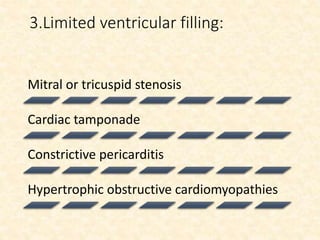
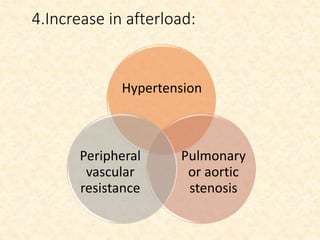
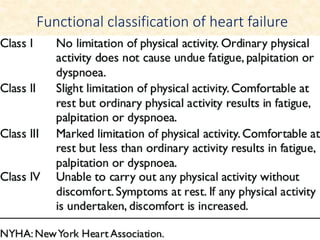
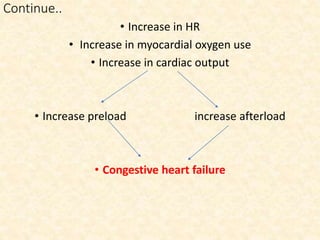
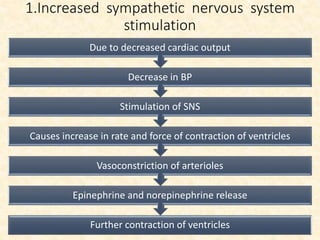
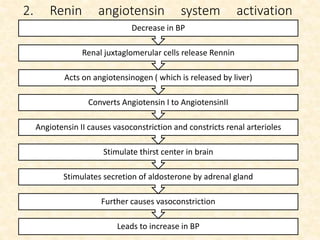
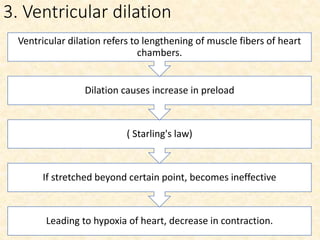
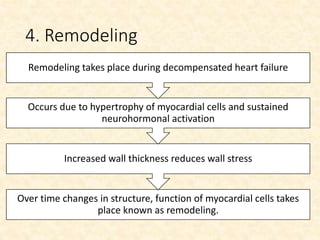
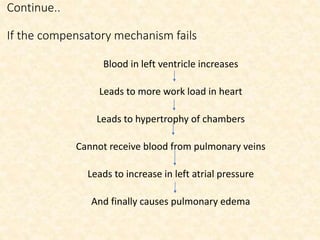
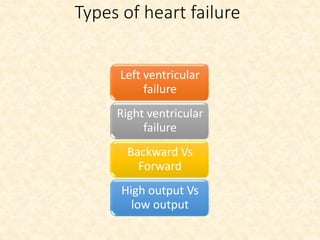
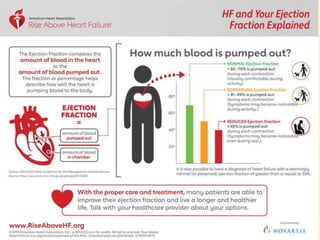
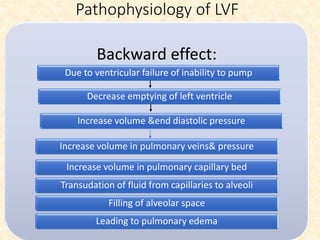
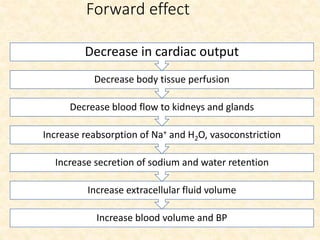
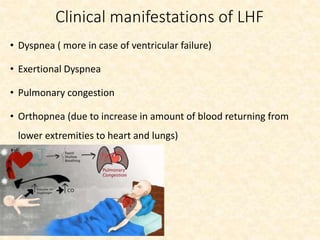
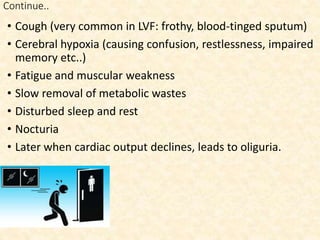
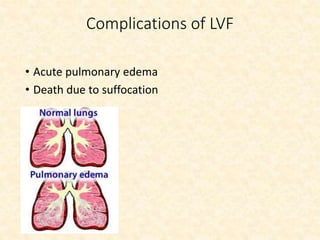
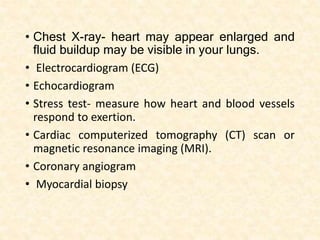
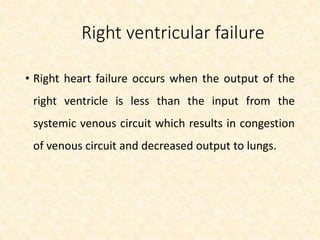
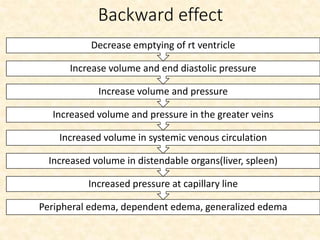
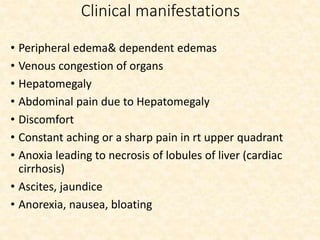
This document provides an overview of heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure. It defines HF as a state where the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet metabolic demands, resulting in organ hypoperfusion. Common causes include cardiomyopathies, myocardial infarction, and ischemic heart disease. Symptoms include edema, shortness of breath, fatigue, and reduced exercise tolerance. Treatment focuses on reducing preload and afterload through diuretics, vasodilators, and renin-angiotensin system inhibitors to decrease workload on the heart.


















![Continue..
• Sodium nitroprusside (Nipride) is a potent IV vasodilator
that reduces both preload and afterload.
• Morphine. Morphine sulfate reduces preload and
afterload.
• Positive Inotropes. Inotropic therapy increases myocardial
contractility. Drugs include β-adrenergic agonists (e.g.,
dopamine [Intropin], dobutamine [Dobutrex], epinephrine,
norepinephrine [Levophed]), the phosphodiesterase
inhibitor milrinone (Primacor), and digitalis.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heartfailure-200411152423/85/Heart-failure-44-320.jpg)



![• Vasodilators:
• hydralazine
(Apresoline)*
• isosorbide dinitrate/
hydralazine (BiDil)*
• nitrates (e.g.,
nitroglycerin [Nitro-Bid],
isosorbide dinitrate
[Isordil])
• nesiritide (Natrecor)†
• nitroprusside (Nipride)†
• Reduce cardiac afterload,
leading to increased CO
• Dilate the arterioles of
the kidneys, leading to
increased renal perfusion
and fluid loss
• Decrease BP
• Decrease preload
• Relieve symptoms of
heart failure (e.g., dyspnea)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heartfailure-200411152423/85/Heart-failure-48-320.jpg)



