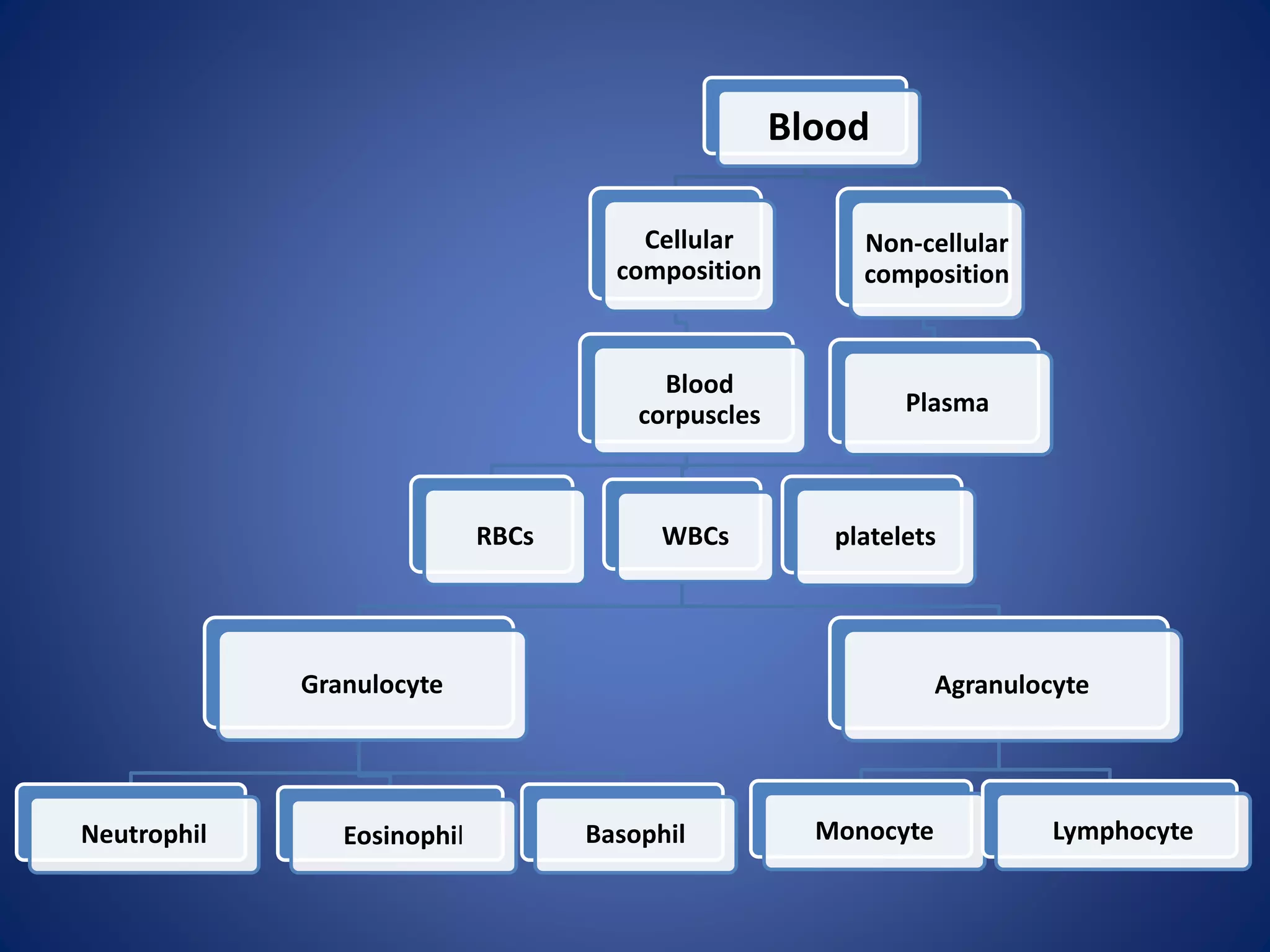
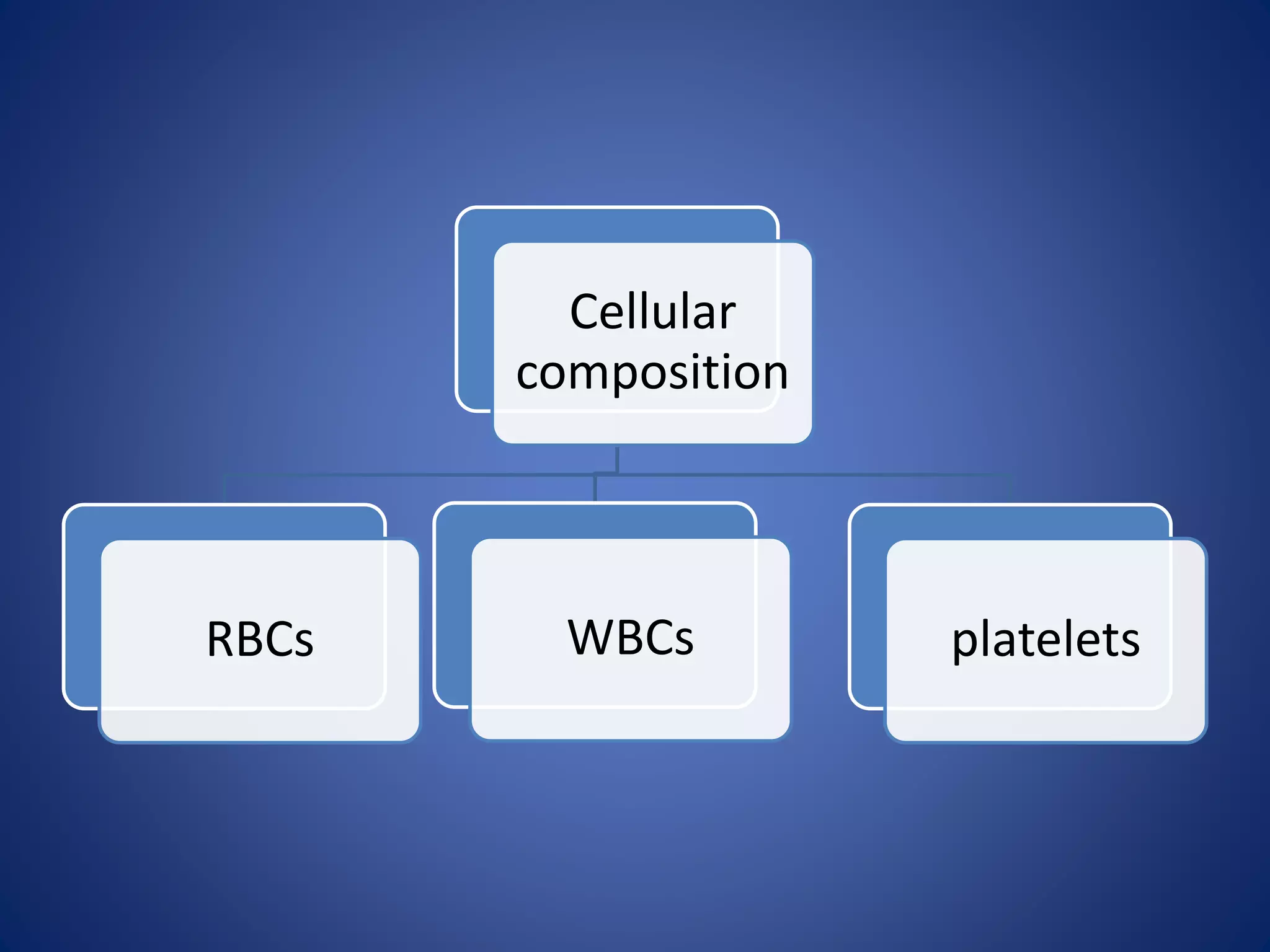
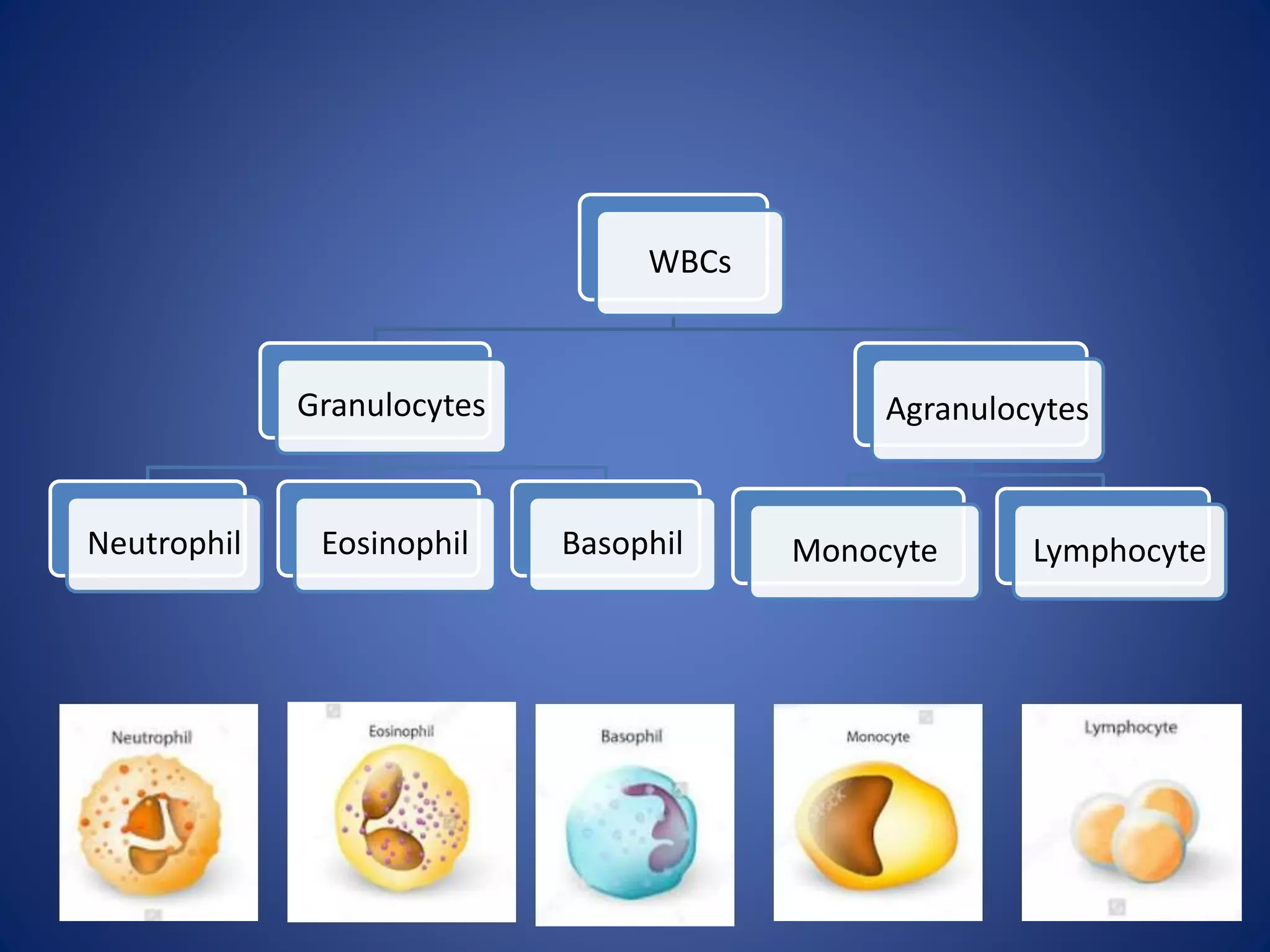
