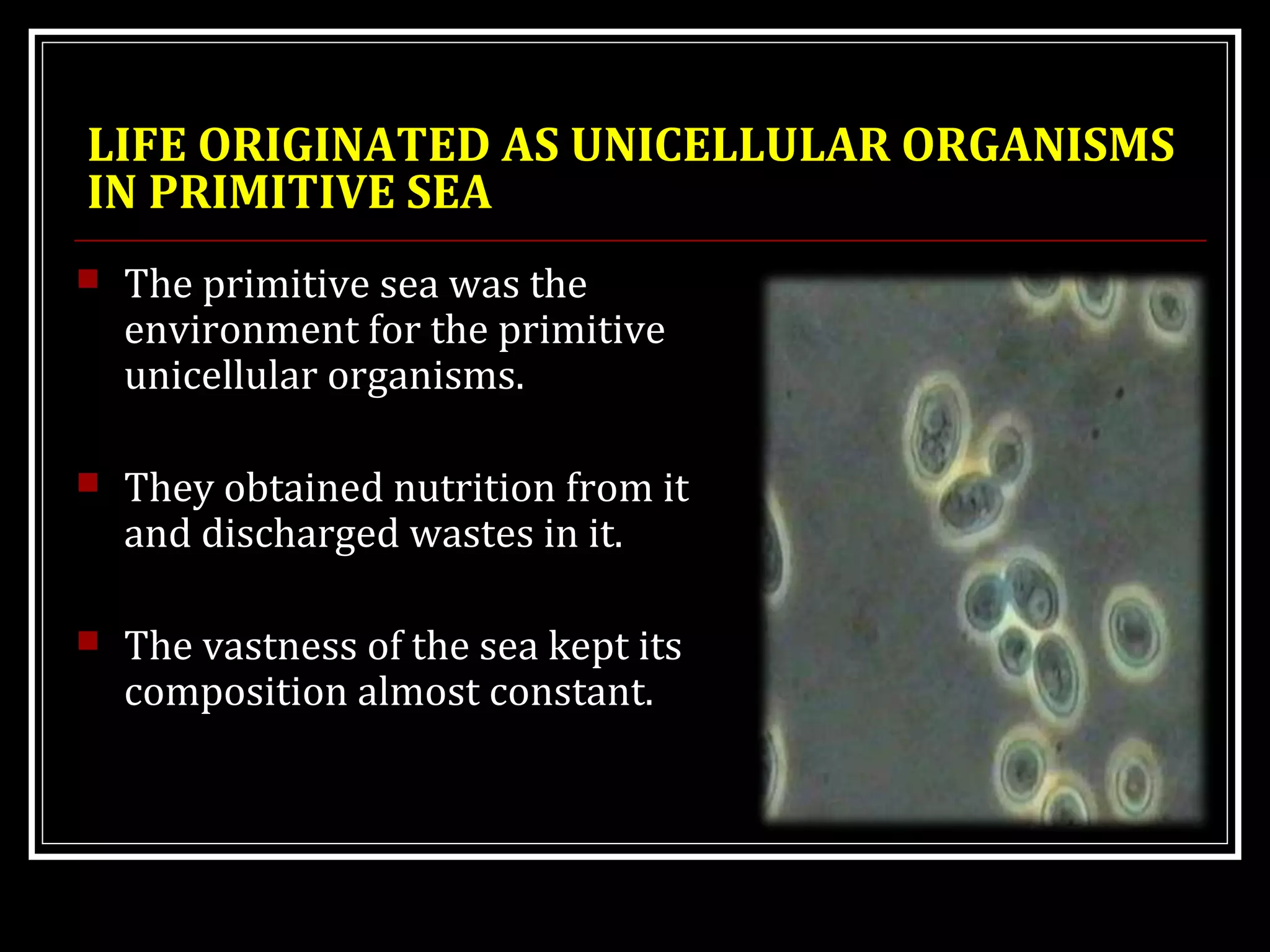
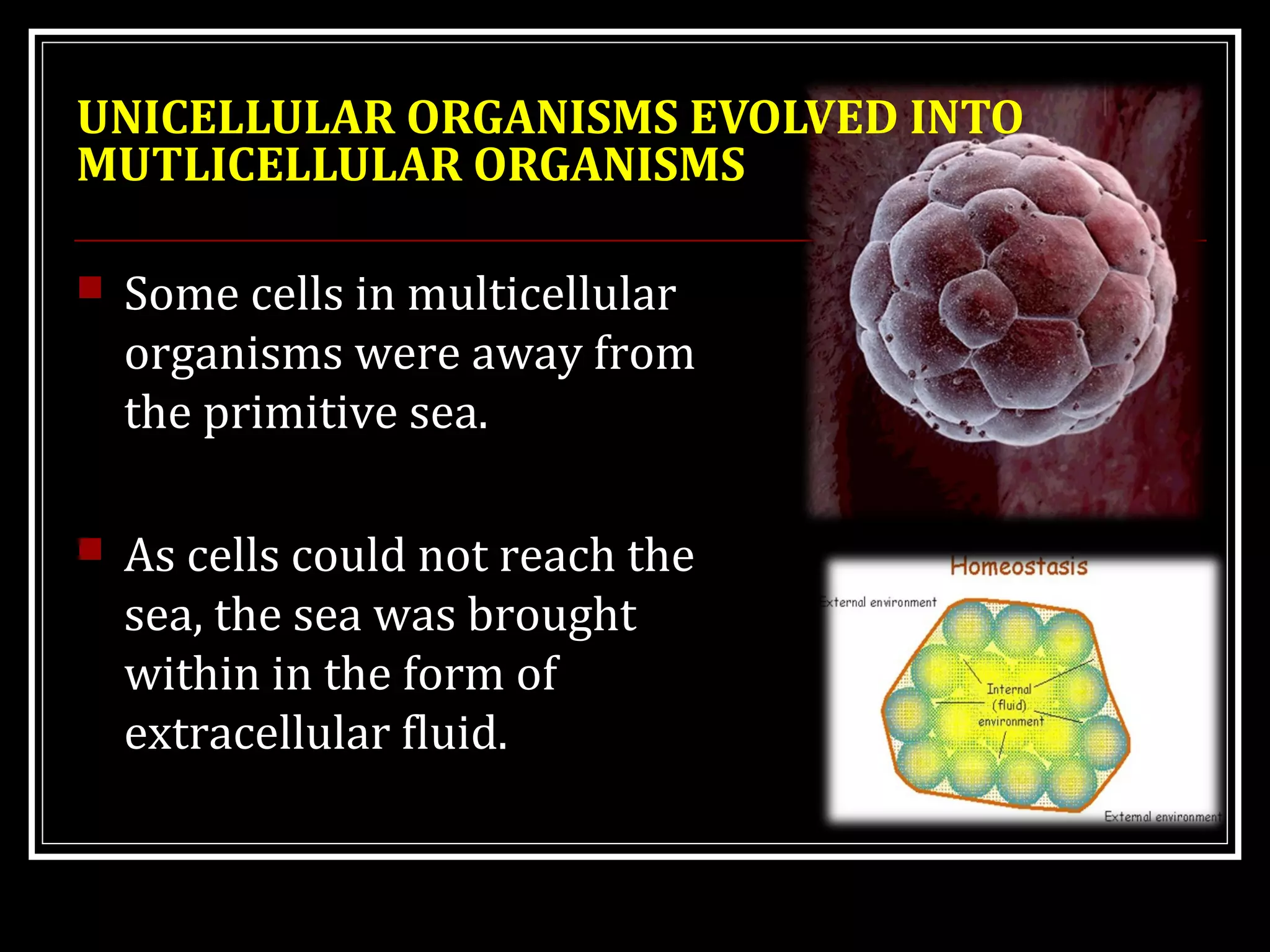
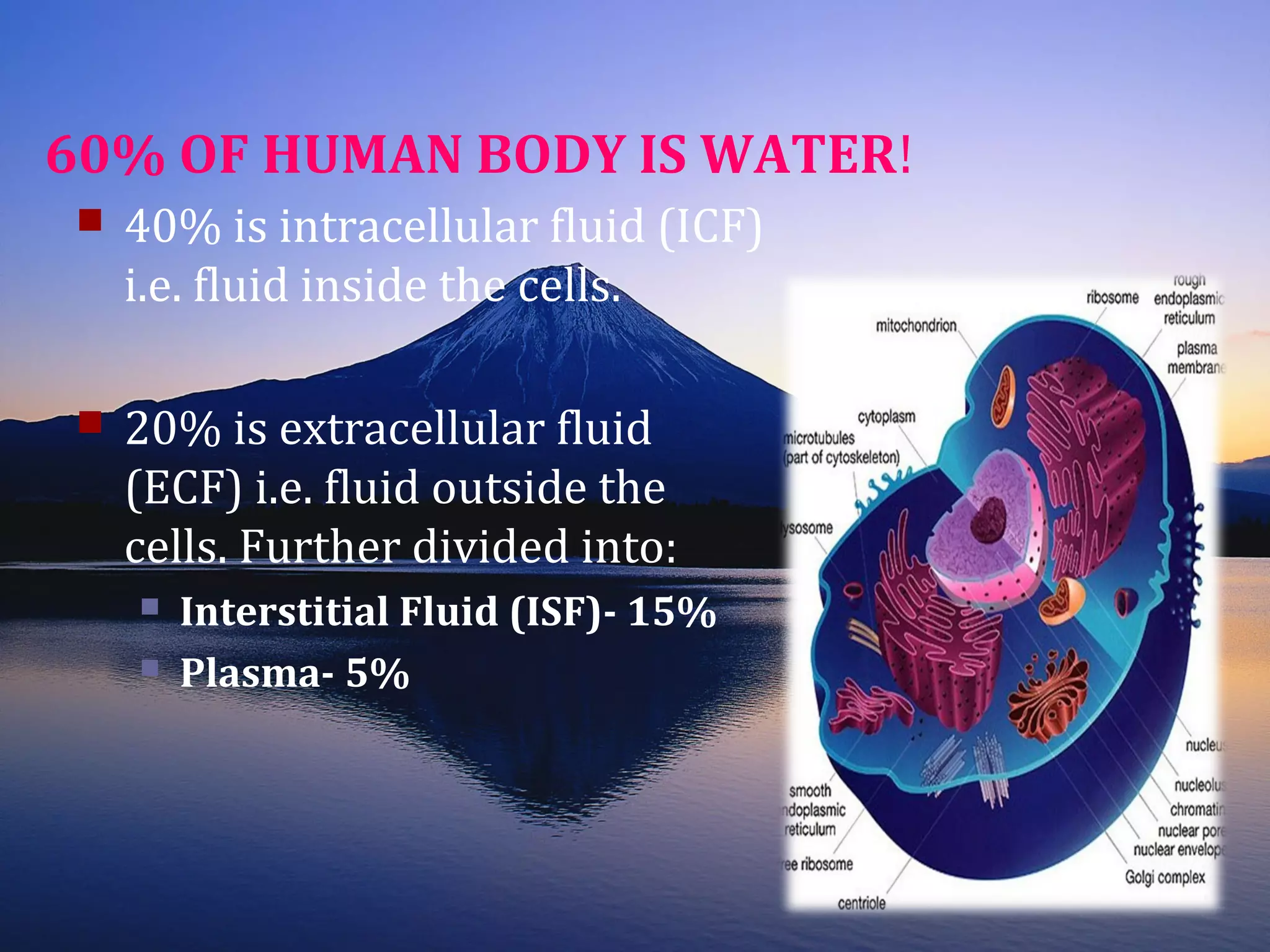
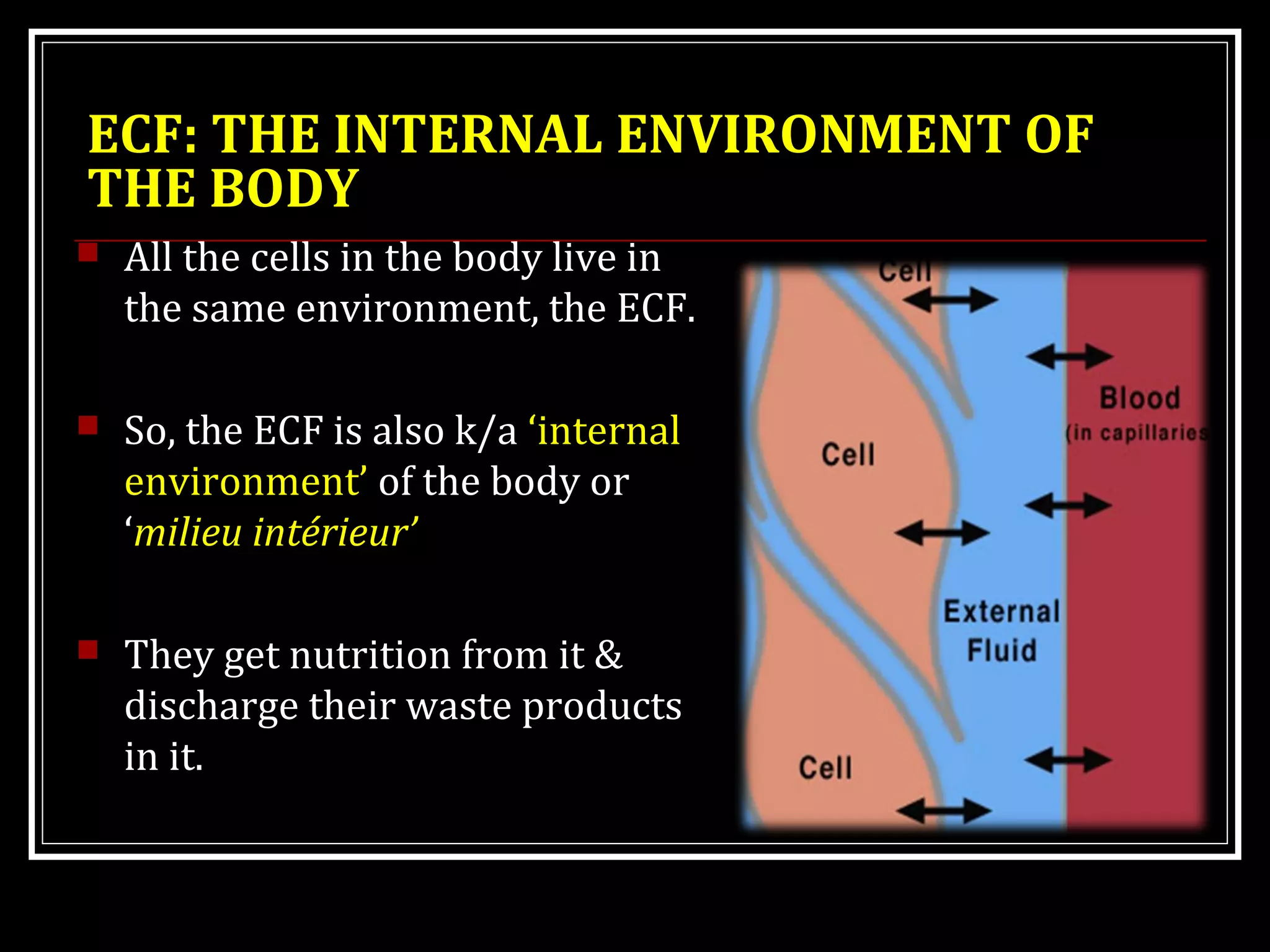
