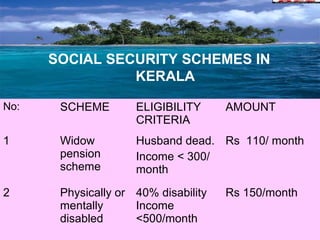
Social security is defined as security provided by society against certain risks like sickness, invalidity, maternity, old age, and death. It has two planks - social assistance which provides voluntary assistance to the poor and needy through public funds, and social insurance which involves pooling of resources through contributions from employees, employers, and the state to provide benefits as a right not proportional to contributions. The document then outlines the history and evolution of social security in countries like Germany, USA, and India as well as various social security schemes for different populations in India like industrial workers, civil servants, the general public, and specific schemes in Kerala.