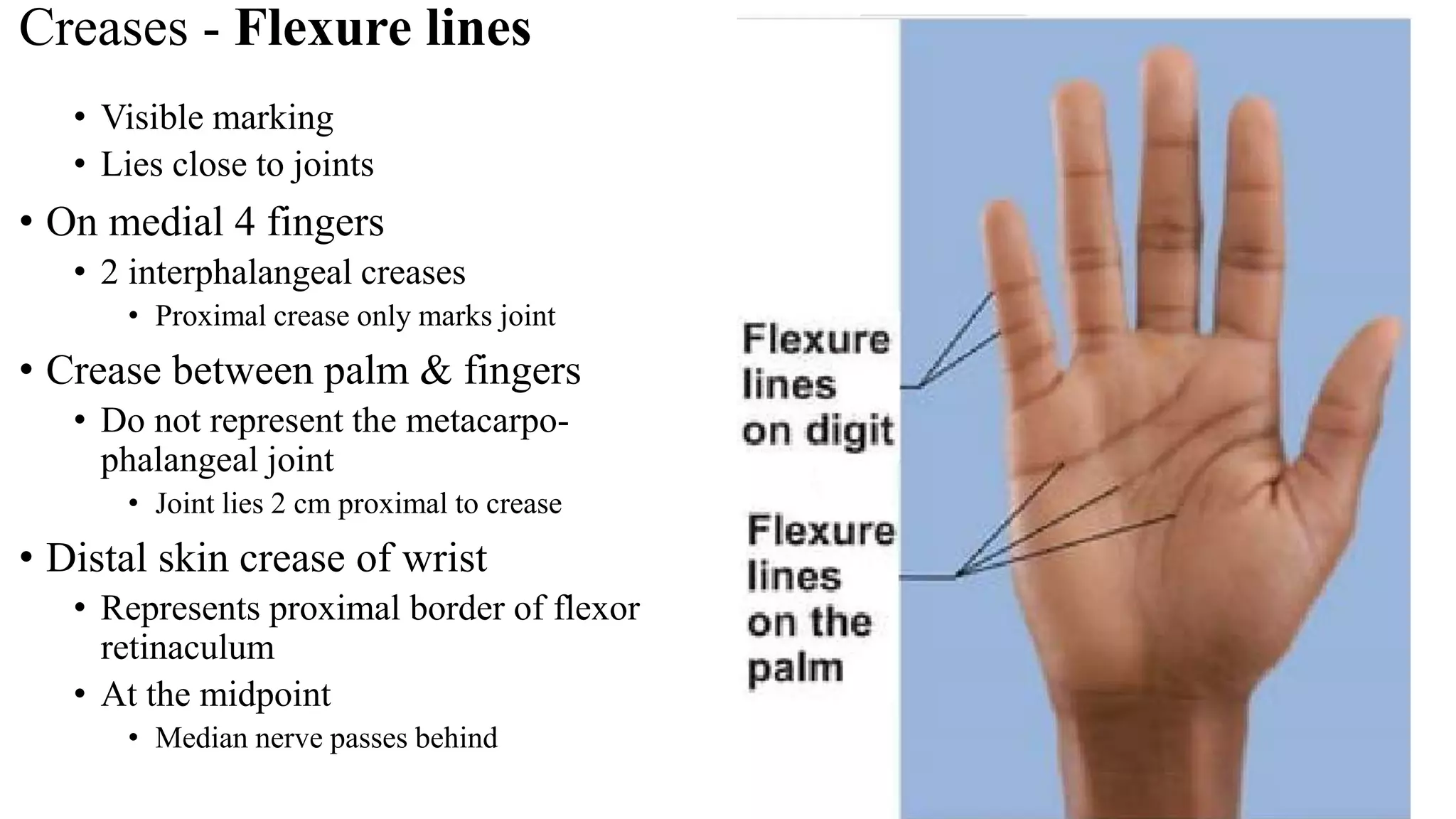
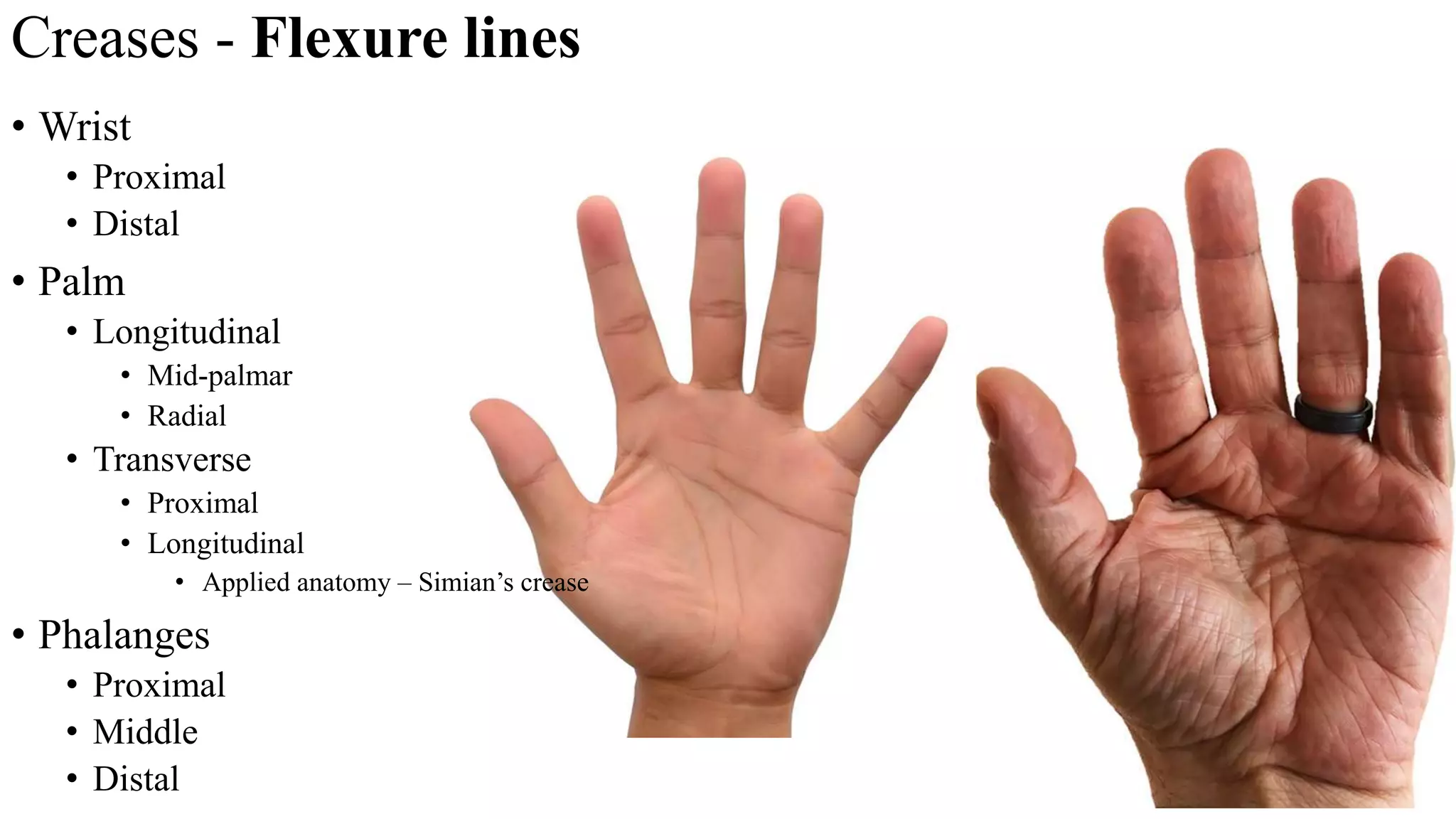
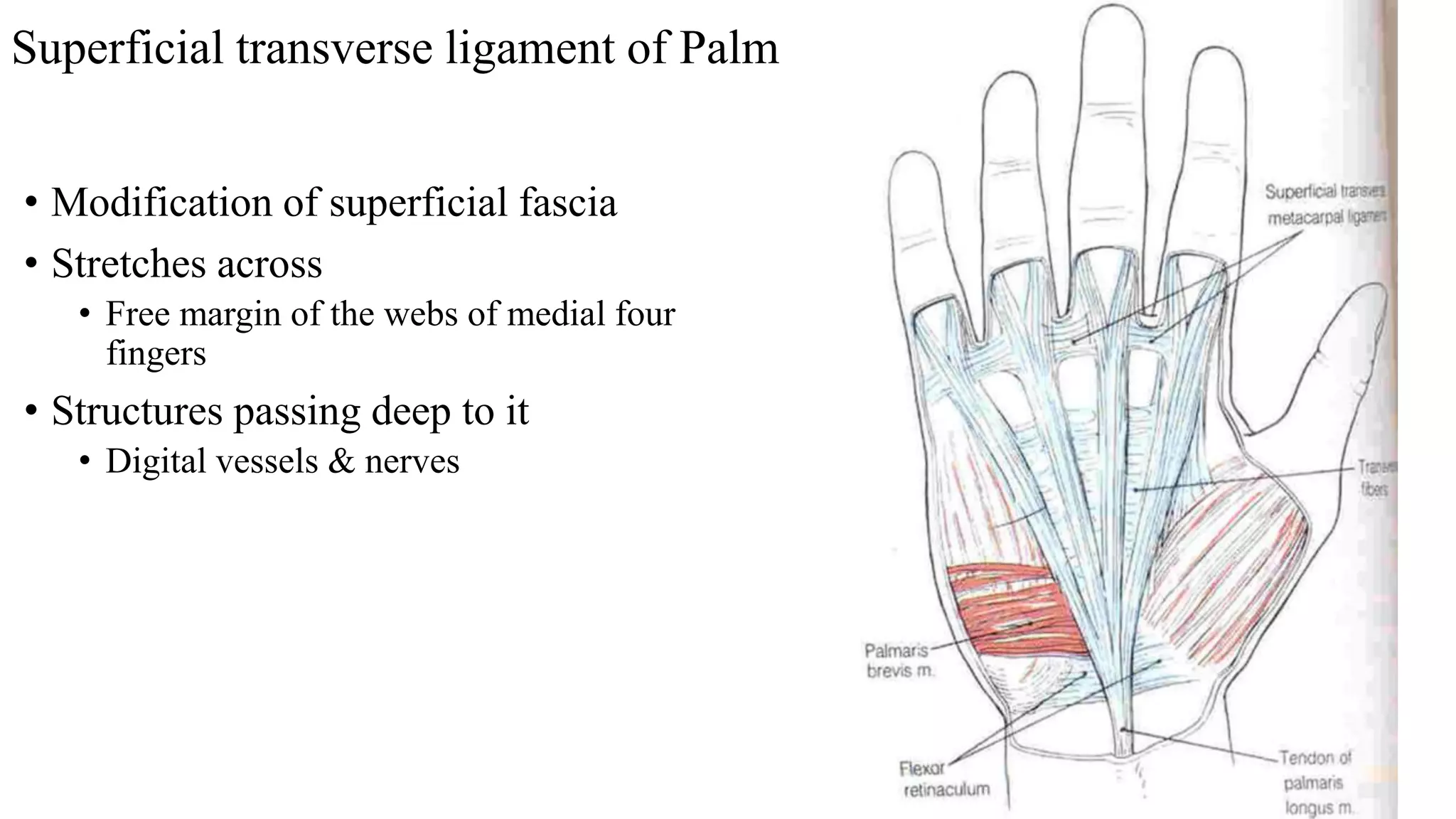
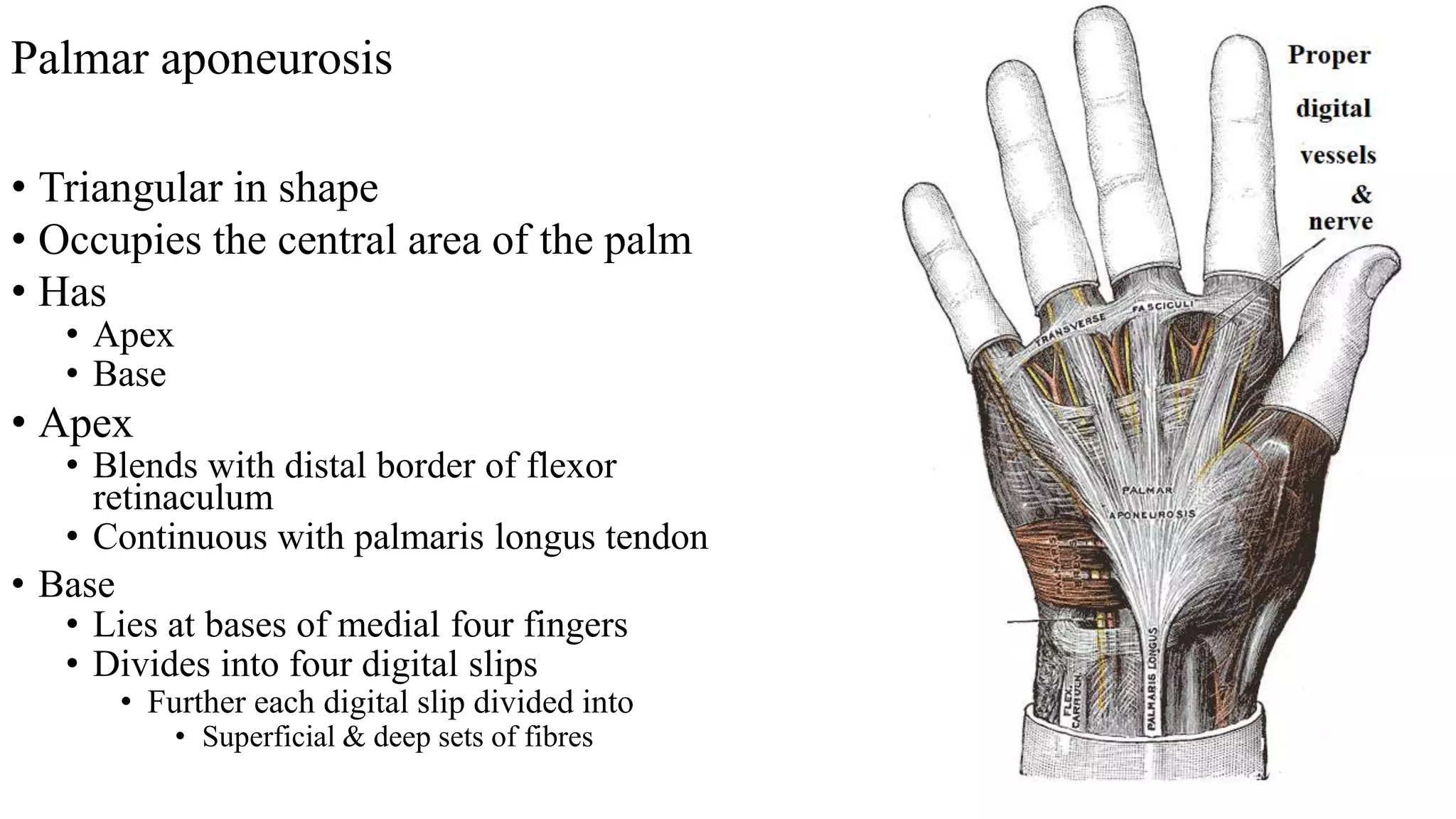
