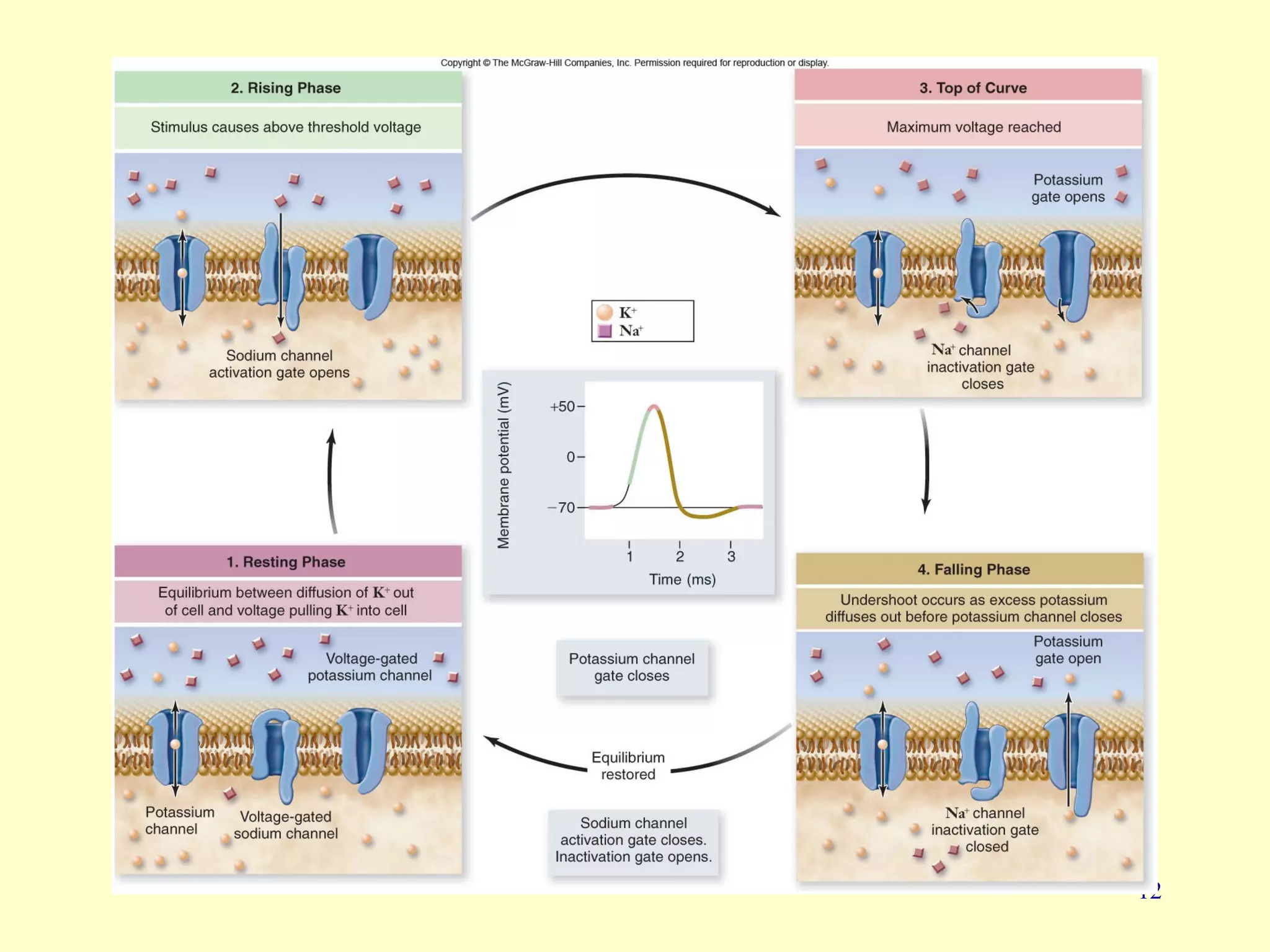
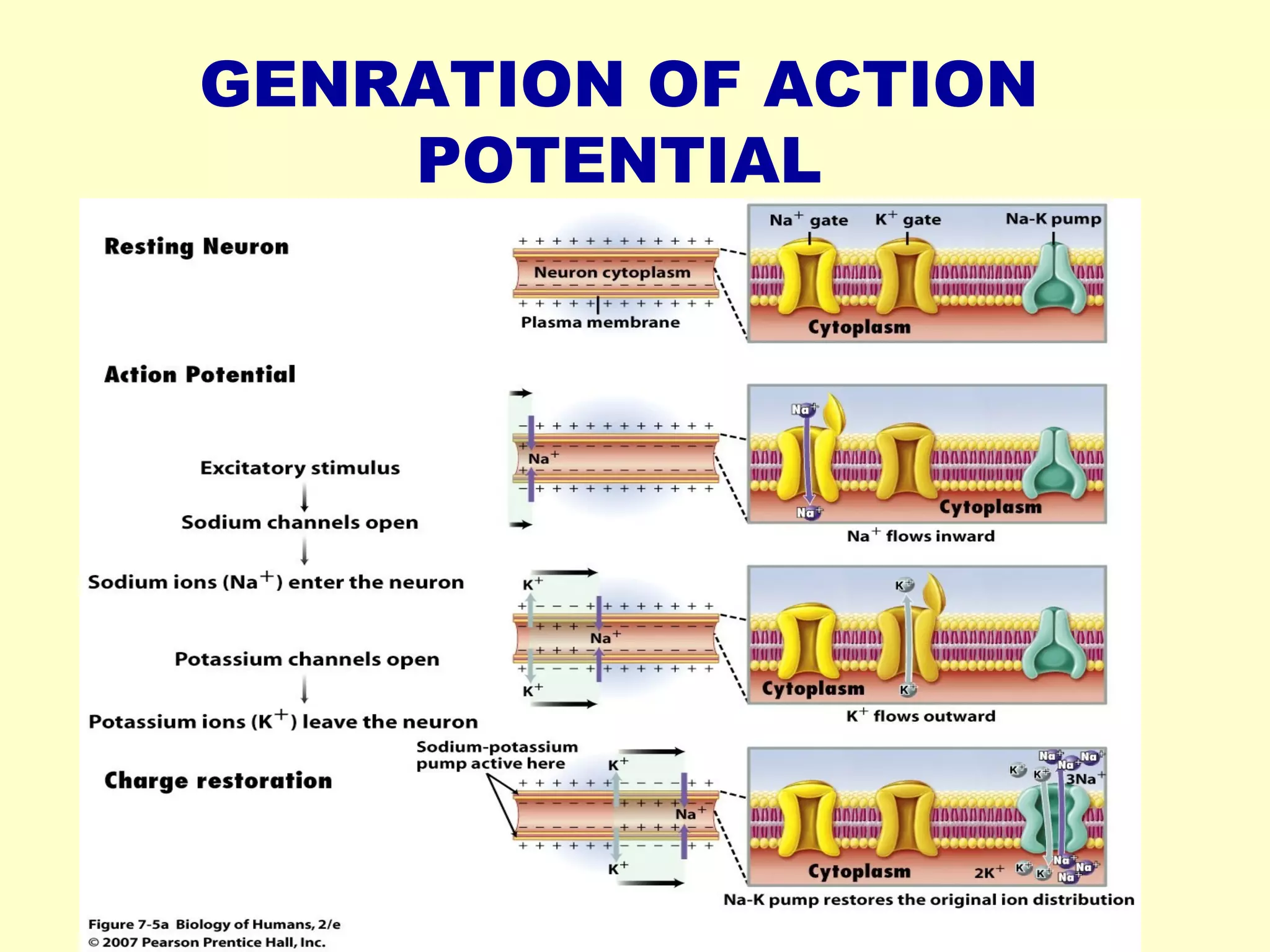
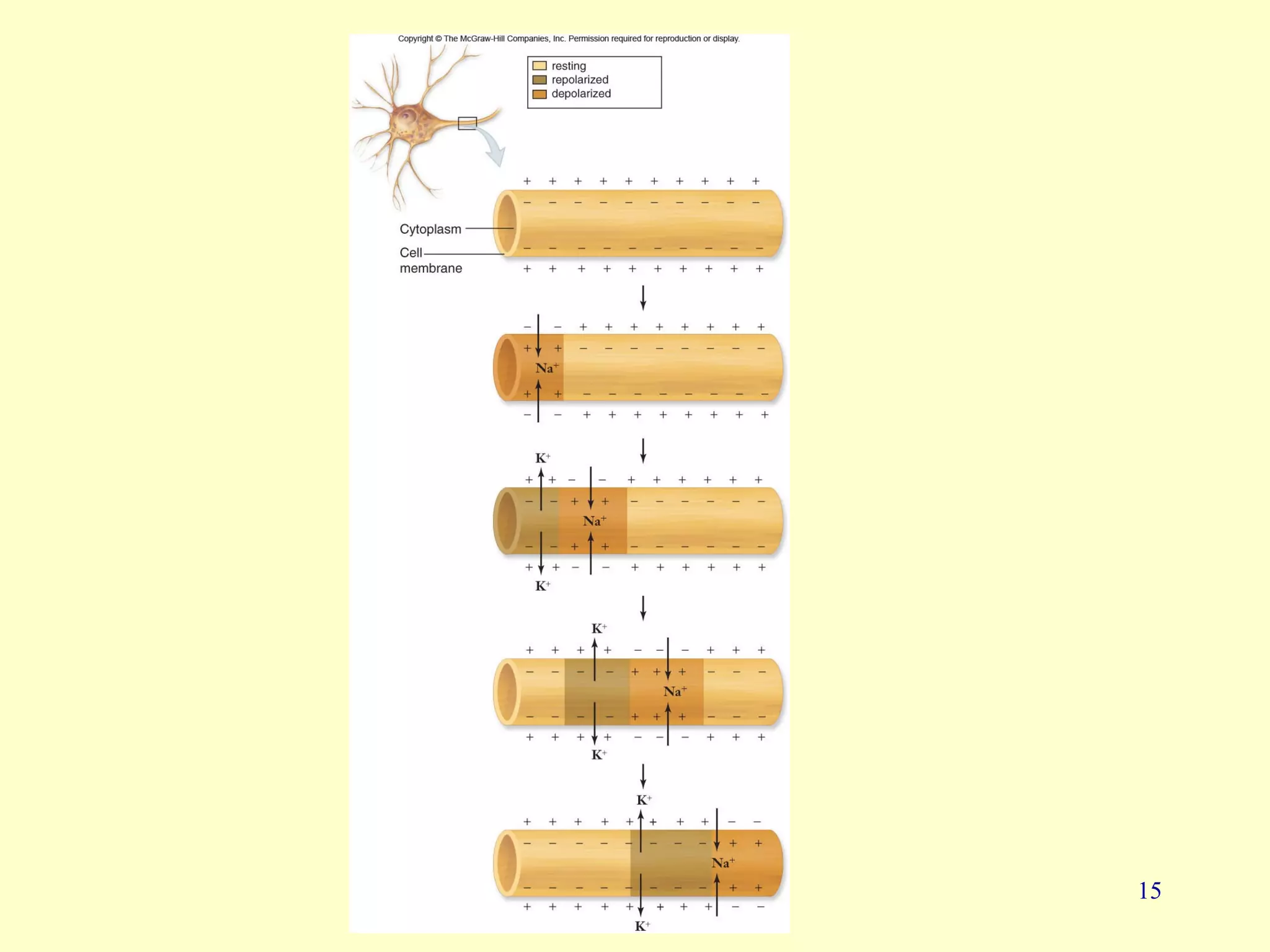
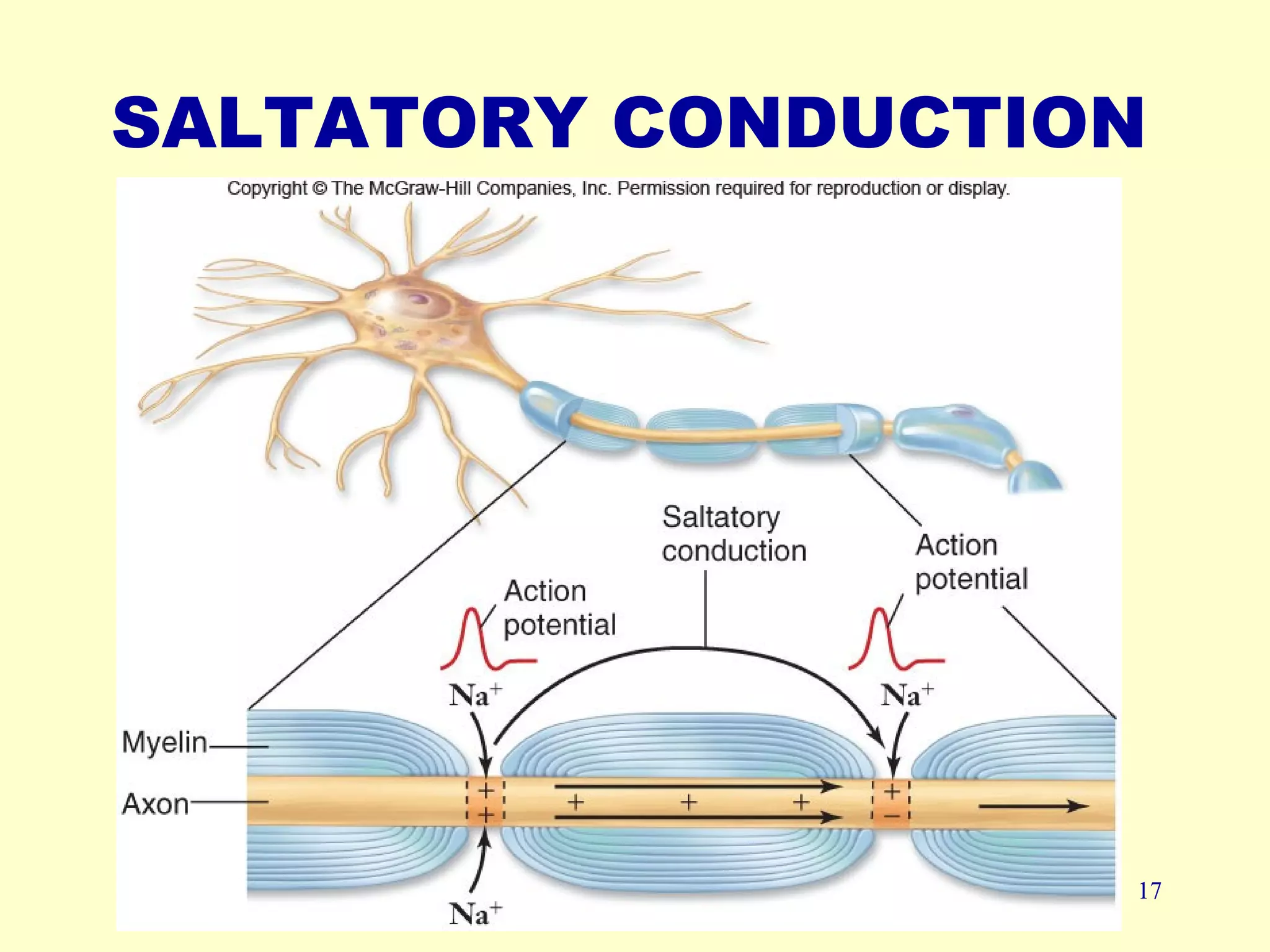
Nerve impulse conduction involves the generation and propagation of action potentials along neurons. At rest, neurons maintain a negative resting potential due to an unequal distribution of ions across the cell membrane. When stimulated, the opening of voltage-gated sodium channels causes rapid depolarization and the generation of an action potential. This potential then propagates along the axon as adjacent regions are depolarized, triggering their own action potentials. At synapses, the action potential is converted to a chemical signal via neurotransmitter release, which can then trigger a new action potential in the post-synaptic cell. Myelination and large axon diameters increase conduction velocity.


