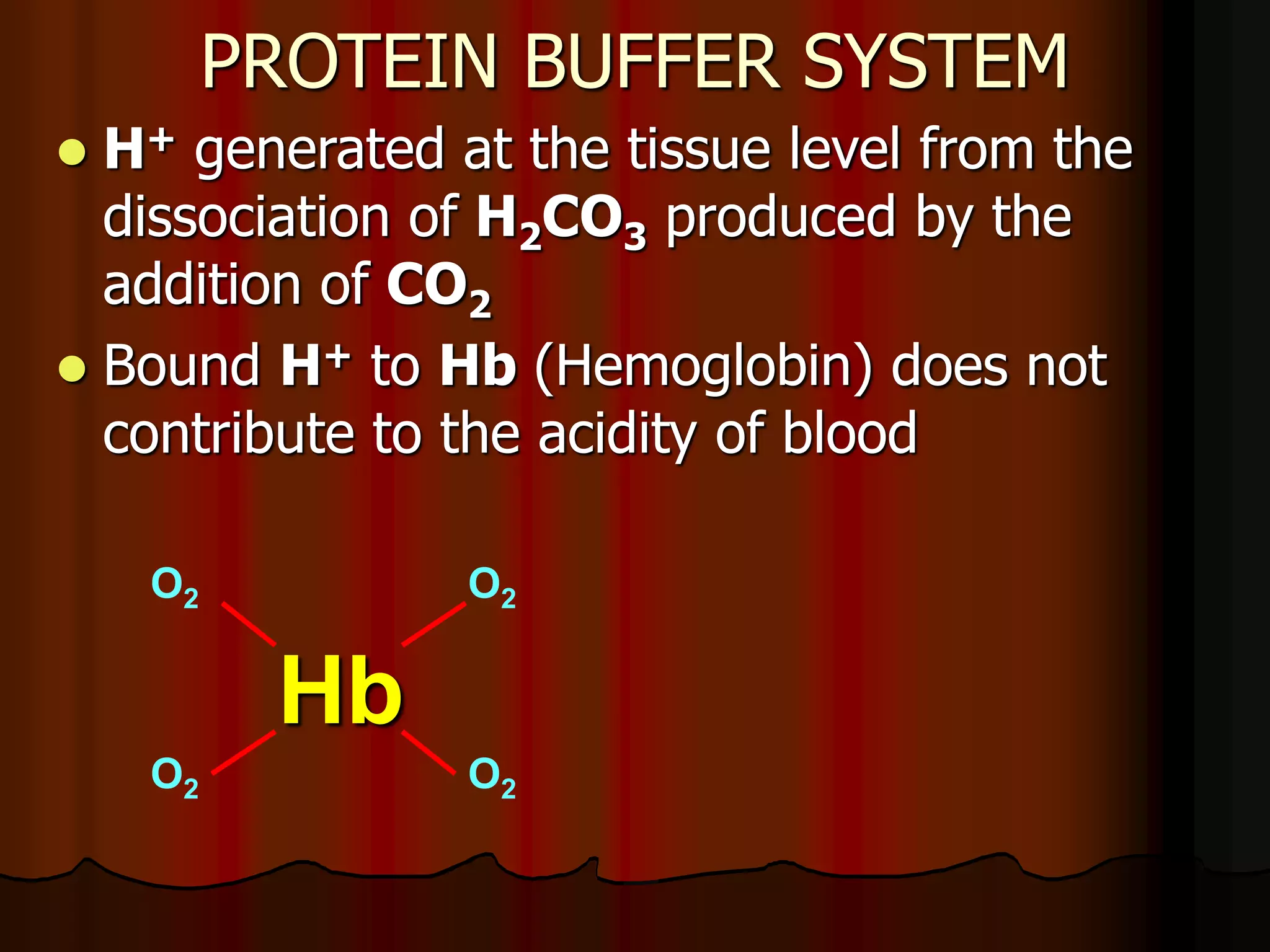






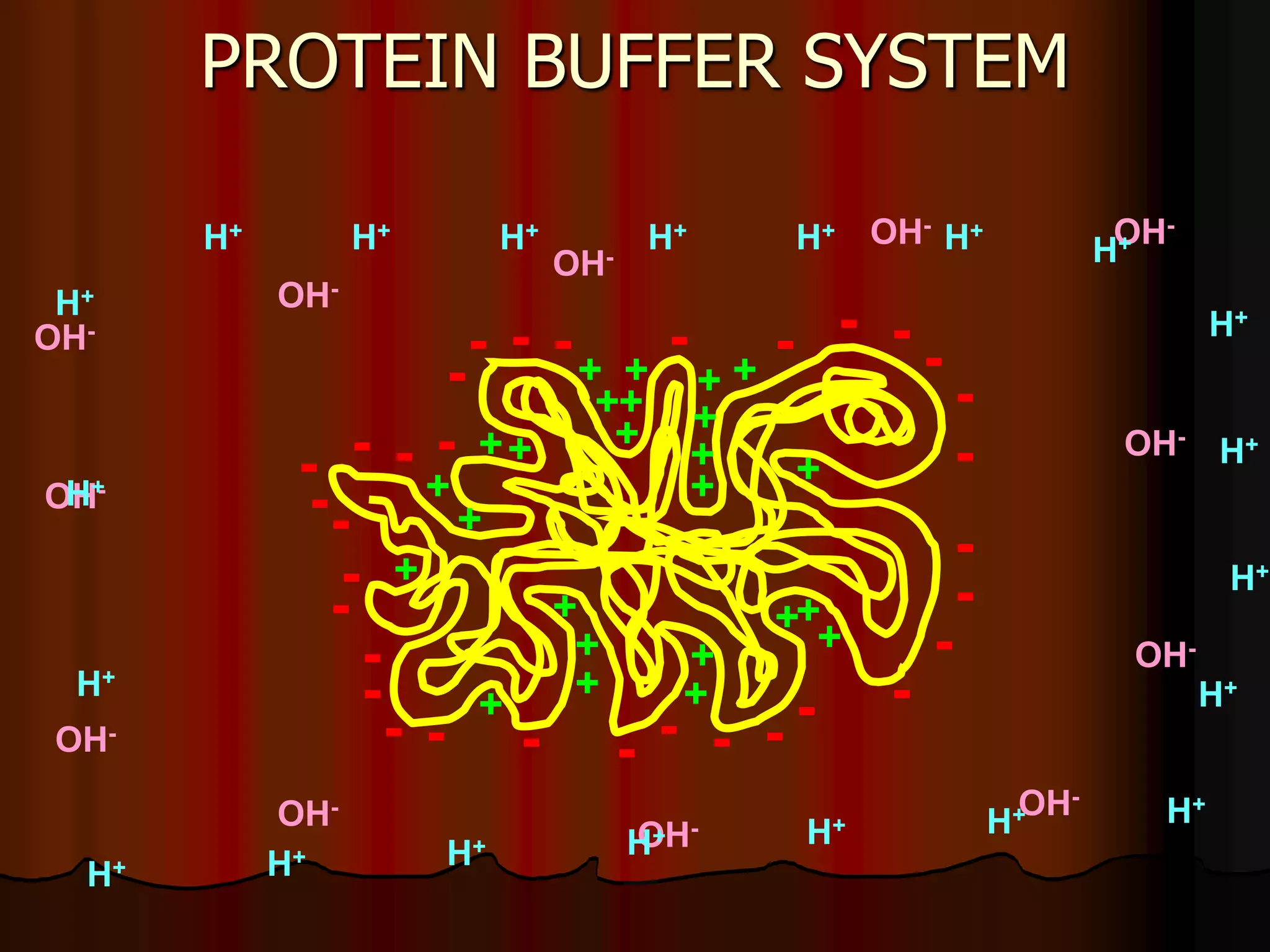

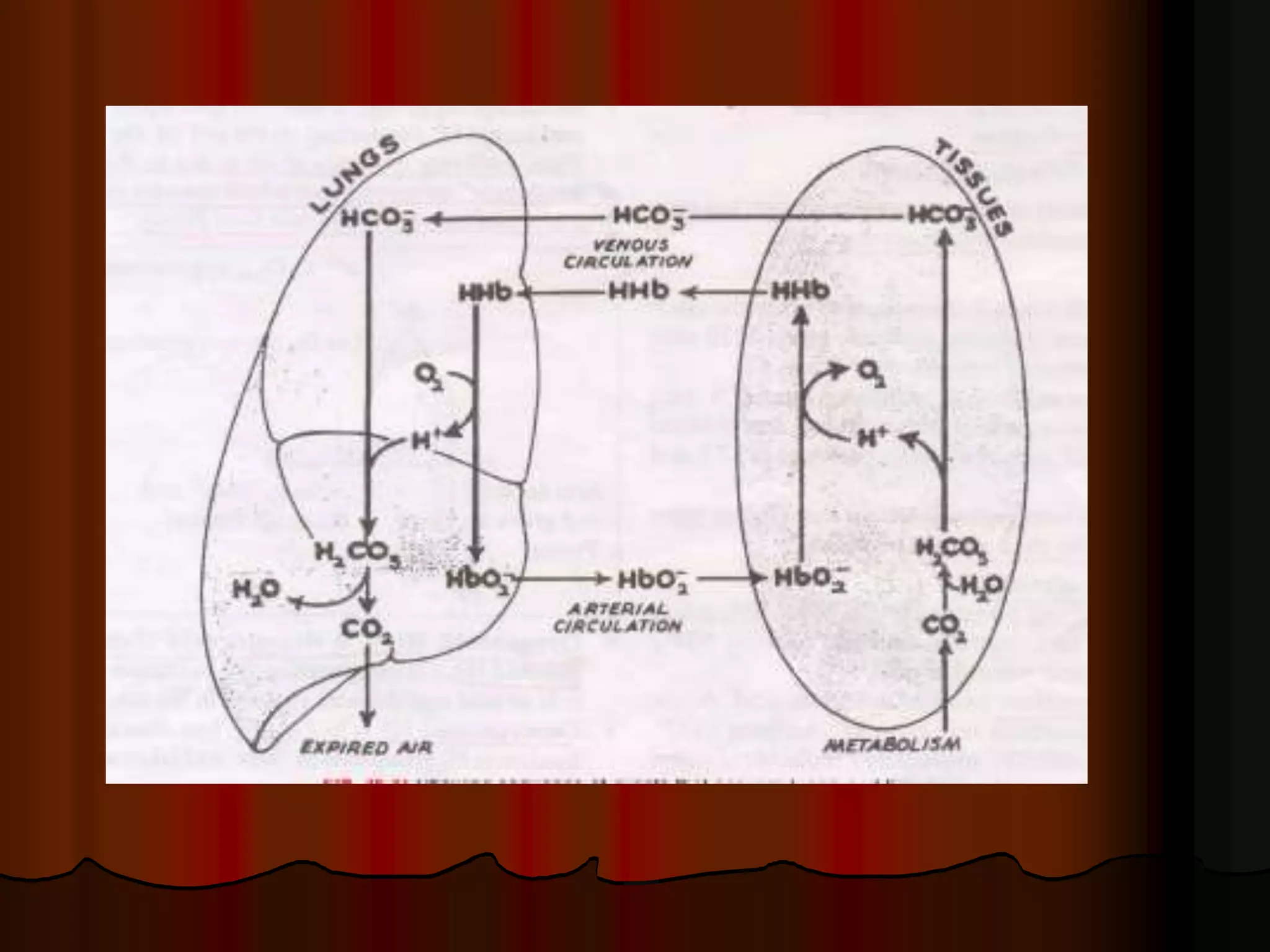
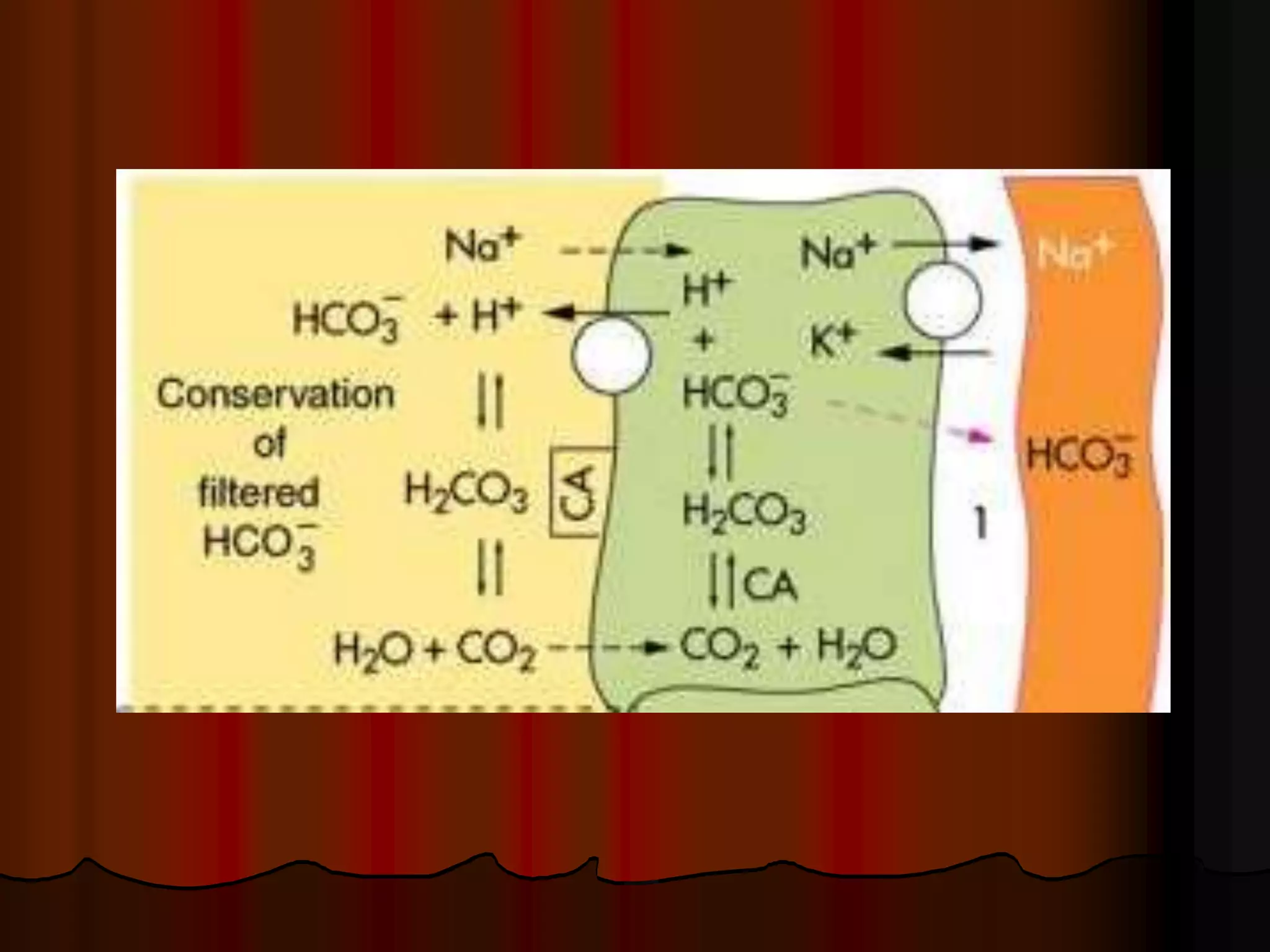
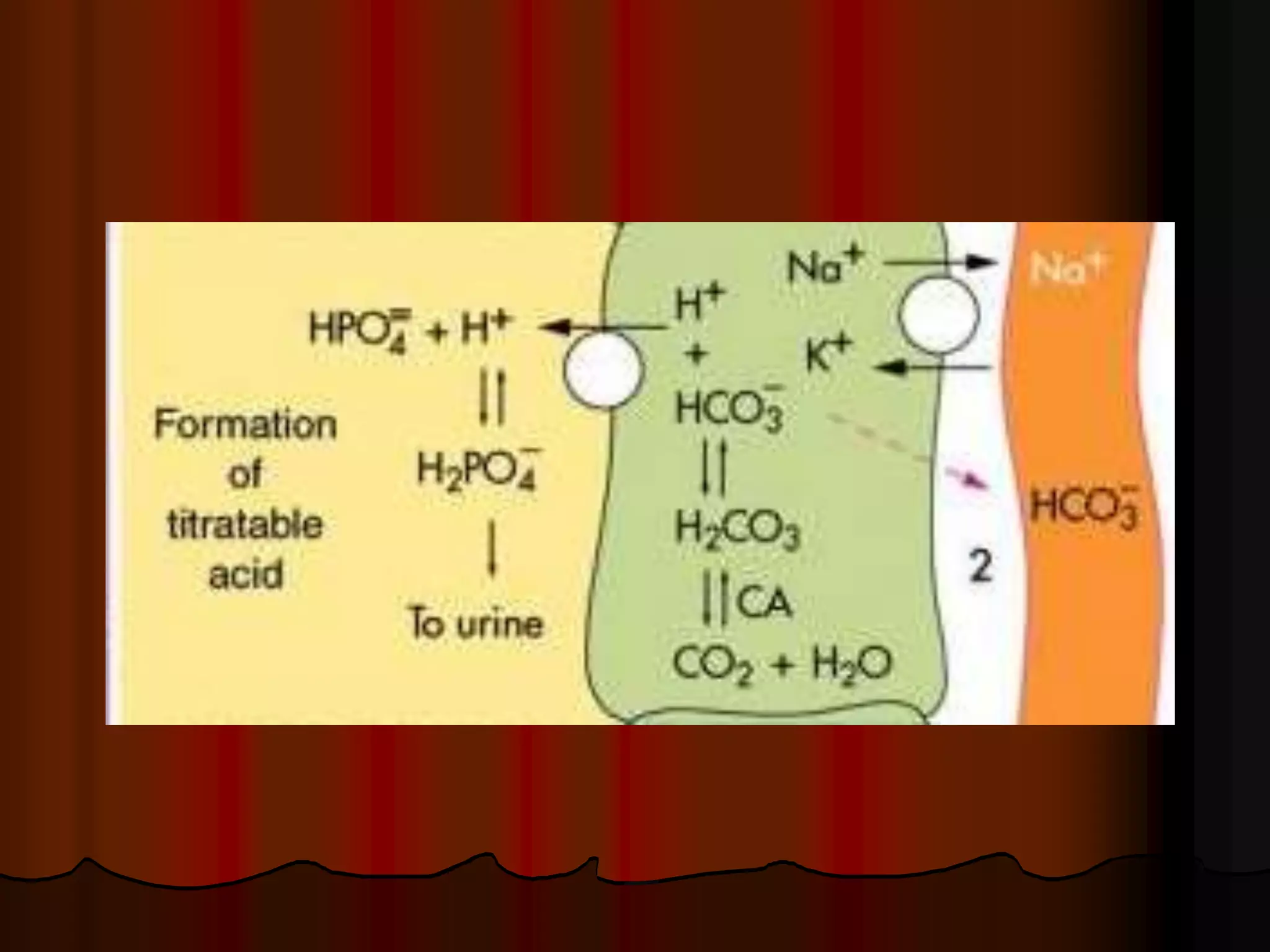