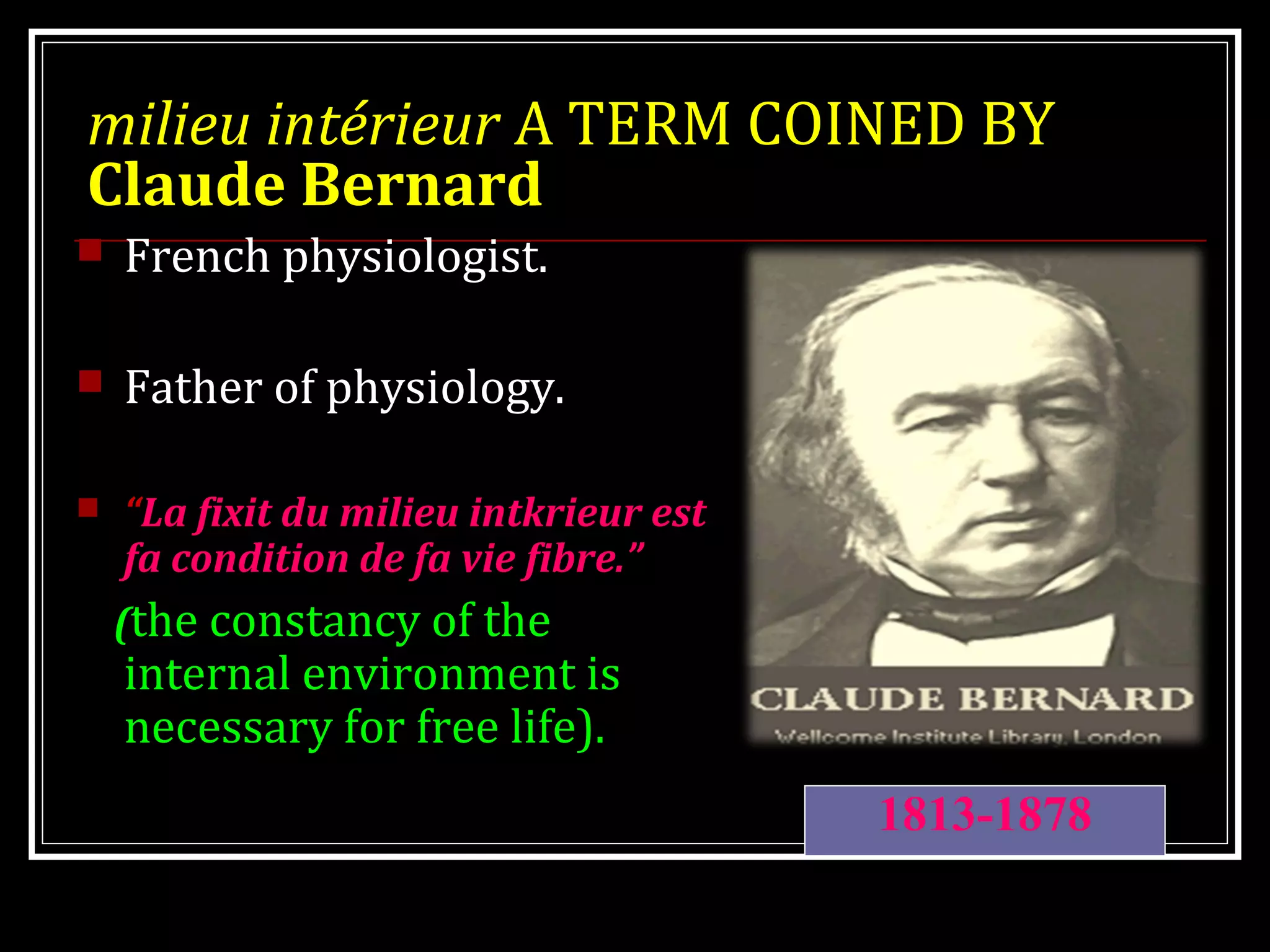
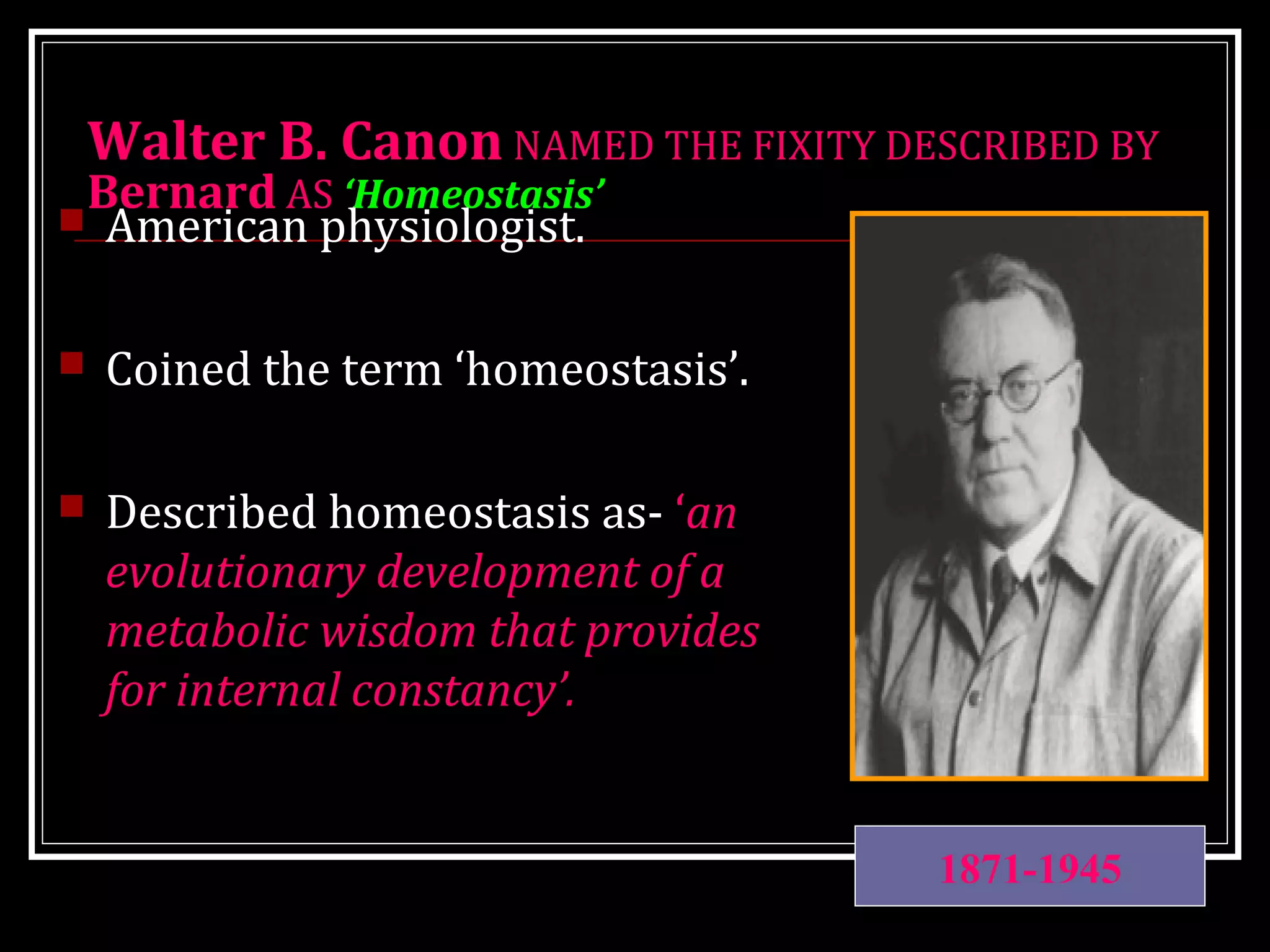
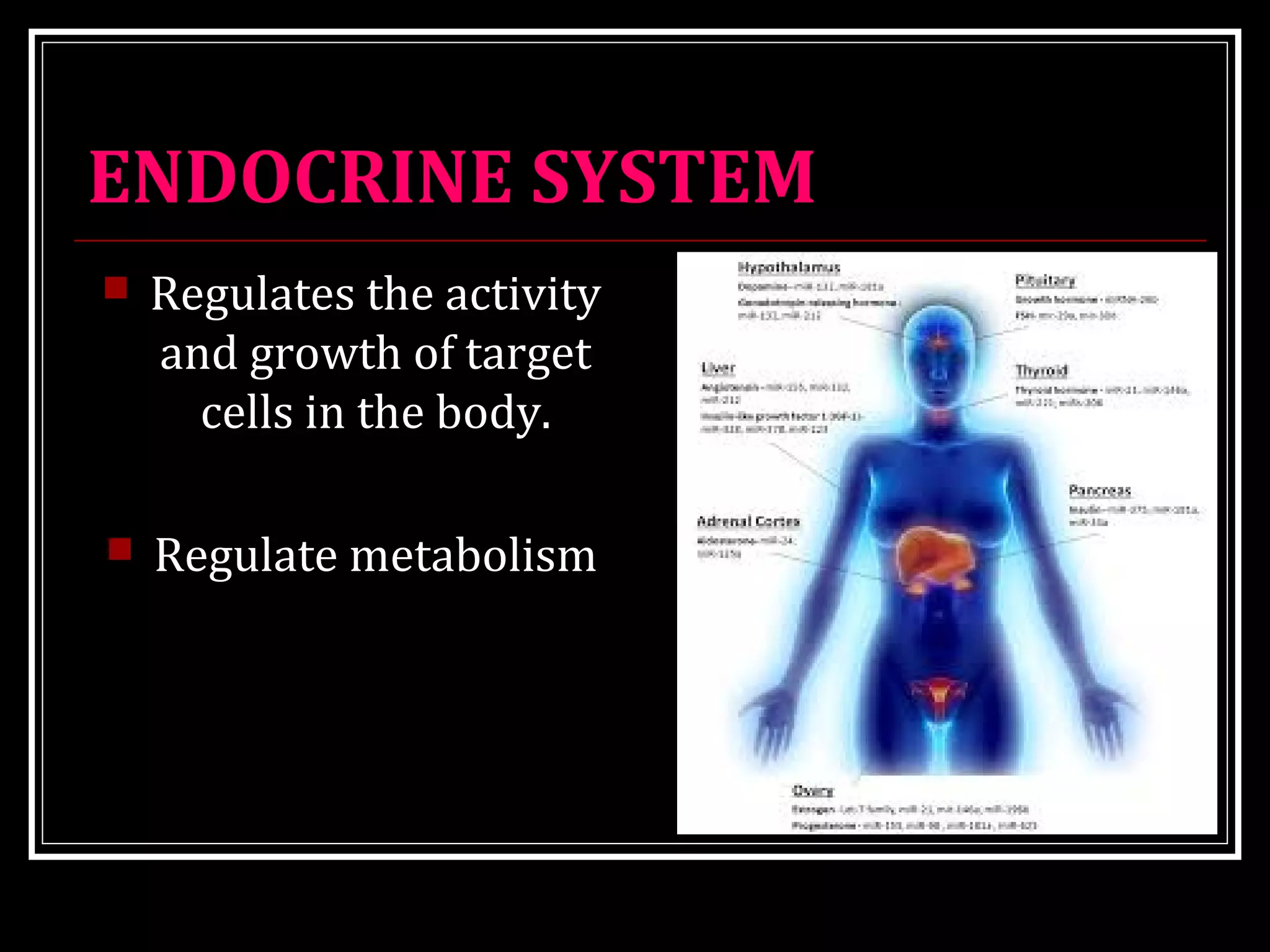
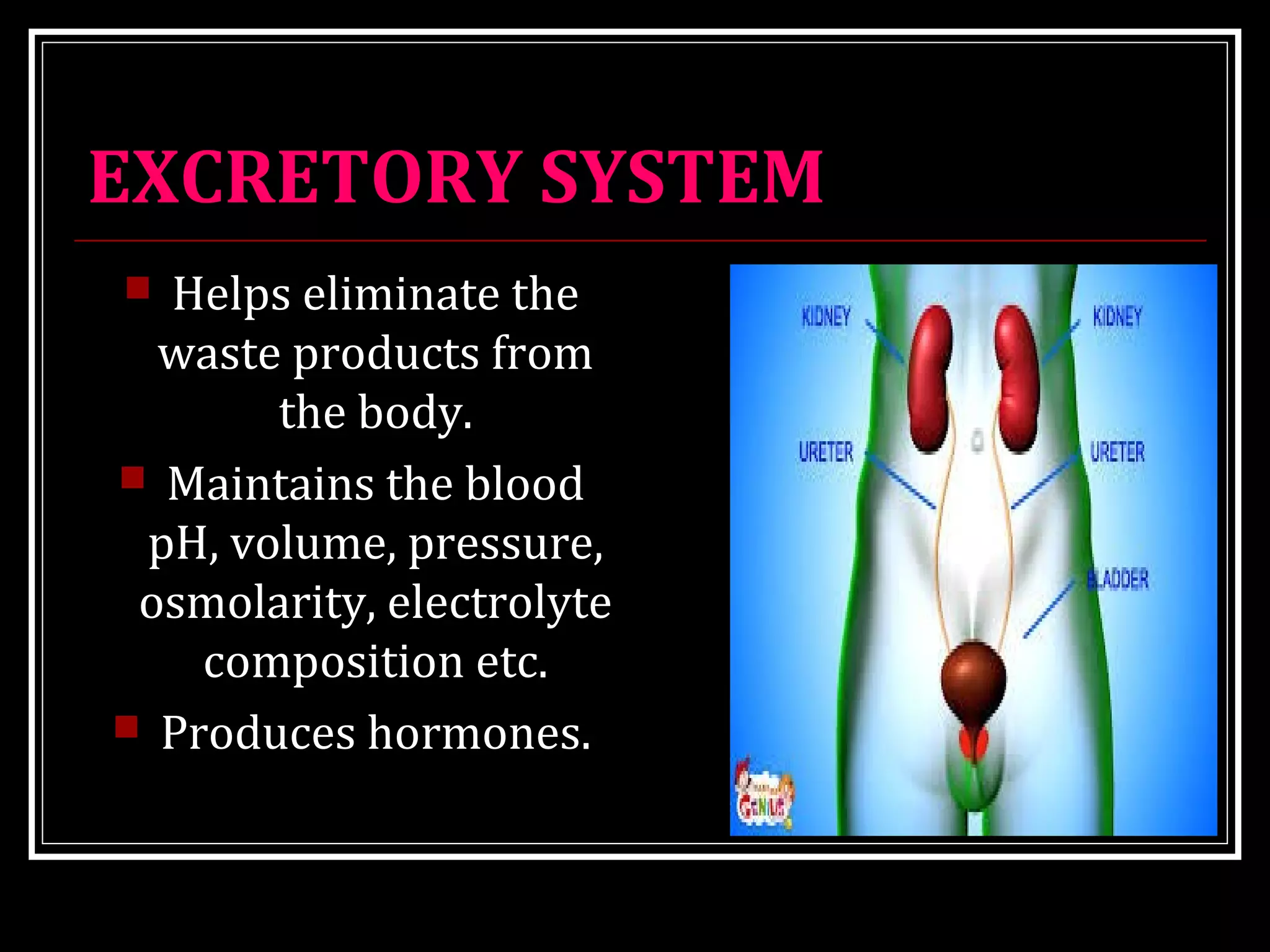
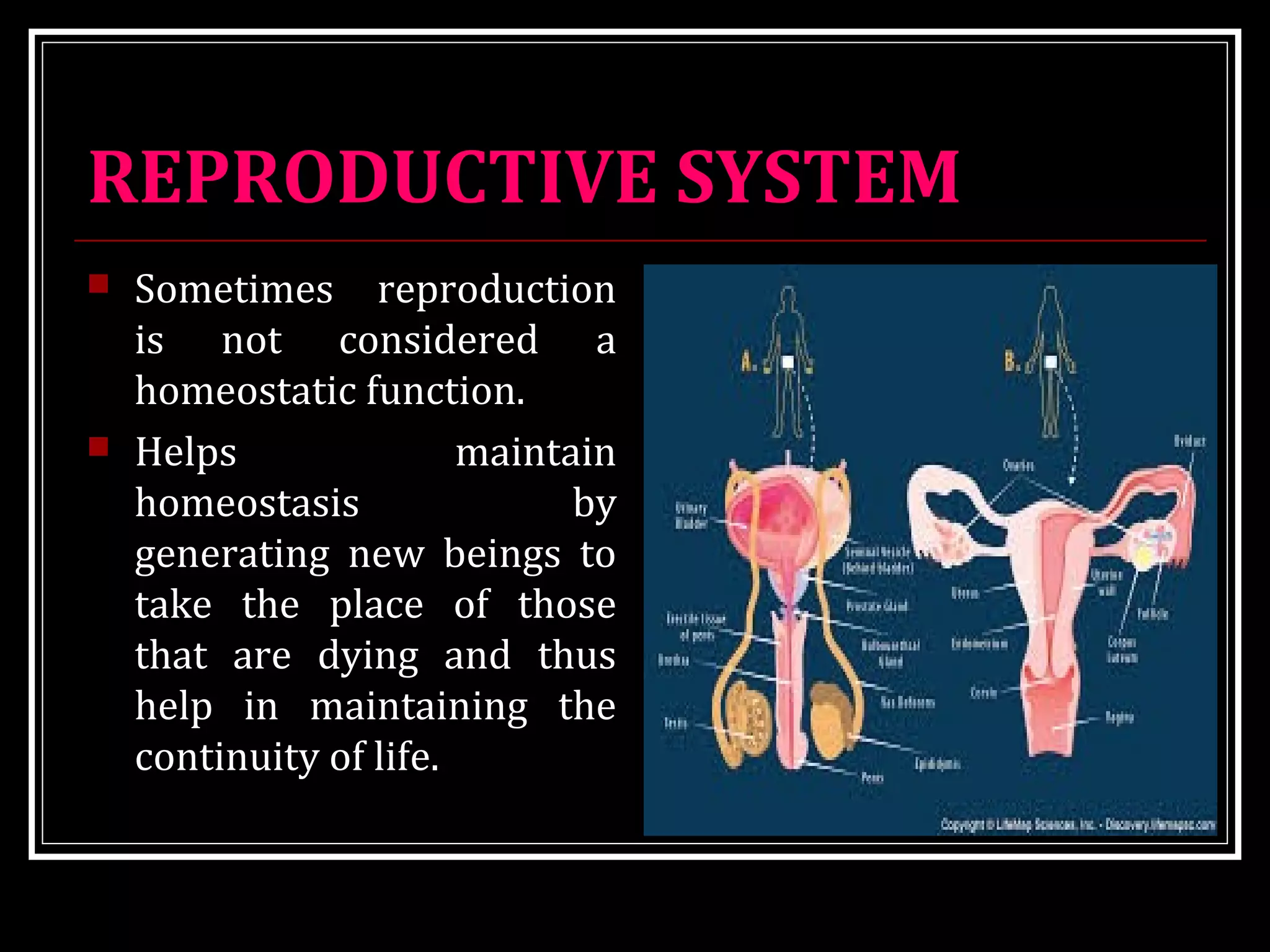
