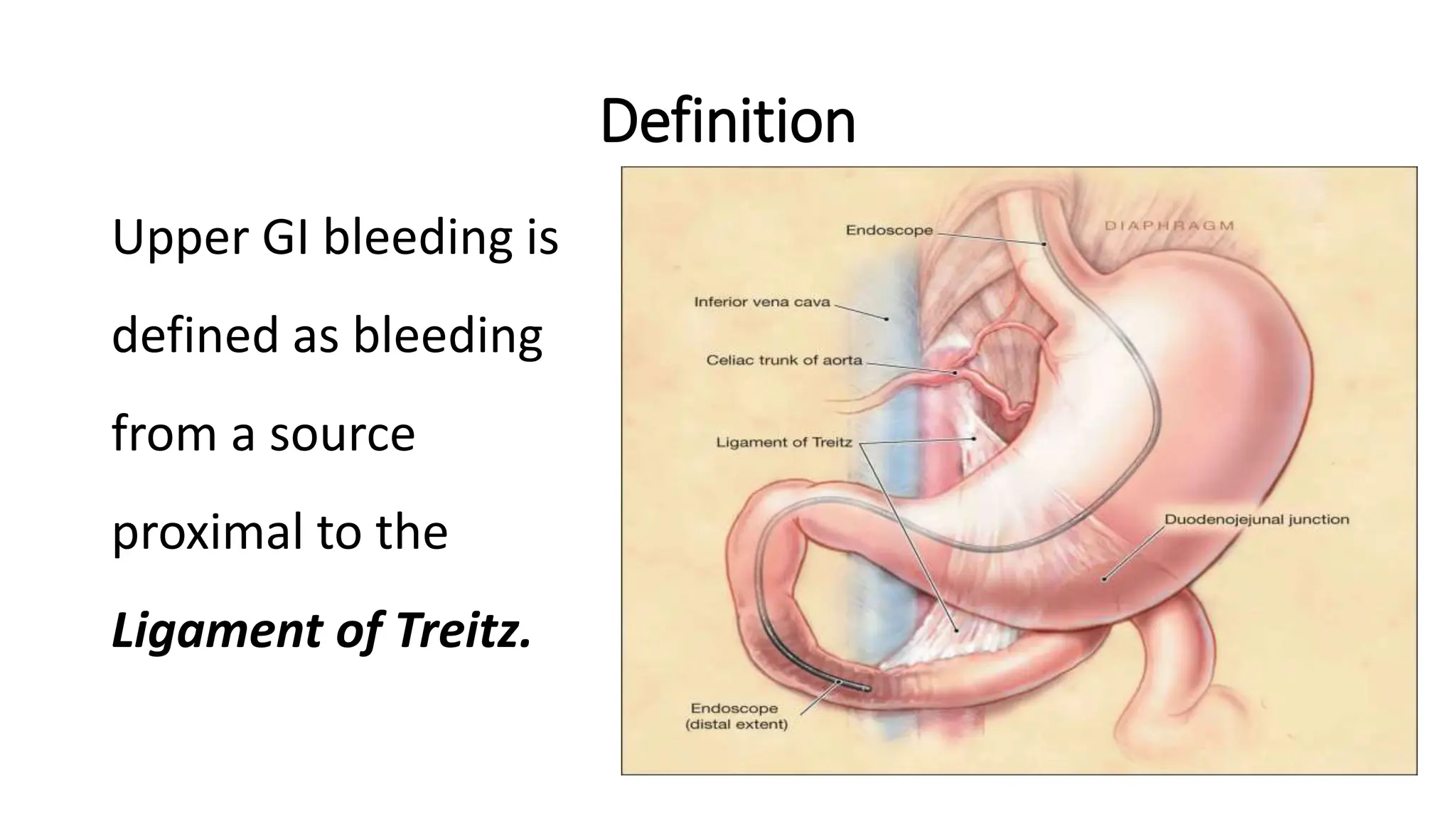
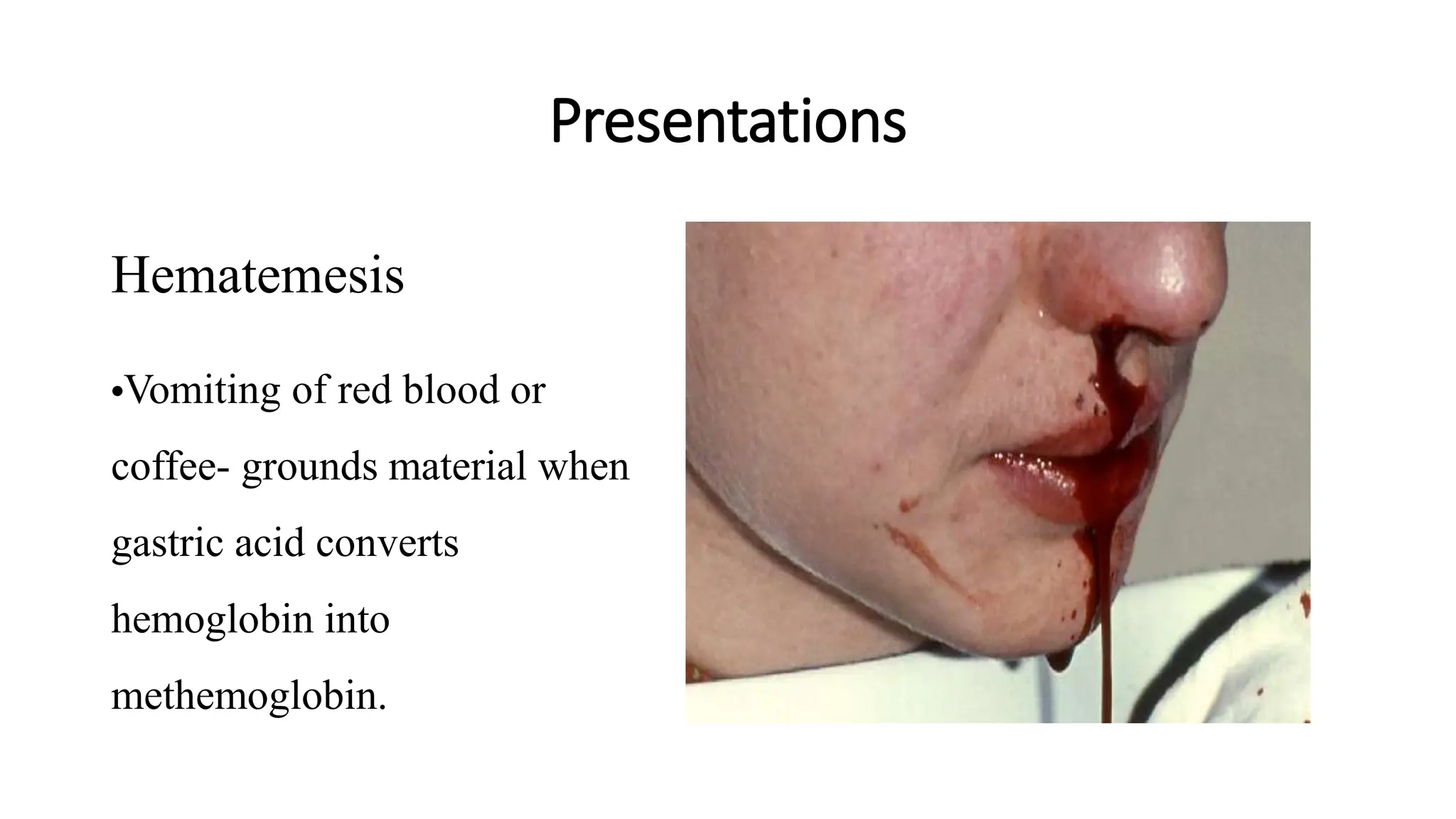
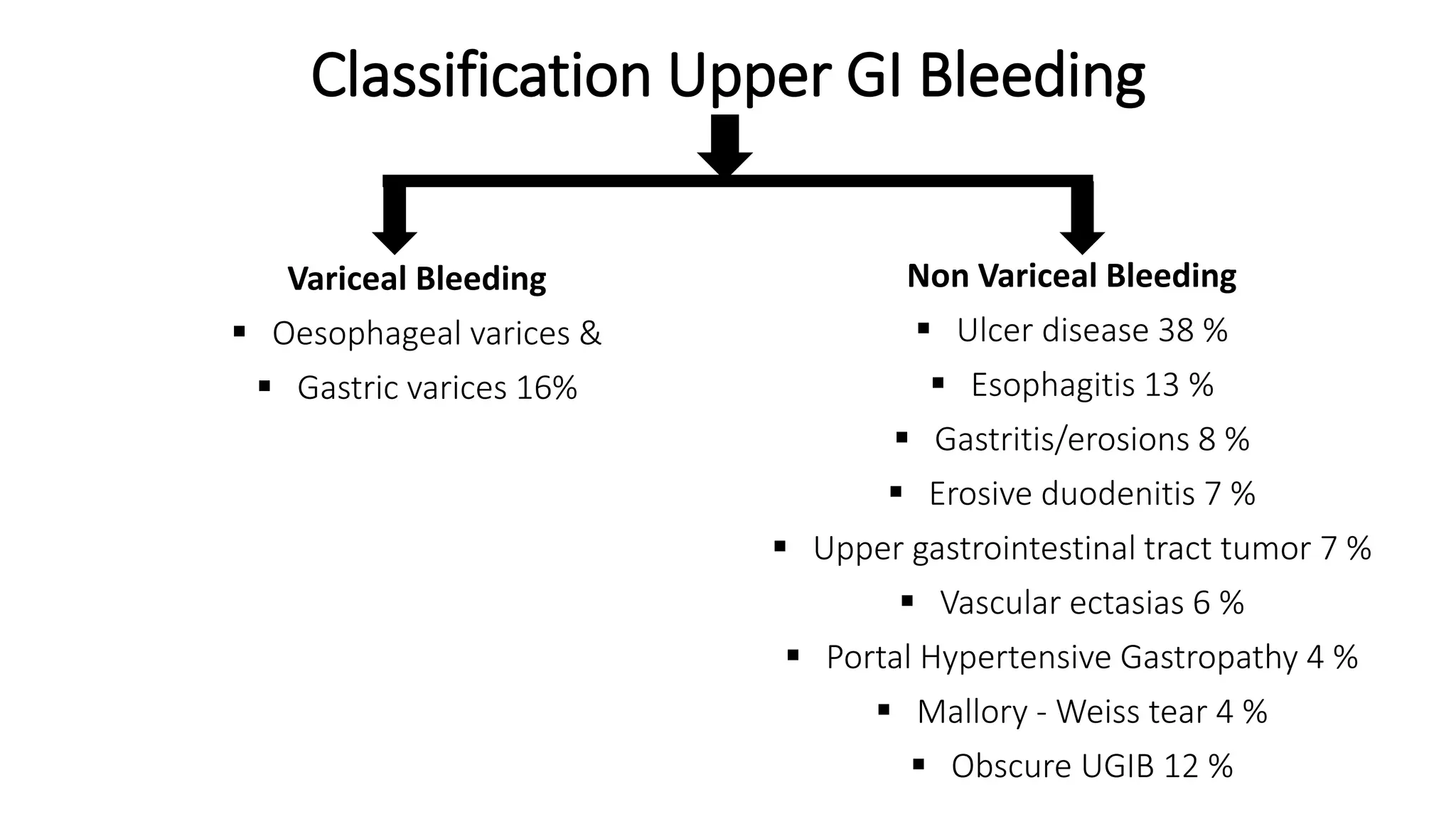
