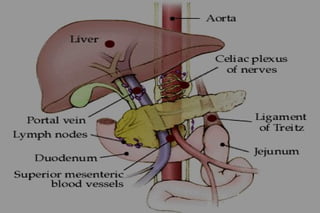
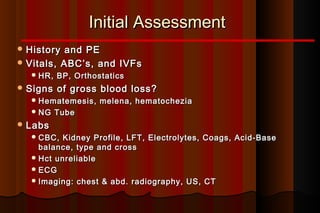
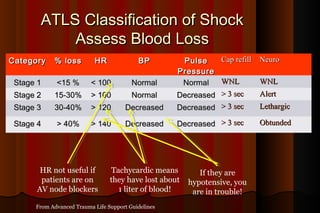
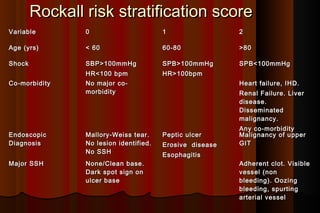
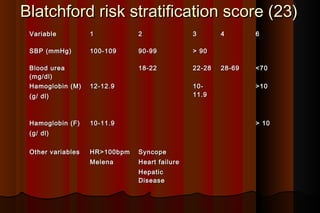
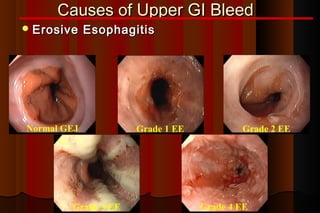
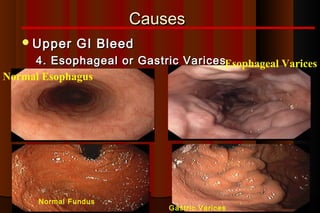
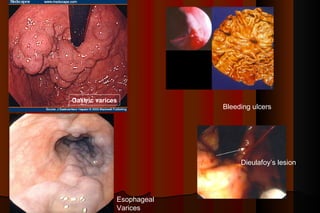
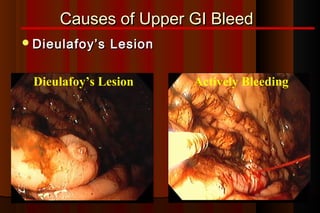
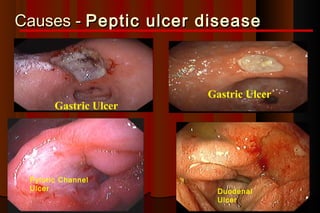
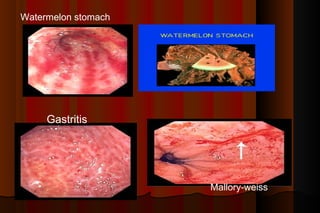
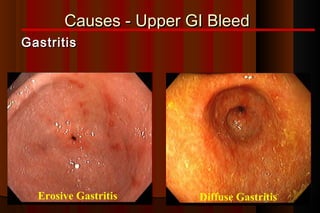
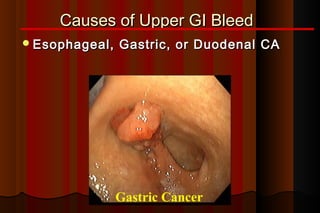
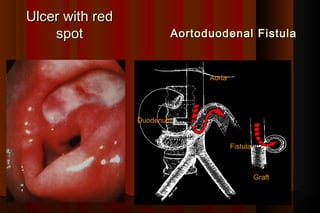
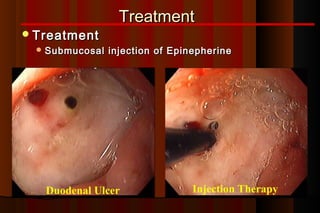
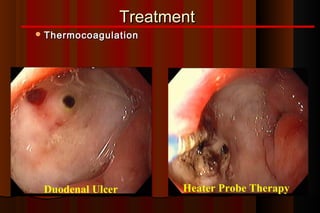
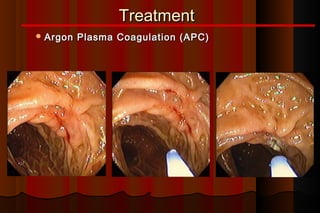
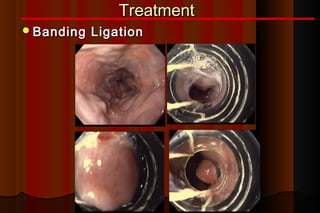
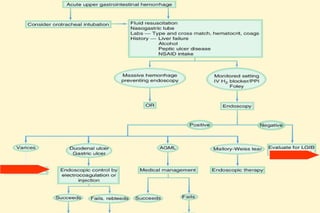
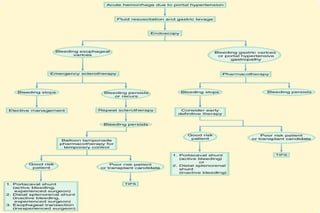
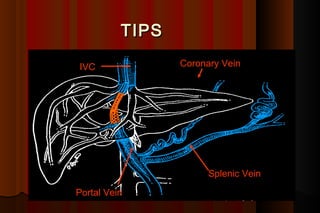
Upper gastrointestinal bleeding is a common medical condition that requires prompt assessment and treatment. Key steps in evaluation include determining hemodynamic stability, performing nasogastric aspiration to identify the source and activity of bleeding, and endoscopy within 24 hours of presentation to identify the cause and risk stratify patients. Resuscitation focuses on restoring circulating volume through blood transfusions and intravenous fluids while controlling active bleeding endoscopically. Risk stratification scores like Rockall and Blatchford are used to determine patient disposition and guide management.