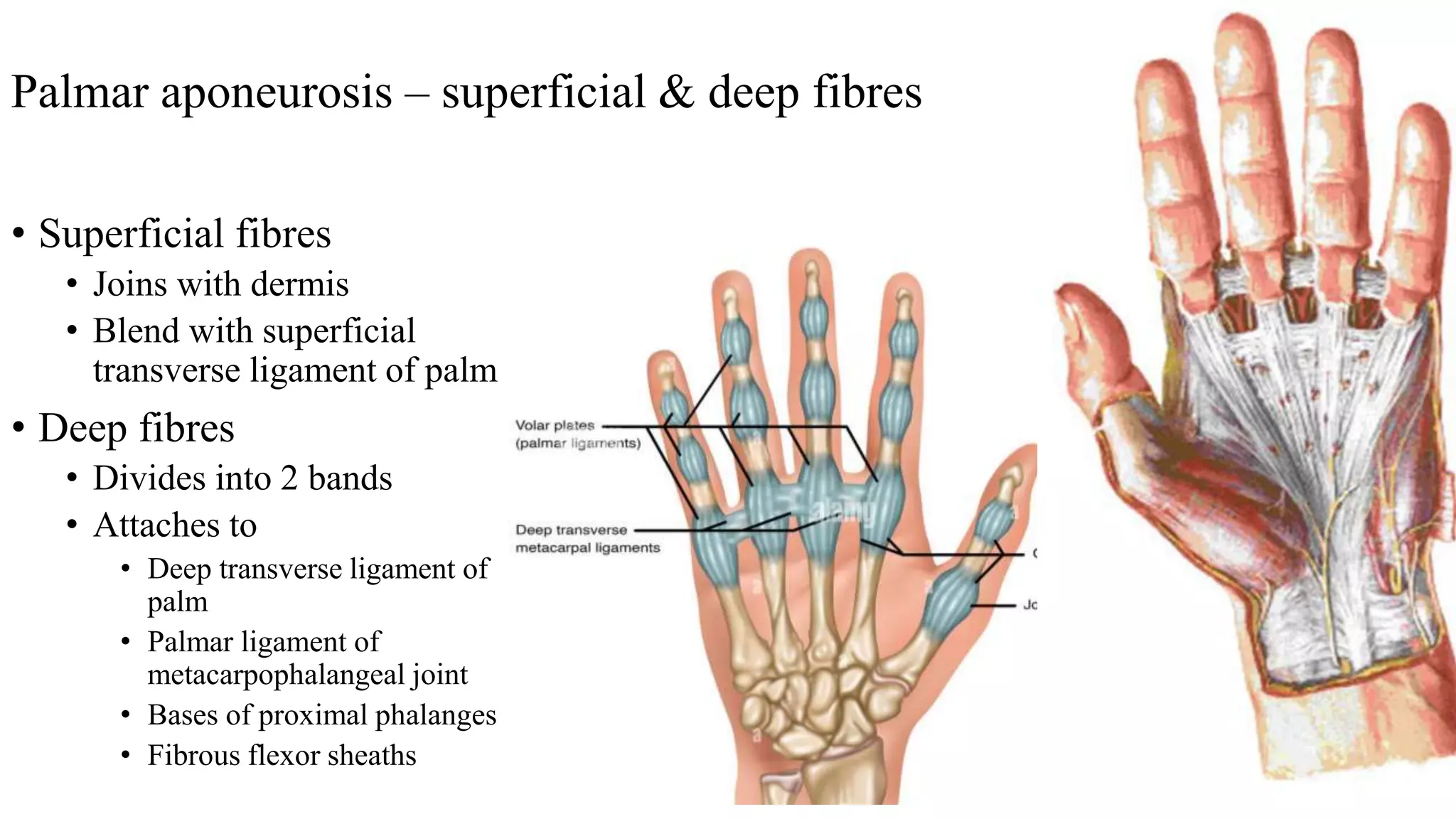
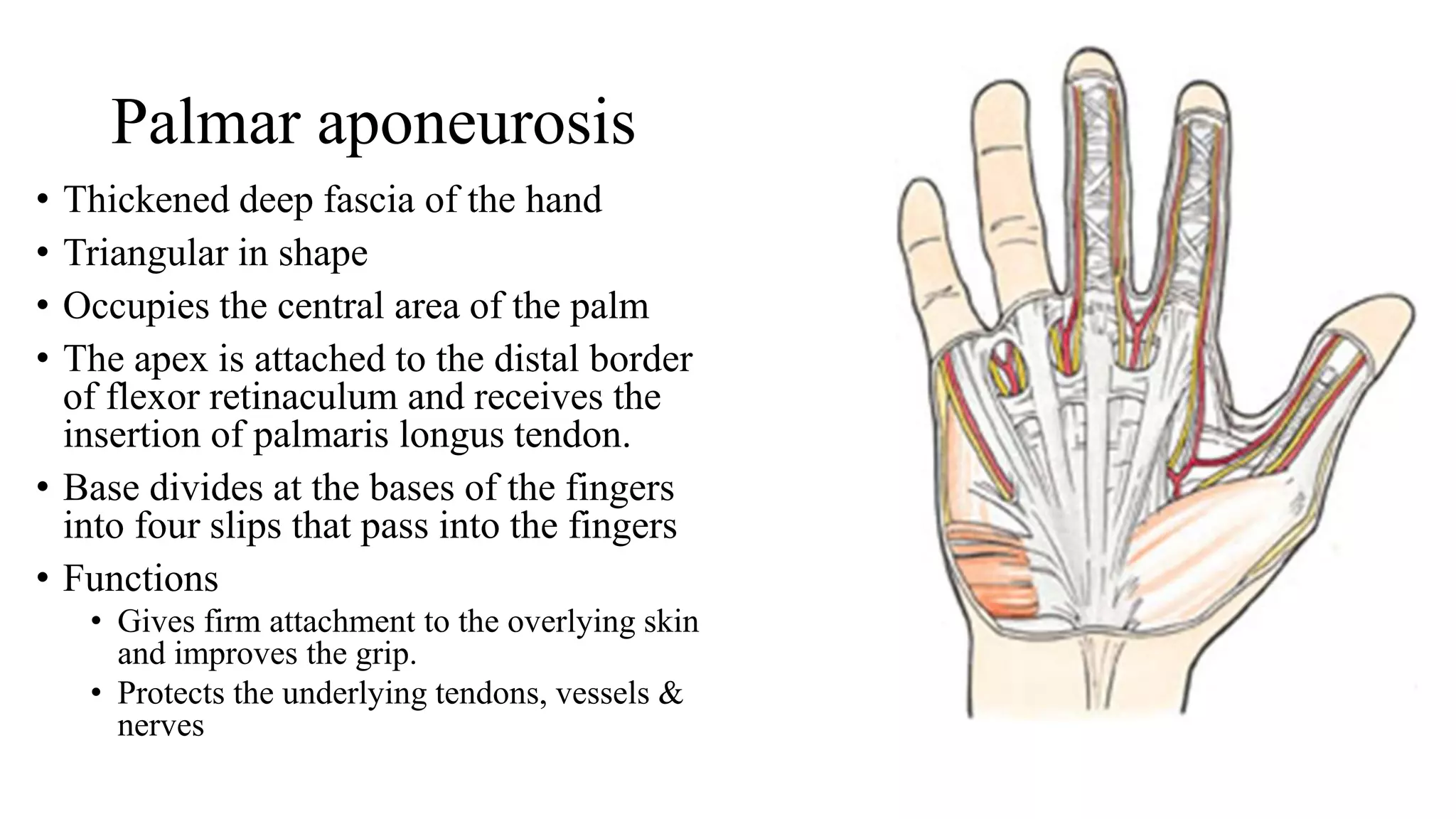
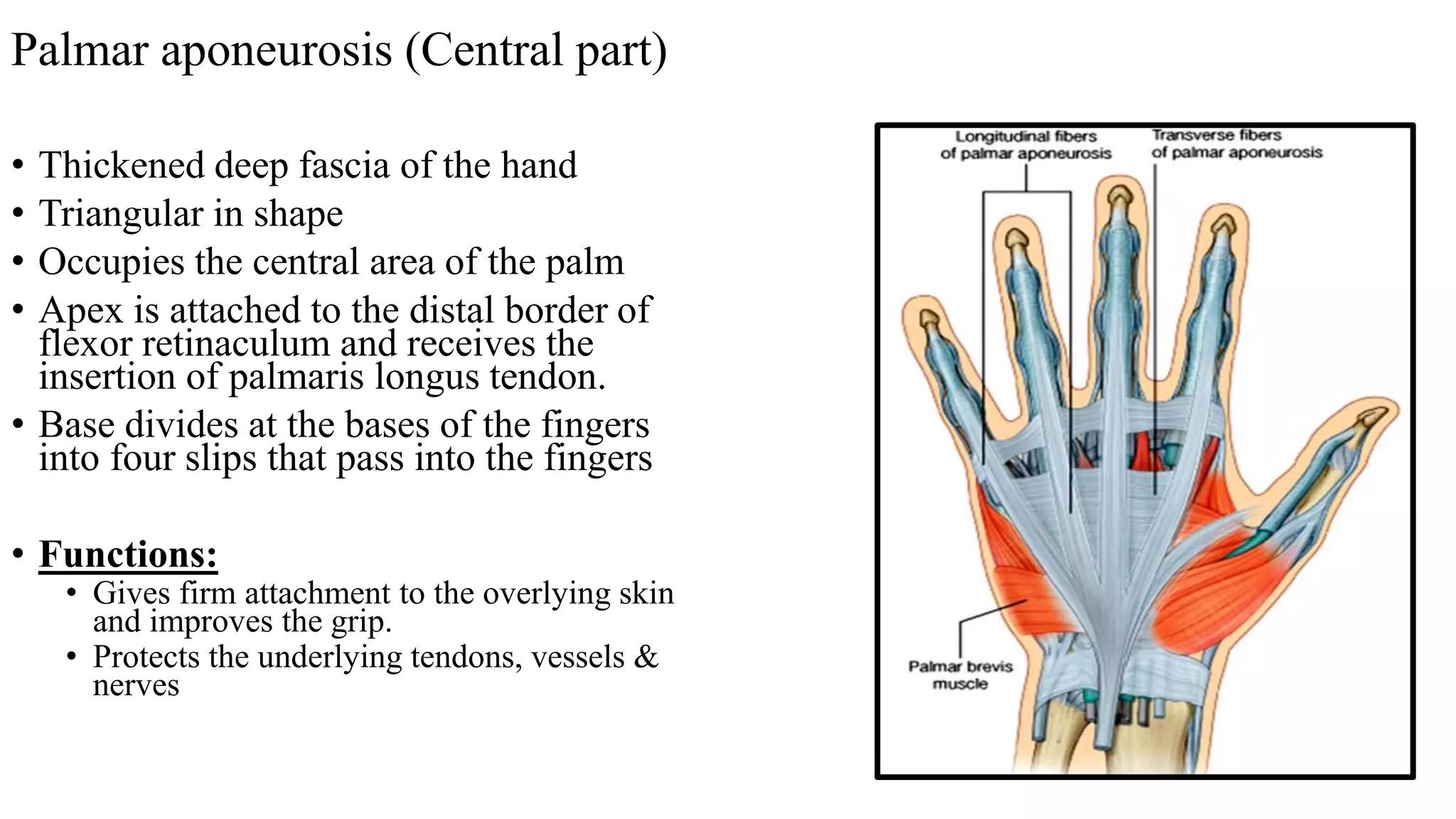