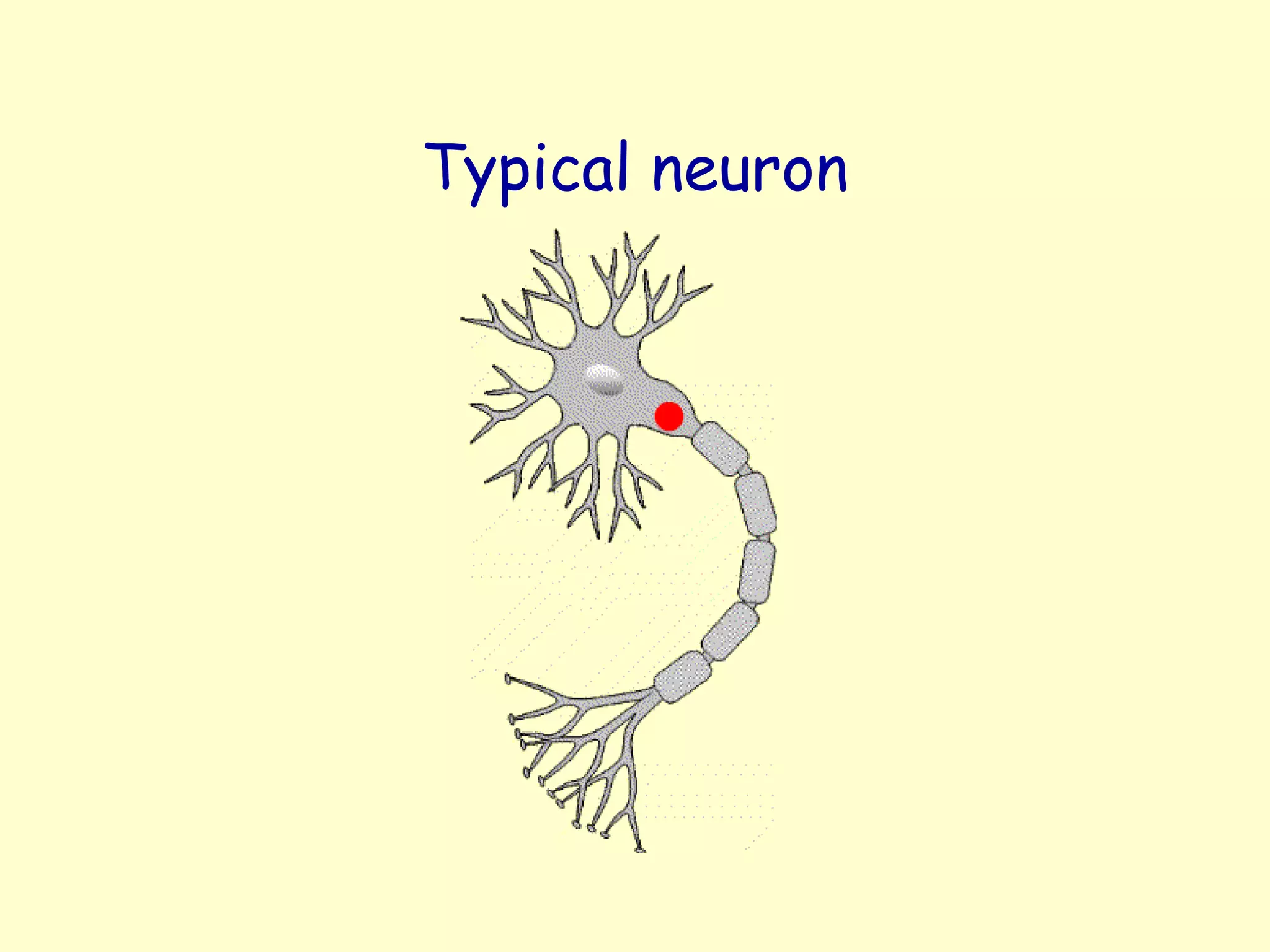
![Neuron
• Dendrite - conducts “signal” toward the cell body -- [input zone]
– often short, numerous & highly branched
– signal comes from sensory cell or neighboring neuron
• Axon - usually a single fiber -- [conducting zone]
– conducts signal away from cell body to another neuron or effector cell
• Axon Ending
– a cluster of branches (100’s to 1000’s)
– each with a bulblike synaptic knob
– relays signal to next neuron / effector