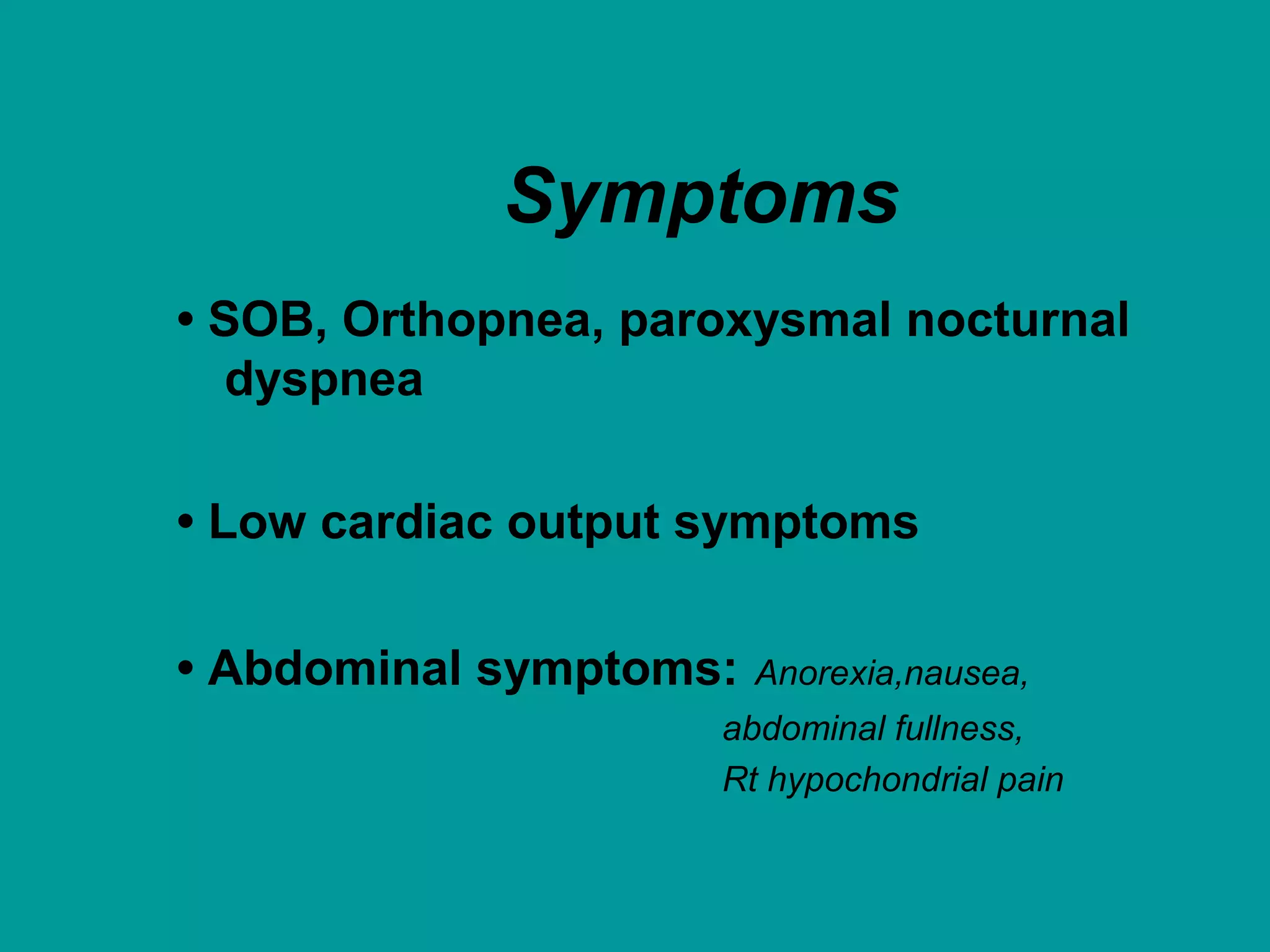
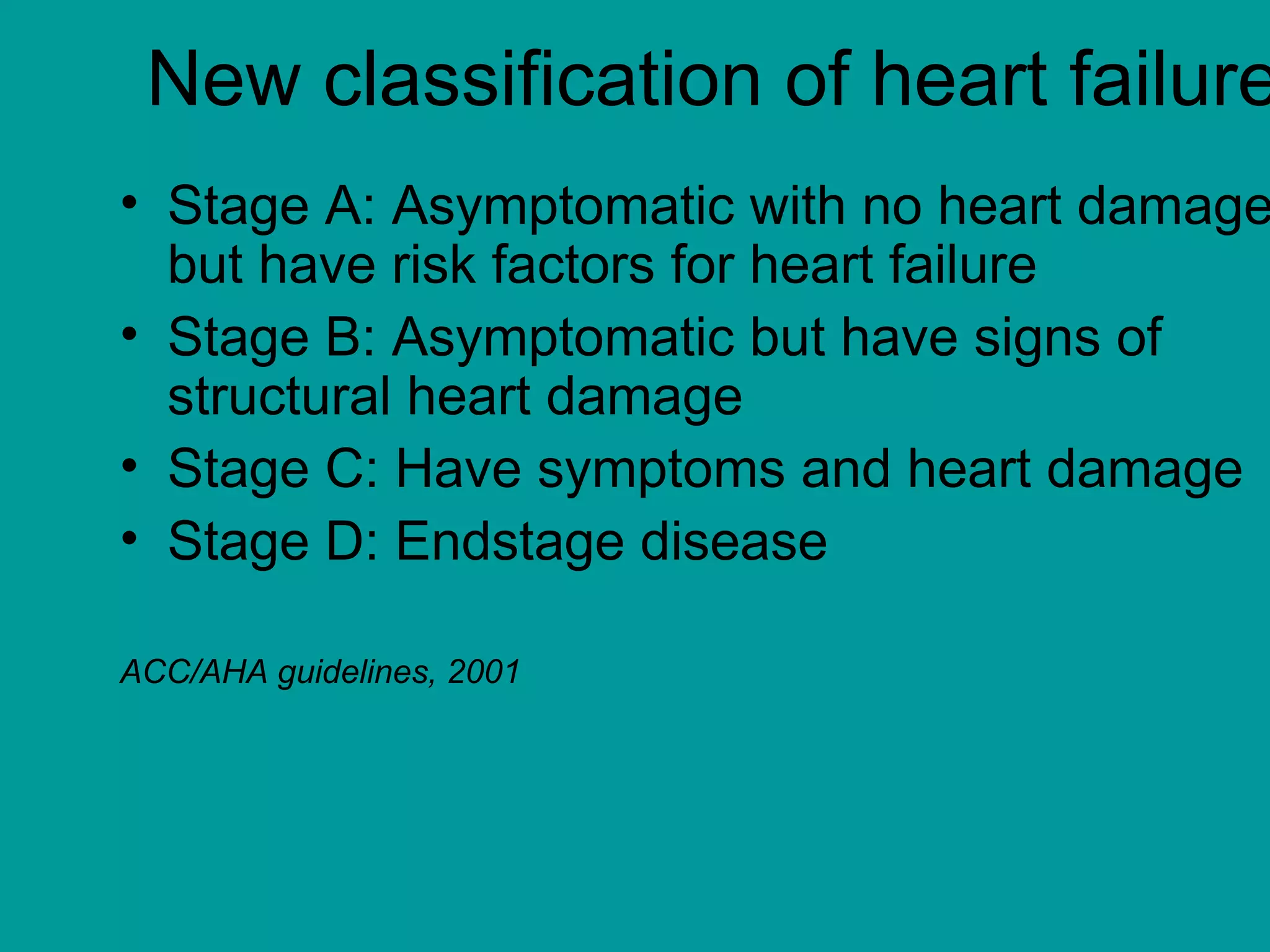
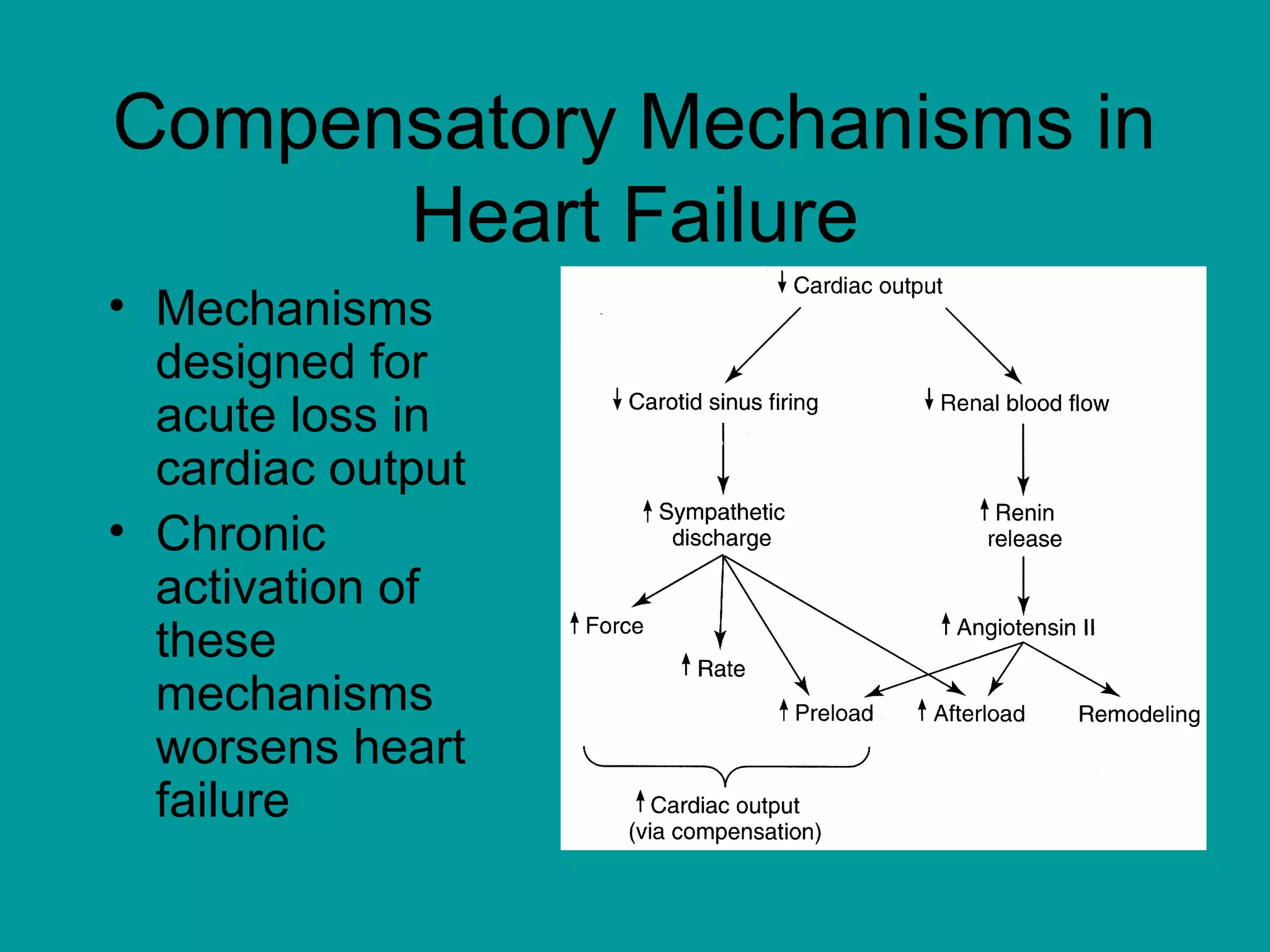
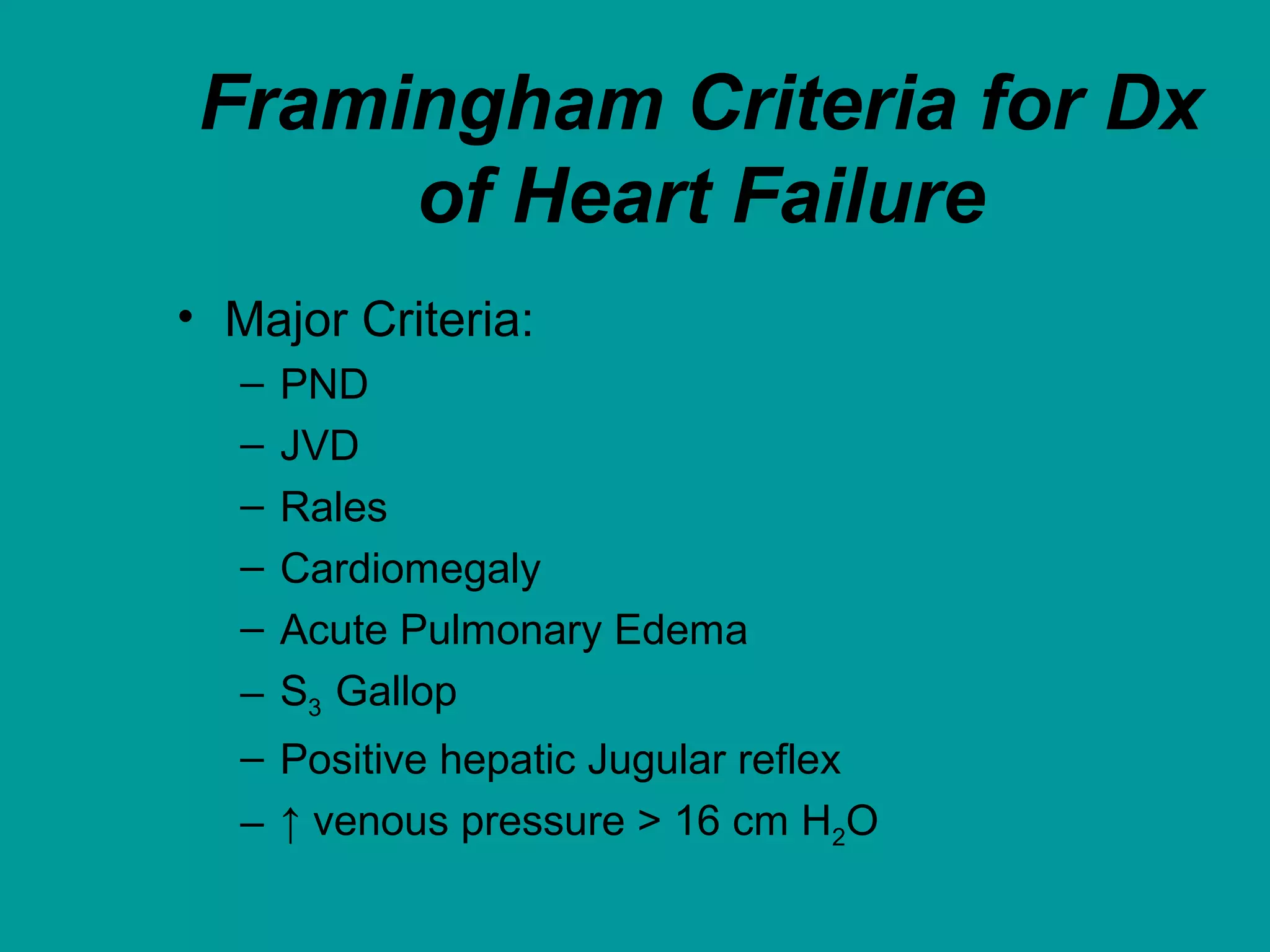
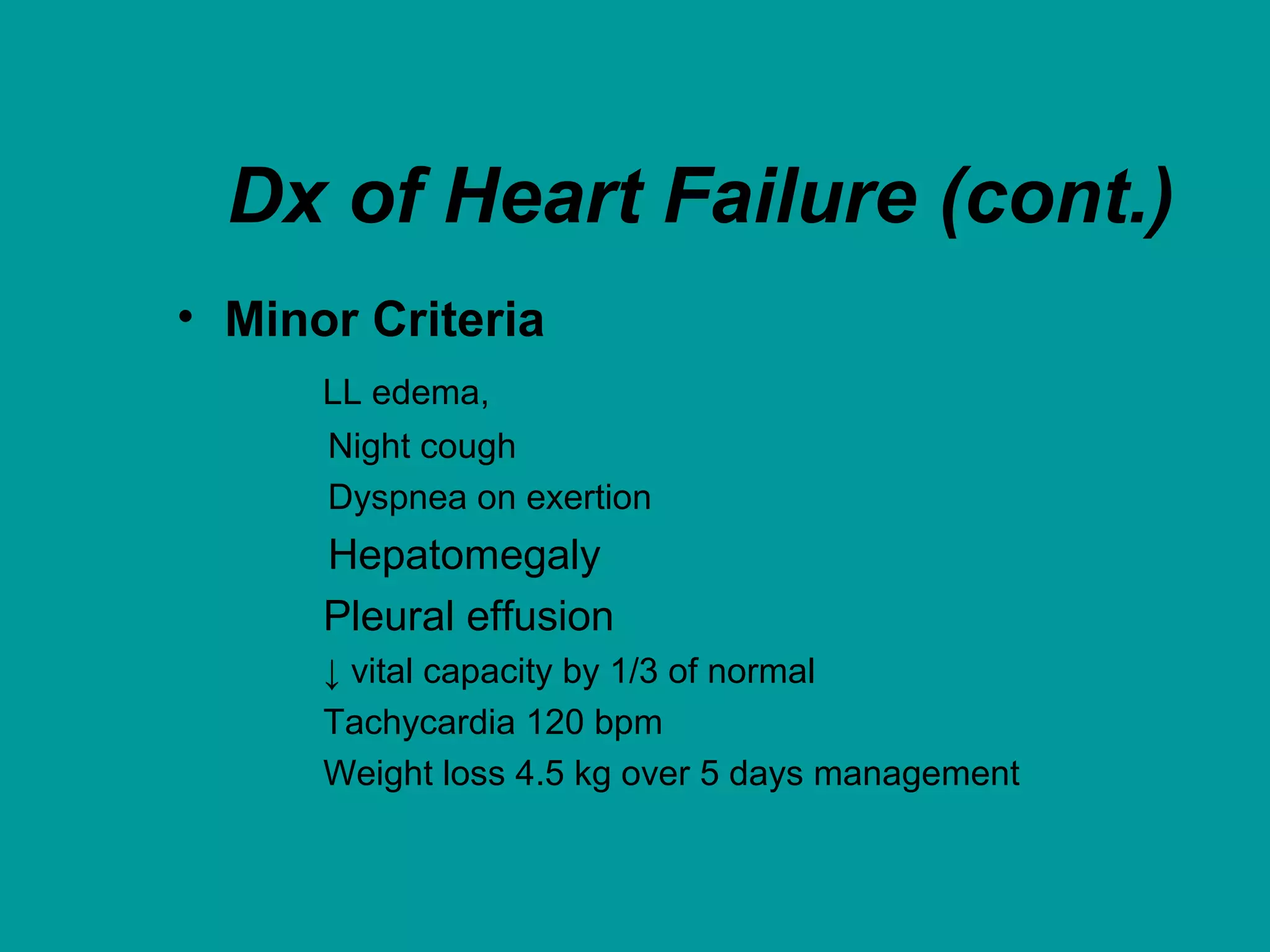