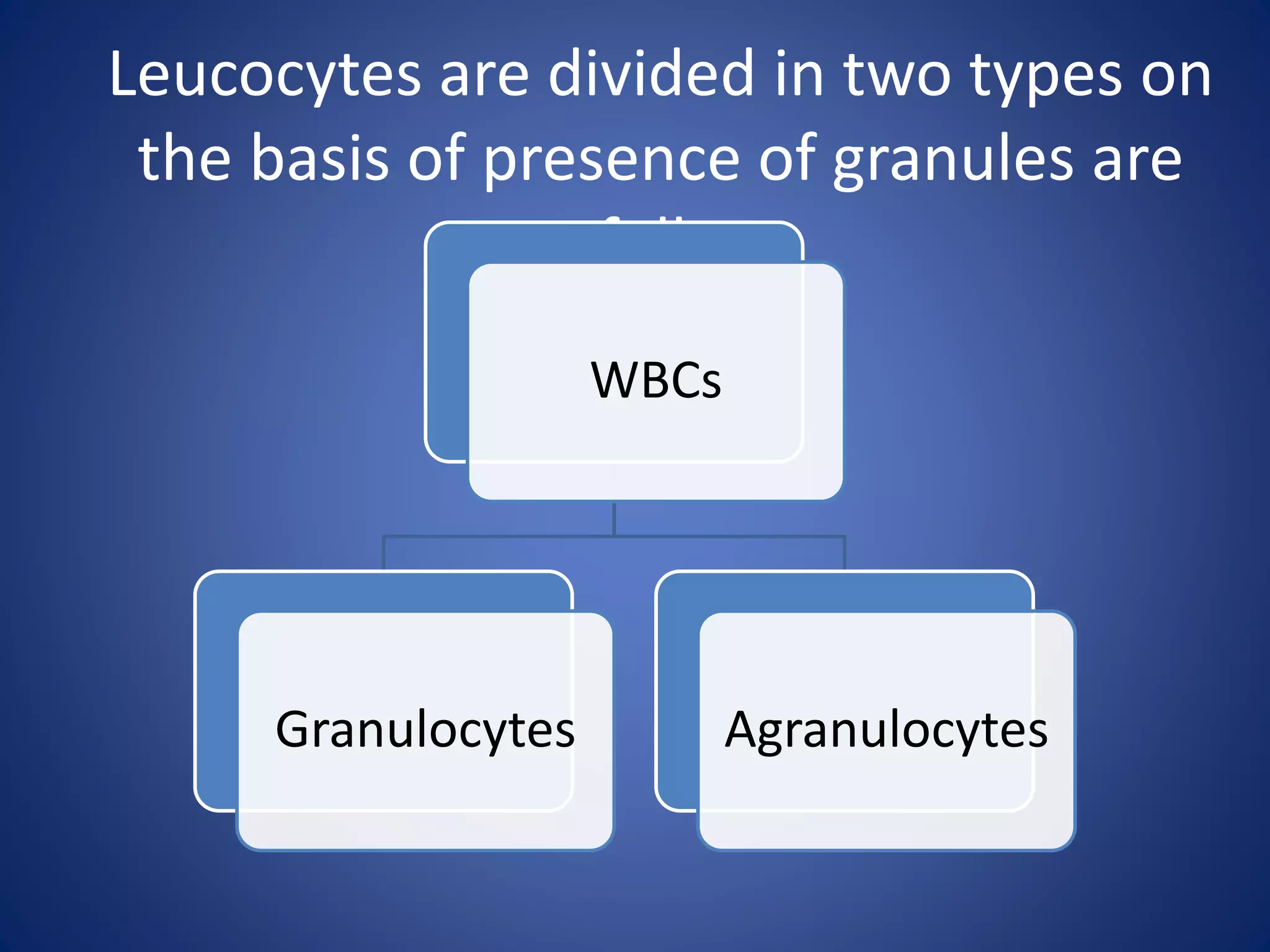
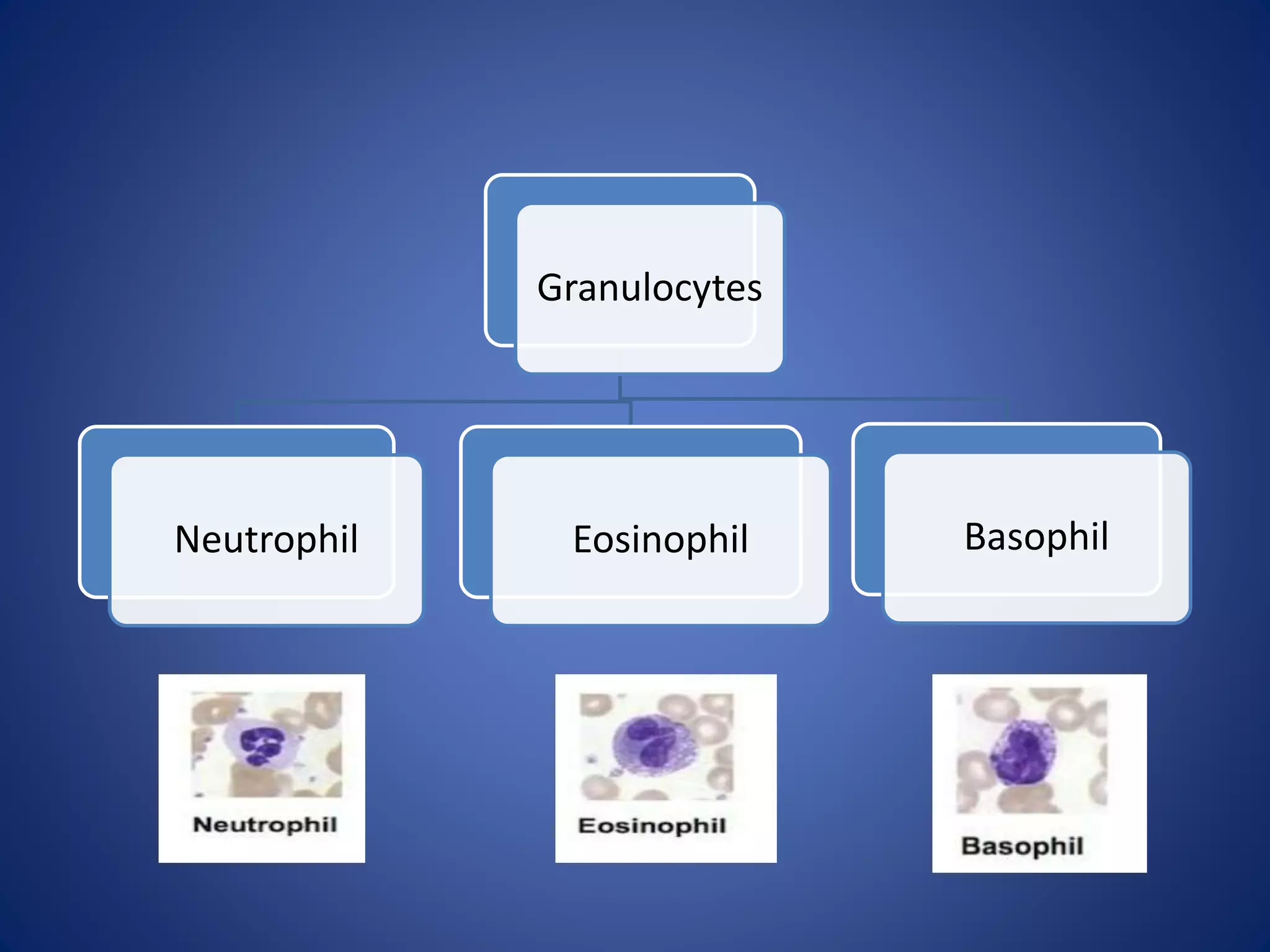
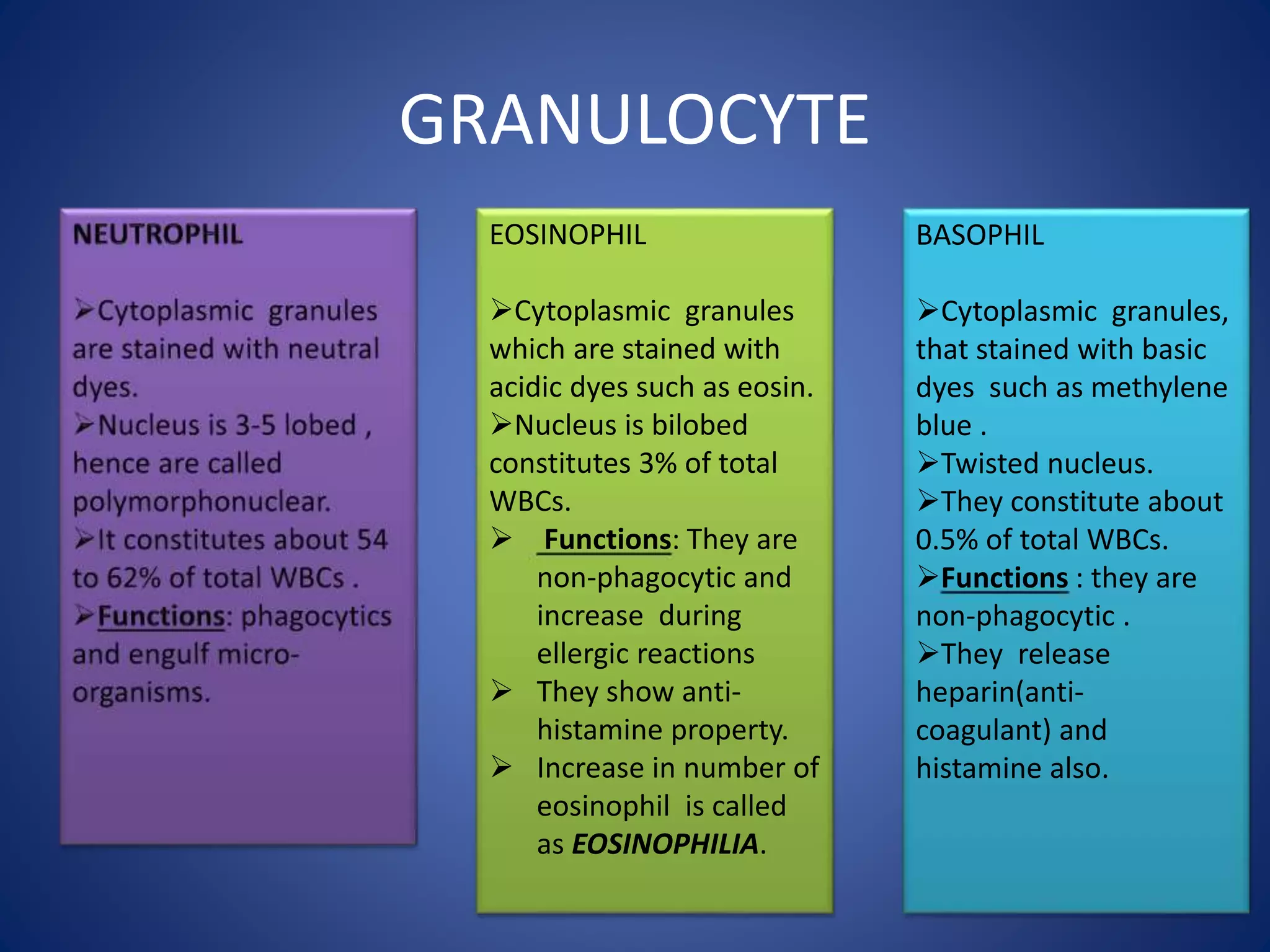