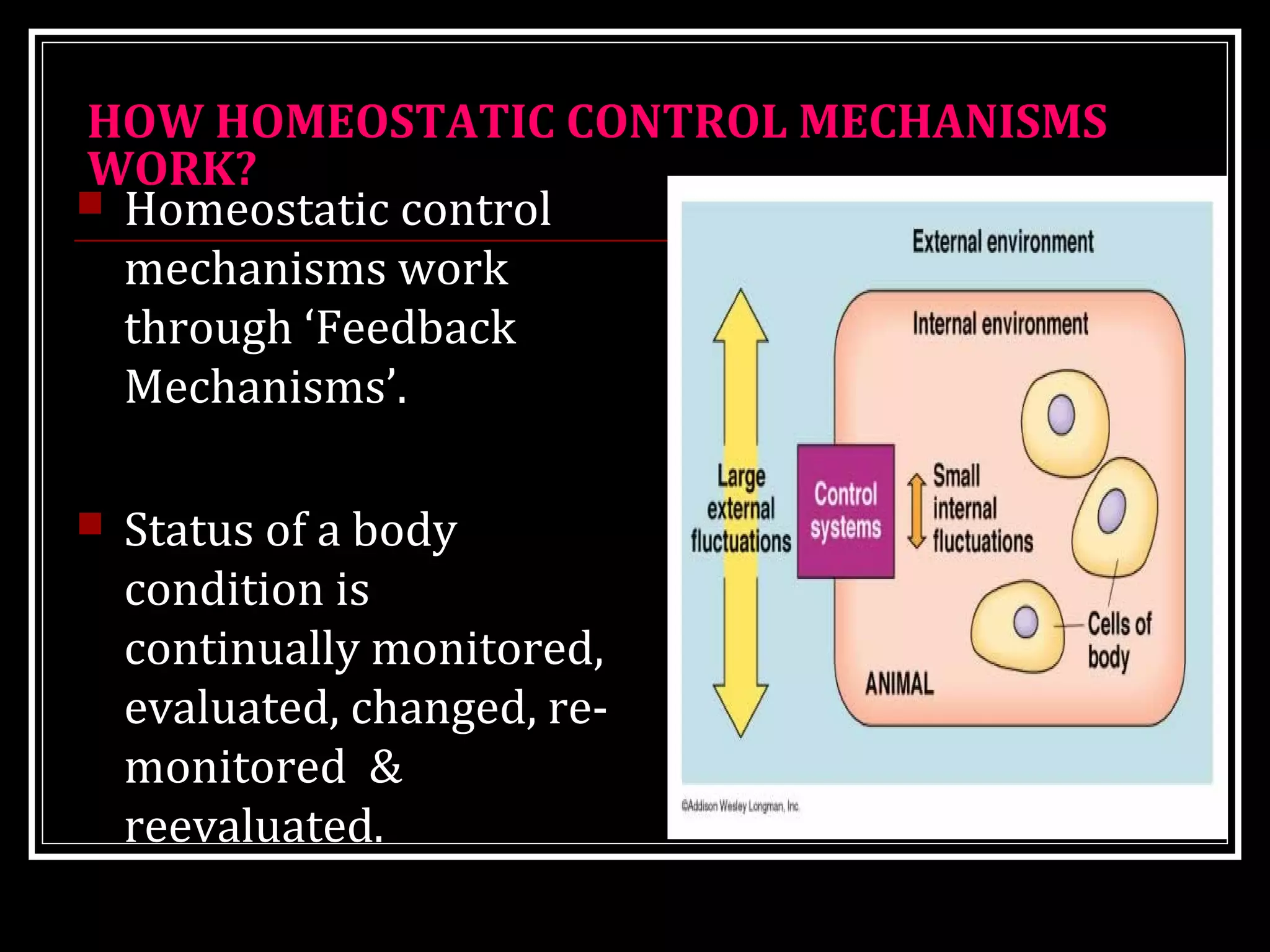
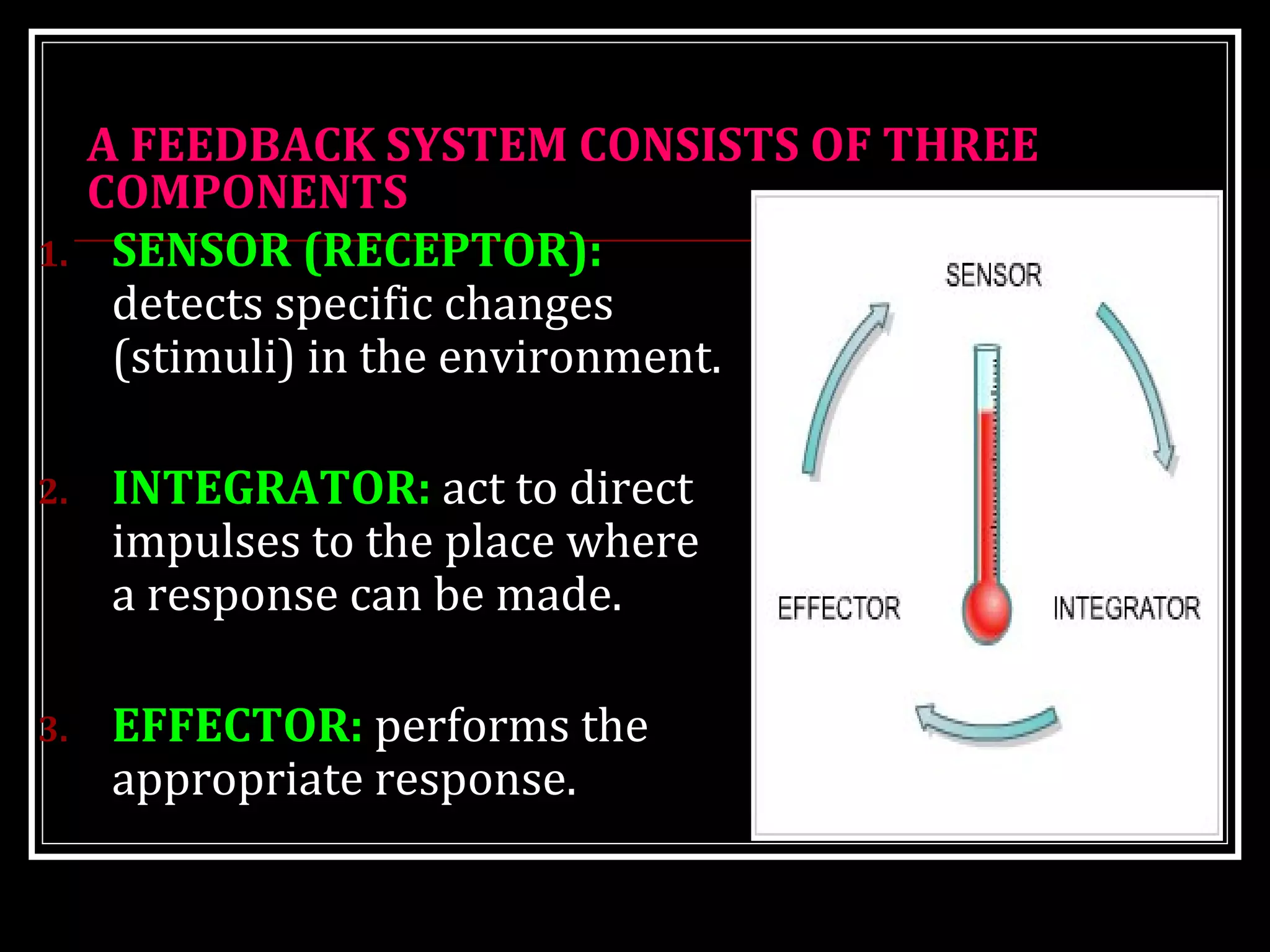
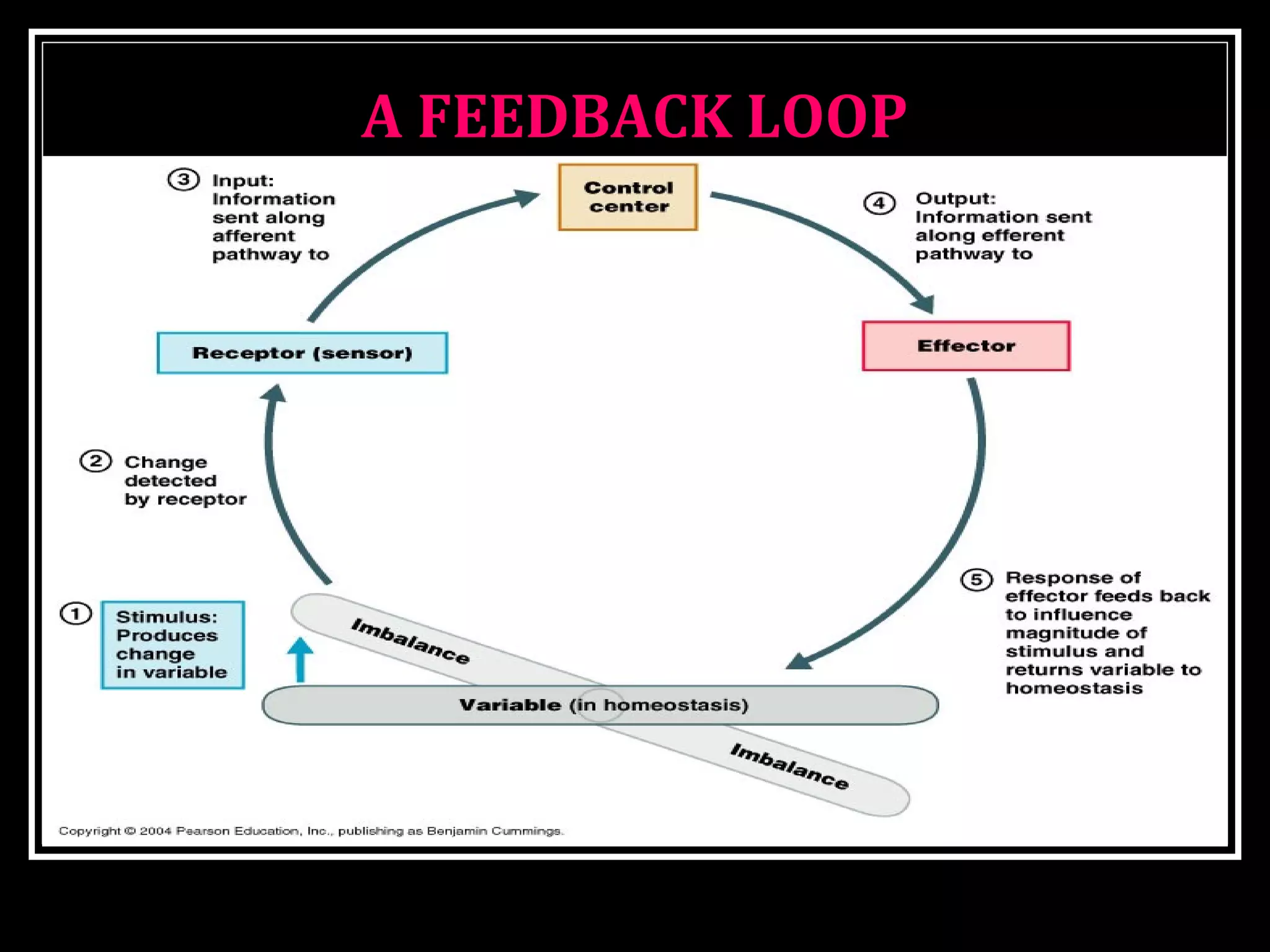
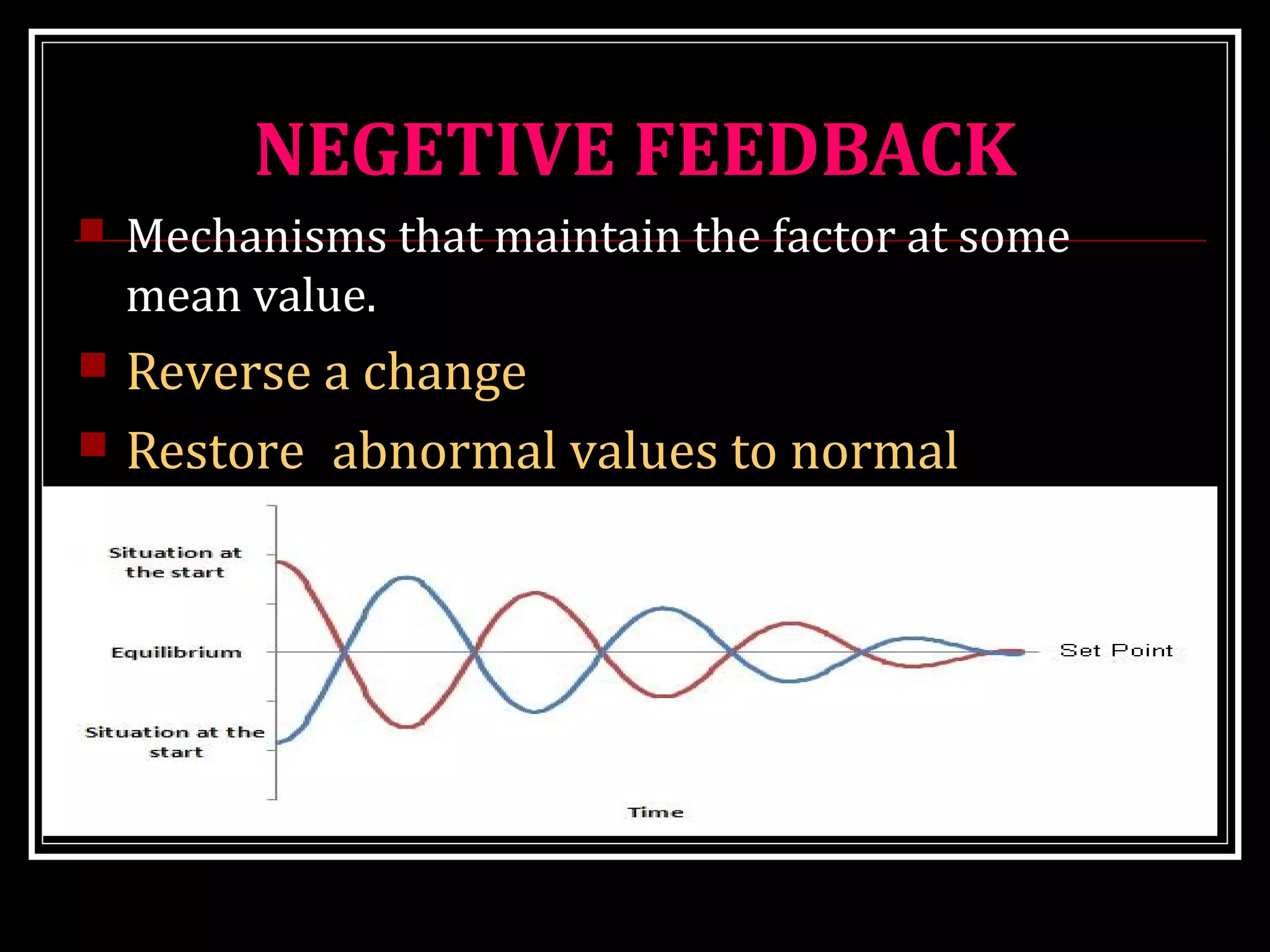
