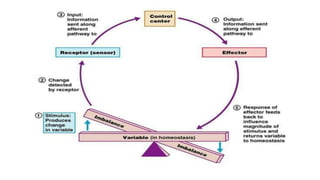
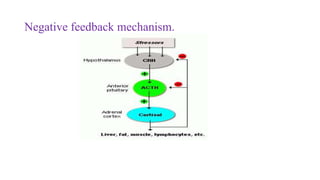
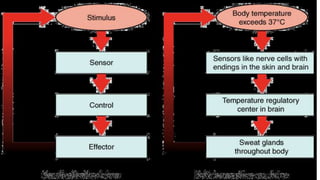
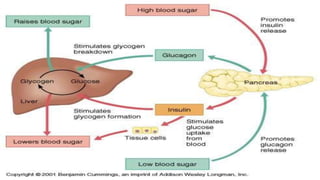
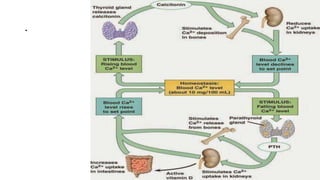
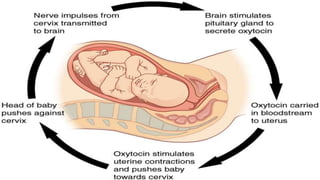
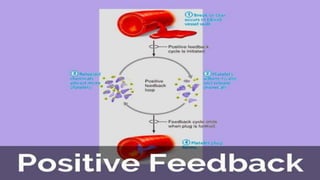
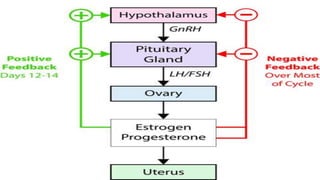
Homeostasis refers to the maintenance of a stable internal environment in the body. It involves negative feedback loops that counteract changes to keep properties like temperature and pH levels within normal ranges. The concept of homeostasis was introduced by Walter Cannon in 1930 and forms the basis of physiology. It works through a cyclical system of receptors that detect changes, a control center that activates effectors to correct deviations and restore balance. Most processes use negative feedback loops while some emergency responses employ positive feedback. Disruptions to homeostasis can cause illness.