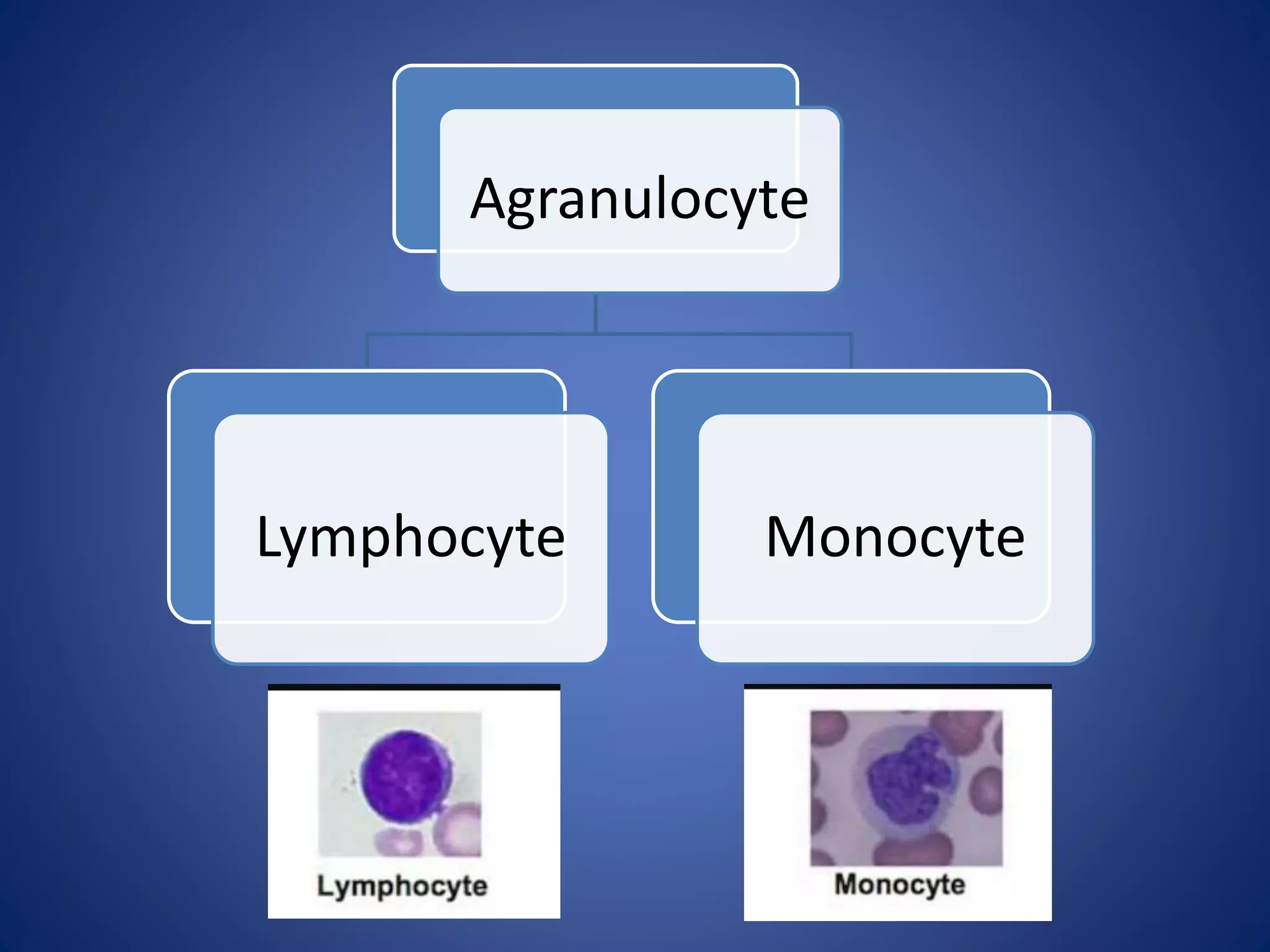
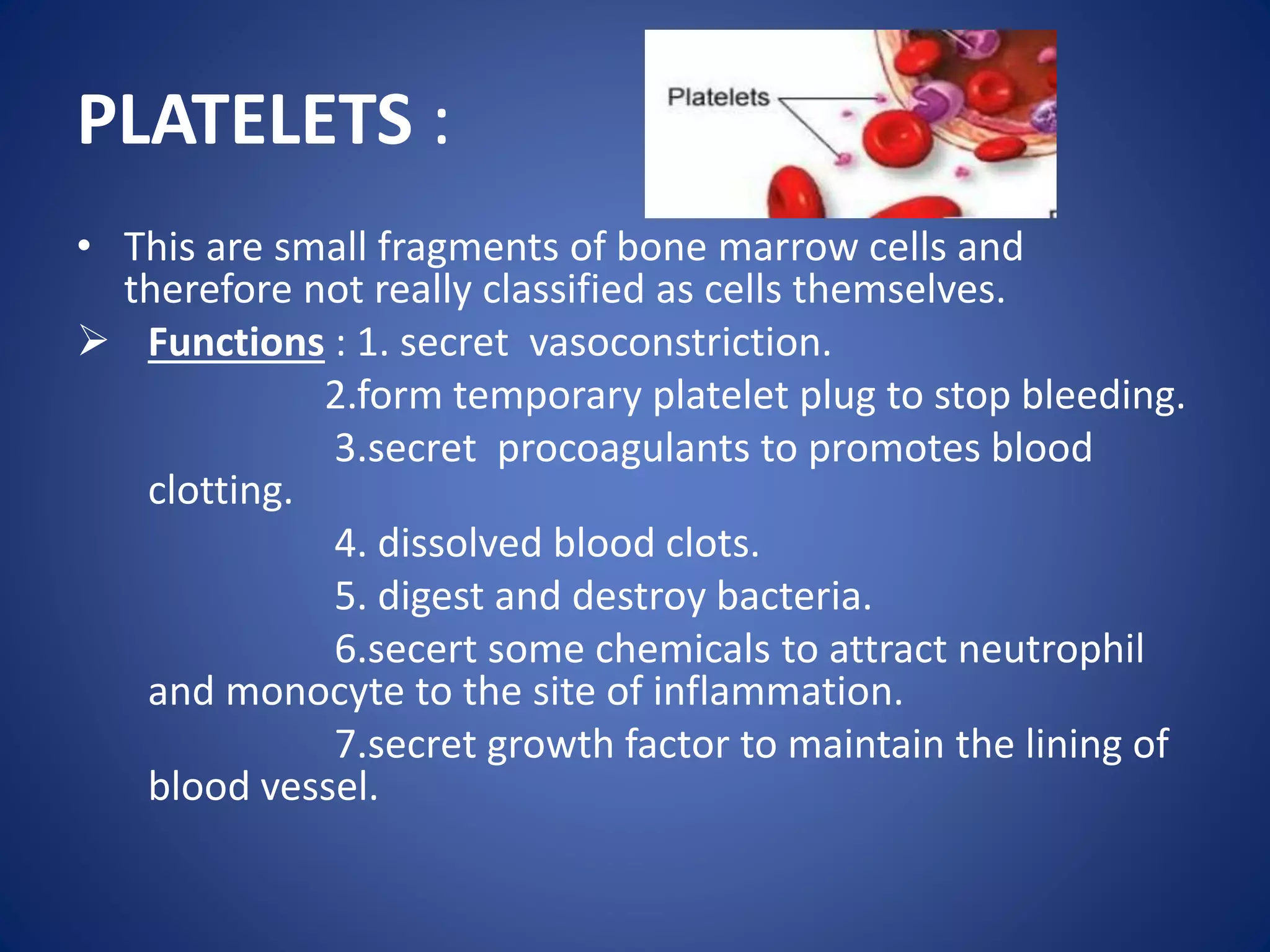
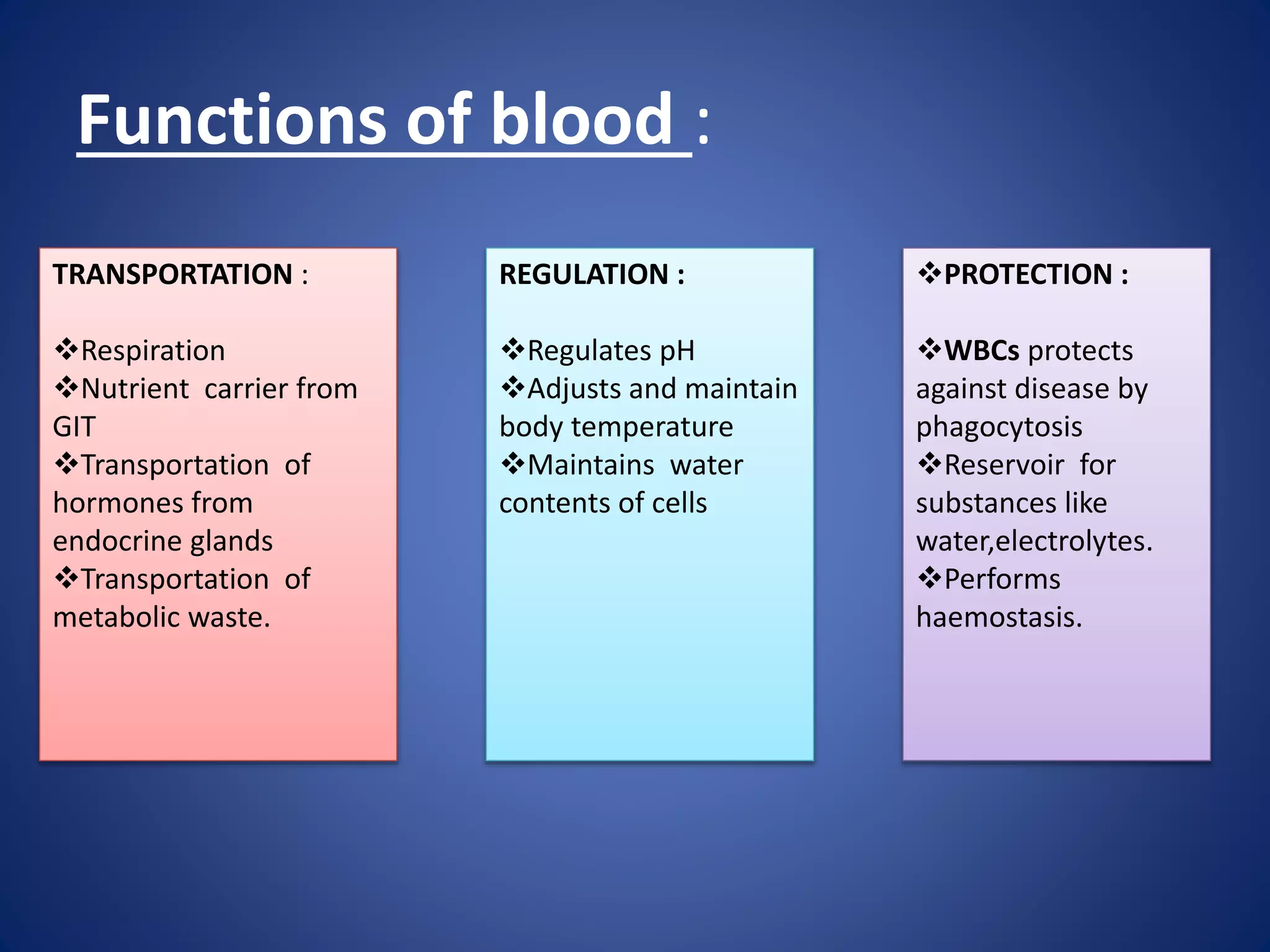
Blood is composed of plasma and cells. Plasma is 92% water and contains proteins, nutrients, waste products, gases and regulatory substances. Cells include red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Red blood cells carry oxygen and are biconcave and enucleated. White blood cells help fight infection - granulocytes contain granules and include neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils, while agranulocytes lack granules and comprise lymphocytes and monocytes. Platelets help form clots to stop bleeding. Together, blood regulates pH, transports substances around the body, protects against disease, and performs hemostasis.