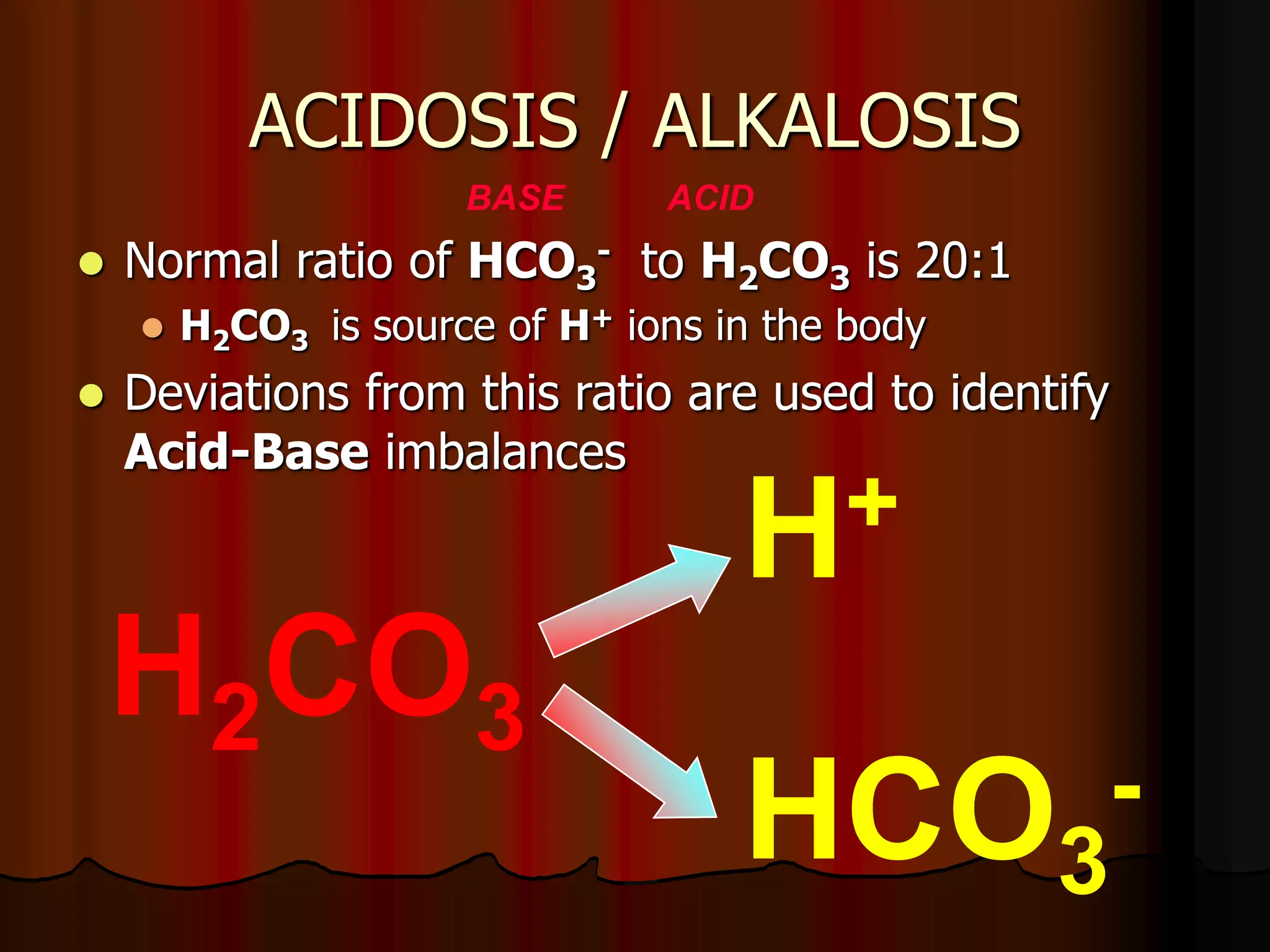



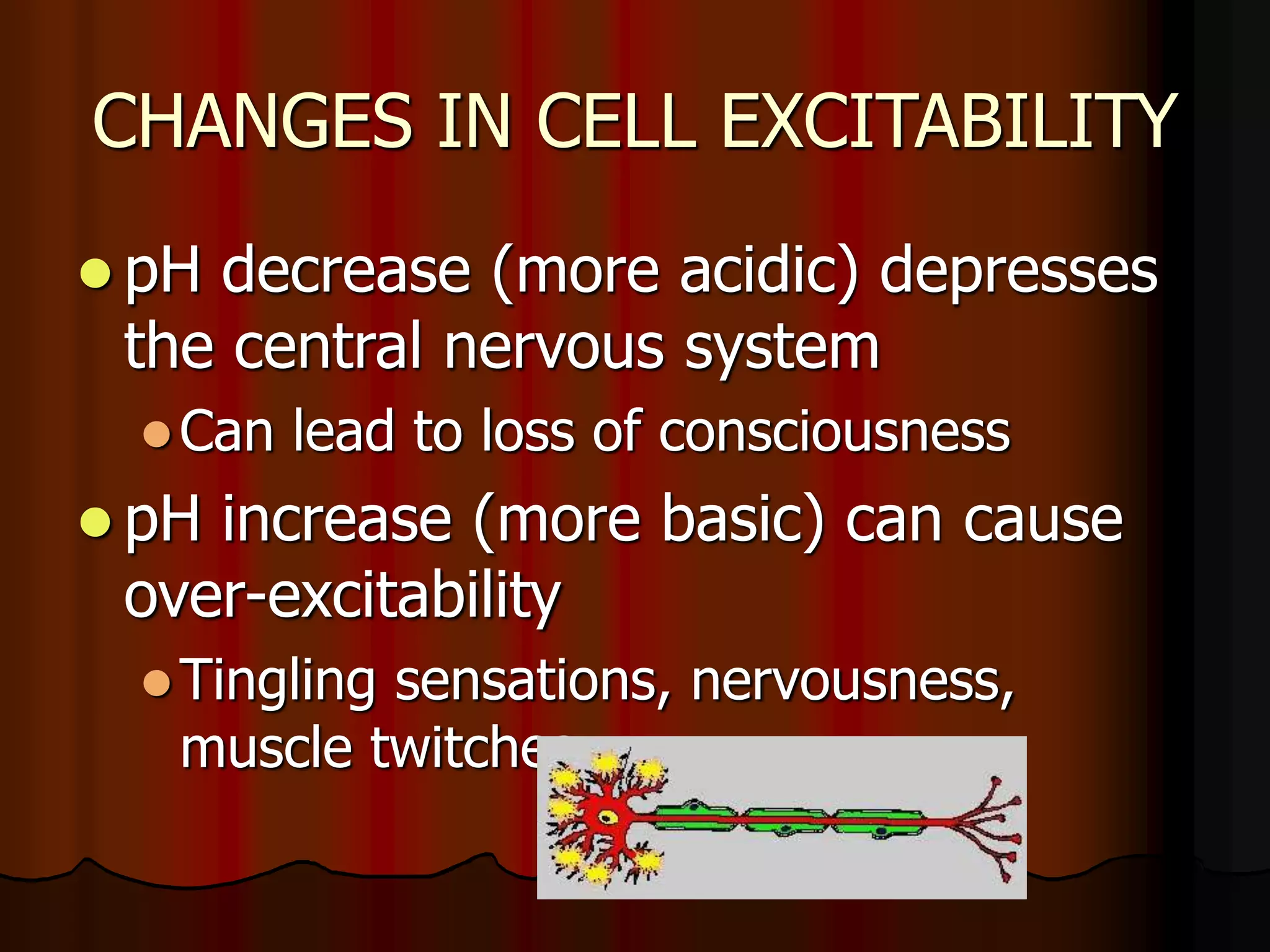
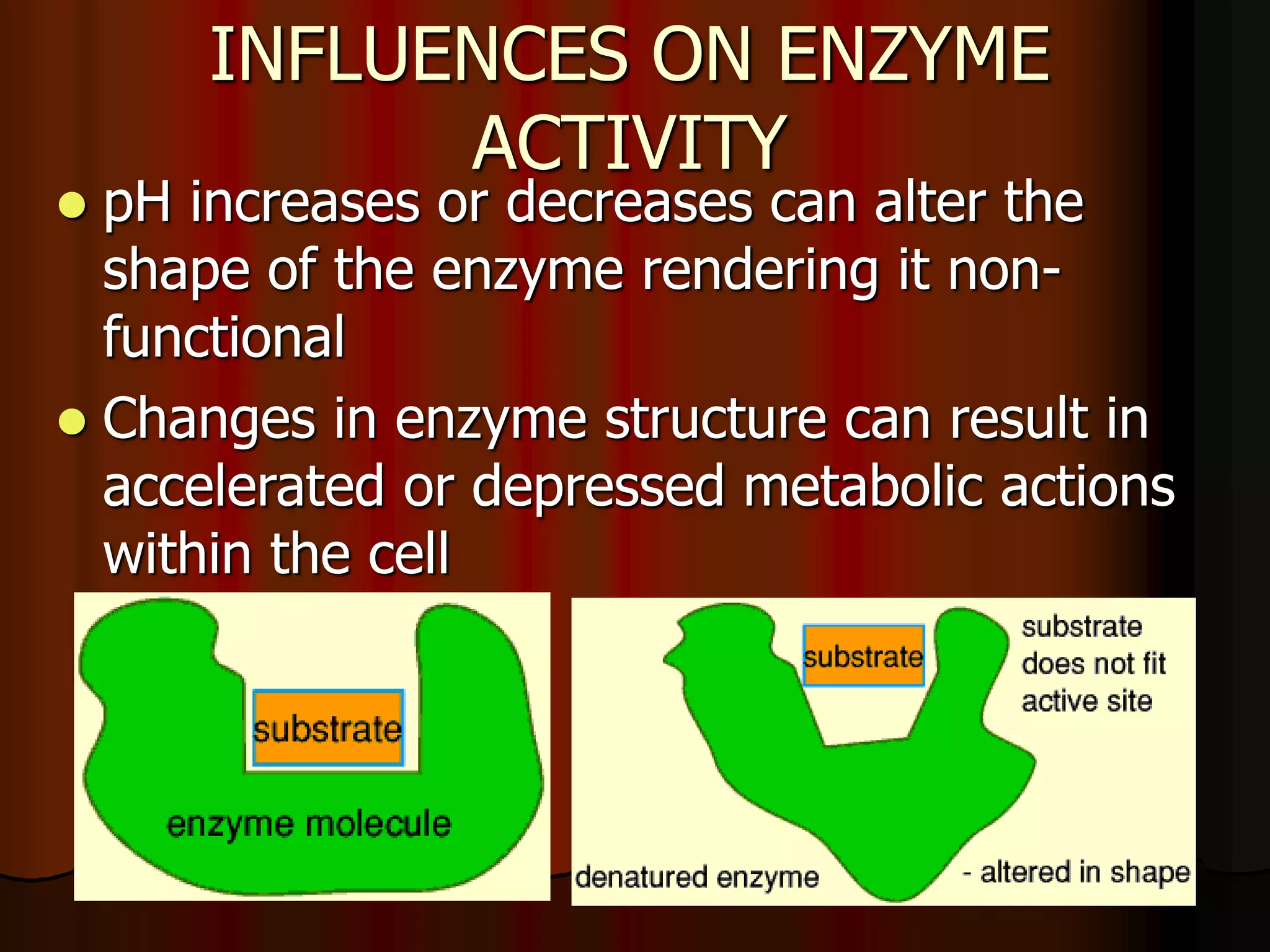
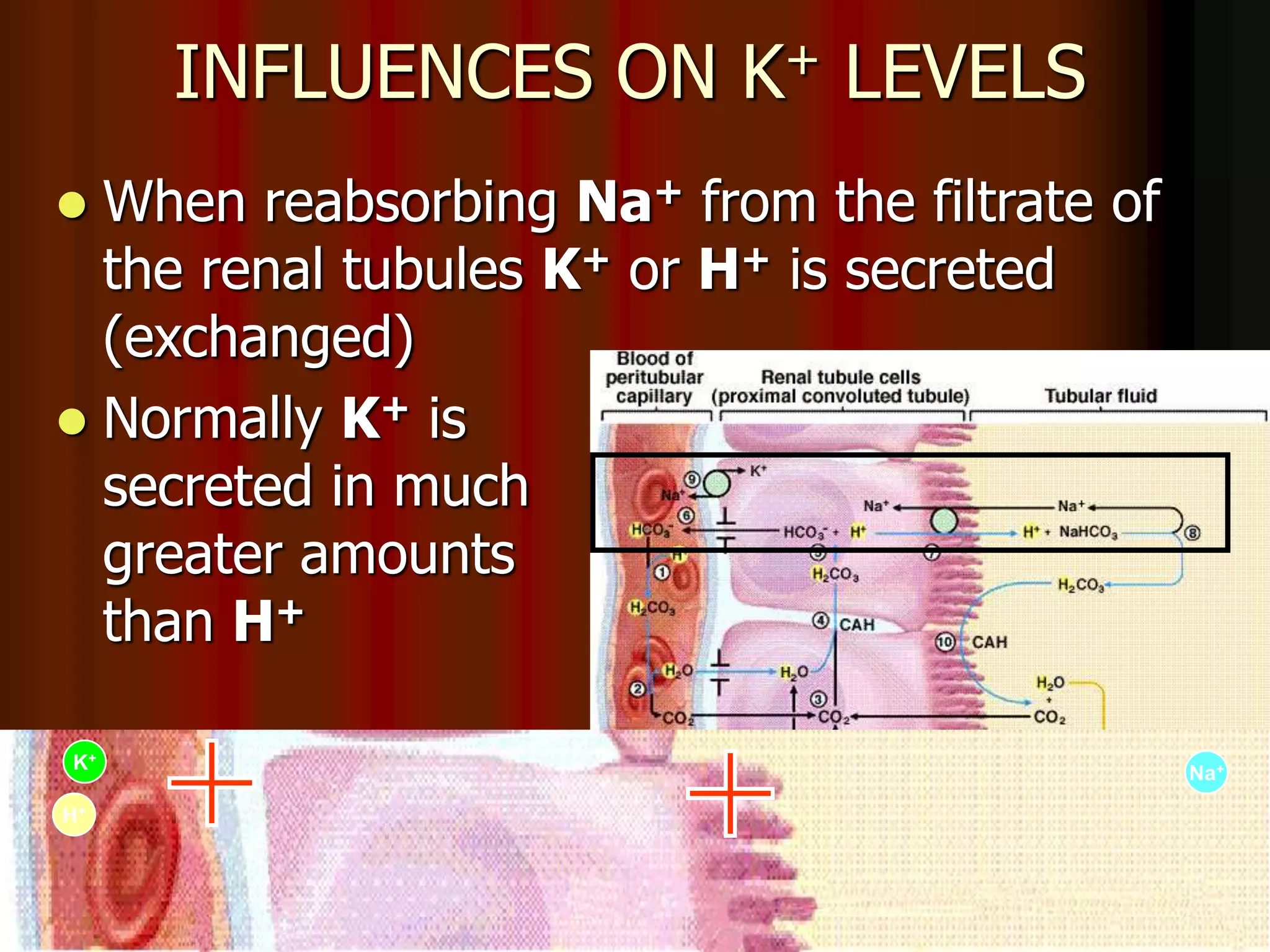