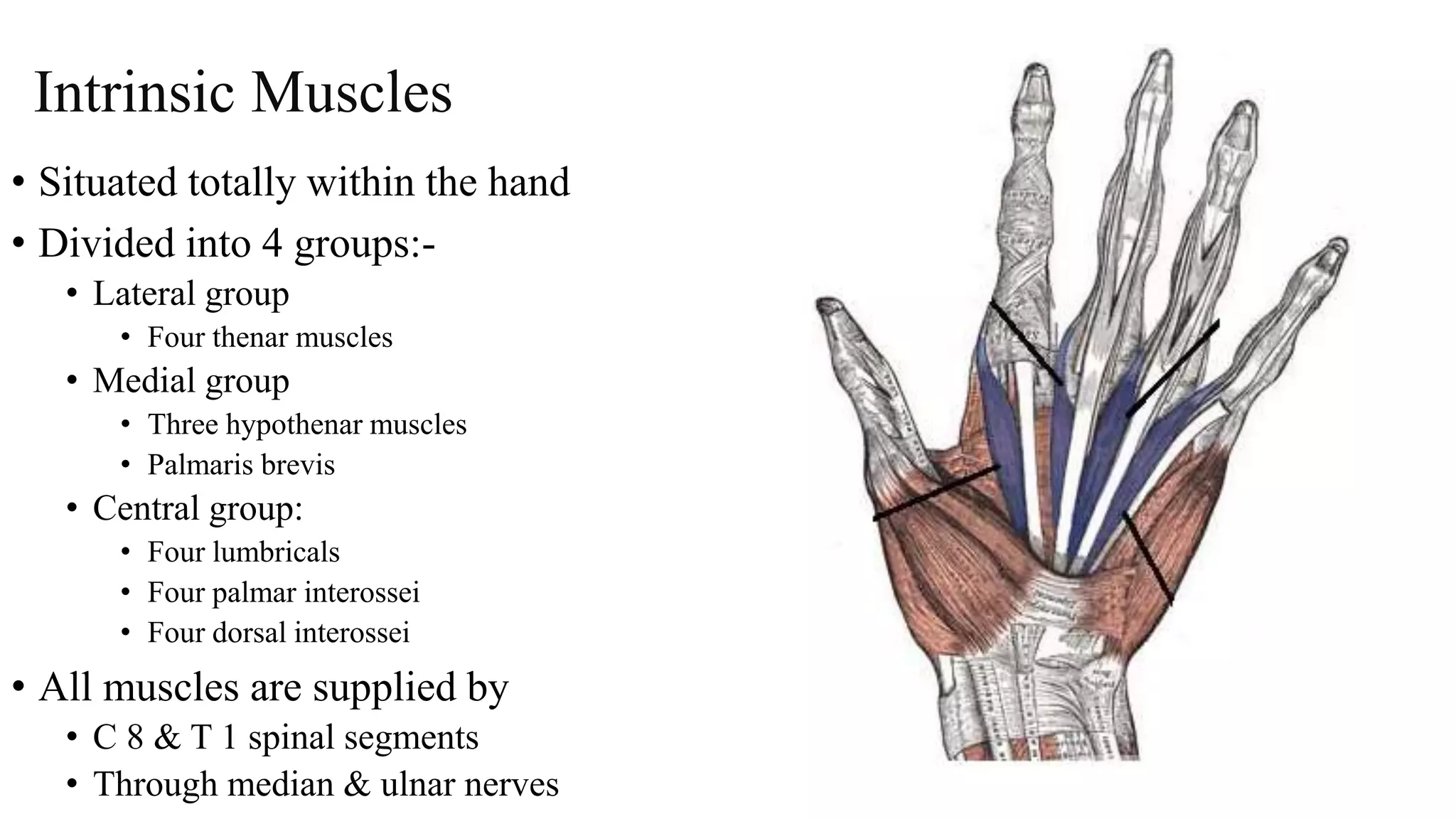
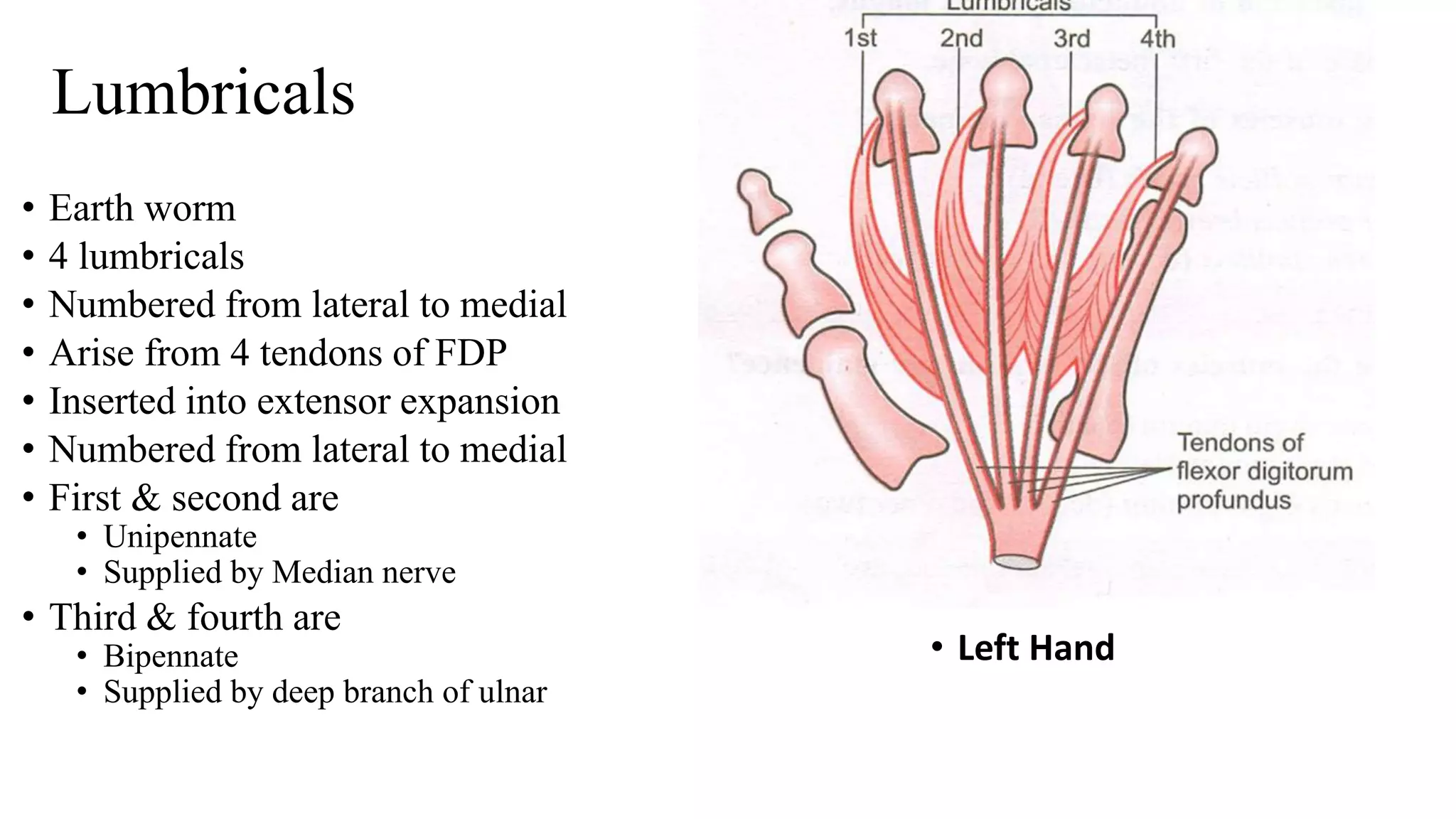
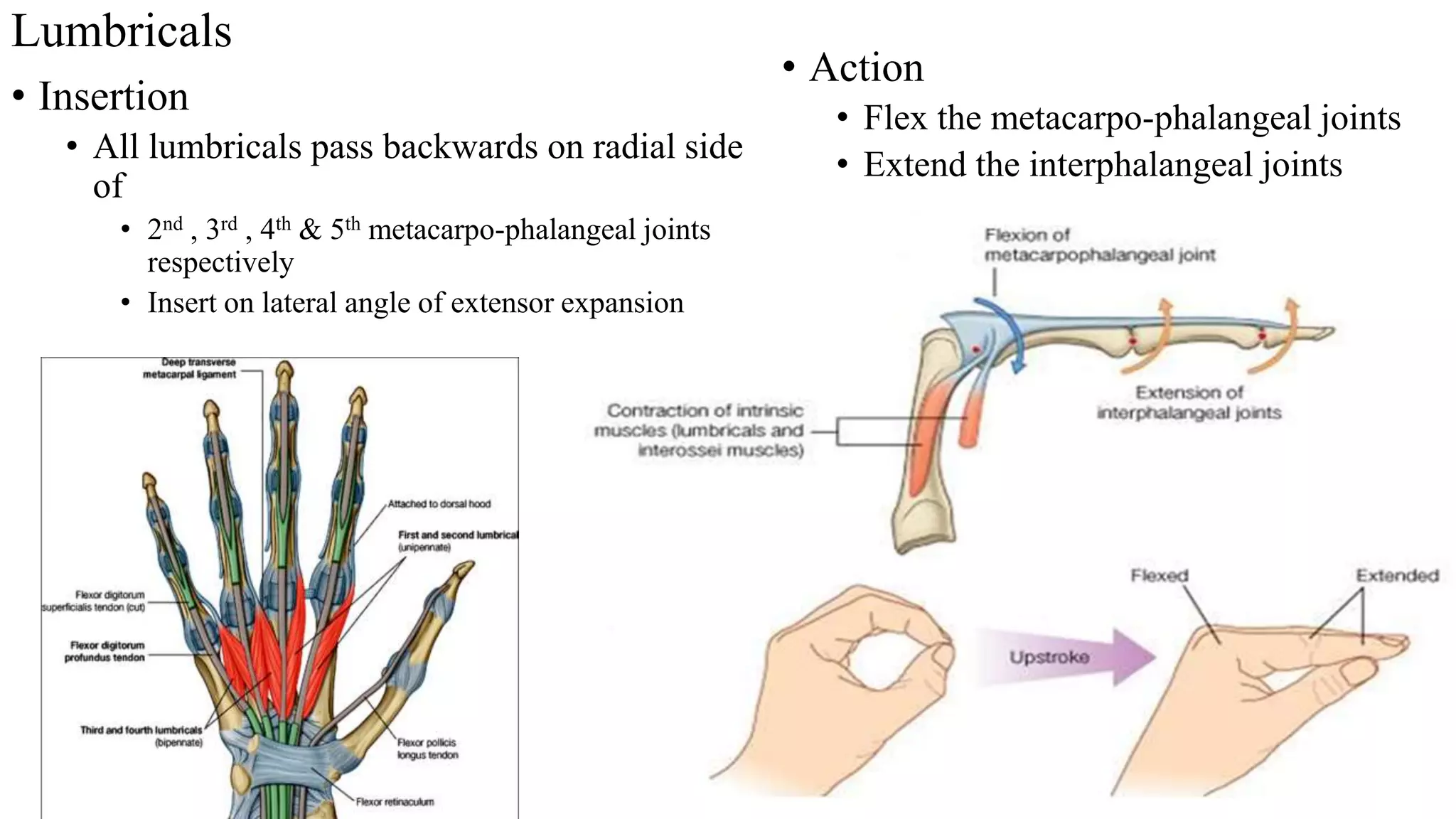
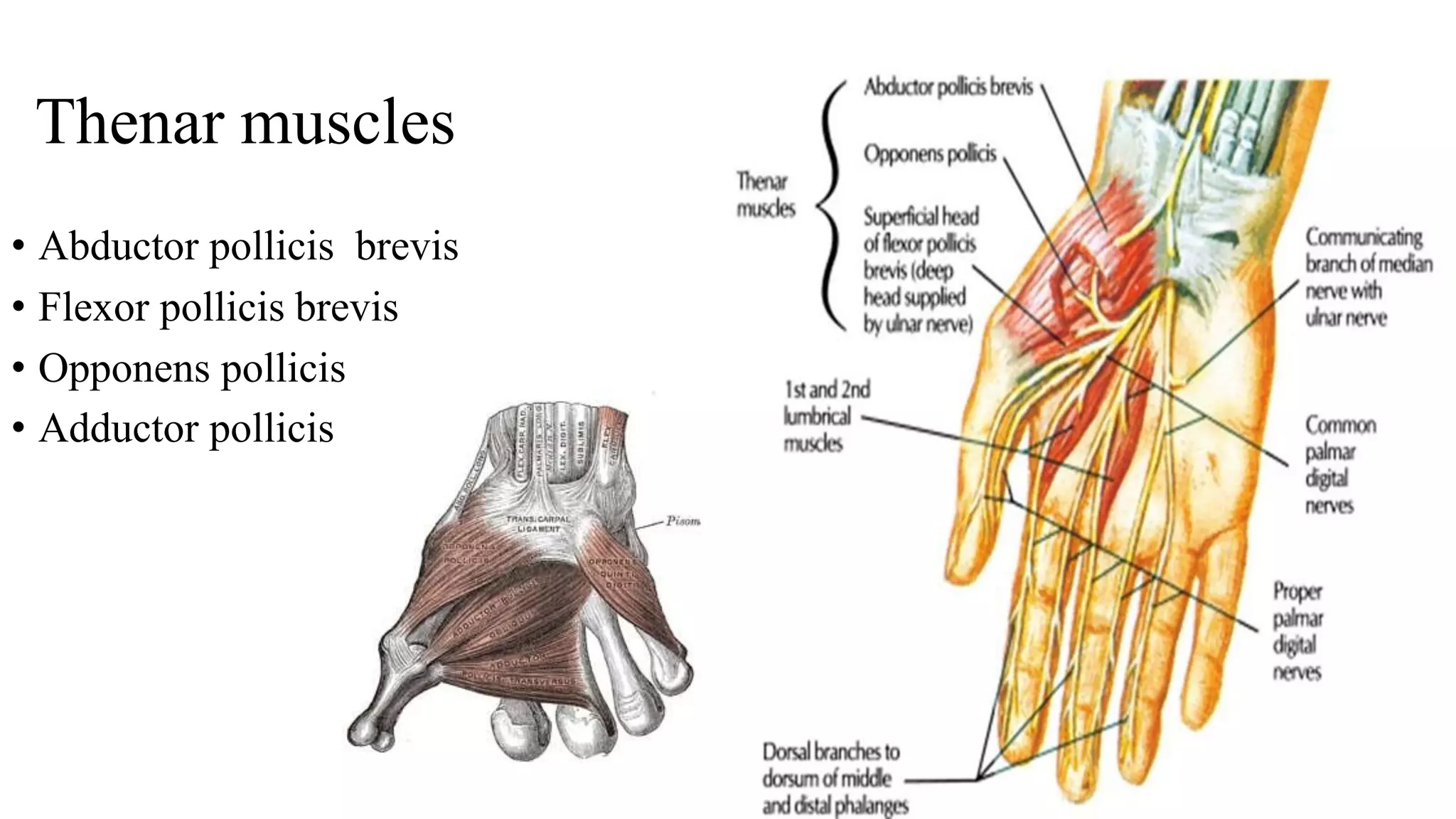
