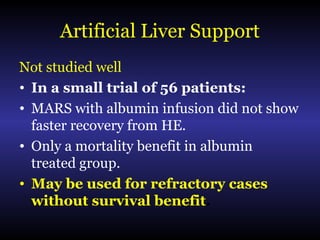
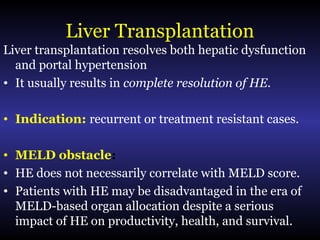
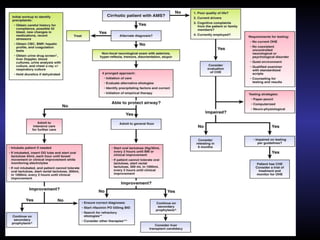
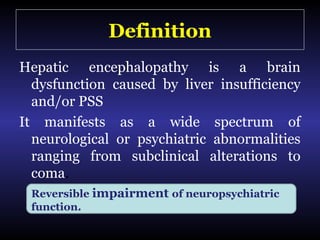
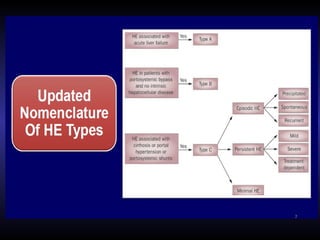
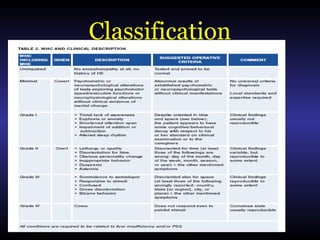
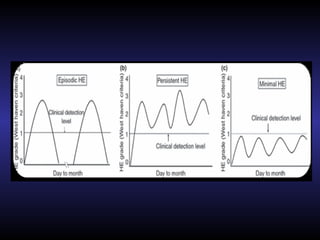
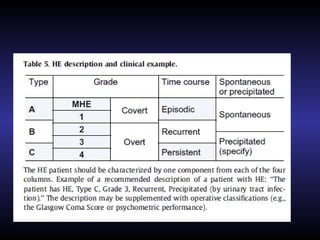
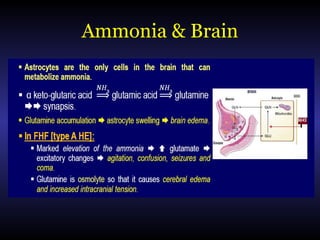
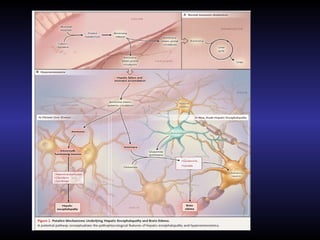
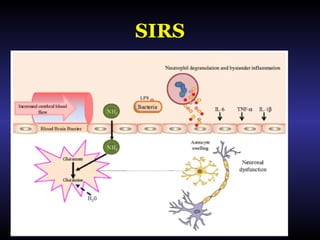
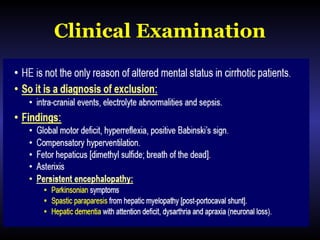
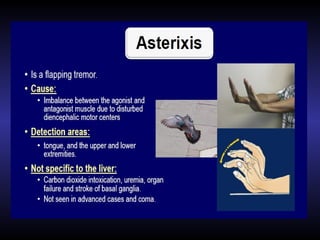
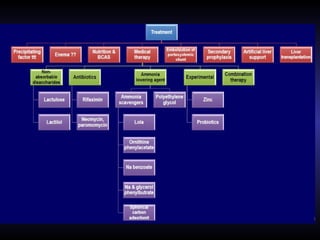
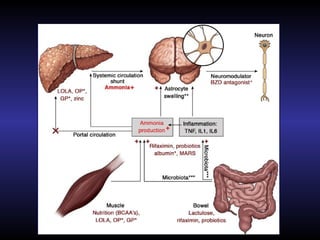
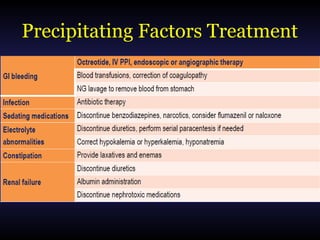
Hepatic encephalopathy is a brain dysfunction caused by liver disease or portosystemic shunting. It presents as a wide range of neurological or psychiatric abnormalities from mild alterations to coma. The prevalence is 30-40% in those with cirrhosis and risk of first episode is 5-25% within 5 years of cirrhosis diagnosis. Recurrence risk after an initial episode is 40% within 1 year. Ammonia, systemic inflammation, manganese, genetics, and oxidative stress may all contribute to pathogenesis. Diagnosis involves clinical exam and testing like serum ammonia levels or neuropsychological tests on phone apps. Management involves treating precipitating factors, lactulose, antibiotics like rifaximin, and









































![LOPA
• Is similar to LOLA
• OP (OCR-002) combines ornithine and
PAA.
• It supplies urea cycle with ornithine.
• Phenylacetate + glutamine
phenylacetylglutamine [easily excreted]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hepaticencephalopathyfinal-170904165218/85/Hepatic-Encephalopathy-Pathophysiology-Evaluation-And-Management-61-320.jpg)






![Prophylaxis
• There is no primary prophylaxis ???.
• No drug was shown to prevent 1st HE
episode after TIPS [Riggio et al., 2005].
• ??? Prevention of CHE to OHE.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hepaticencephalopathyfinal-170904165218/85/Hepatic-Encephalopathy-Pathophysiology-Evaluation-And-Management-68-320.jpg)
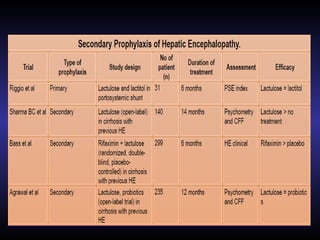
![Secondary Prophylaxis
It is the prevention of second HE episode after index
episode.
• Lactulose can be used.
• 46% recurrence of OHE due to lactulose misuse.
• Combined lactulose and rifaximin have a
decreasing risk of both breakthrough HE episodes
as well as hospitalizations when compared with
lactulose alone.
• Probiotics [VSL#3] in a recent study is equal to
lactulose [Agrawal et al., 2012].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hepaticencephalopathyfinal-170904165218/85/Hepatic-Encephalopathy-Pathophysiology-Evaluation-And-Management-69-320.jpg)