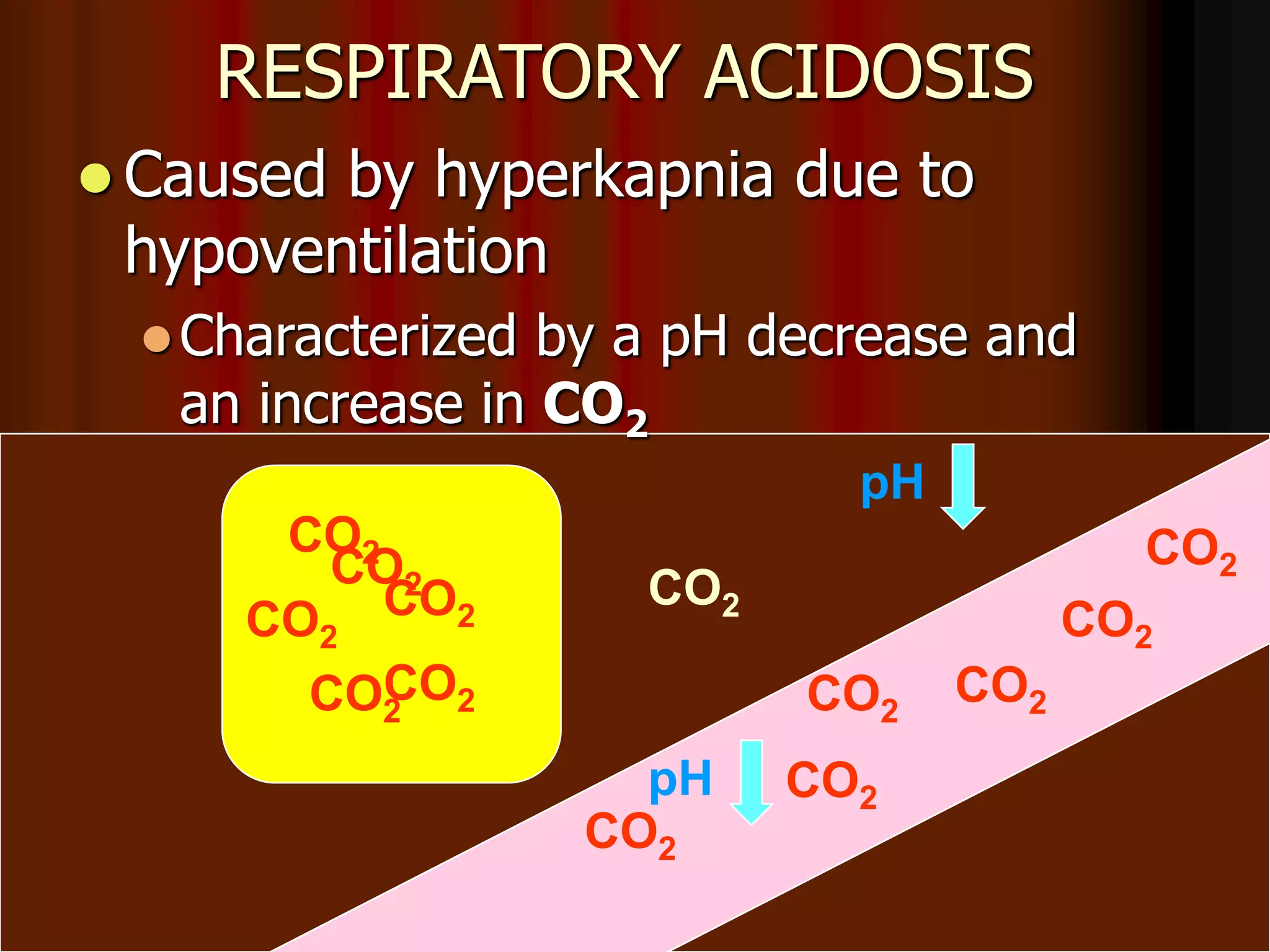
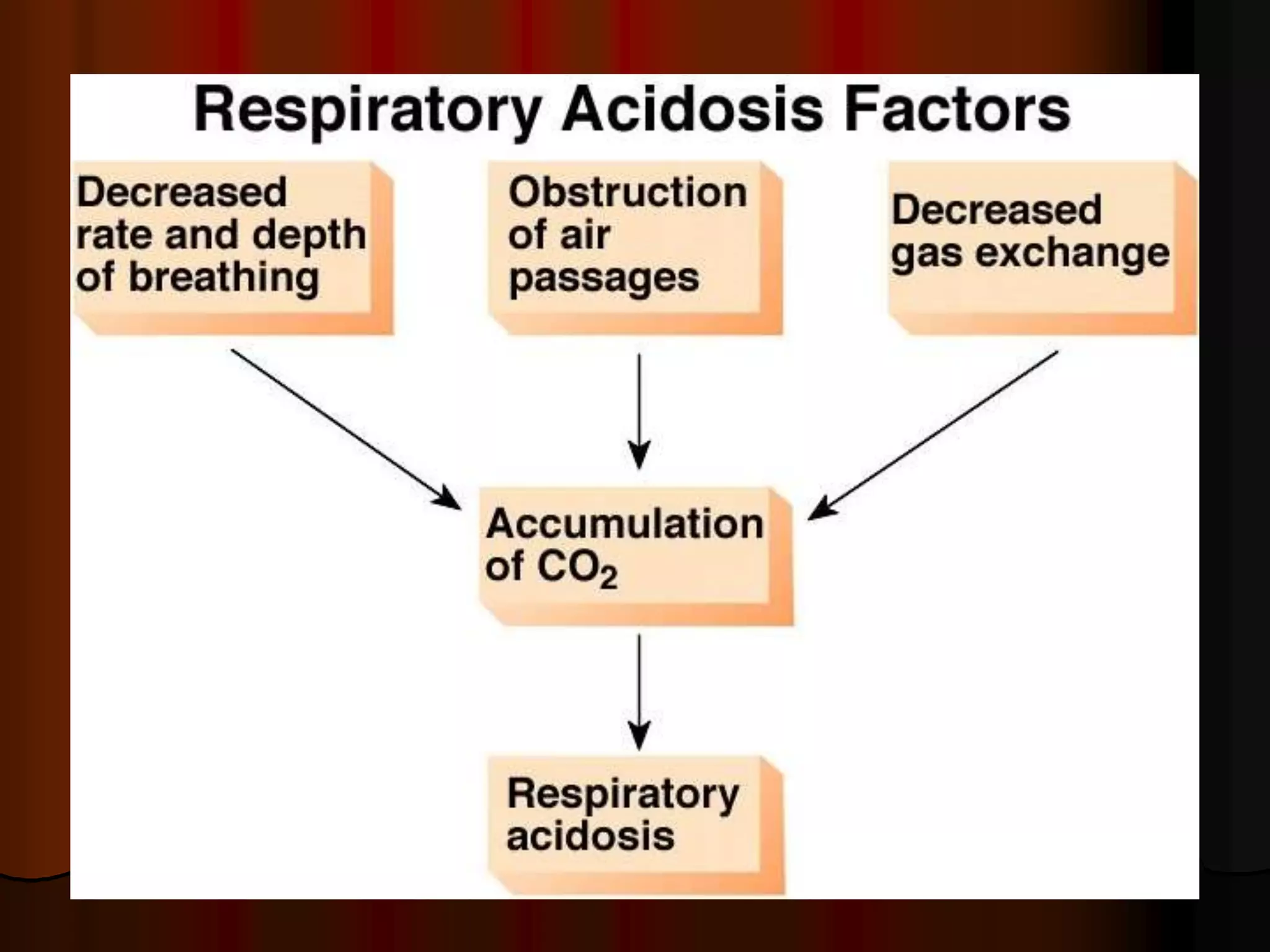


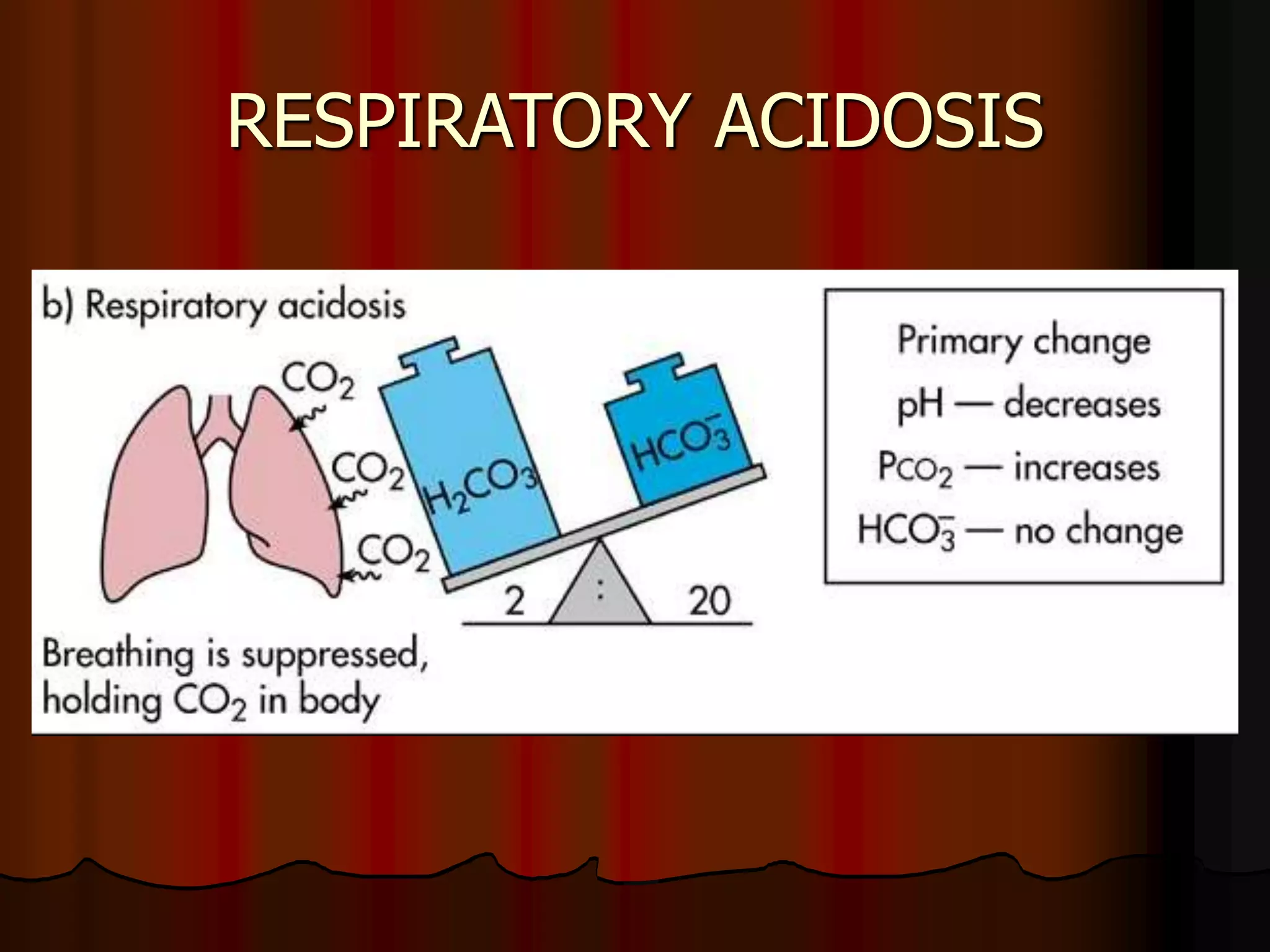
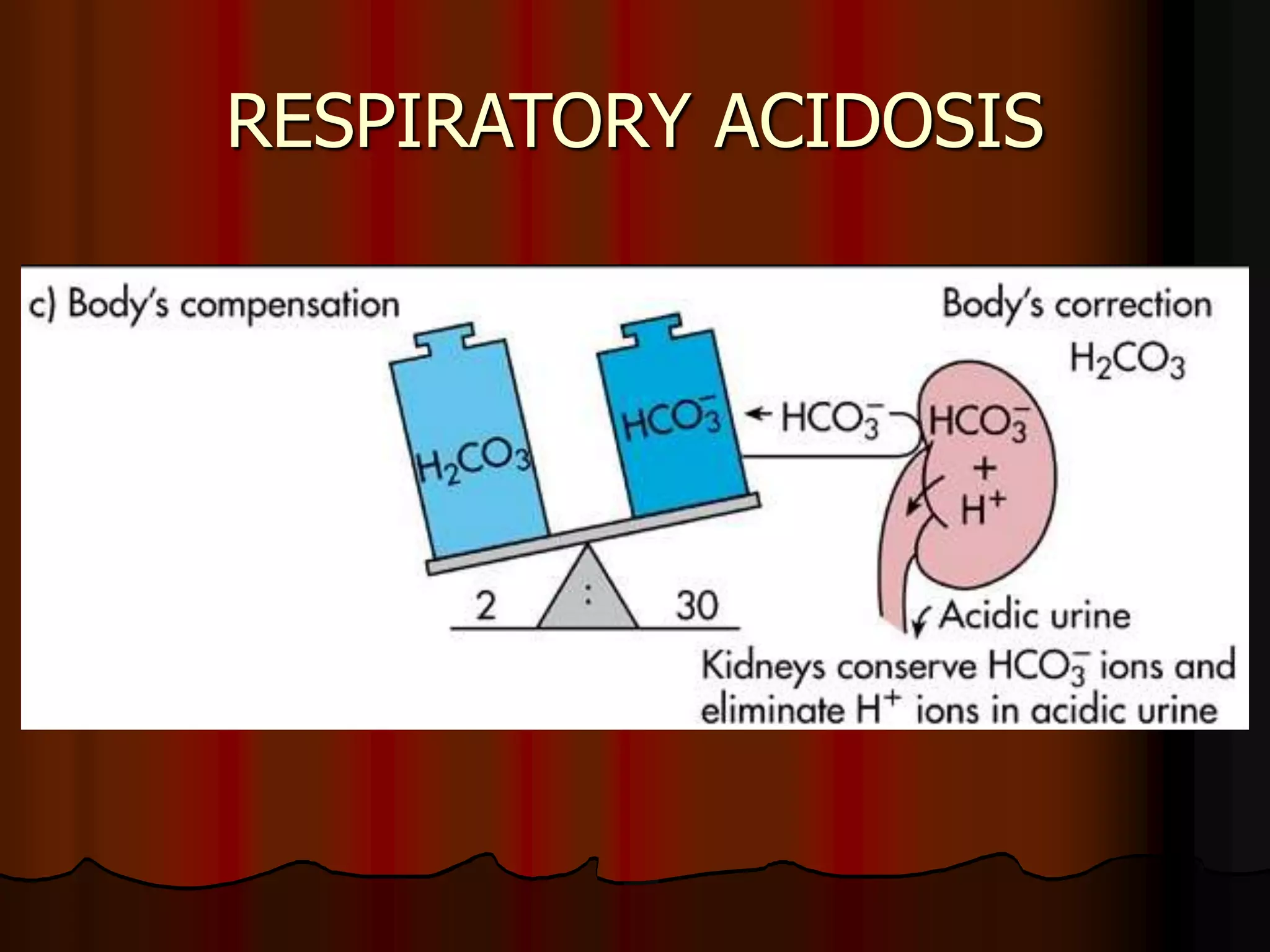
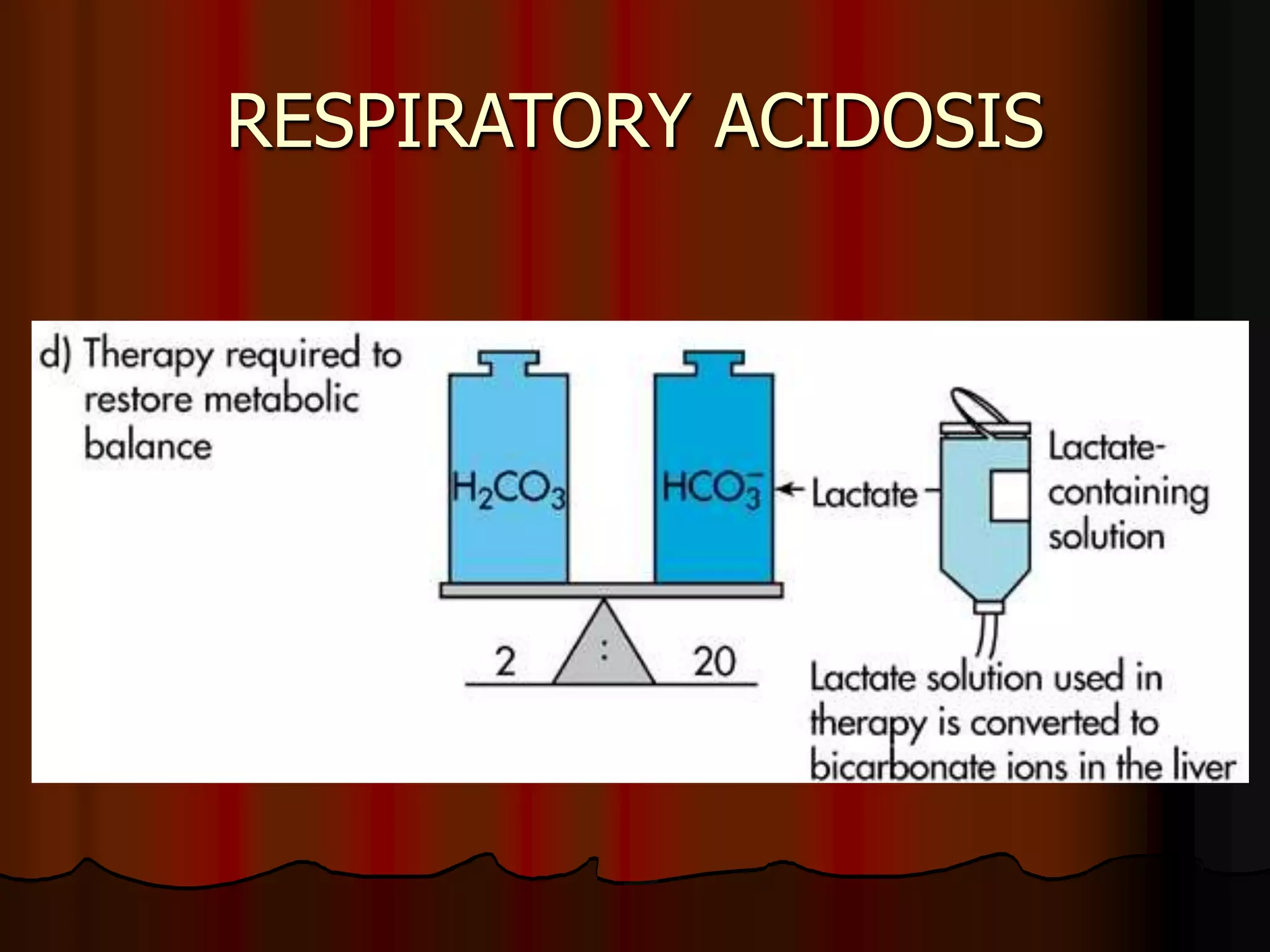