cell](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nerveimpulseconduction-141230052013-conversion-gate02/75/Nerve-impulse-conduction-4-2048.jpg)








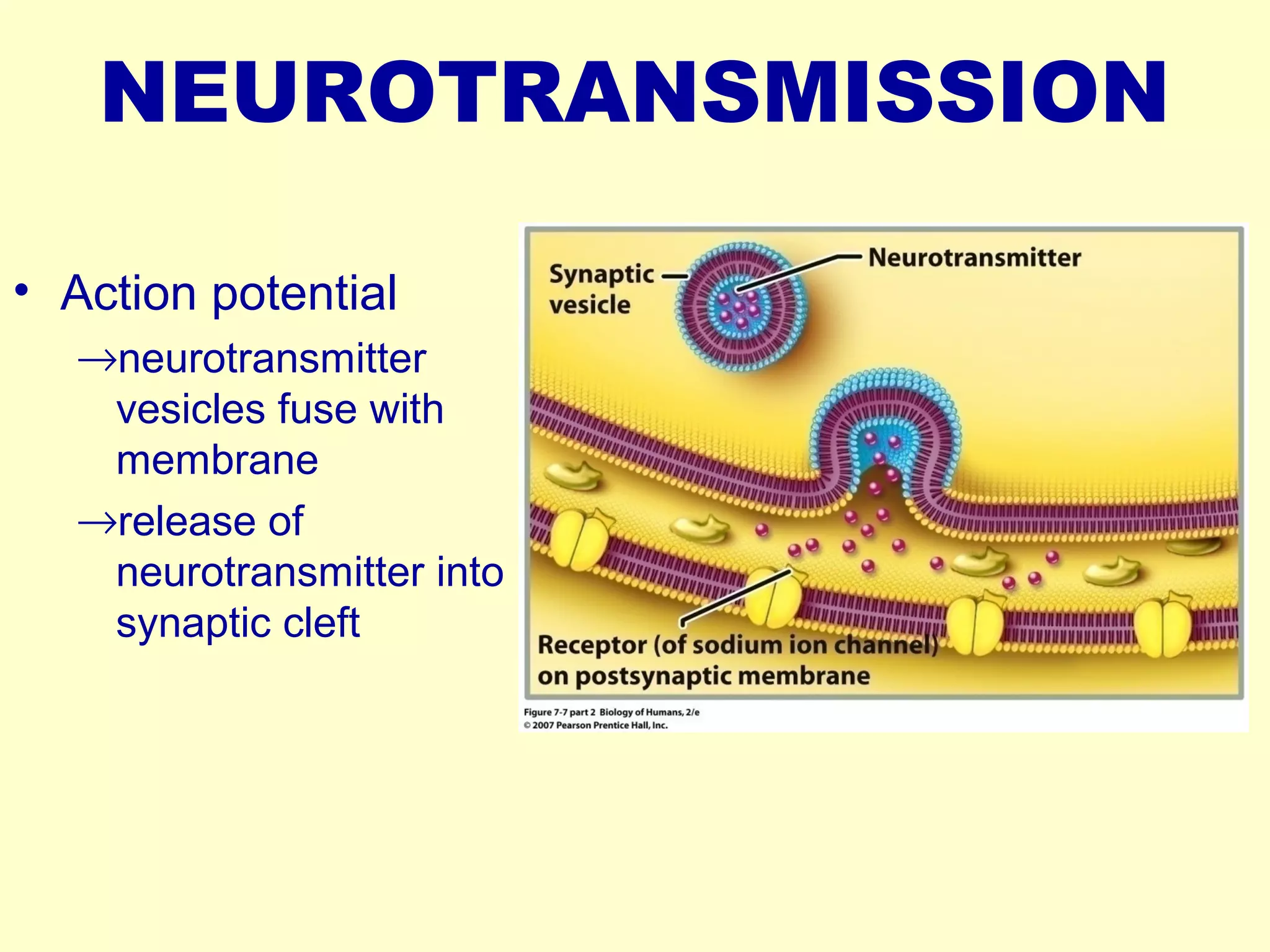
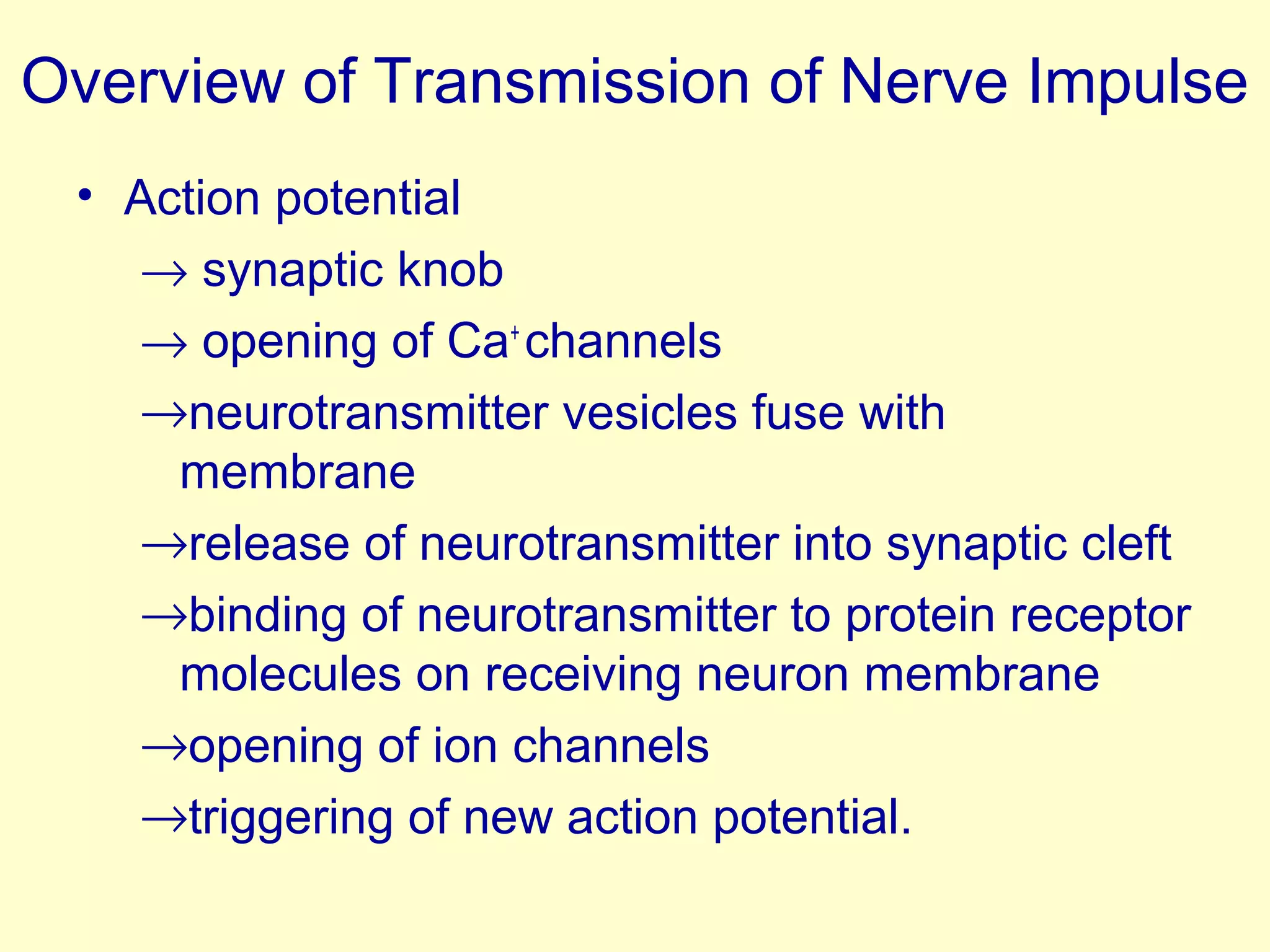
![NEUROTRANSMISSION
• Electrical [no synapse]
– common in heart & digestive tract - maintains steady,
rhythmic contraction
– All cells in effector contain receptor proteins for
neurotransmitters
• Chemical - skeletal muscles & CNS
– presence of gap (SYNAPTIC CLEFT) which prevents action
potential from moving directly to receiving neuron
– ACTION POTENTIAL (electrical) converted to CHEMICAL
SIGNAL at synapse (molecules of neurotransmitter) then
generate ACTION POTENTIAL (electrical) in receiving
neuron](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nerveimpulseconduction-141230052013-conversion-gate02/75/Nerve-impulse-conduction-18-2048.jpg)
![NEUROTRANSMISSION
• Presynaptic neuron
• Vesicles
• [Calcium channels]
• Synaptic cleft
• Postsynaptic neuron
• Neurotransmitter receptor](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nerveimpulseconduction-141230052013-conversion-gate02/75/Nerve-impulse-conduction-20-2048.jpg)