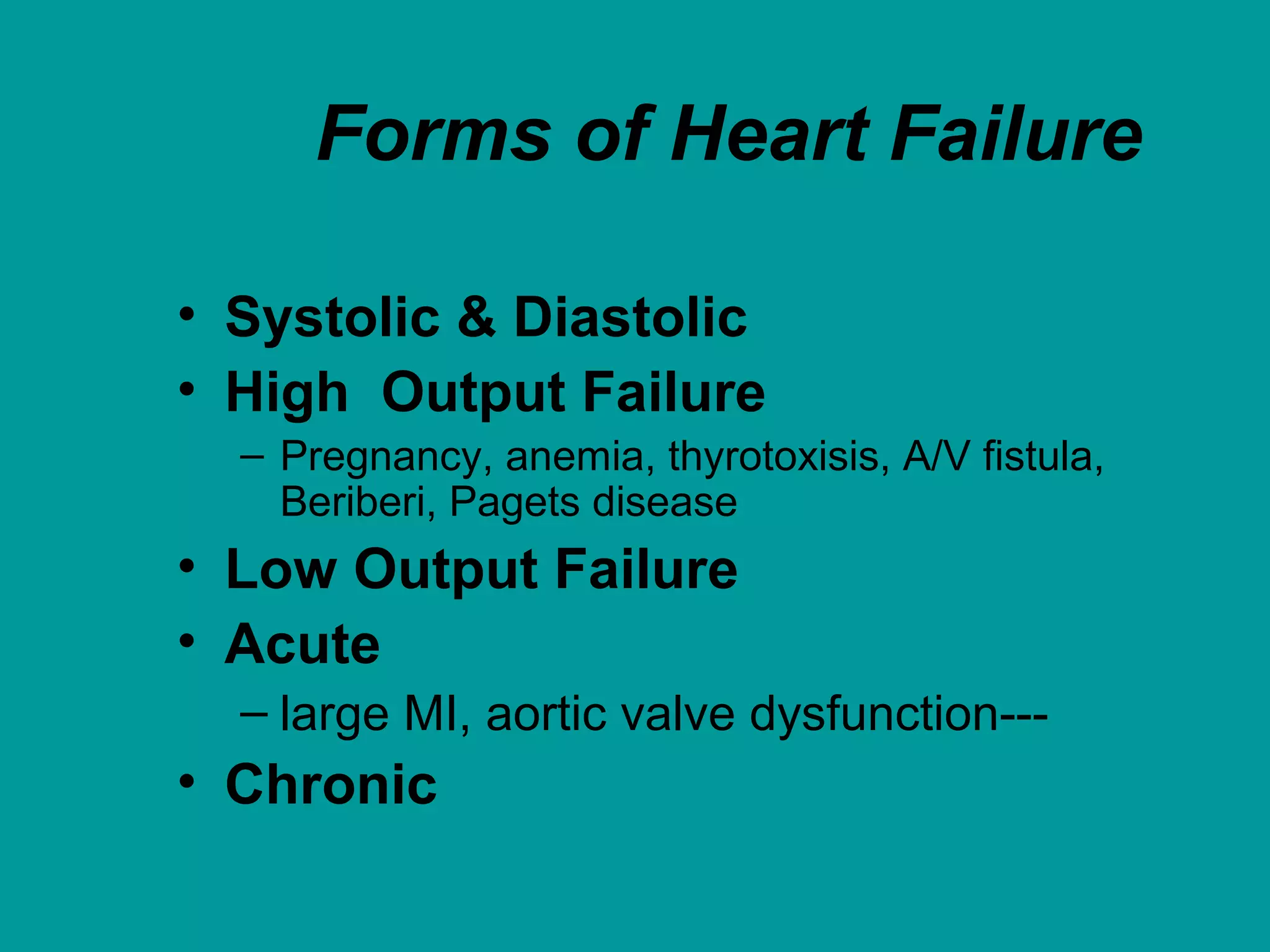
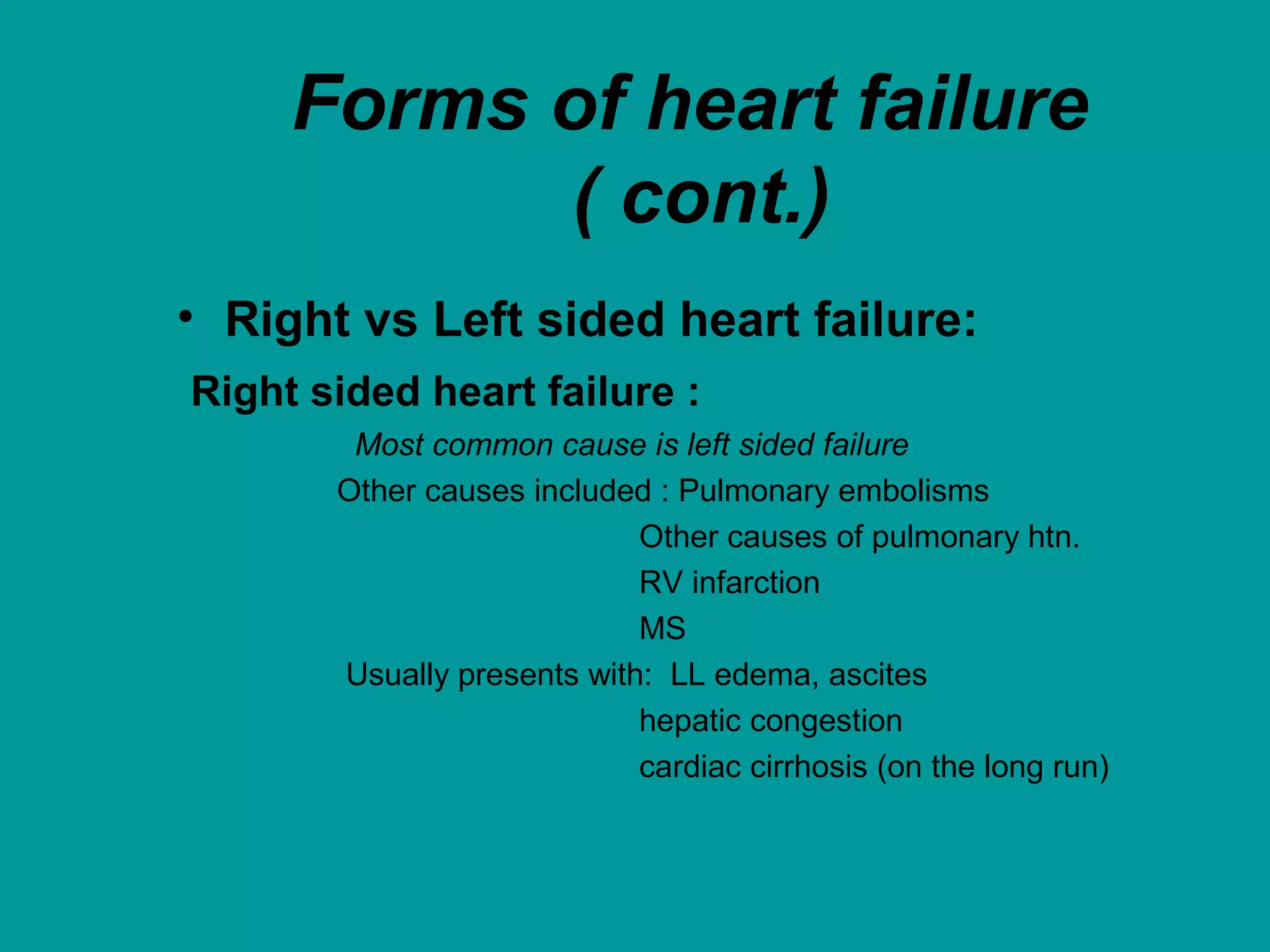
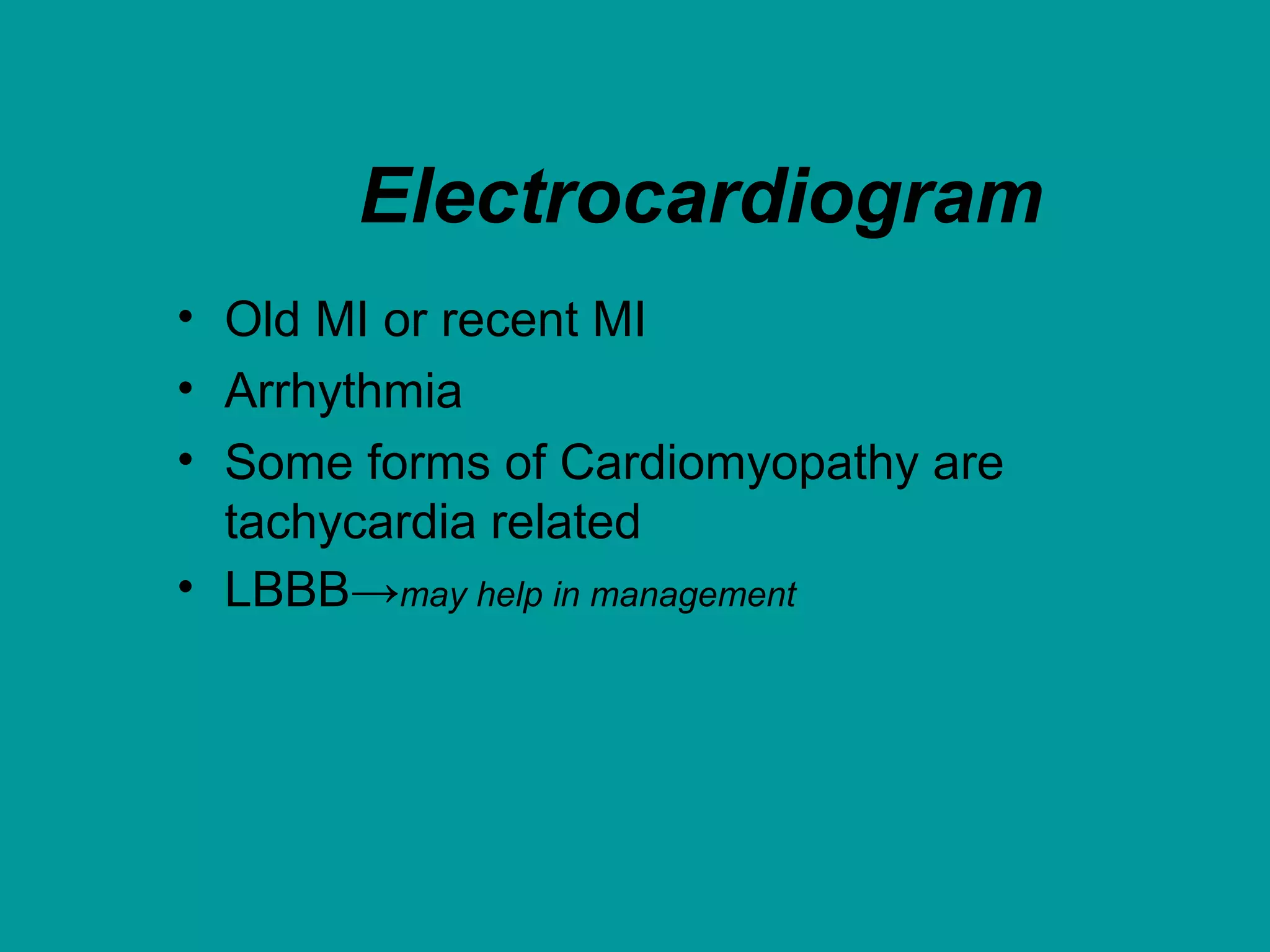
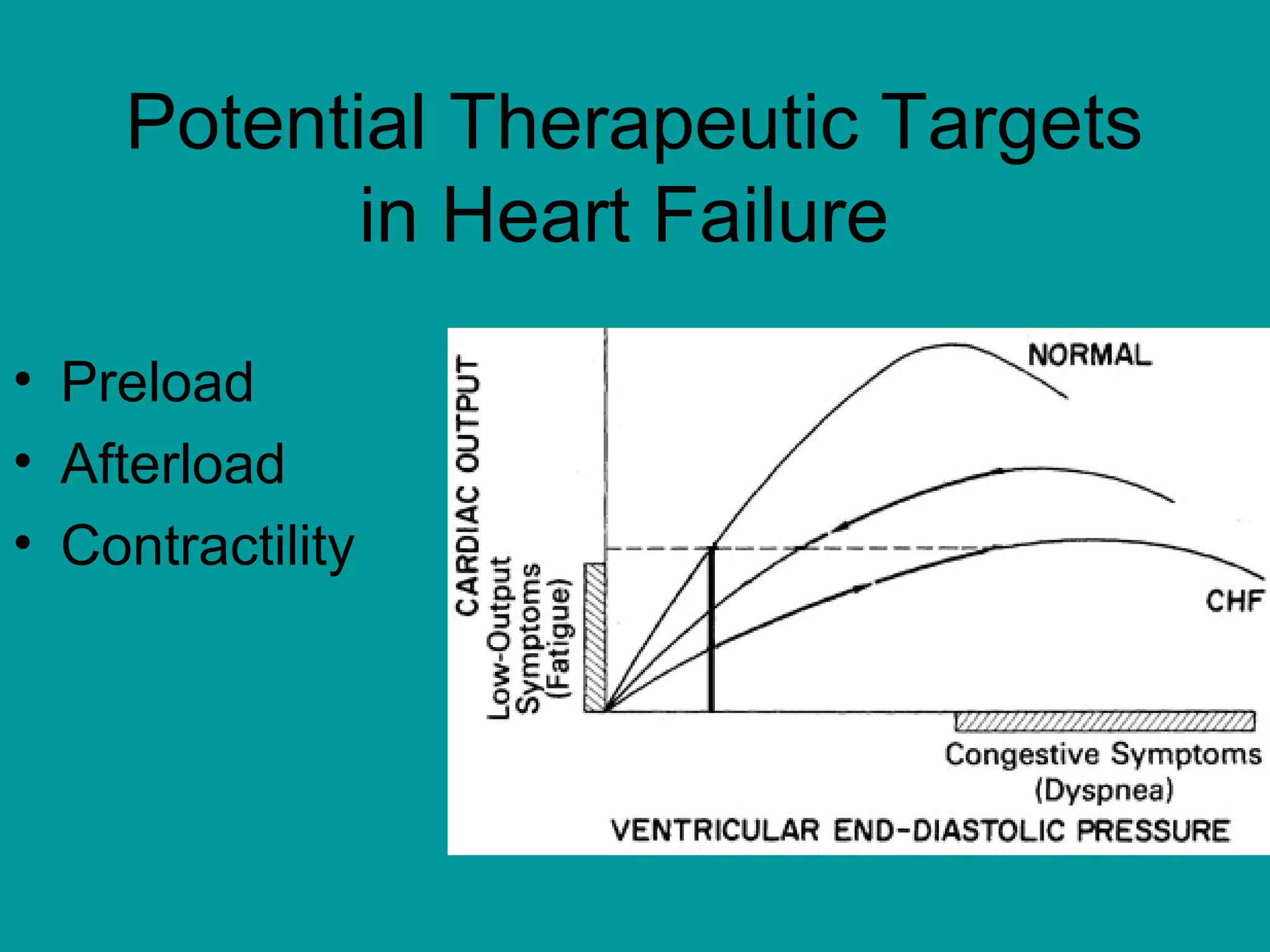
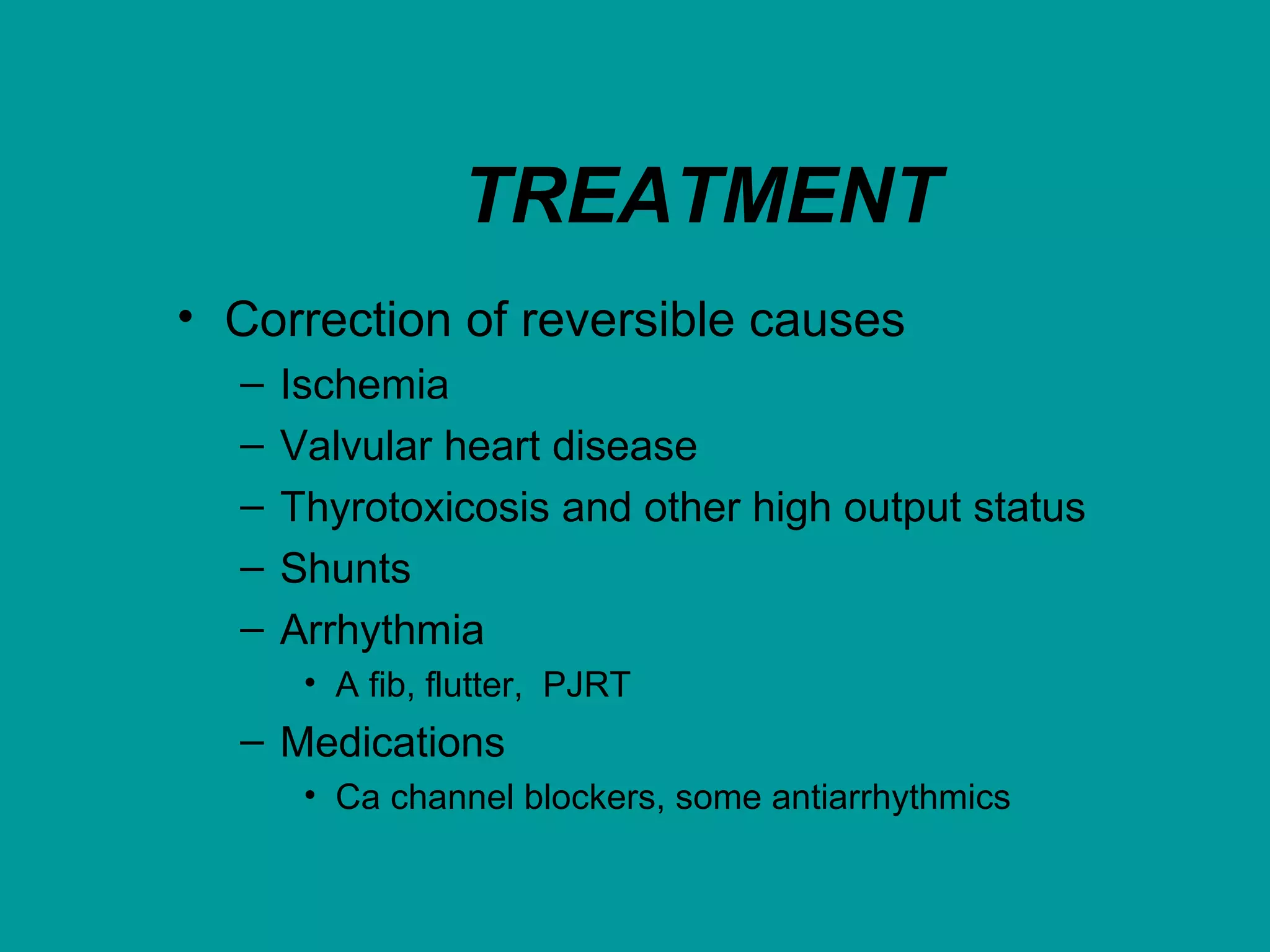