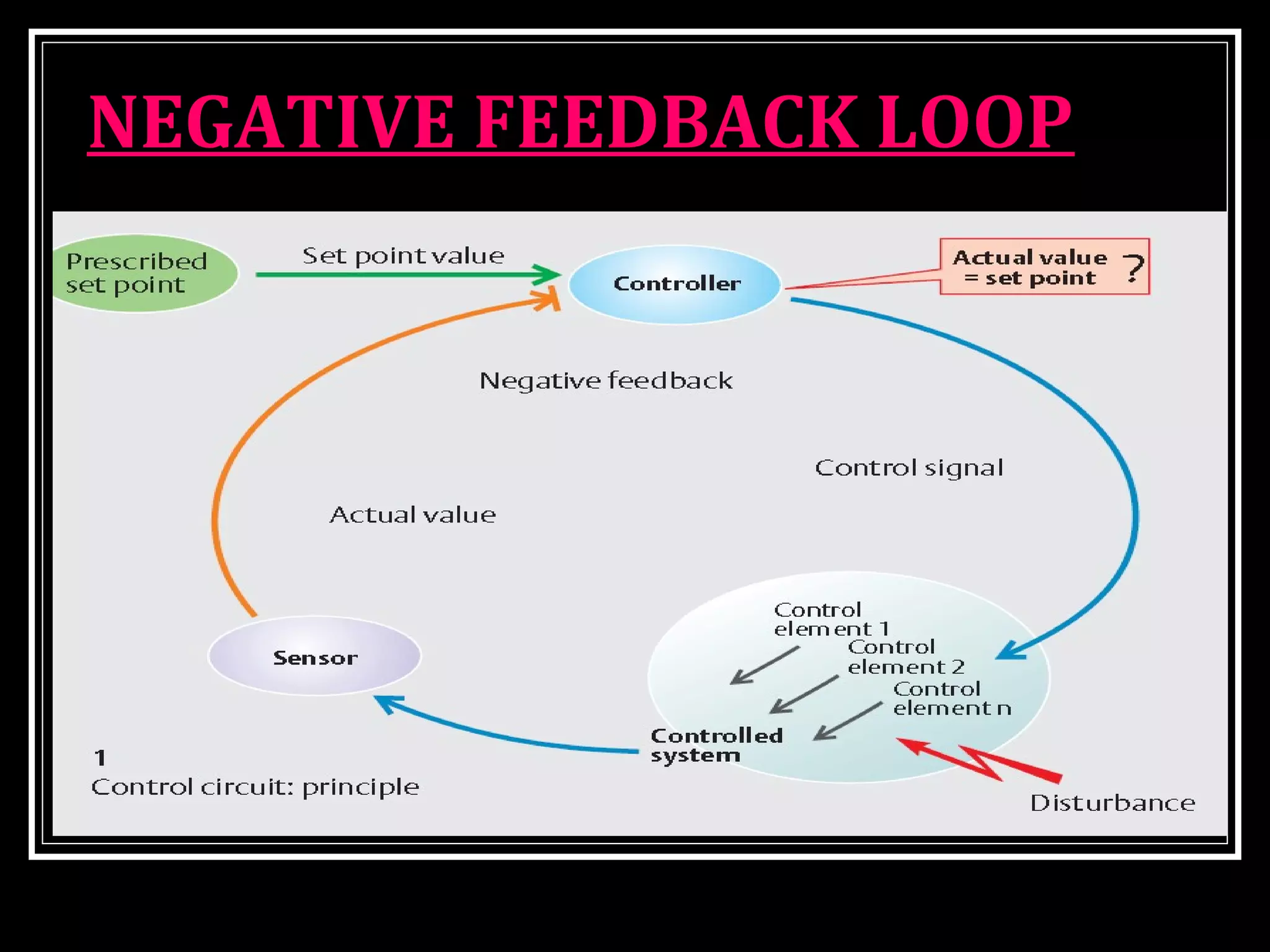
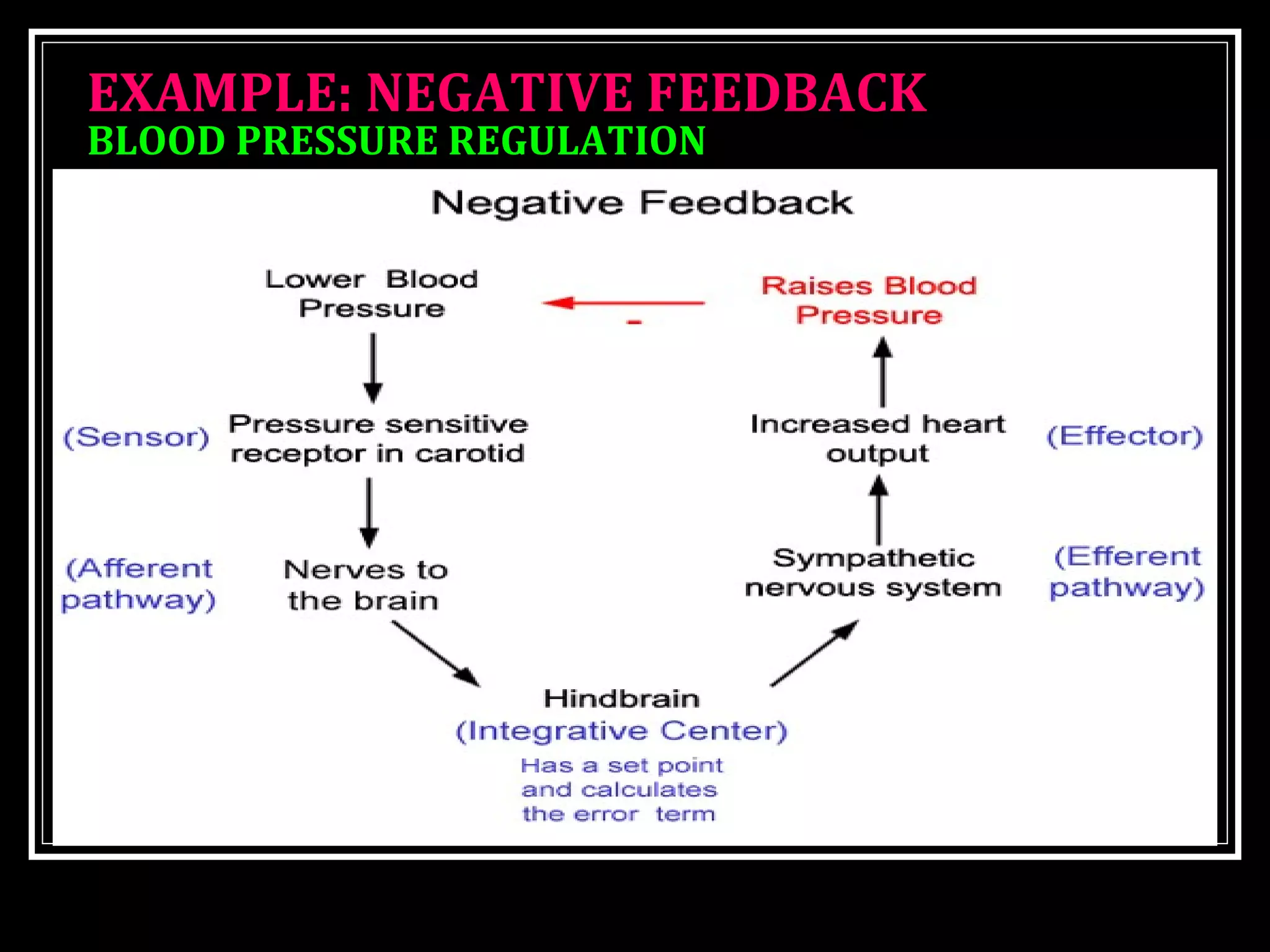
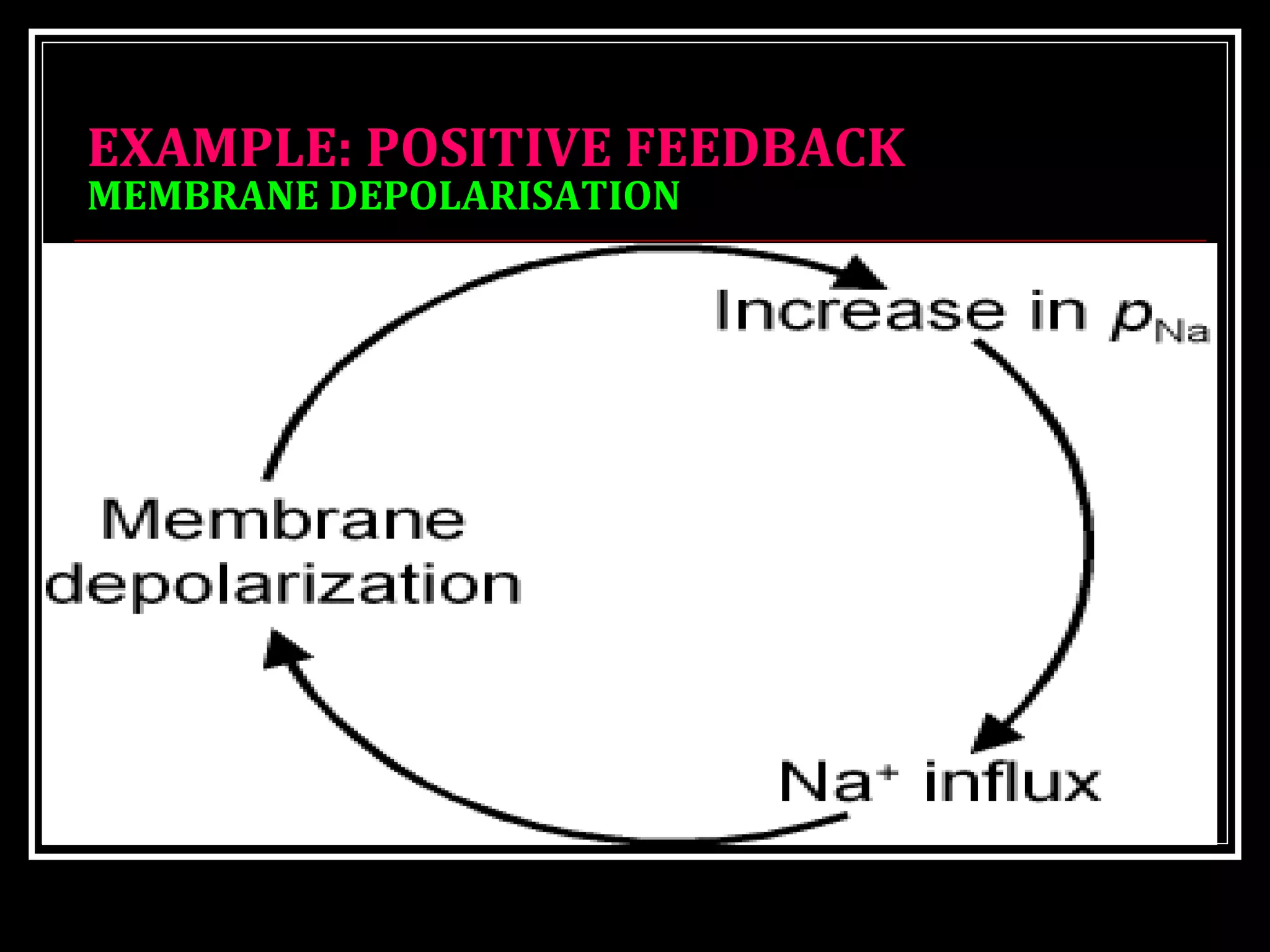
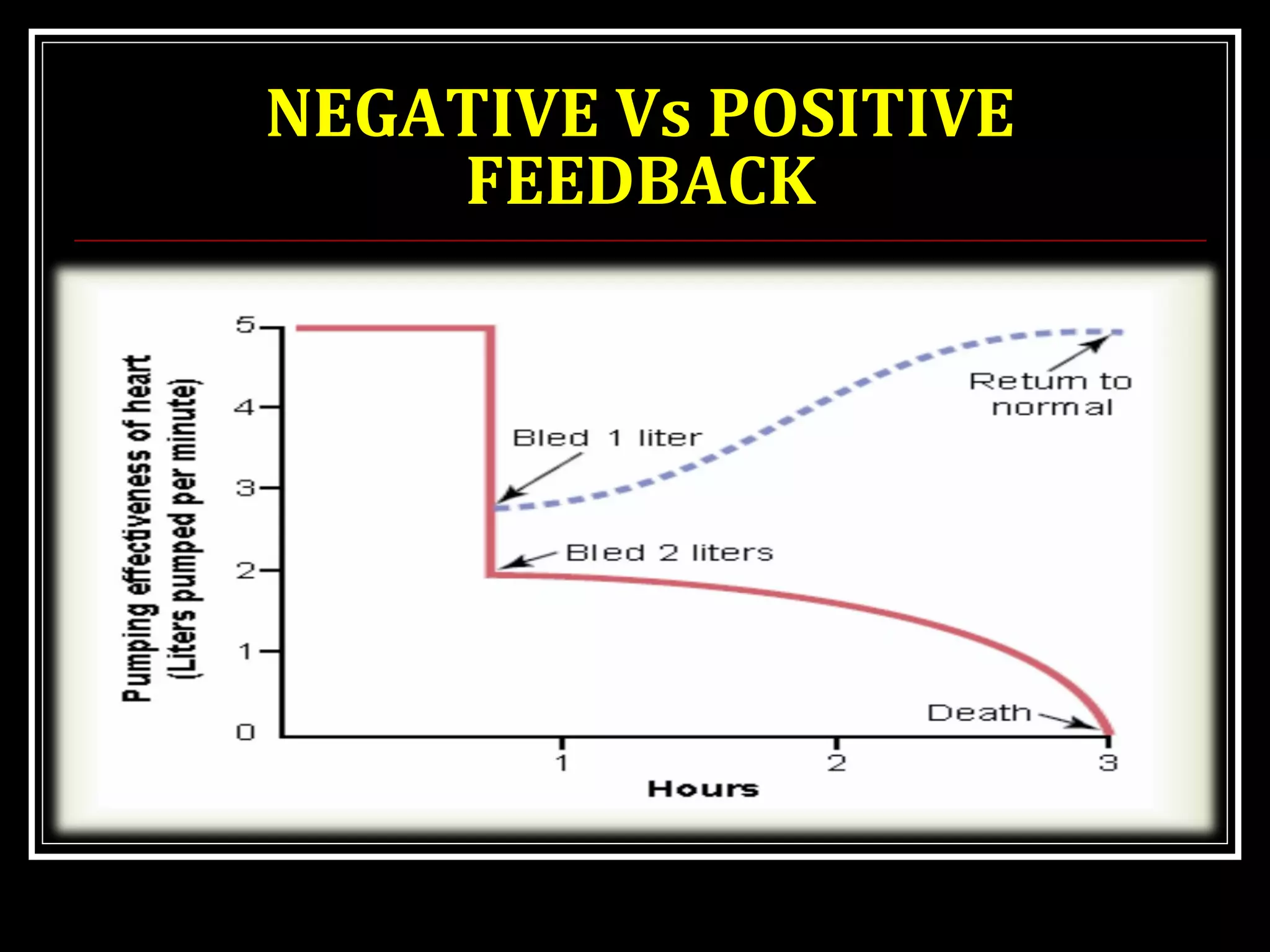
