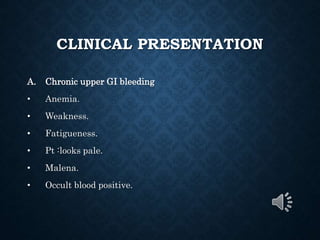
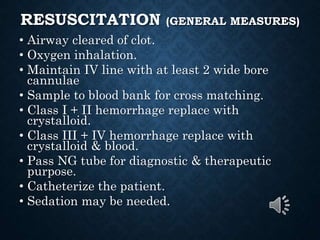
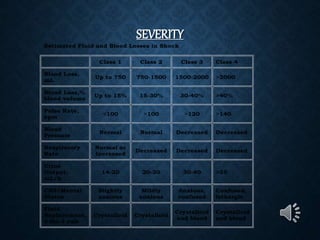
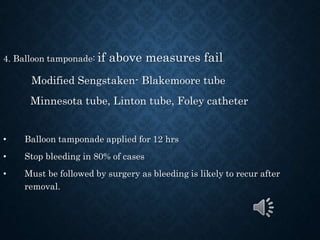
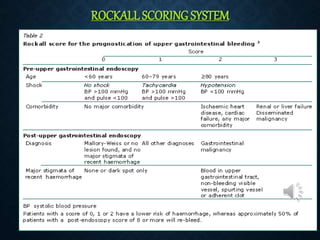
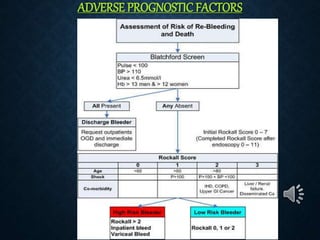
This document provides an overview of upper gastrointestinal bleeding, including its causes, presentation, diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. The most common causes are peptic ulcer disease, erosive gastritis/esophagitis, and esophageal varices. Patients may present with hematemesis, melena, or occult blood loss. Diagnosis involves history, examination, endoscopy, and other investigations. Treatment depends on the underlying cause but generally involves resuscitation, endoscopic interventions, medications, and sometimes surgery. Prognosis depends on factors like the Rockall score which considers presentation, resuscitation, comorbidities, and underlying disease.





![AETIOLOGY (COMMON CAUSES)
2. Erosive gastritis,
esophagitis, duodenitis
15-30% of cases
Common causative factors are:
ETOH [alcohol], ASA, NSAID’S,STEROIDS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/uppergi-230717194452-3ab130ce/85/uppergi-ppt-7-320.jpg)