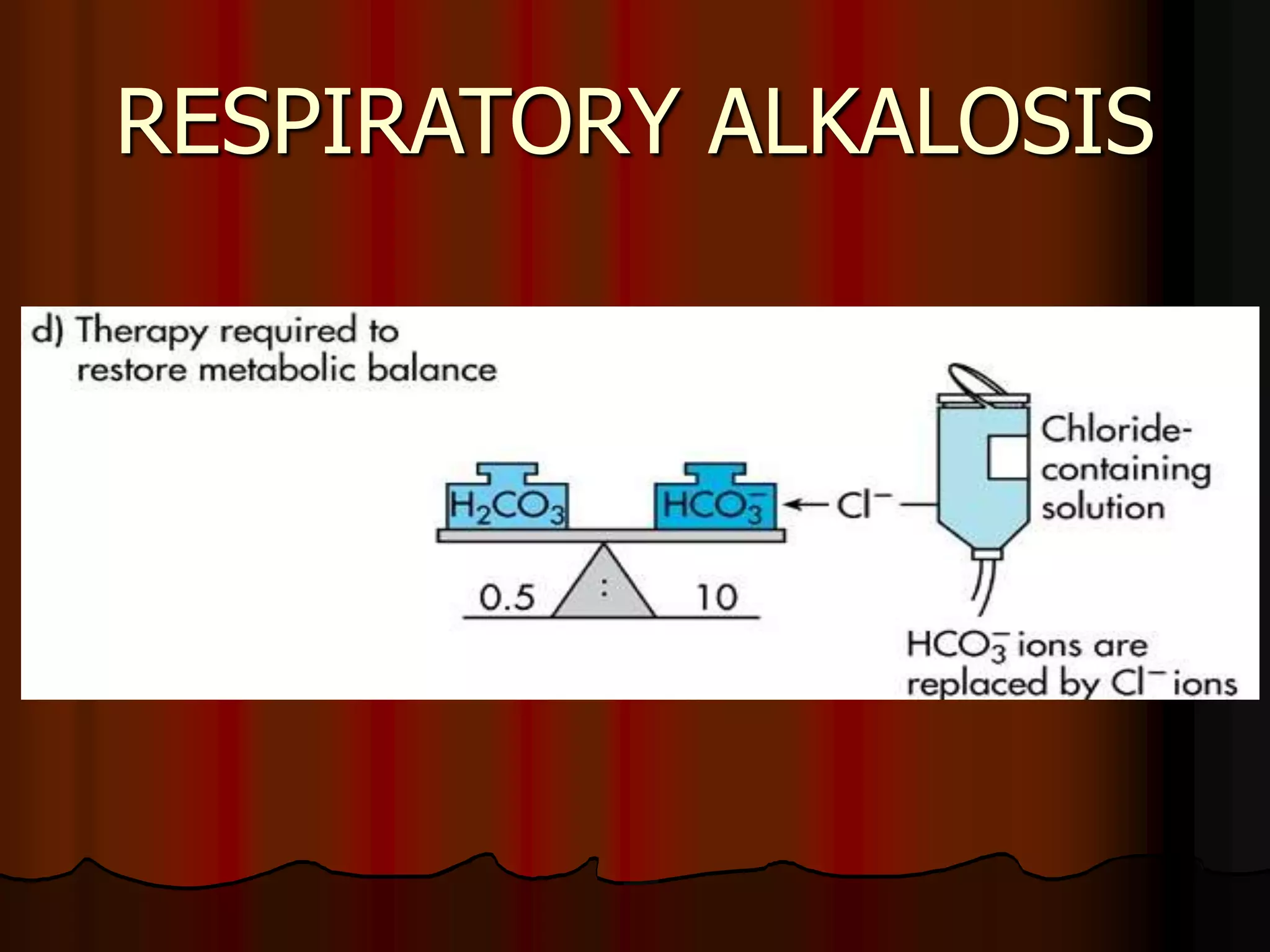



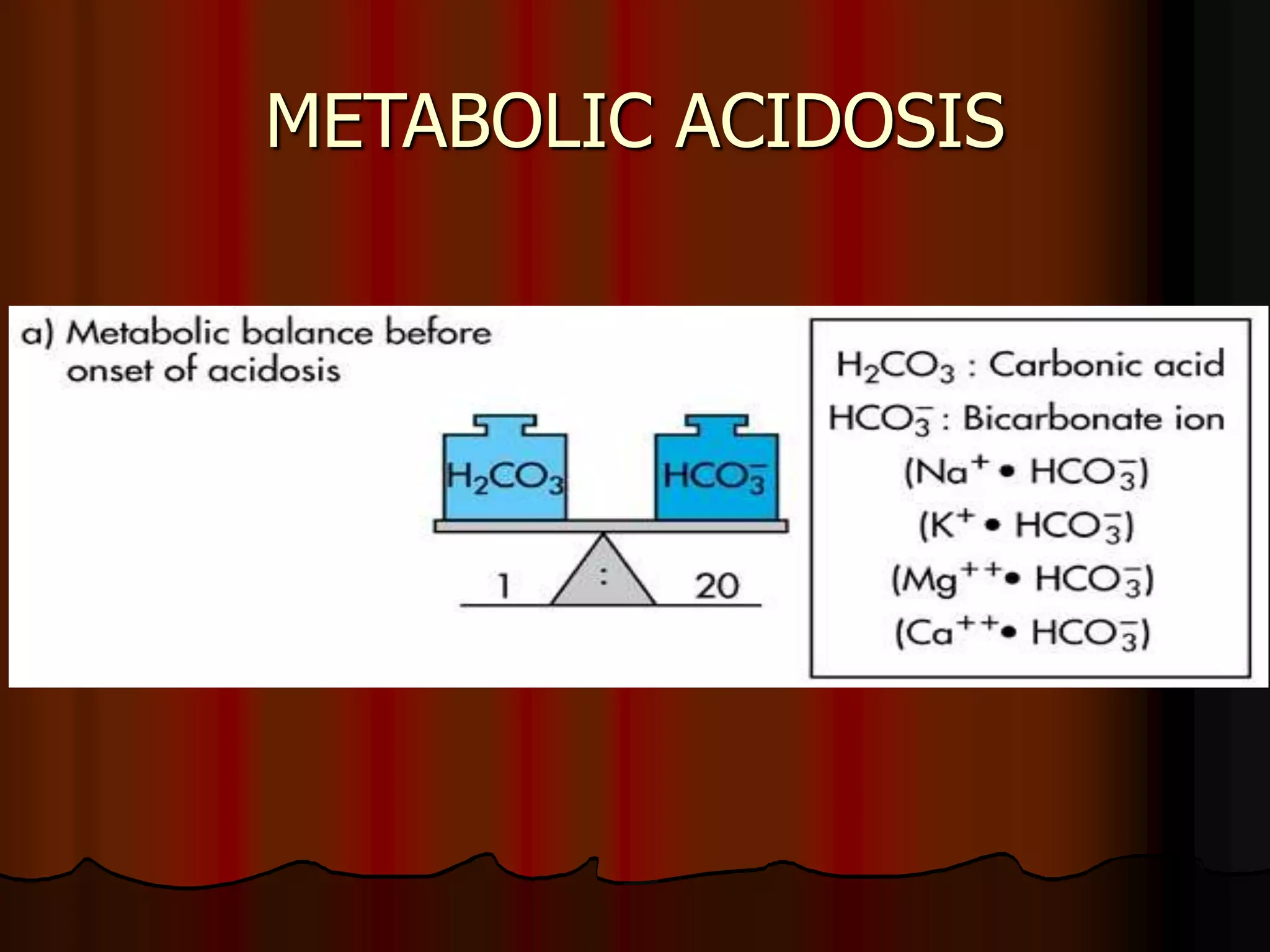
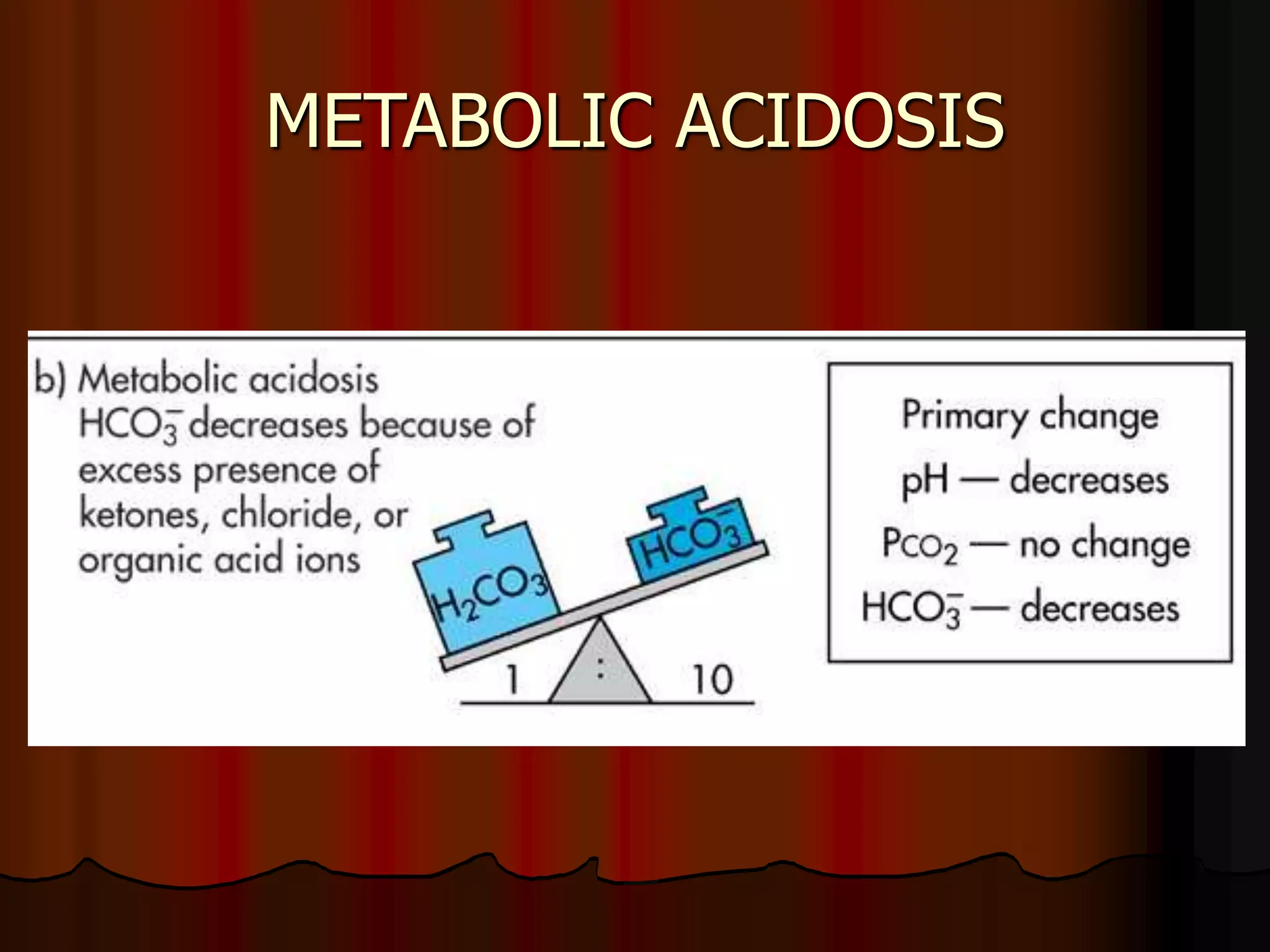

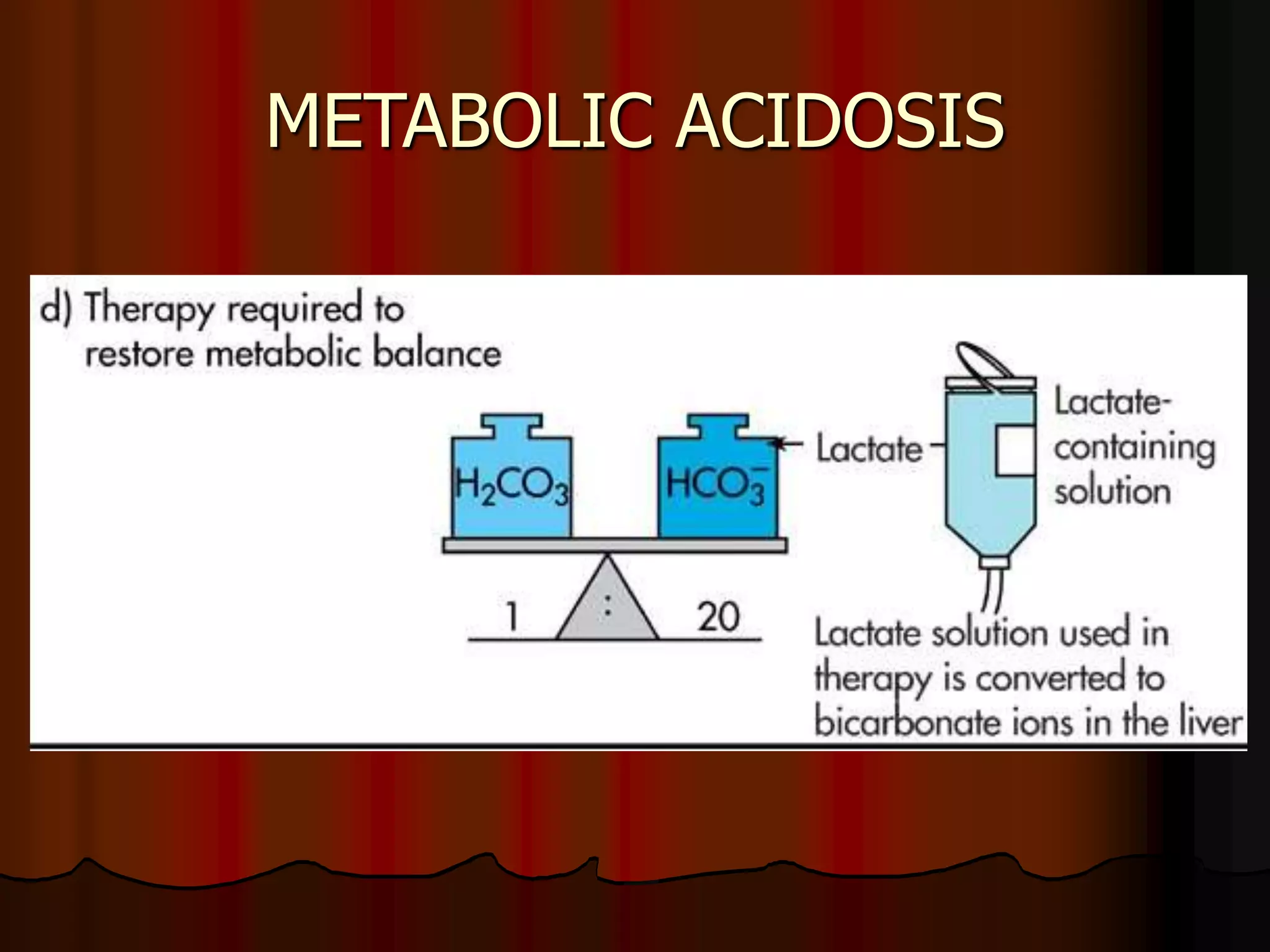