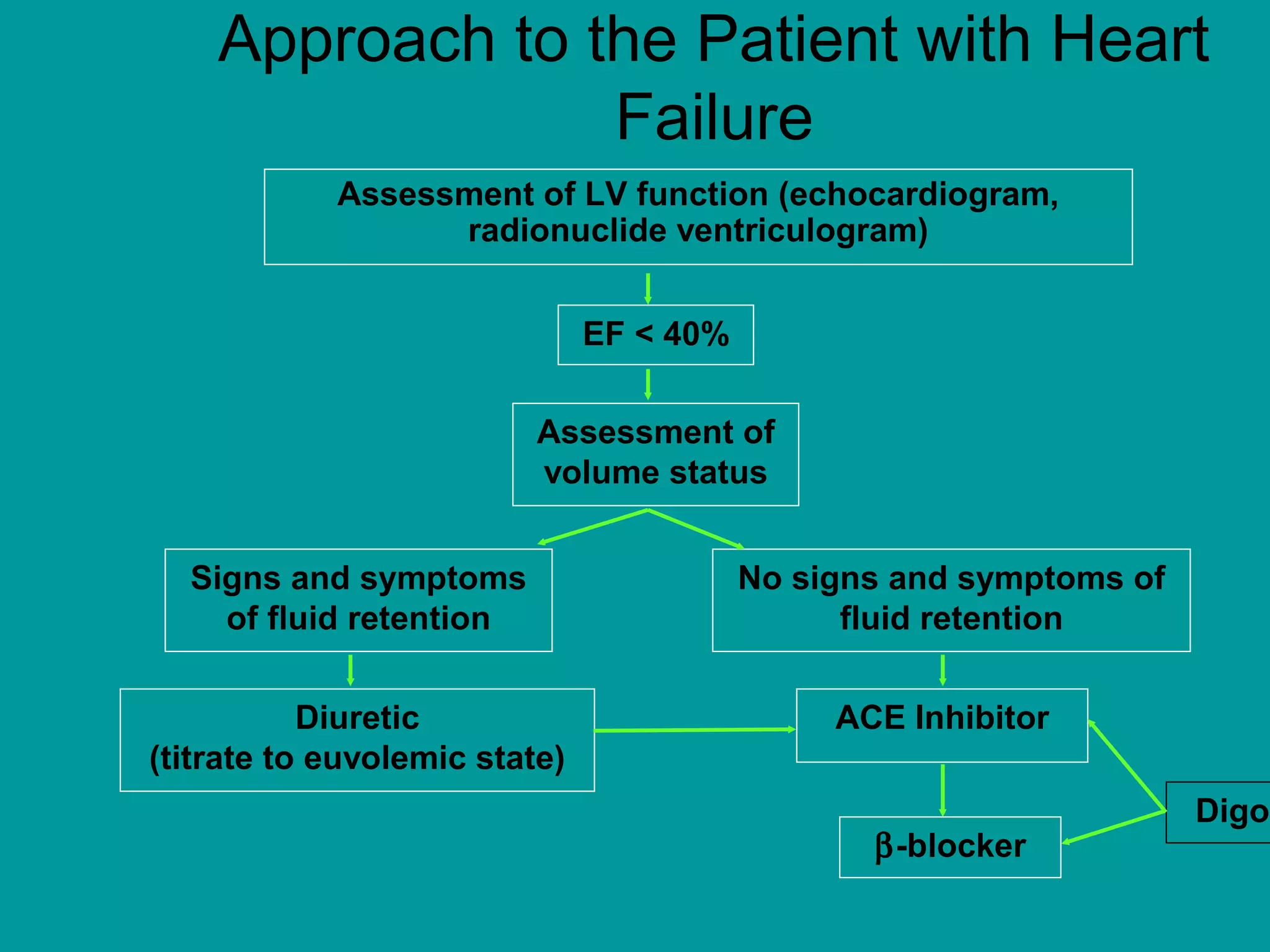
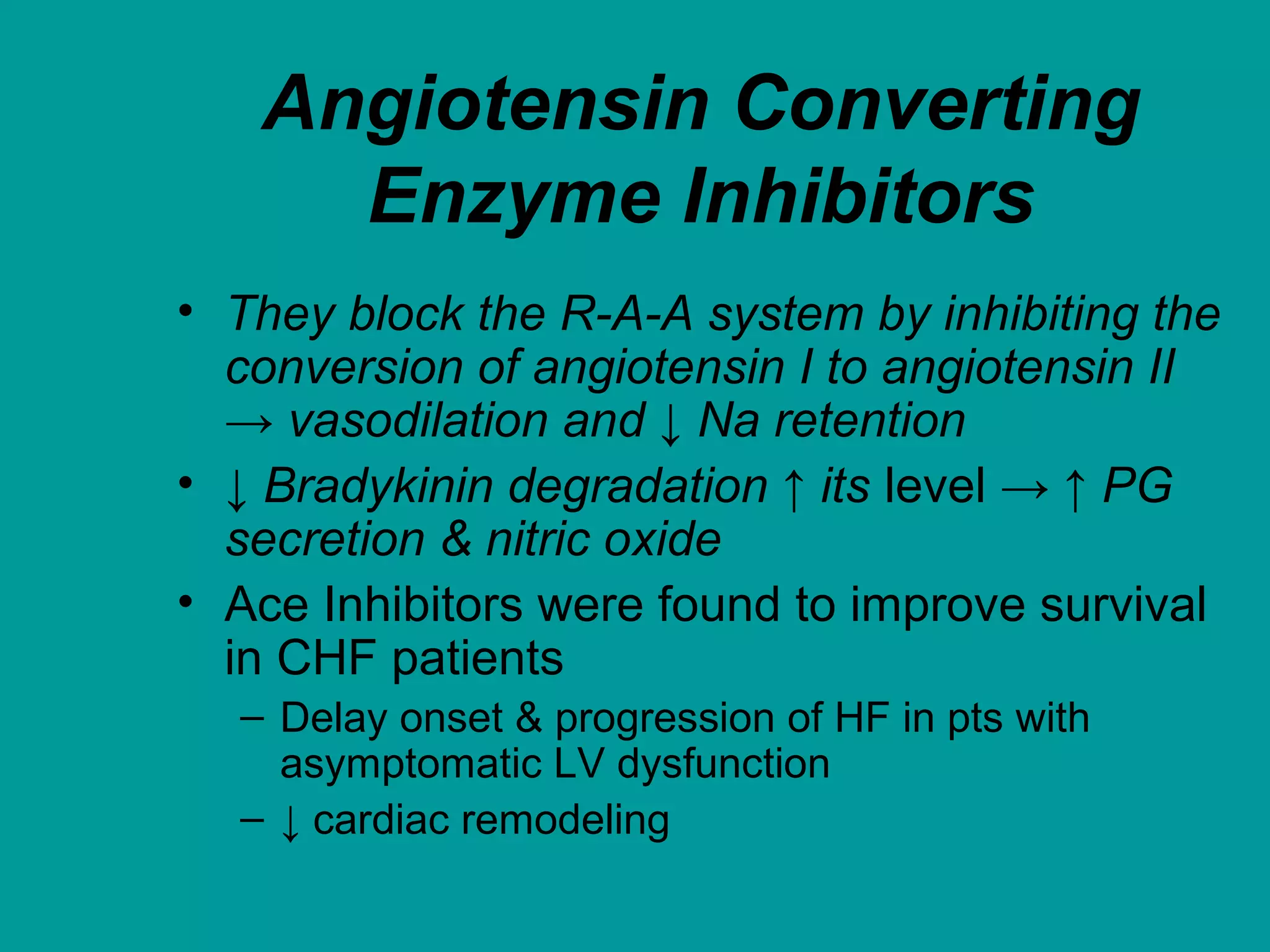
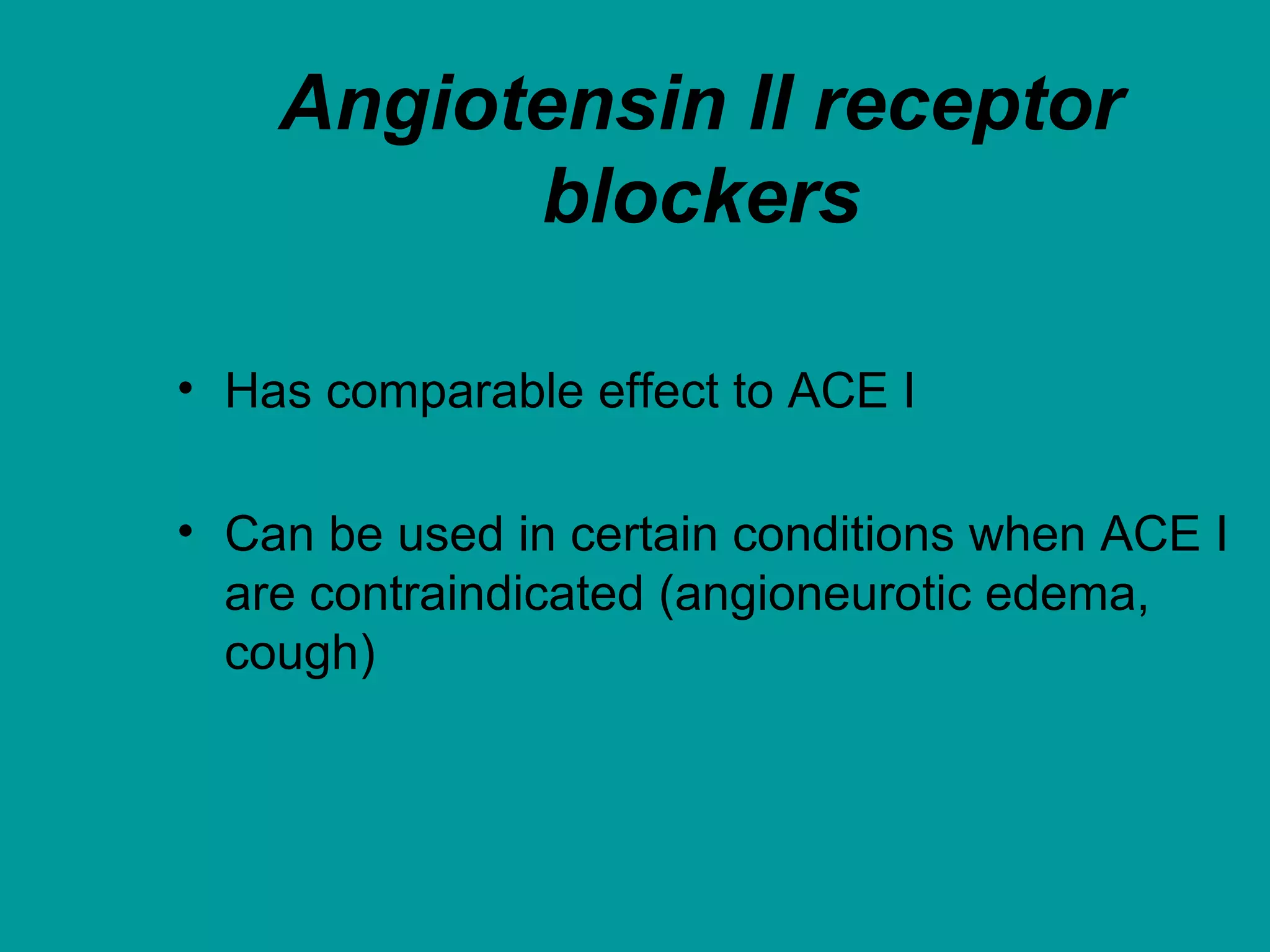
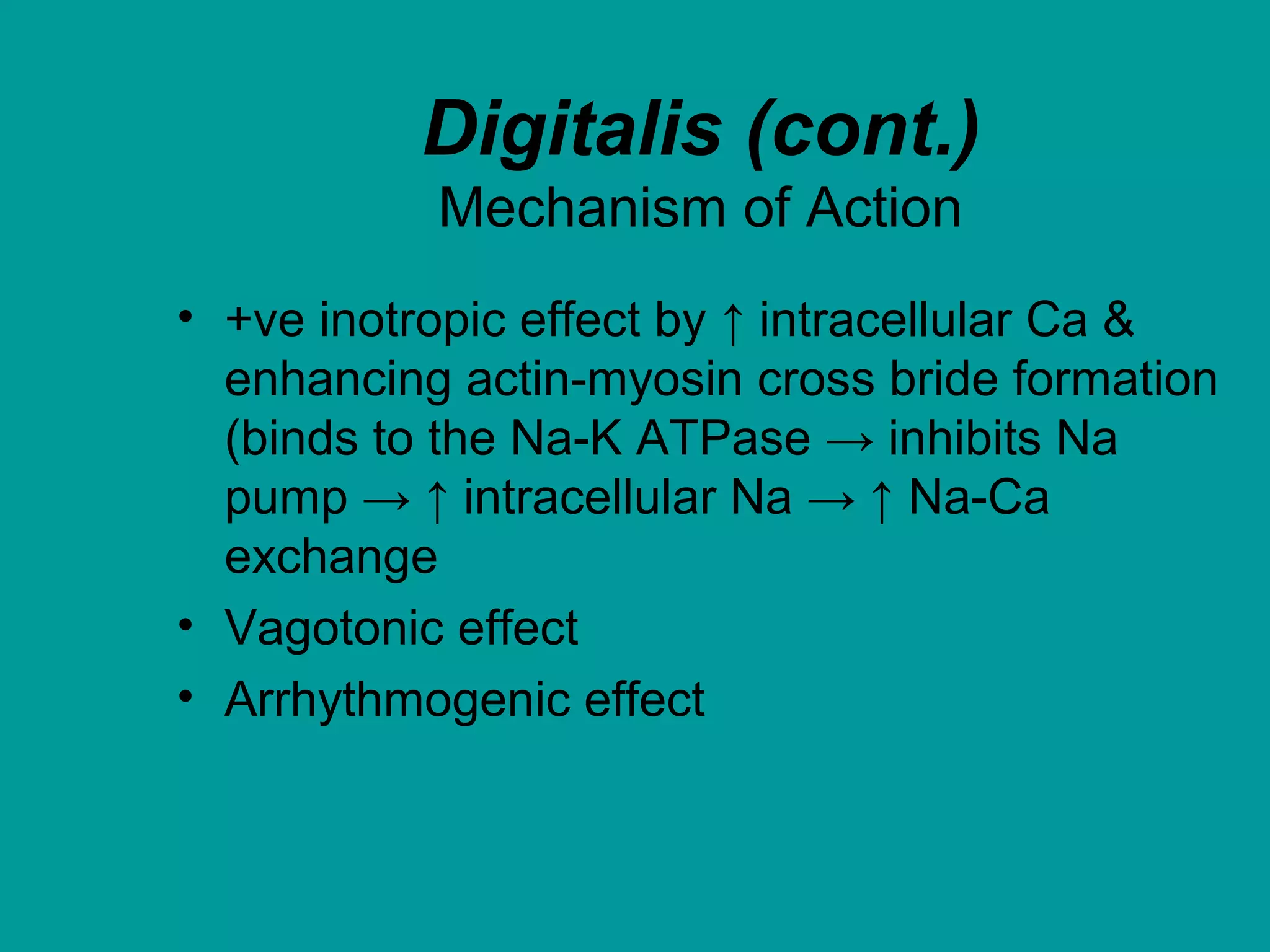
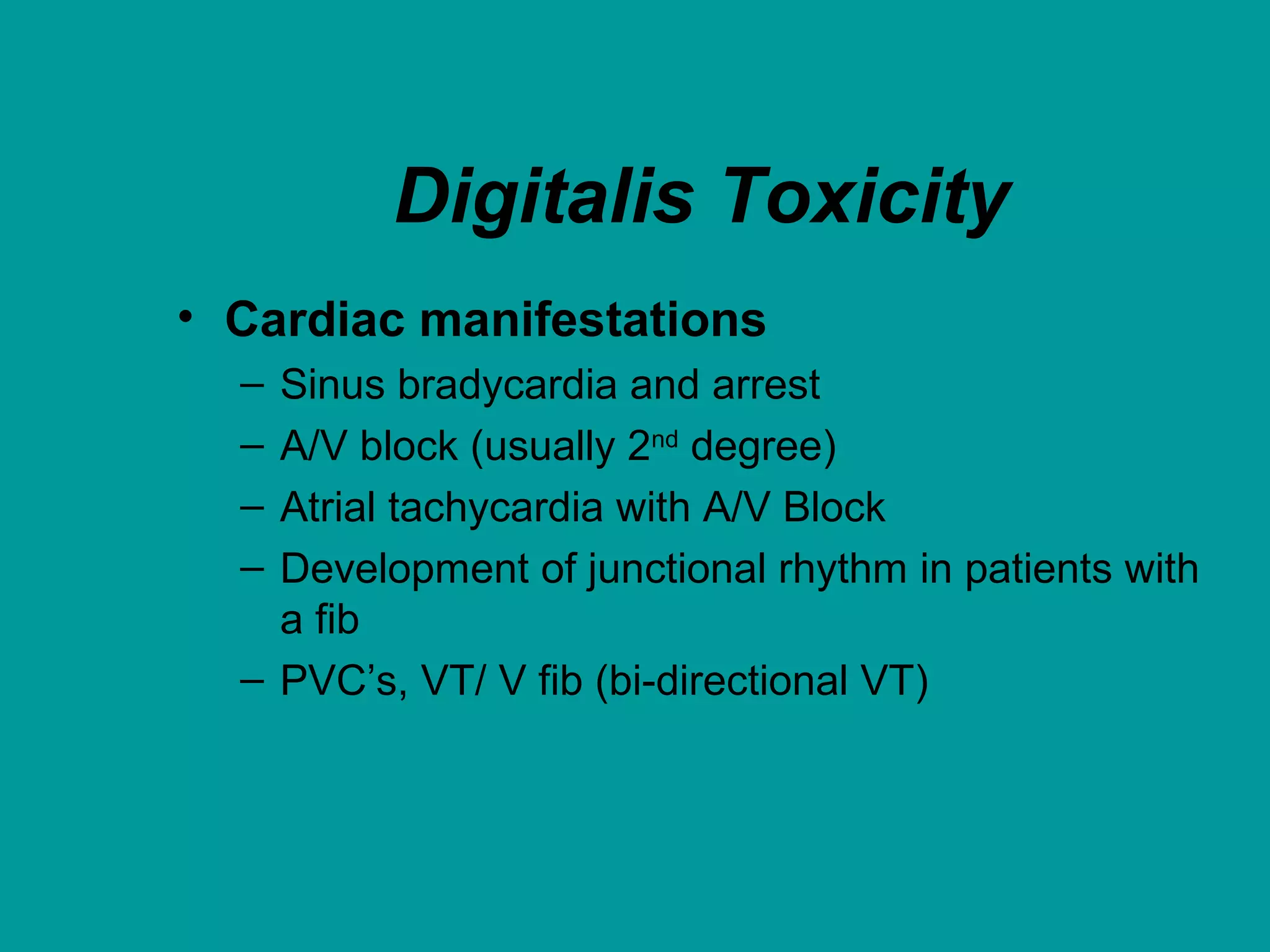
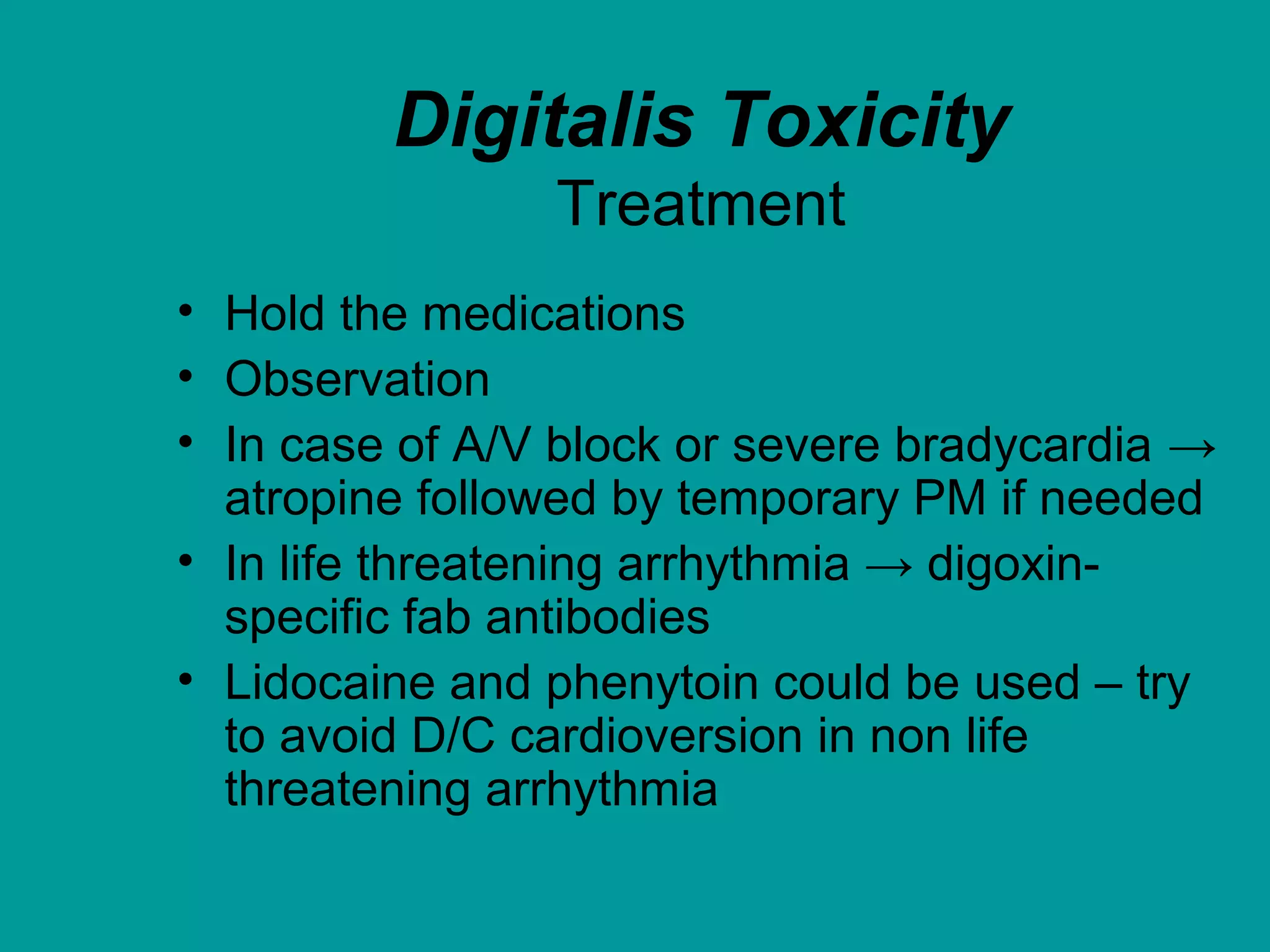
