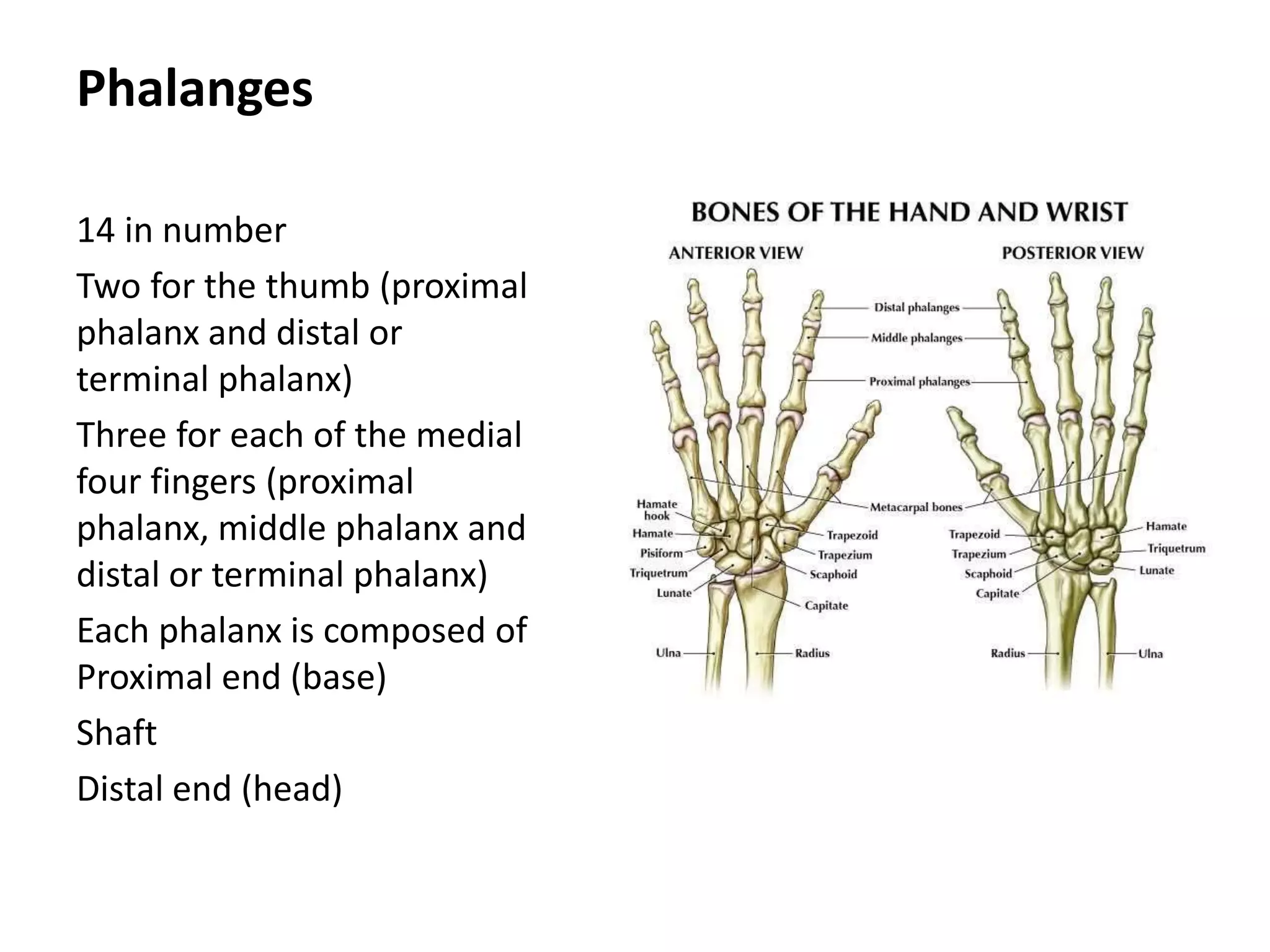
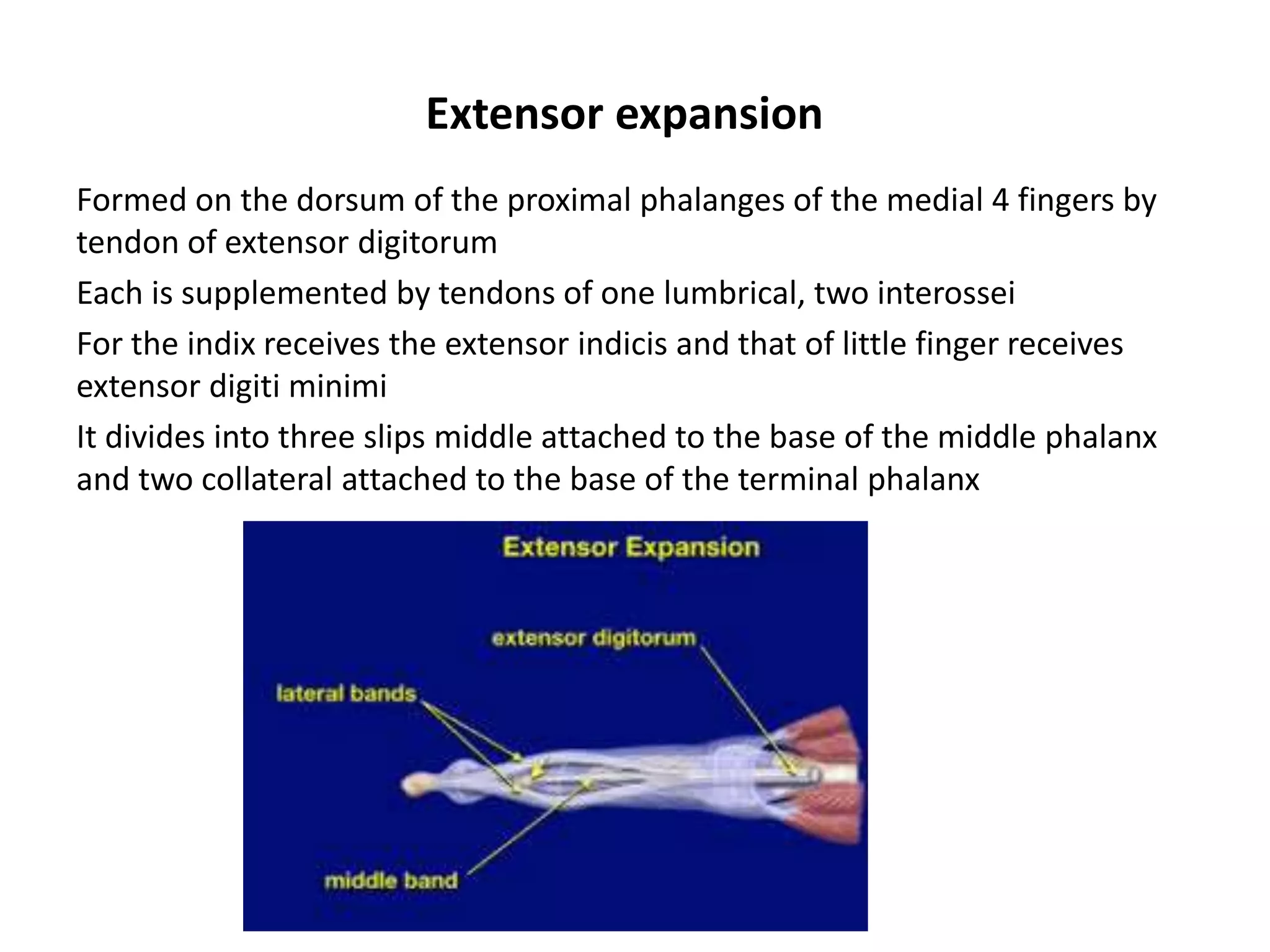
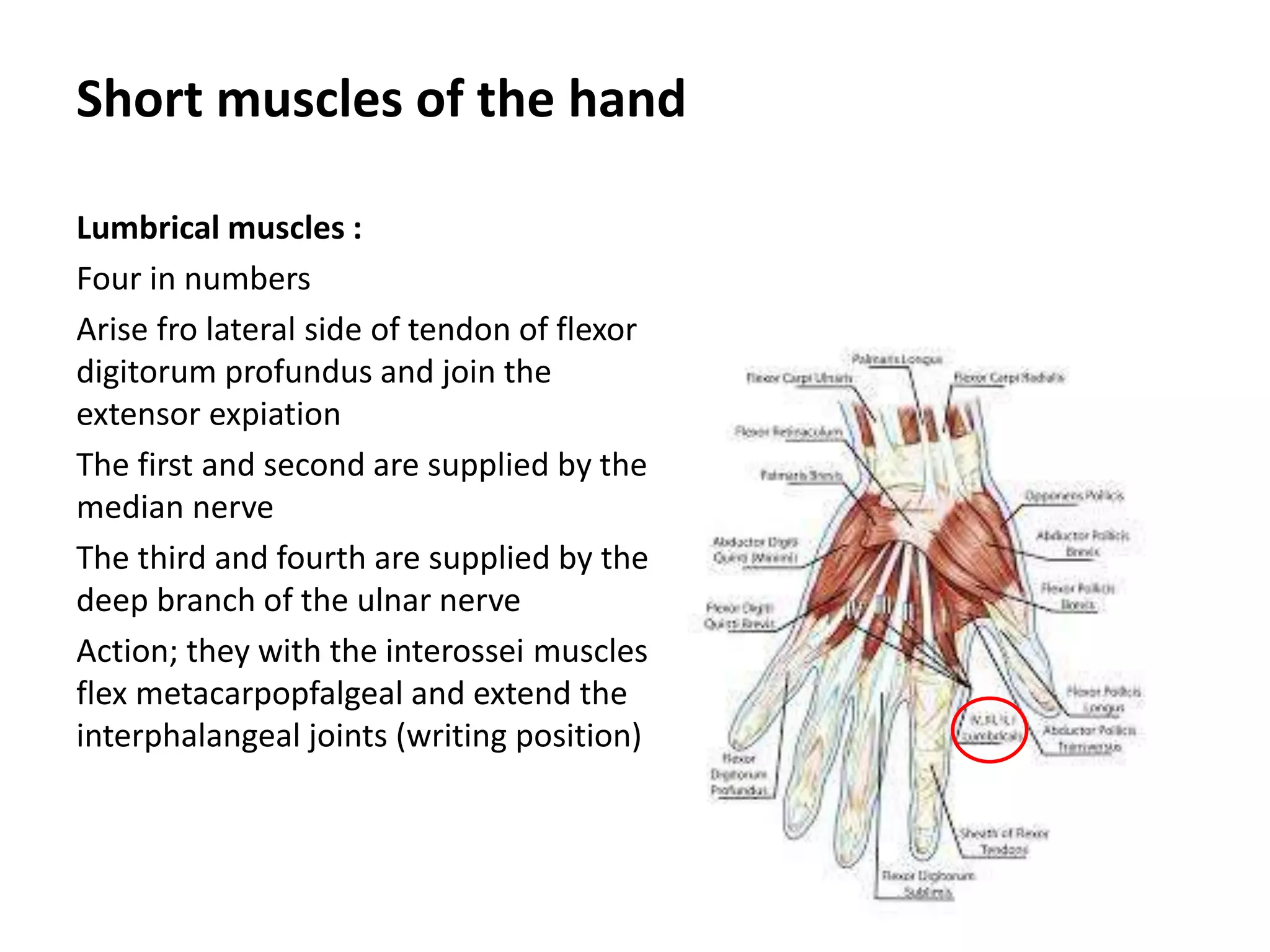
The document summarizes the anatomy of the hand and wrist. It describes the bones that make up the skeleton of the hand including the carpus, metacarpals, and phalanges. It then discusses the muscles, ligaments, tendons, blood vessels and nerves of the hand and wrist. In particular, it outlines the structures that pass through the carpal tunnel and extensor retinaculum.