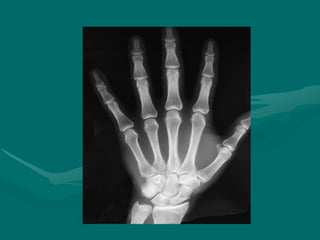
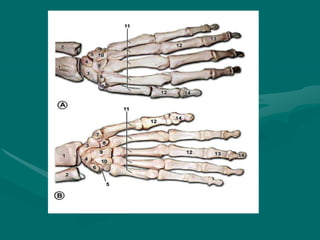
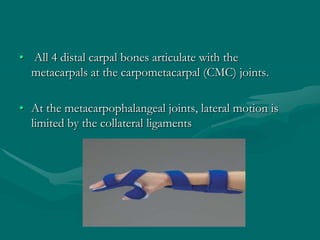
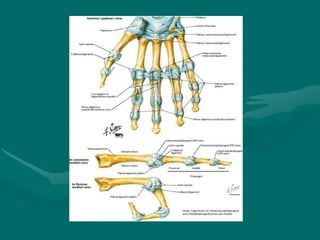
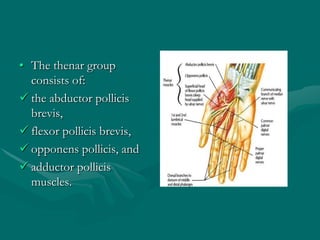
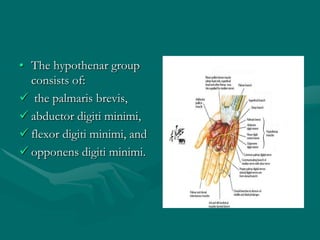
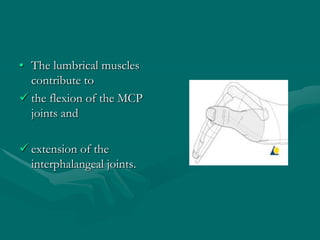
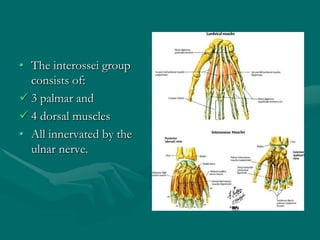
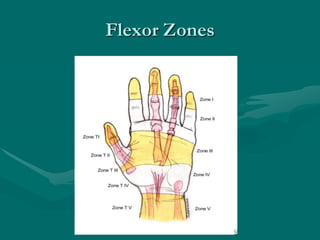
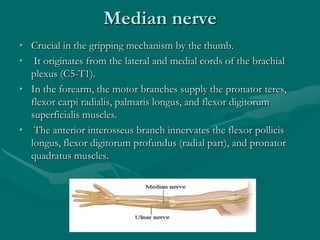
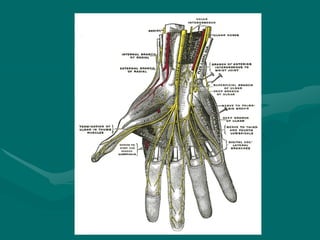
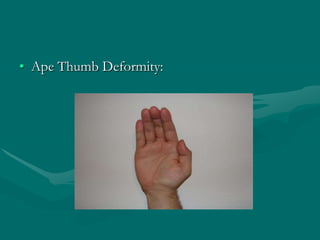
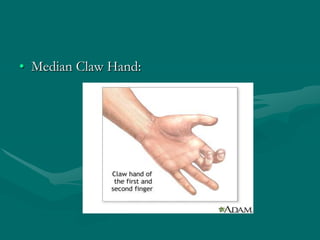
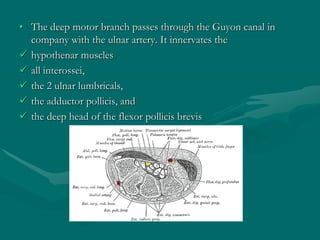
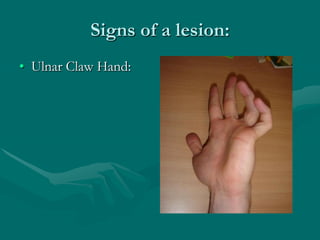
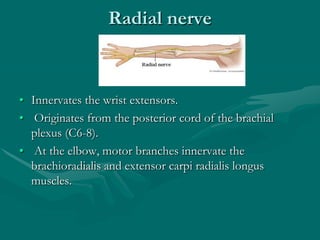
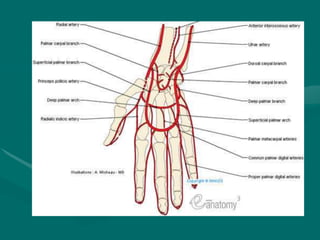
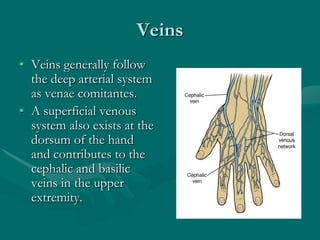
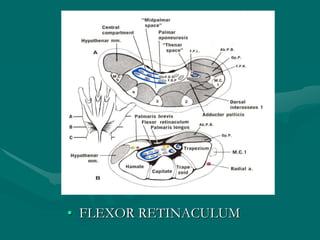
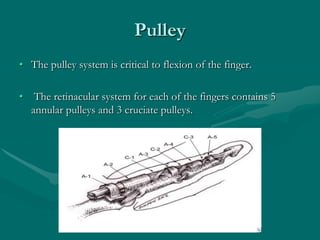
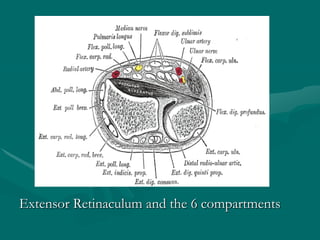
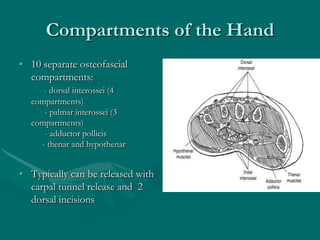
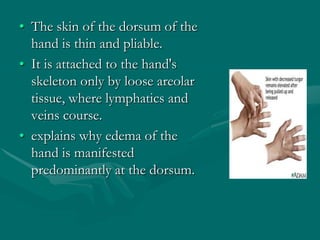
The hand and wrist have 27 bones organized into carpals, metacarpals, and phalanges. The wrist is a complex joint formed by 8 carpal bones with limited motion. Muscles are divided into intrinsic and extrinsic groups, with extrinsic muscles including wrist and digit flexors/extensors. Nerves include the median, ulnar, and radial nerves. The hand has a rich blood supply from the radial, ulnar, and deep palmar arches. Fascia including the flexor and extensor retinacula contain tendons. The hand's skin and pulley system enhance grasping.