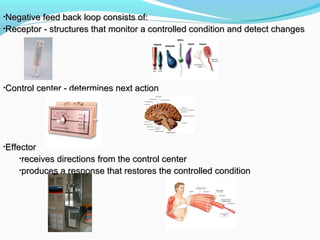
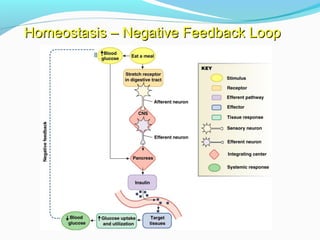
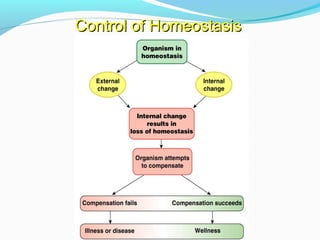
Homeostasis refers to the body's ability to regulate and maintain stable internal conditions necessary for survival, even when external conditions change. It operates through negative and positive feedback loops. Negative feedback loops work to reverse changes that move conditions outside the normal range, like increasing heart rate in response to stress. Positive feedback loops intensify changes, like contractions during childbirth increasing in strength as pressure from the baby rises. Homeostasis is constantly disrupted by internal and external stimuli but feedback loops work to quickly restore equilibrium and prevent conditions from becoming dangerous.