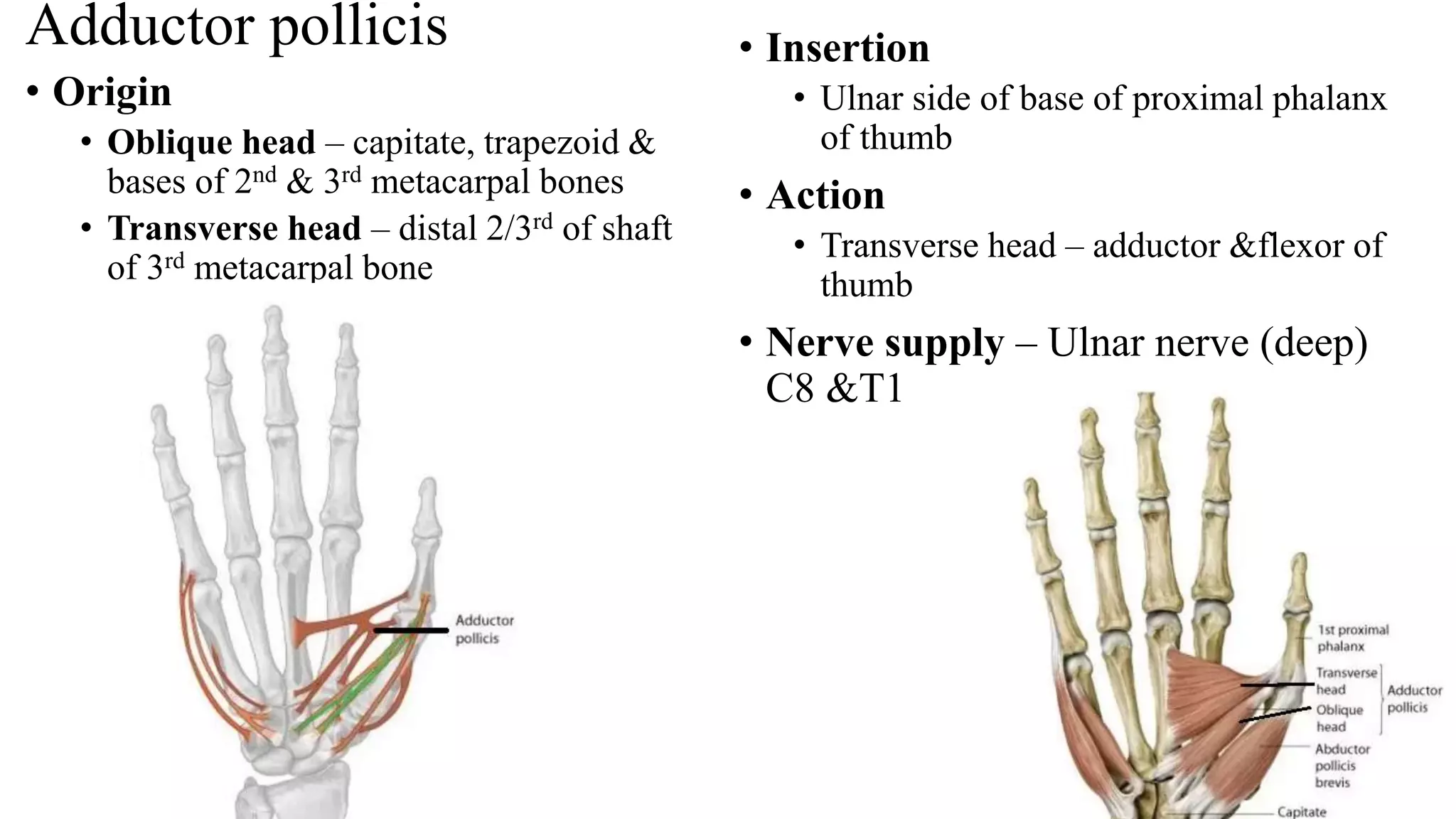
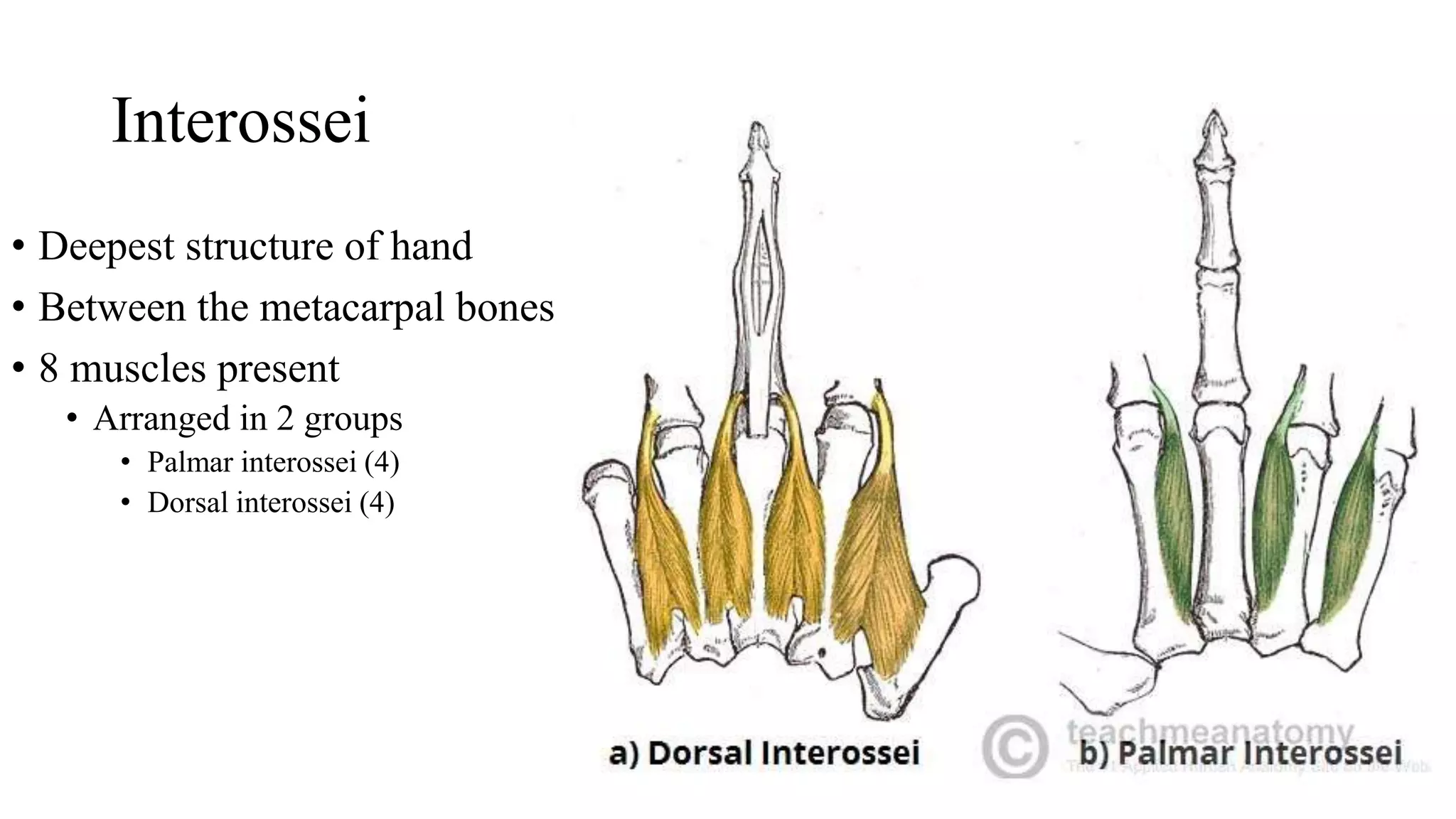
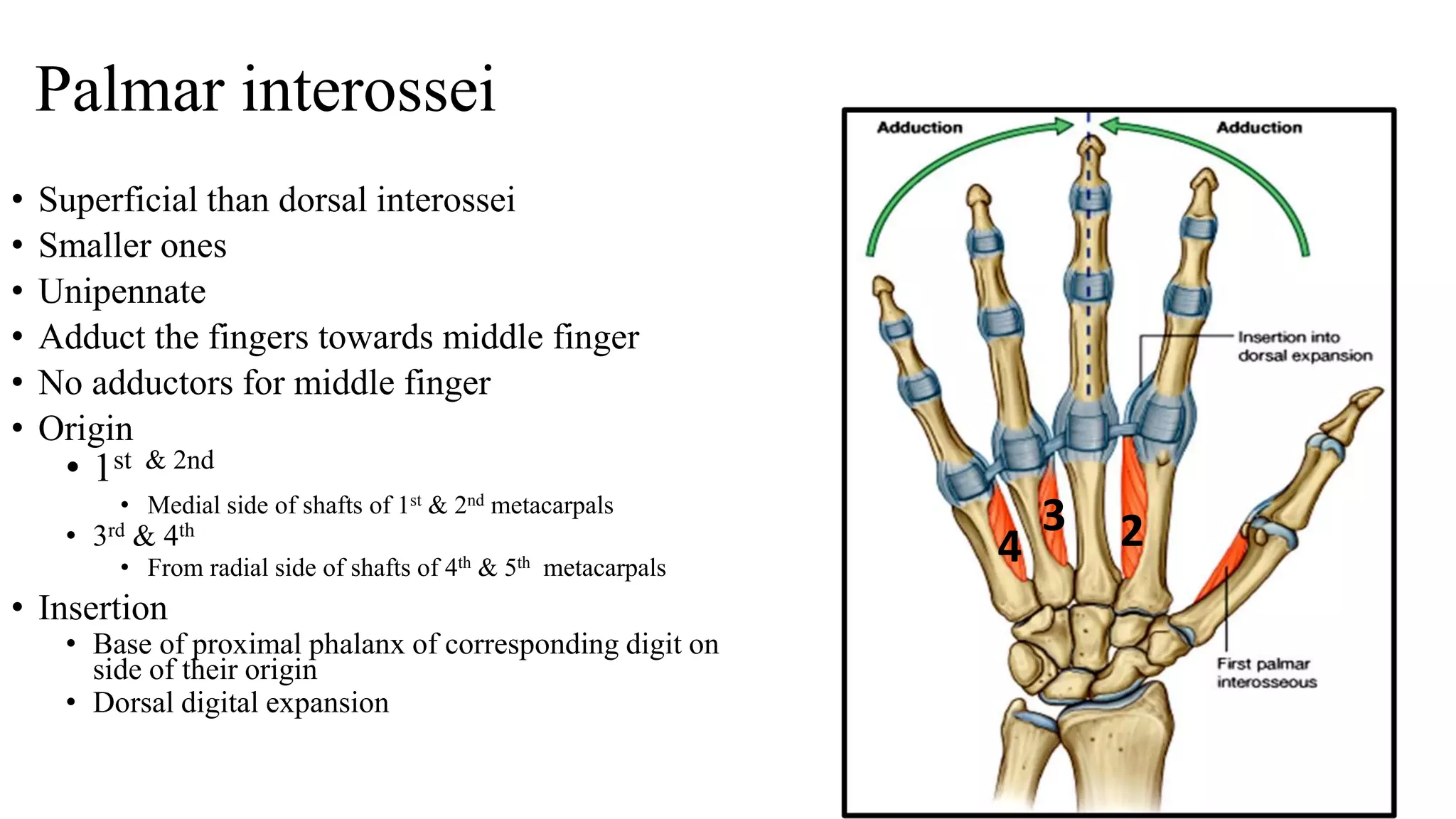
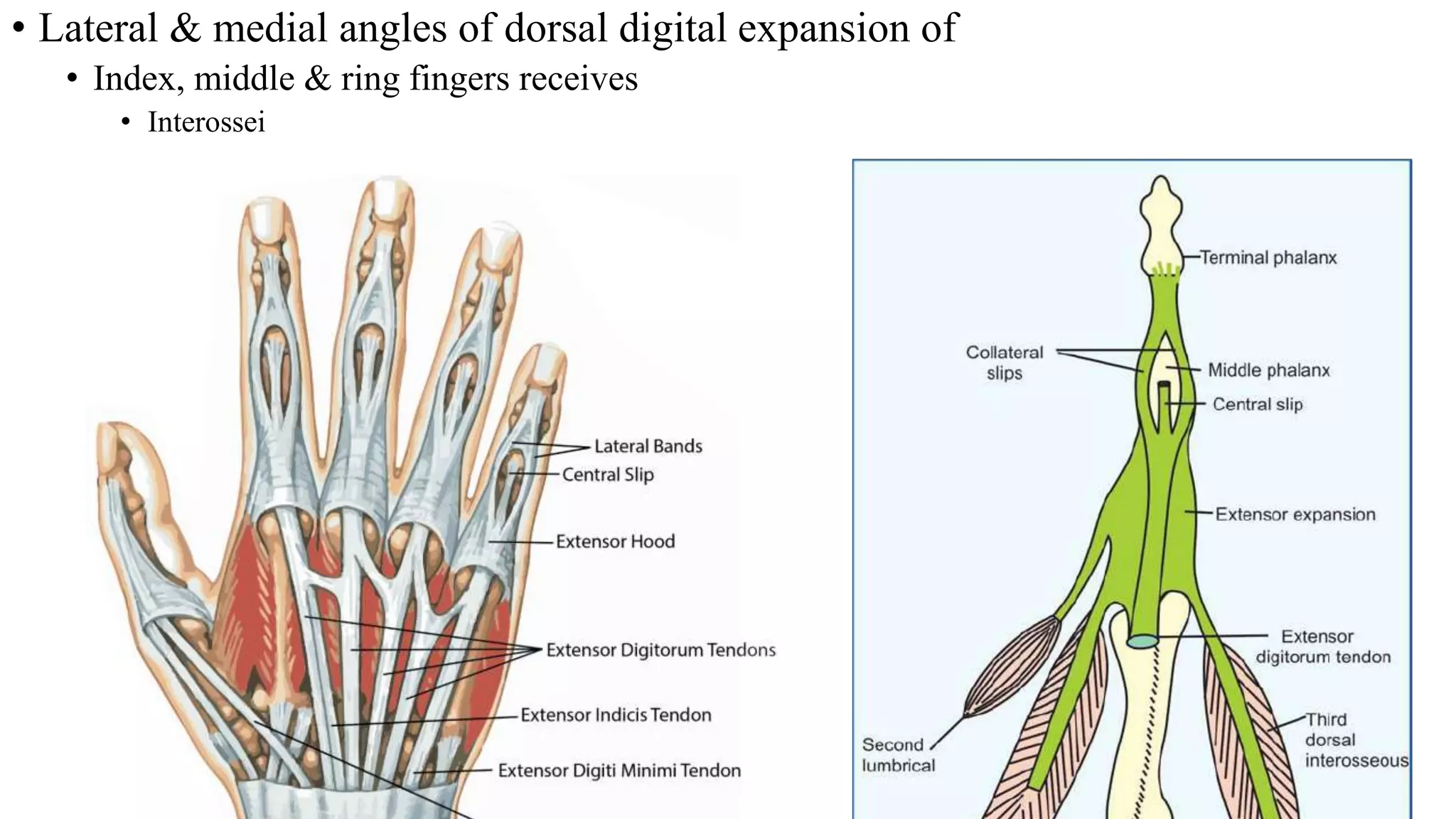
