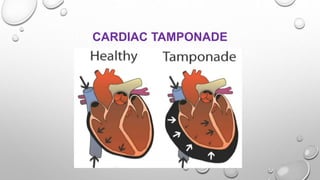
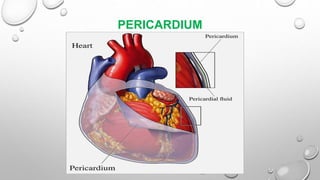
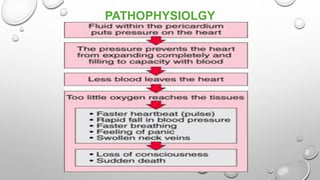
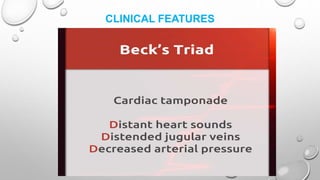
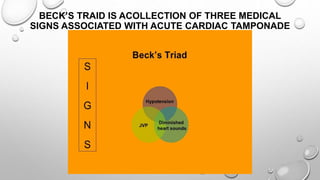
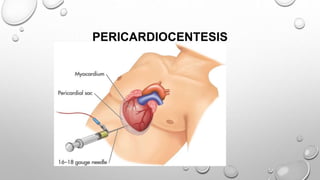
Cardiac tamponade is a life-threatening condition characterized by excessive fluid accumulation in the pericardial sac, leading to impaired cardiac function and reduced stroke volume. It can result from various causes including malignancy, infections, surgery, and trauma, and presents with symptoms such as tachycardia, dyspnea, and muffled heart sounds. Management includes intravenous fluids, antibiotics, and procedures like pericardiocentesis to relieve pressure on the heart.