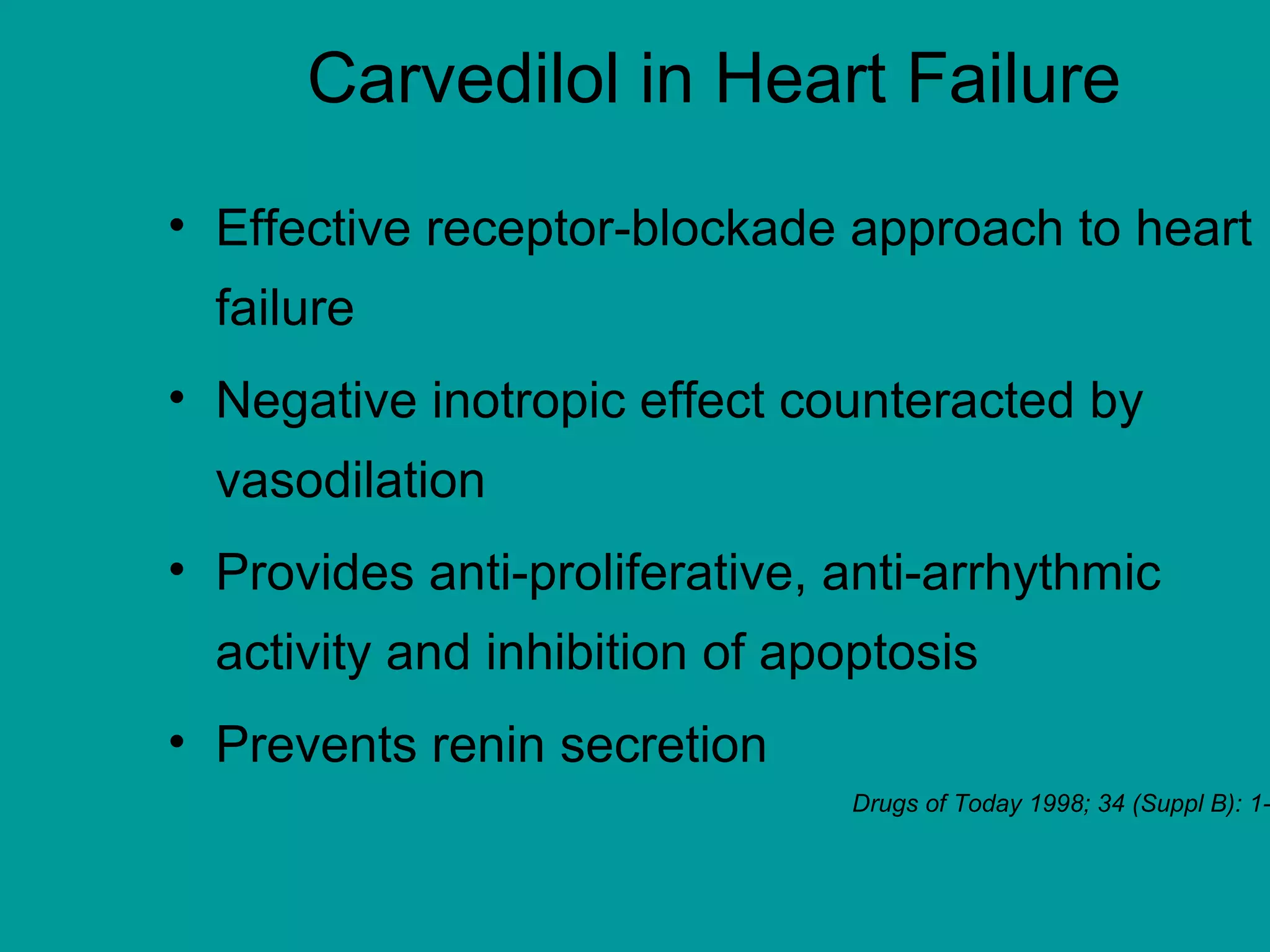
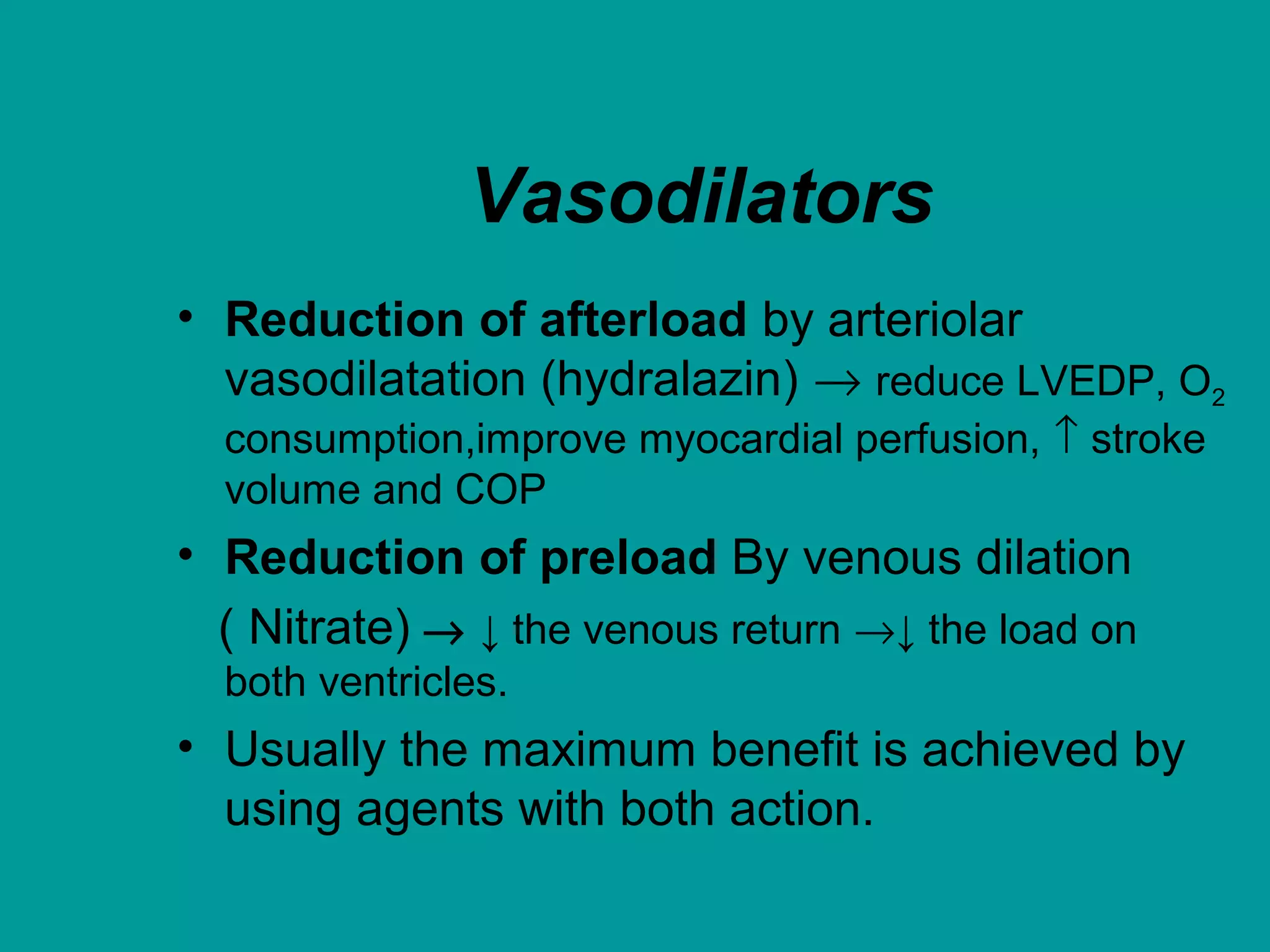
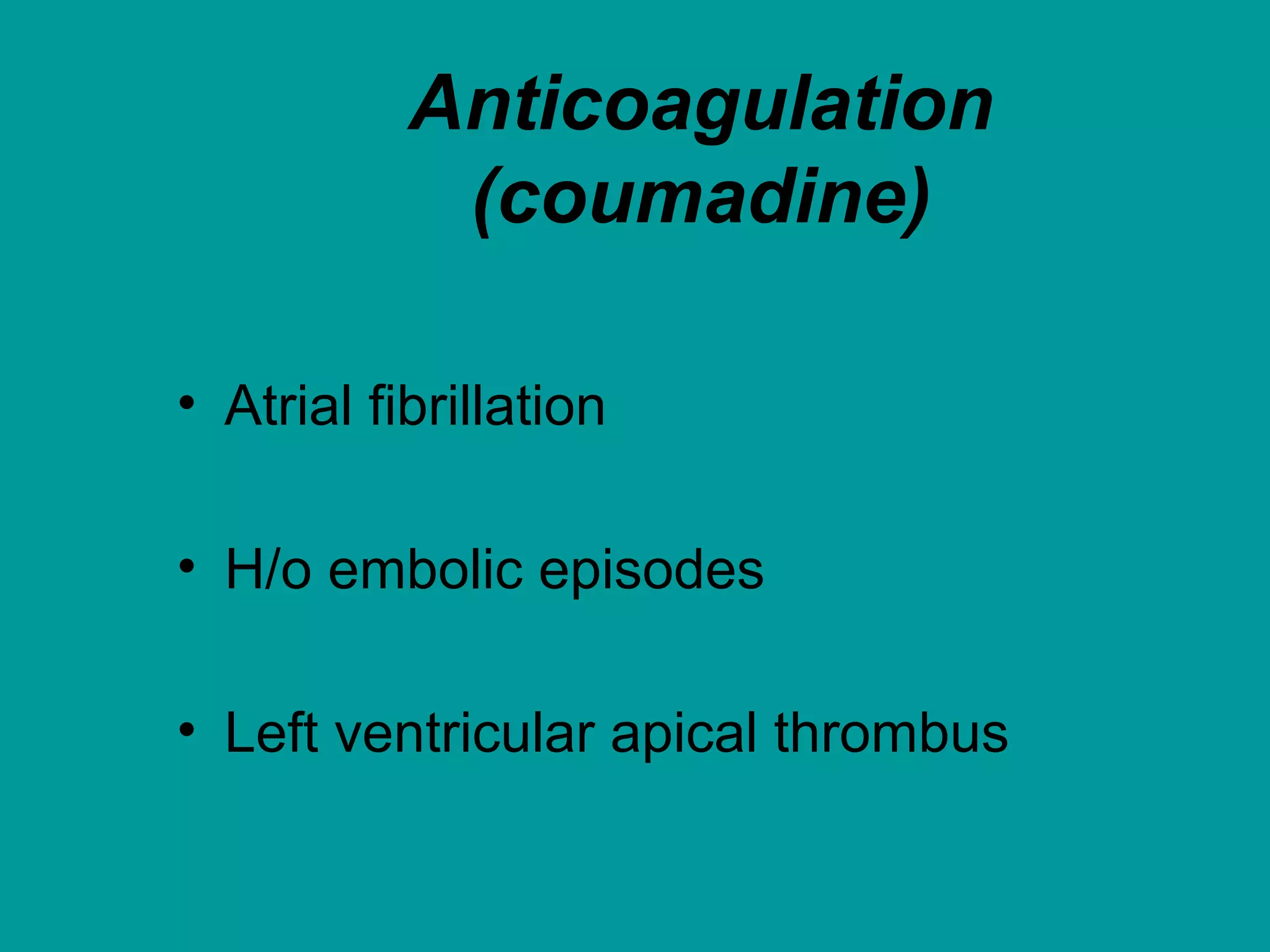
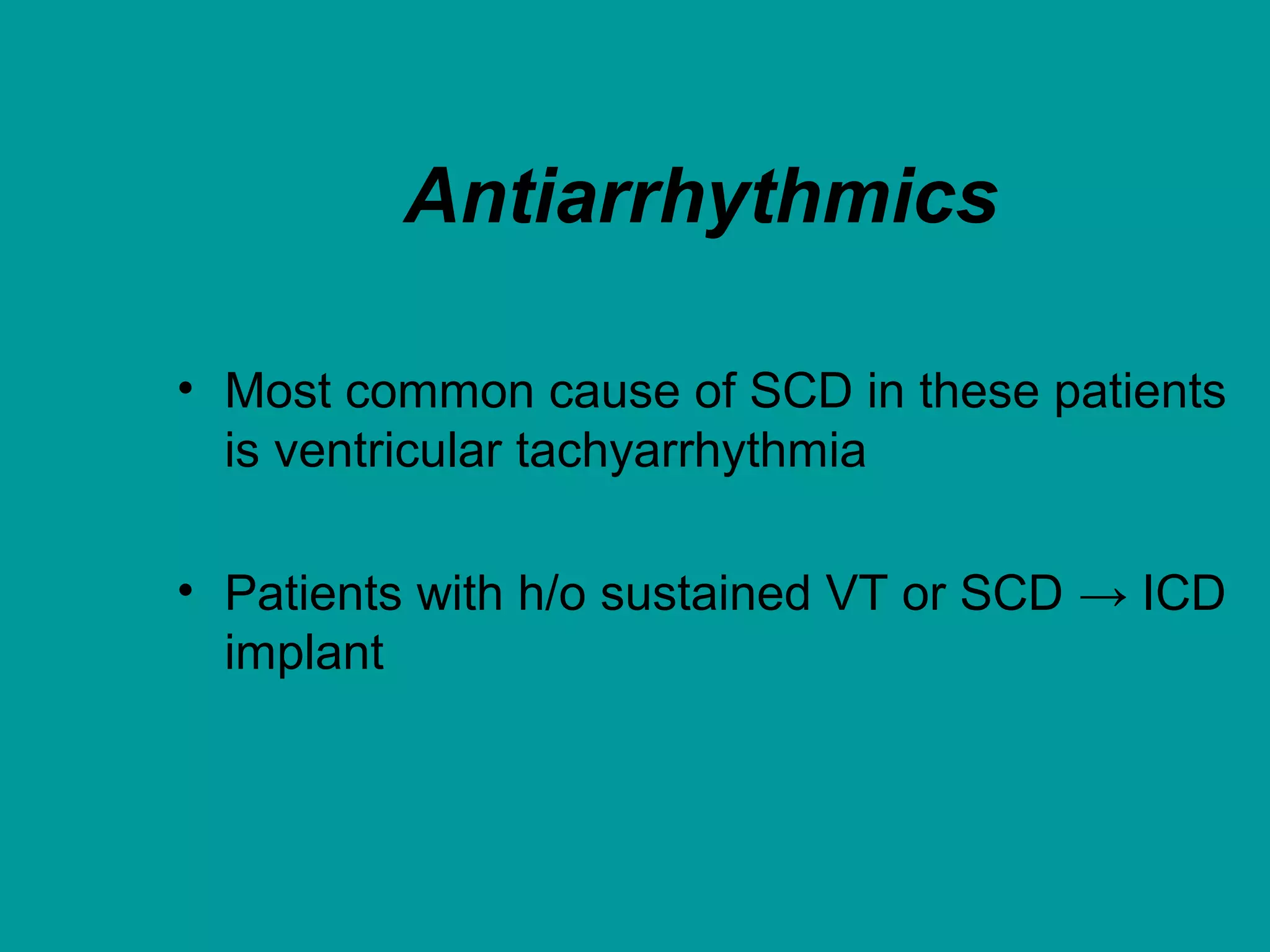
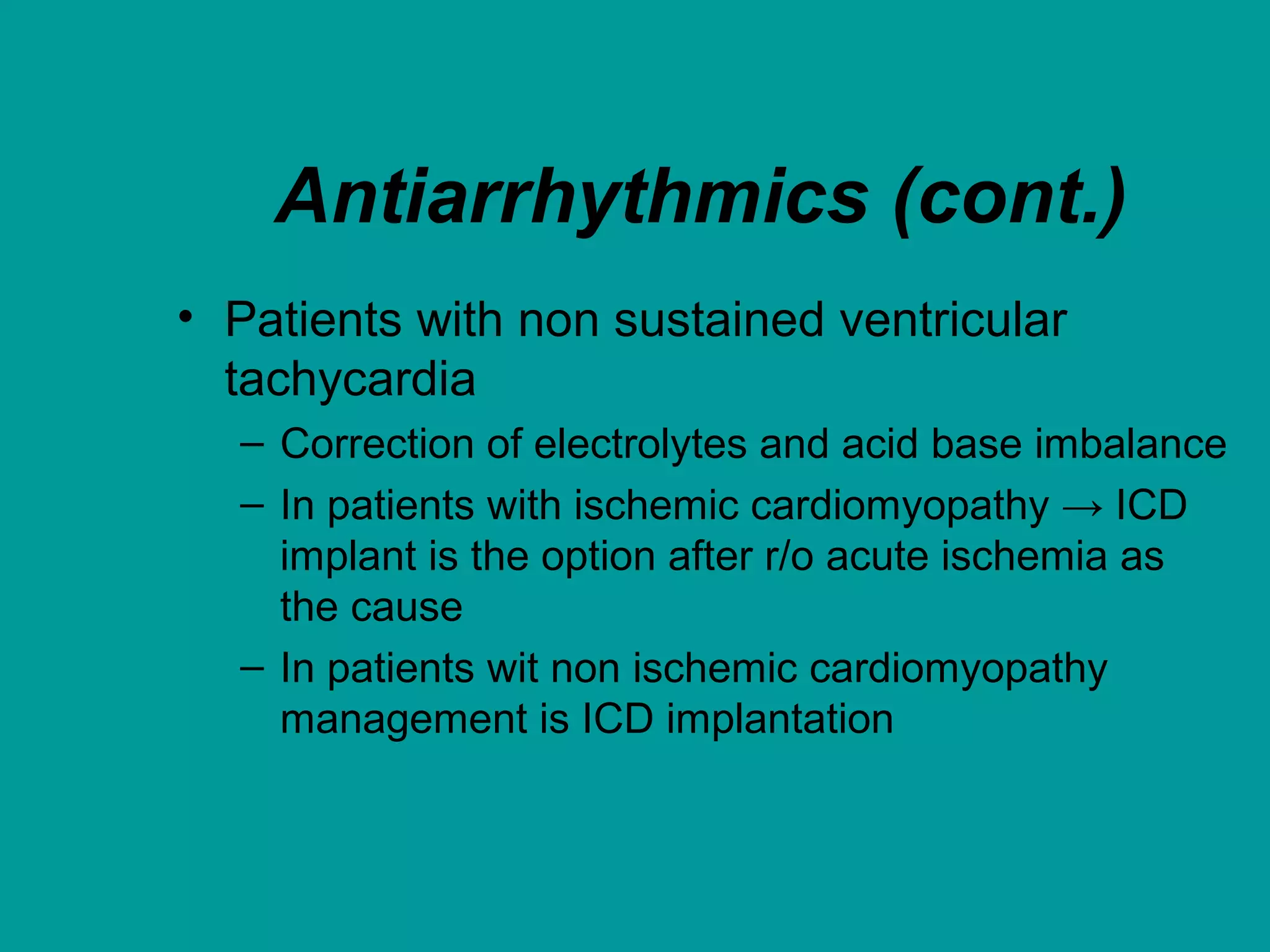
