The document summarizes the anatomy of the hand, including:
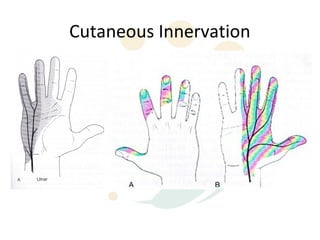
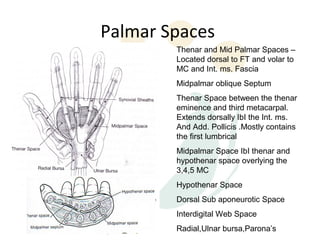
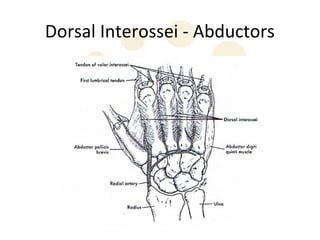
1) The skin, fascia, muscles, blood vessels, and nerves of the palm and dorsum. Key structures include the thenar and hypothenar muscles innervated by the median and ulnar nerves respectively.
2) The flexor tendons in the hand divide into zones as they pass through the carpal tunnel and palm. Extensor tendons are held in place by the extensor retinaculum.
3) Bones and joints of the hand include the carpals that make up the carpal tunnel, the metacarpals, and the interphalangeal joints between phalanges.