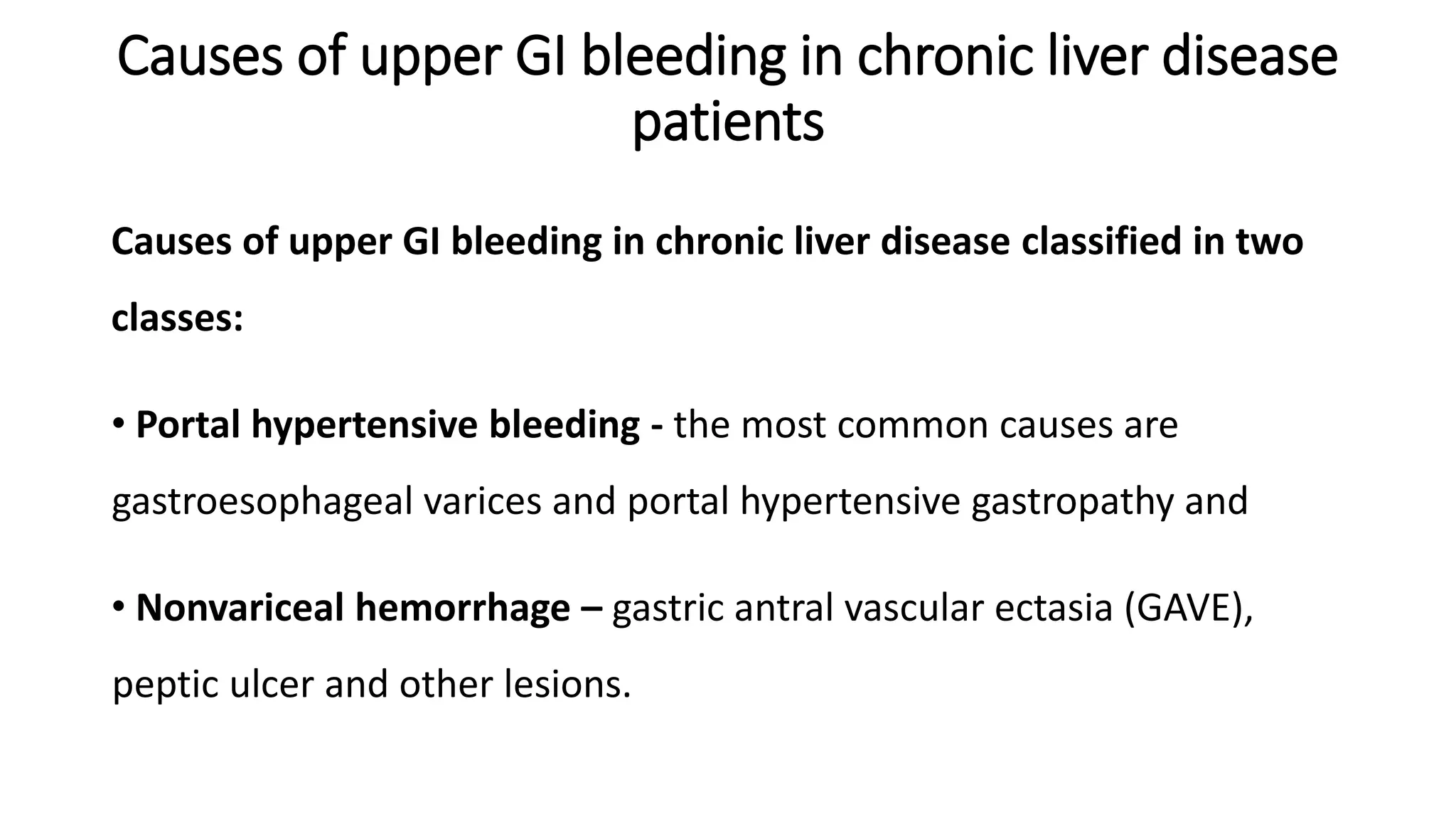
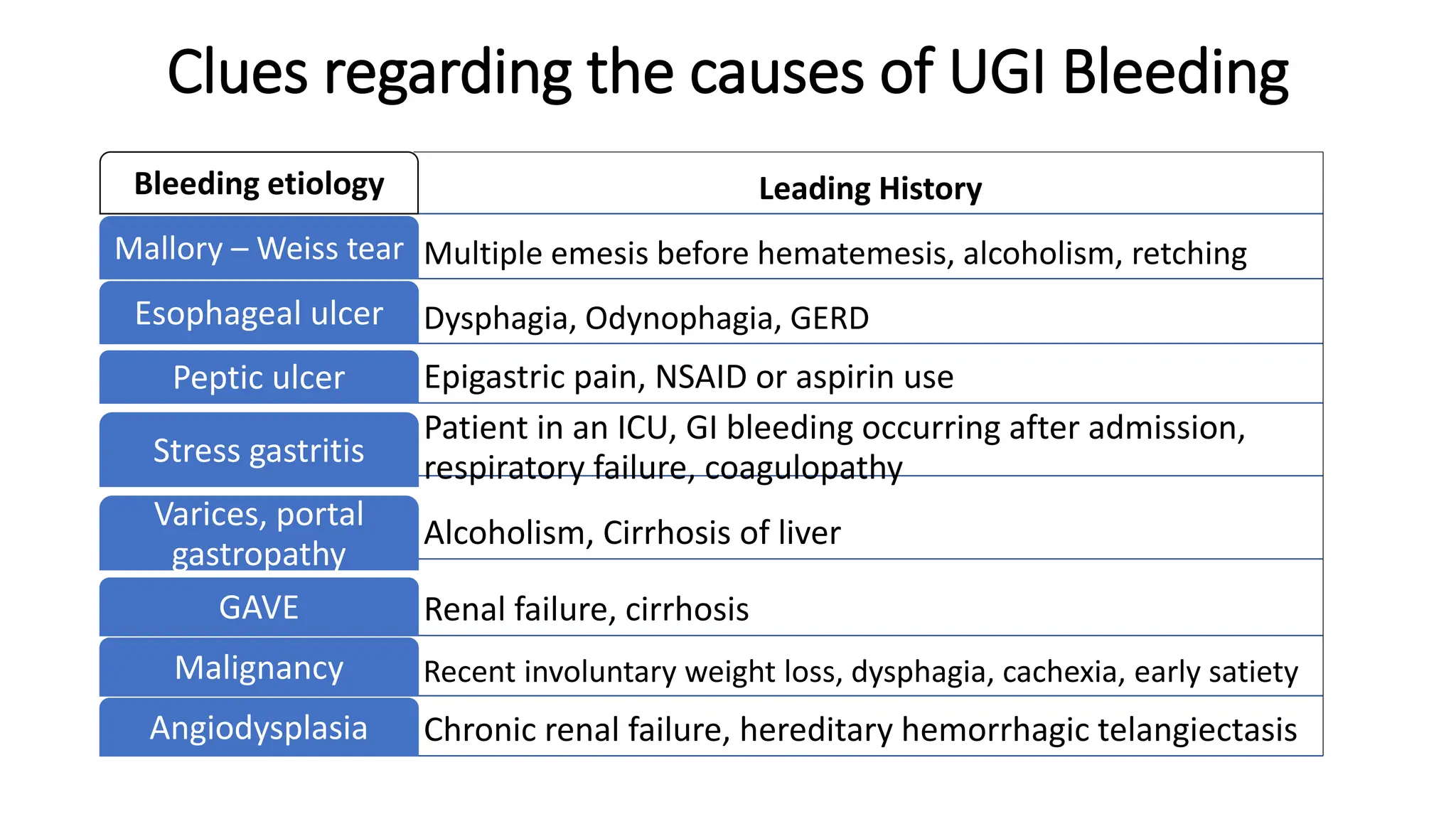
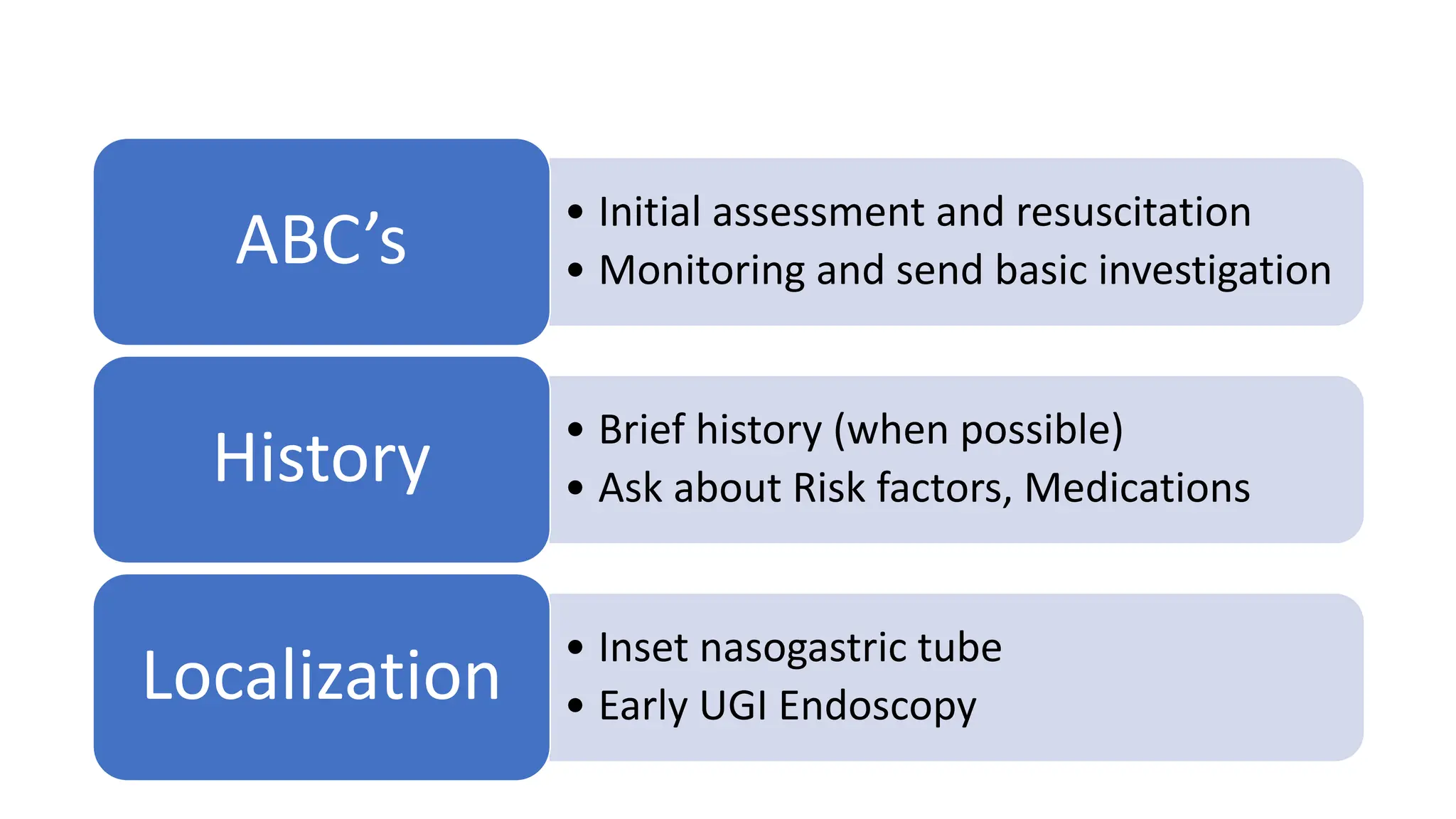
Upper gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding is defined as bleeding from a site proximal to the ligament of Treitz, presenting through symptoms like hematemesis, melena, and hematochezia. The document outlines the causes, management principles, and classification of upper GI bleeding, emphasizing the importance of rapid assessment and intervention. High-risk factors include advanced age, shock on admission, and significant comorbidities, with scoring systems like the Rockall score used to predict prognosis.