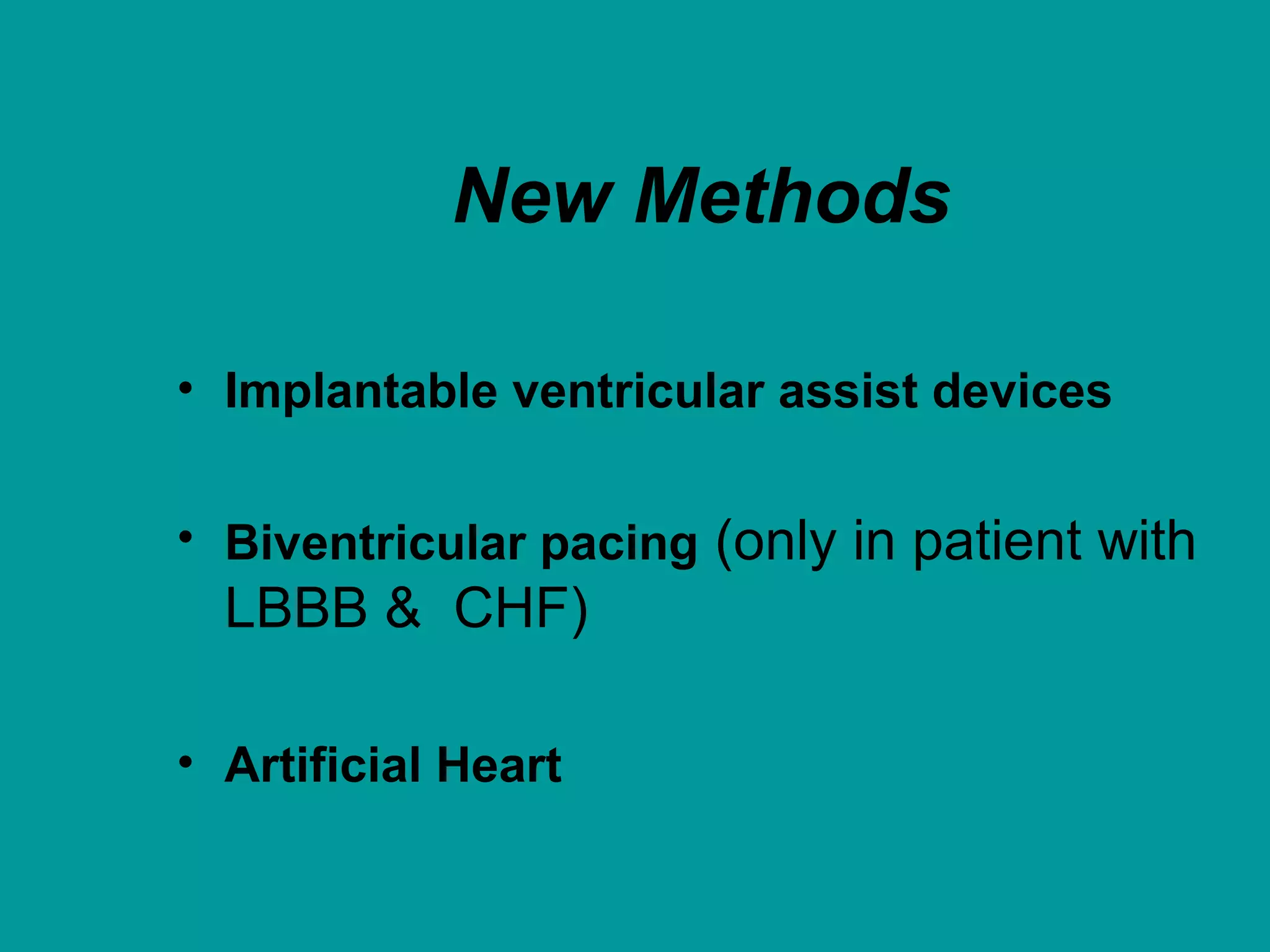
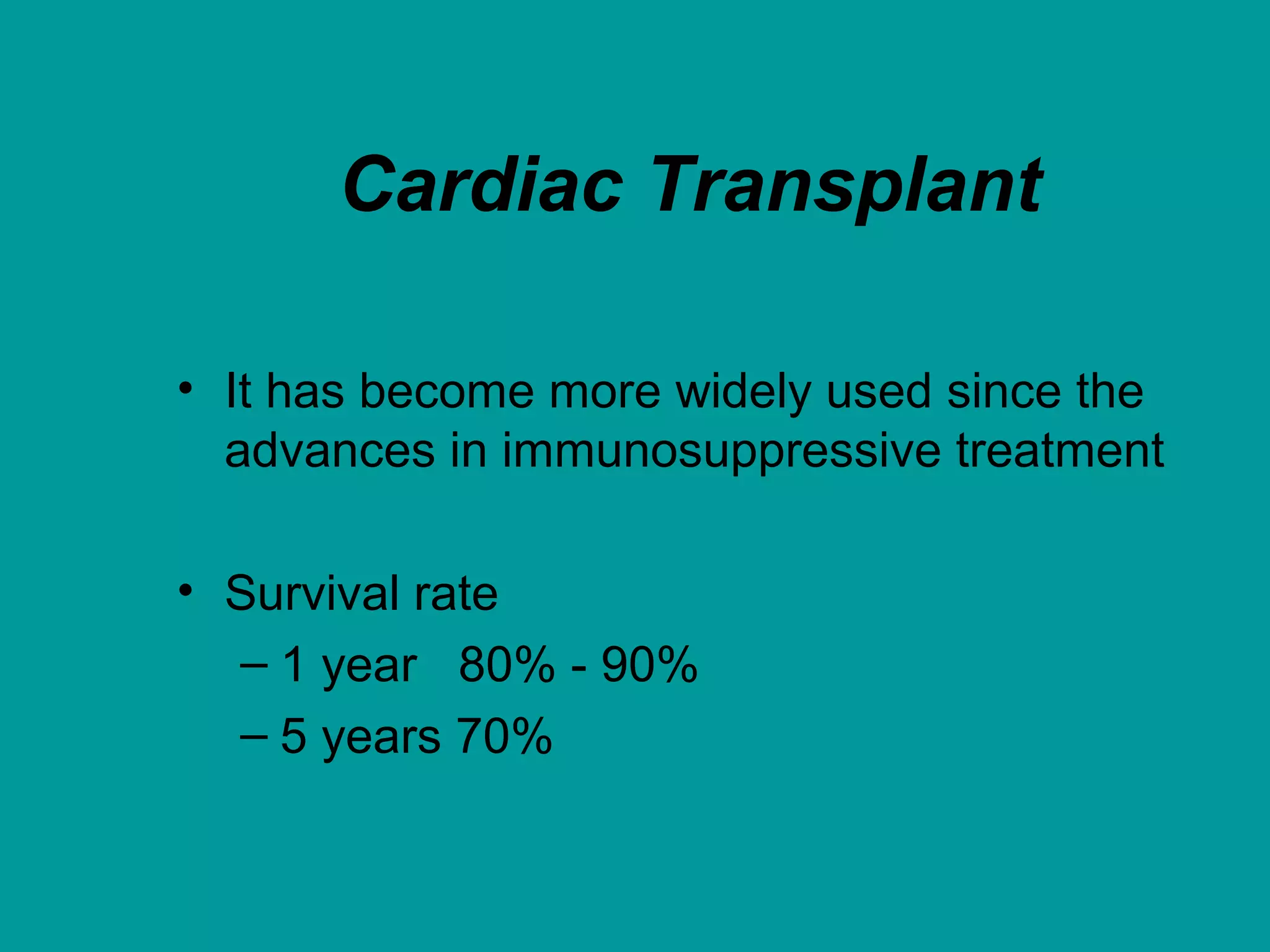
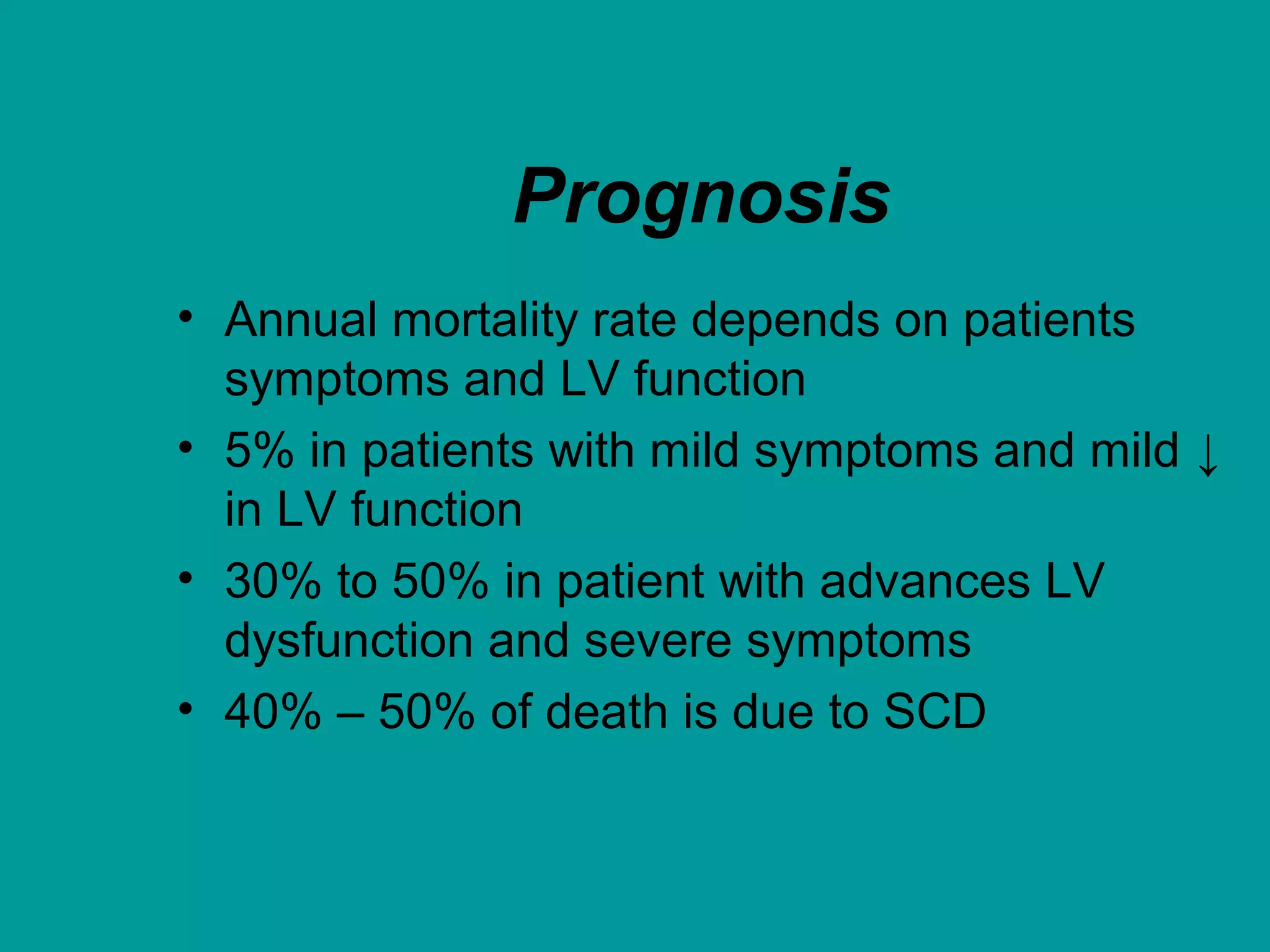
Heart failure is a condition where the heart cannot pump enough blood to meet the body's needs. It is usually due to problems with the structure or function of the heart. Common causes include coronary artery disease, hypertension, and cardiomyopathy. Symptoms include shortness of breath, fatigue, and fluid retention. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms with diuretics and drugs that target the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system like ACE inhibitors. Other treatments include beta-blockers, digitalis glycosides, and managing comorbidities and lifestyle factors like diet and exercise. The goals are to improve quality of life, slow disease progression, and reduce mortality risk.