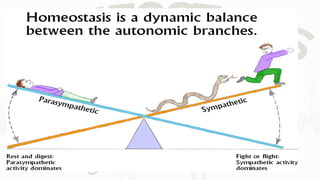
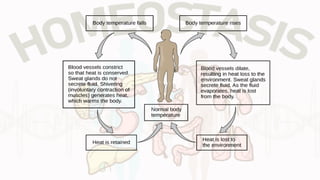
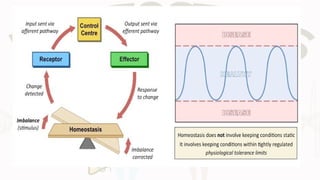
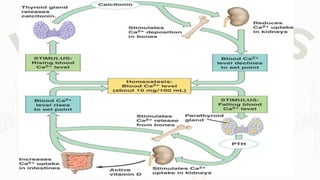
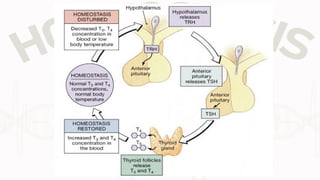
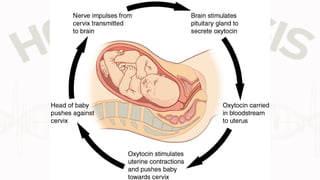
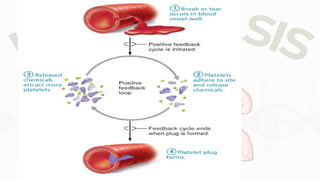
The document discusses the concept of homeostasis, defining it as the stable internal environment of an organism that maintains consistent conditions despite external changes. It details the mechanisms of homeostasis, including autoregulation and extrinsic regulation, and explains the roles of feedback systems, emphasizing the importance of both negative and positive feedback. The conclusion highlights that failure of homeostatic regulation can lead to illness or disease.