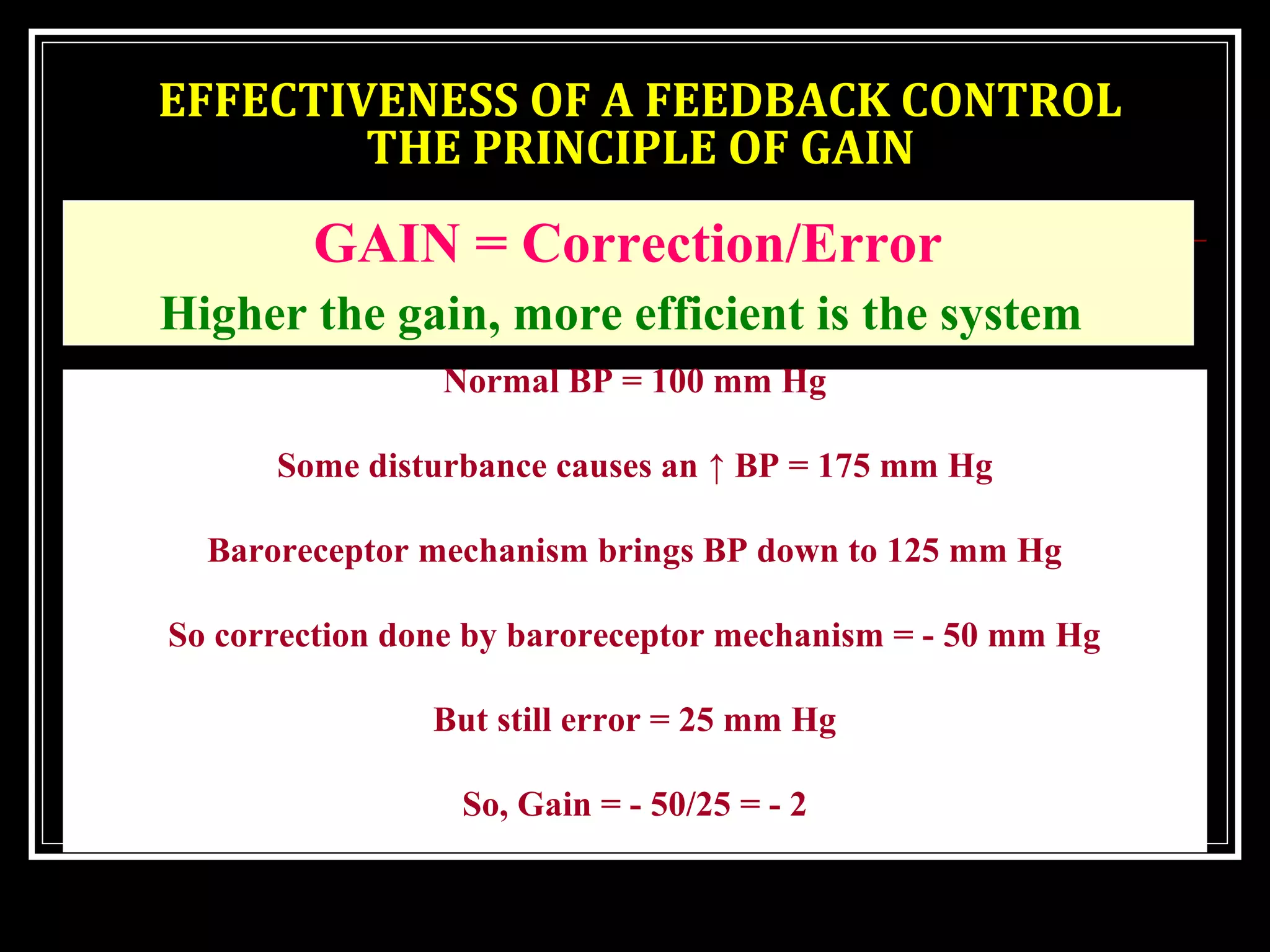
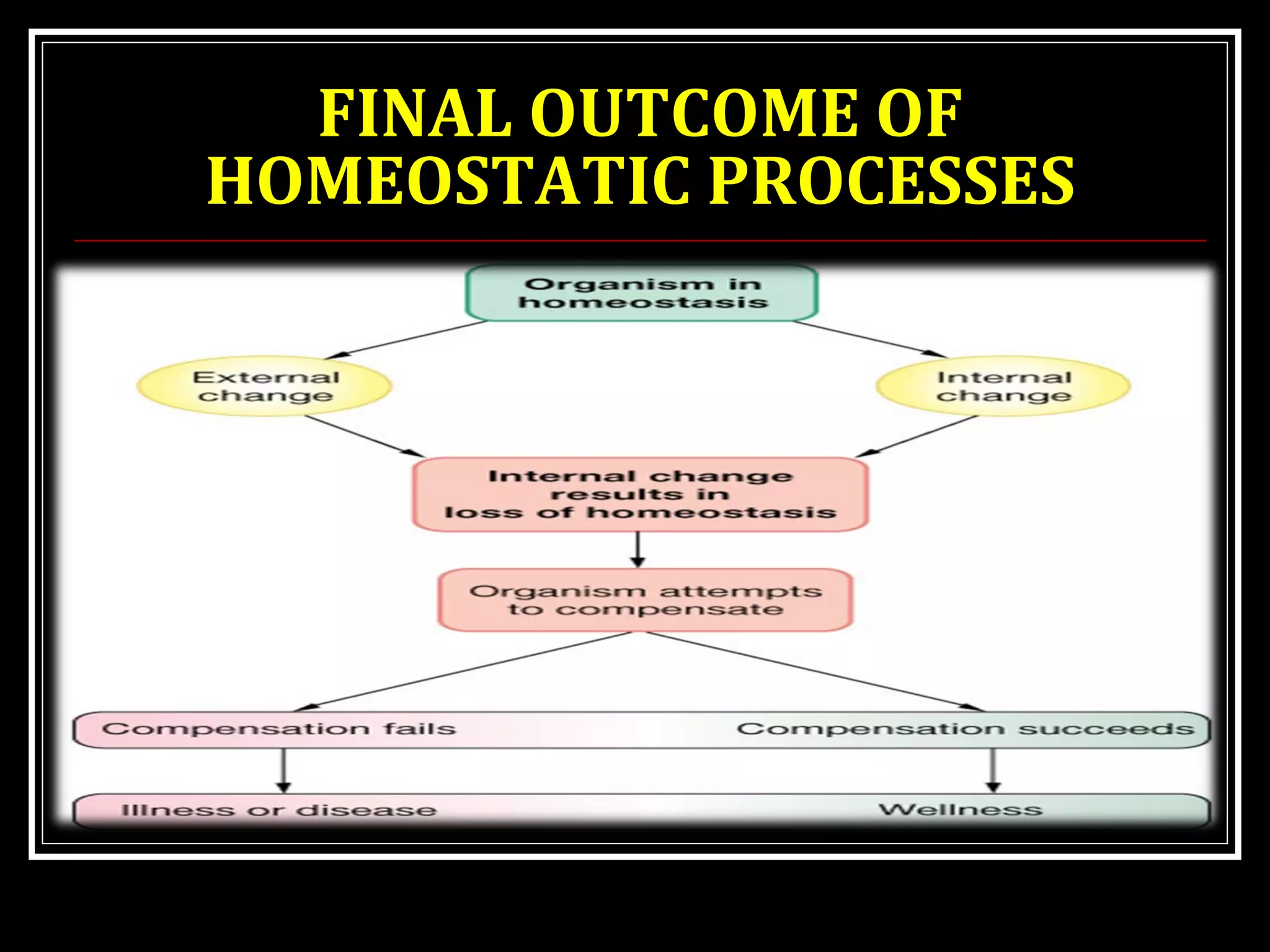
Homeostasis refers to the body's ability to maintain stable internal conditions and regulate physiological processes even when the external environment changes. All body systems work cooperatively through feedback mechanisms to sense changes and restore balance. For example, the cardiovascular system transports materials to cells while the respiratory system regulates gas exchange and pH. When a parameter like blood pressure rises, negative feedback loops bring it back down through effectors like the baroreceptors. This maintains stability and allows the body to function properly despite external fluctuations.