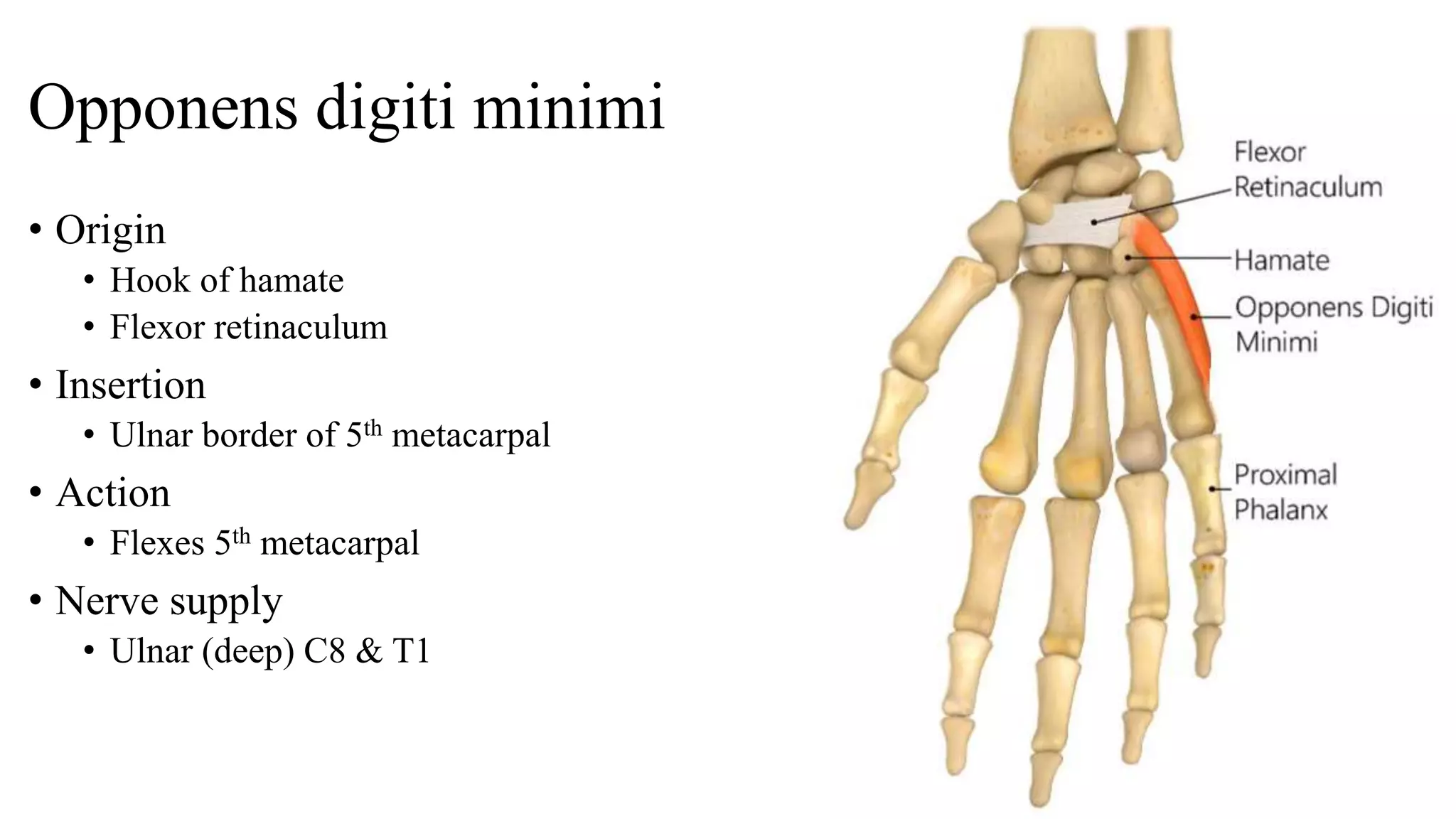
The palmar aponeurosis is a thickened deep fascia located in the central area of the palm. It has a triangular shape with its apex attached to the flexor retinaculum and base dividing into four slips at the bases of the fingers. It functions to improve grip strength and protect underlying structures. The hand contains numerous muscles including the thenar, hypothenar, and intrinsic muscles like the lumbricals and interossei. These muscles allow for delicate hand movements and grip. The median and ulnar nerves innervate various muscles and structures in the hand.