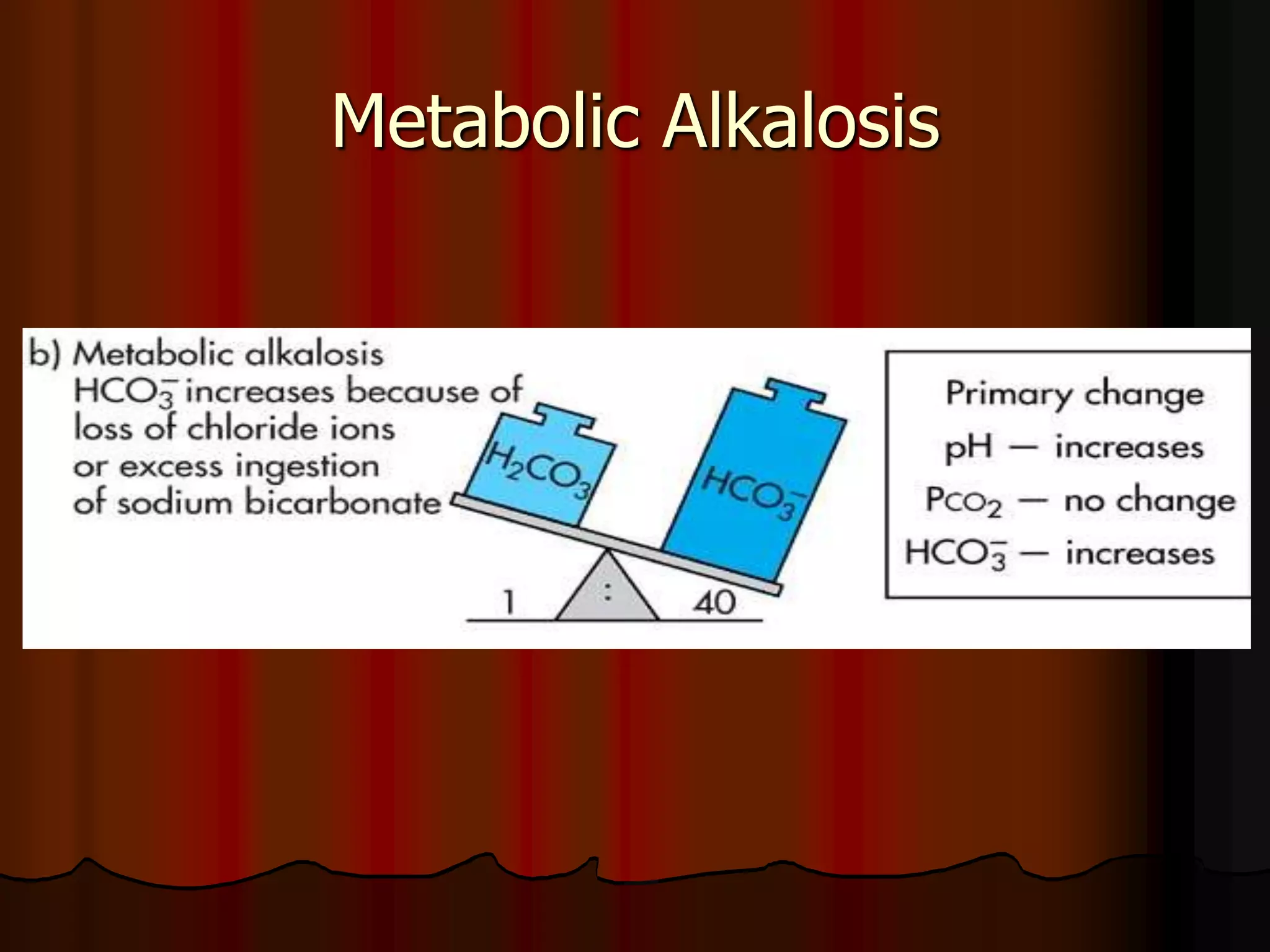
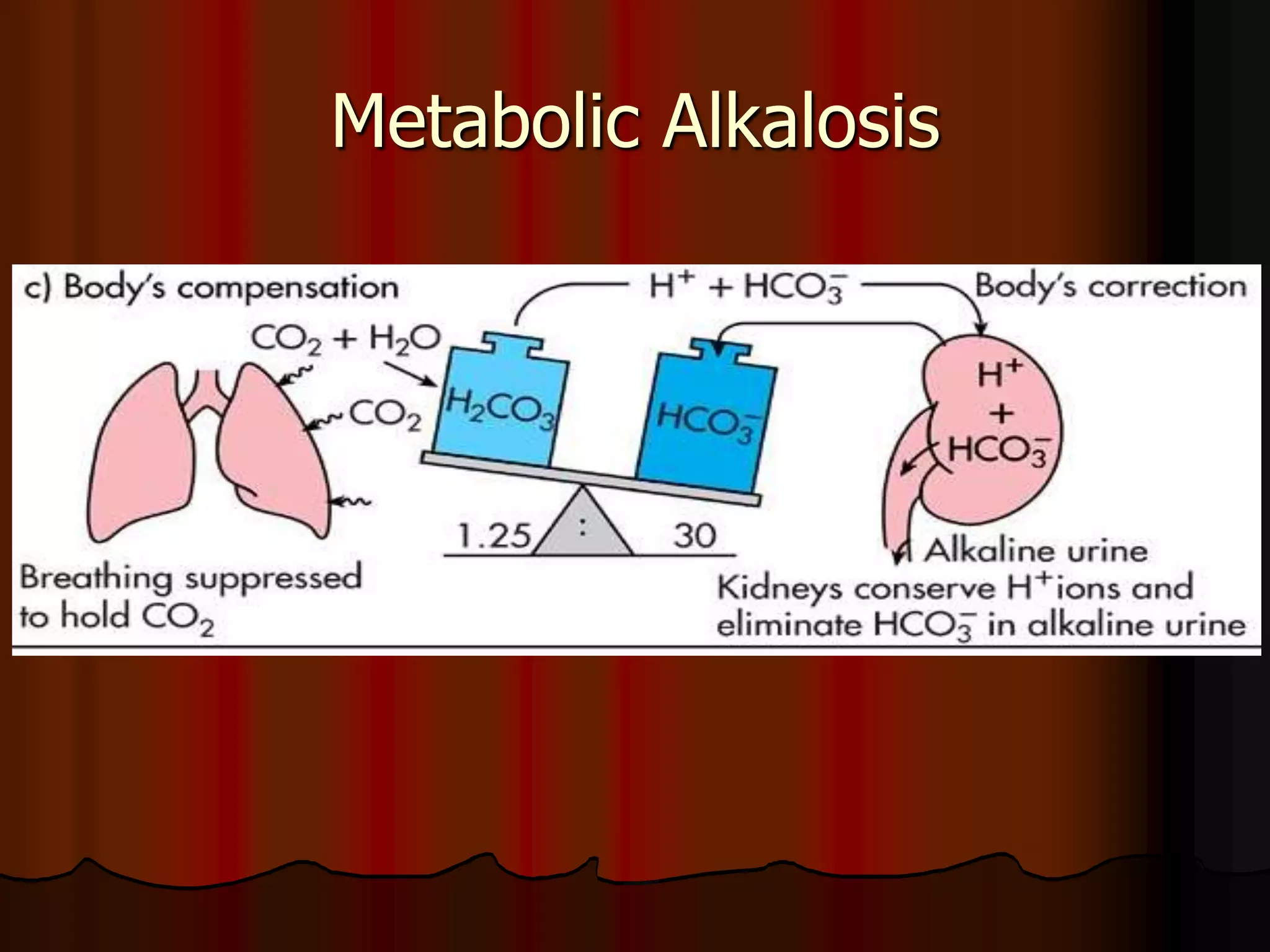
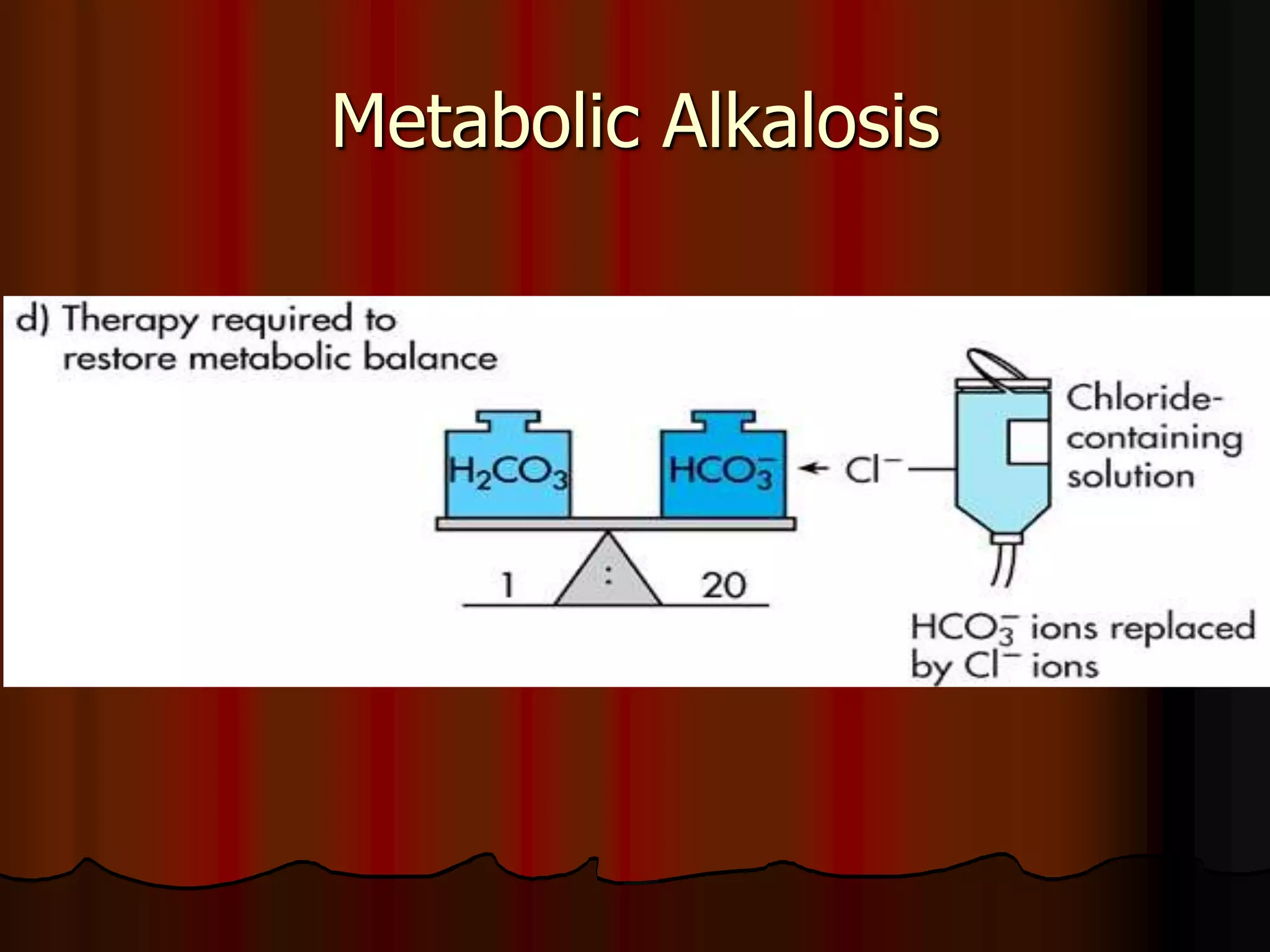
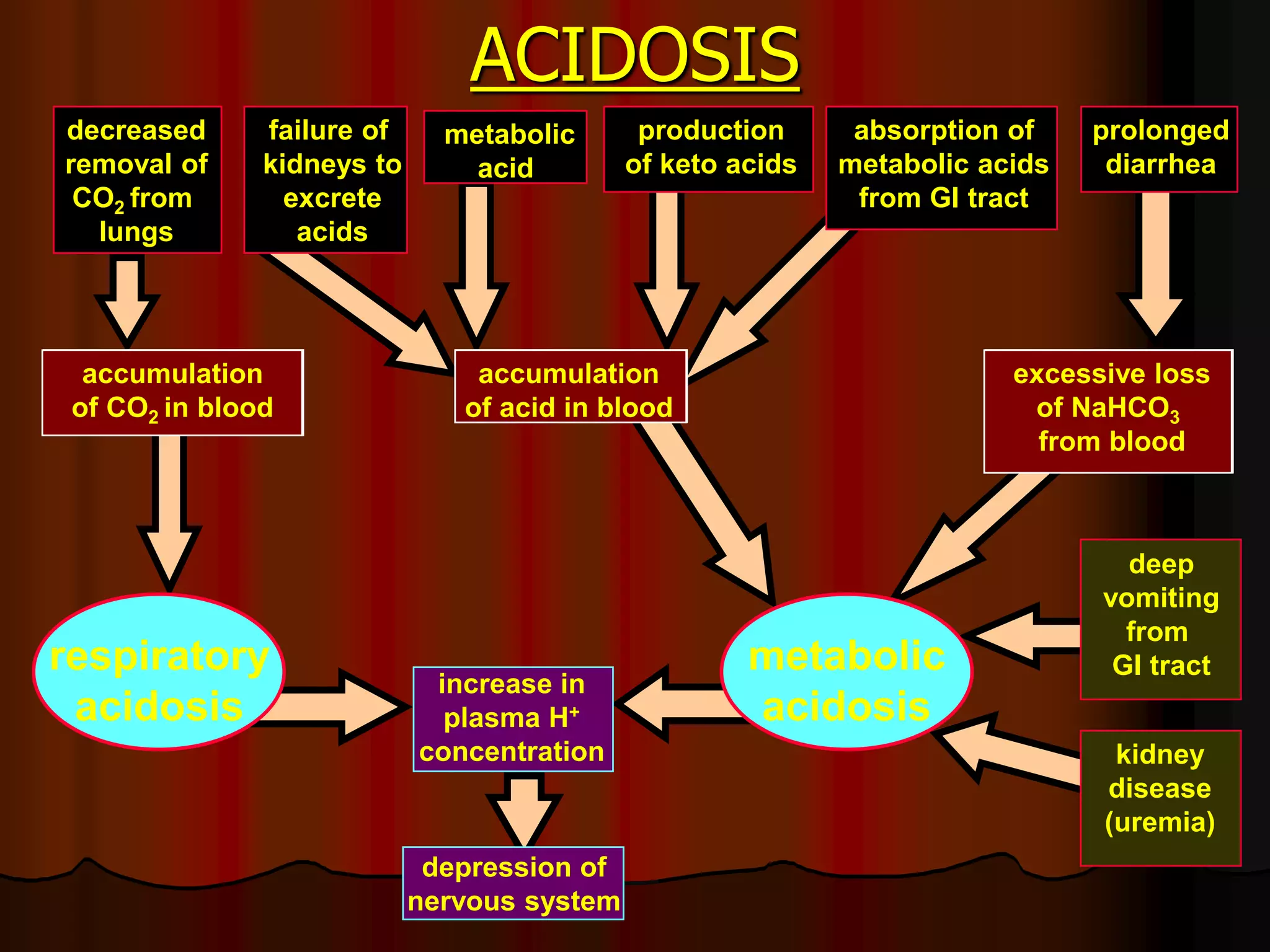
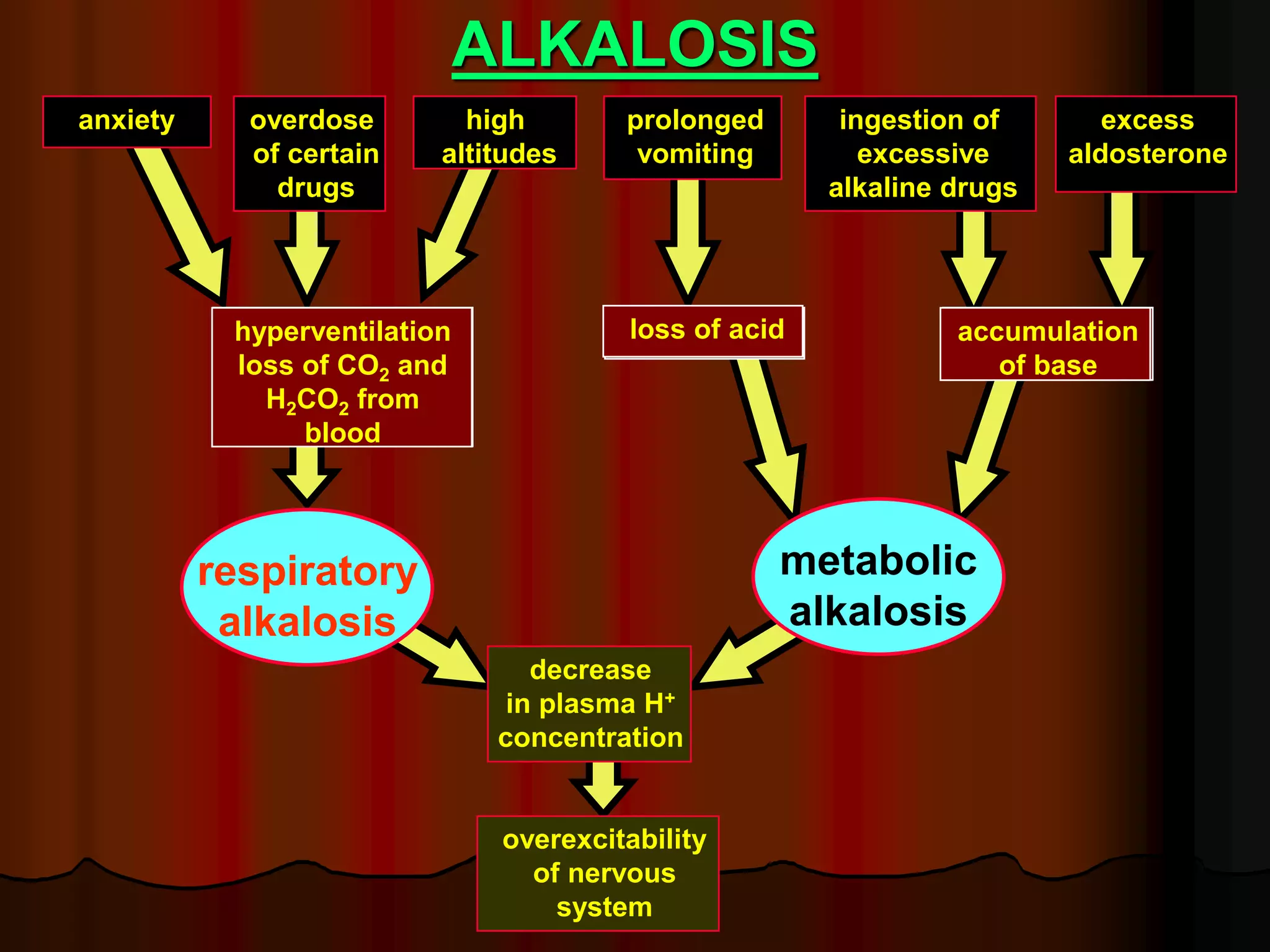


The document discusses acid-base homeostasis, emphasizing its importance in maintaining proper hydrogen ion concentration for cellular function and organ health. It explains the roles of acids, bases, and buffer systems, including bicarbonate, phosphate, and protein buffers, in regulating pH levels and responding to acidosis and alkalosis. Additionally, it outlines factors affecting acid-base balance, such as respiratory and metabolic disturbances, and their physiological consequences.






















































































