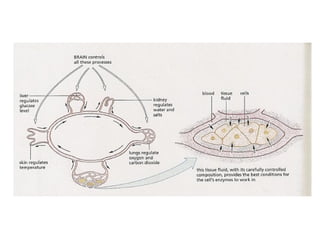
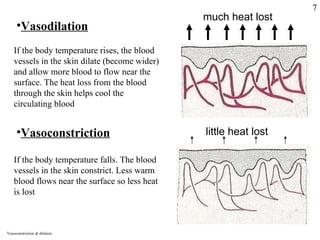
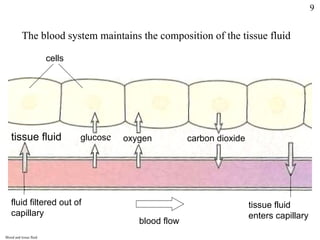
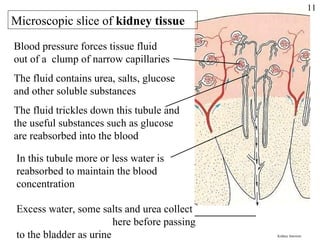
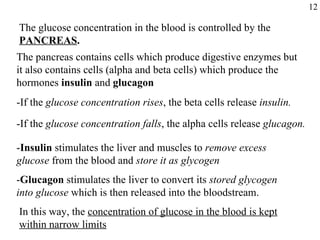
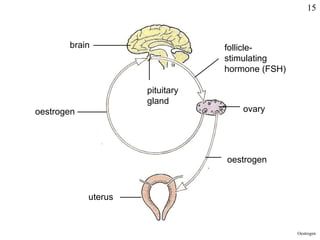
Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of stable internal conditions in the body despite changes in the external environment. Key organs like the skin, kidneys, liver, and endocrine and nervous systems work together to regulate factors such as temperature, pH, water concentration, and glucose levels through negative feedback loops. When detected variations in these conditions occur, systems respond to counteract the change and restore homeostasis.