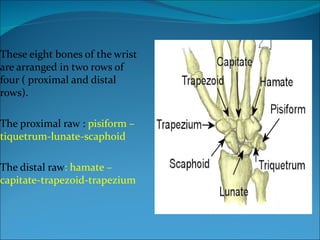
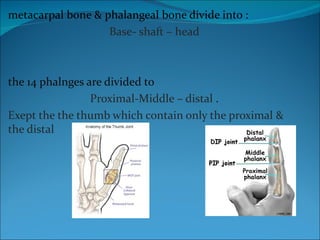
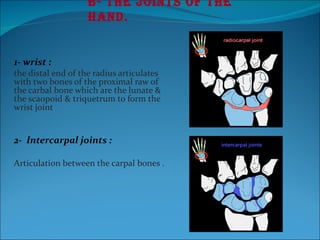
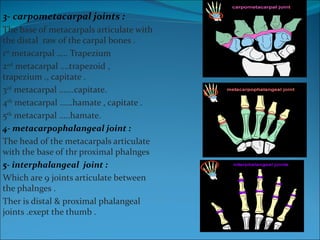
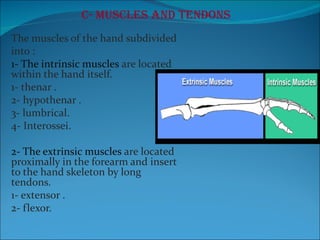
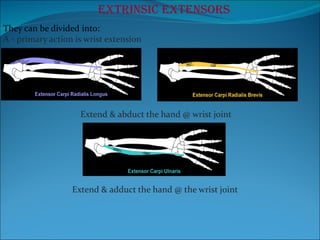
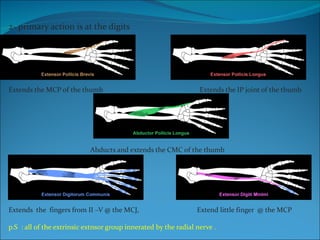
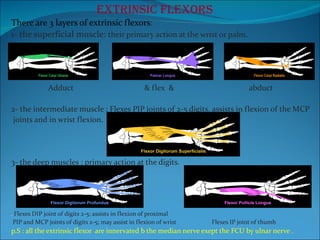
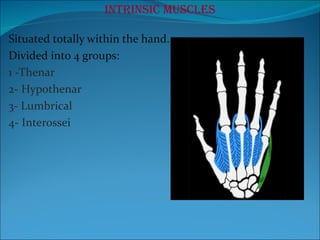
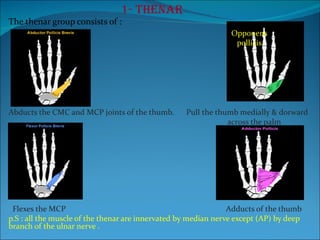
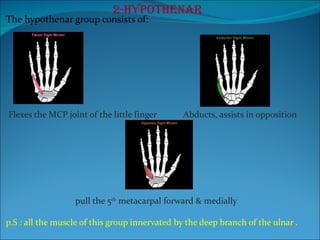
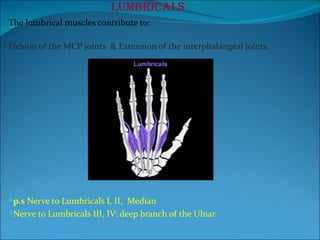
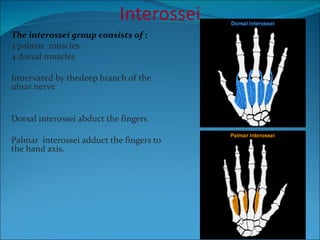
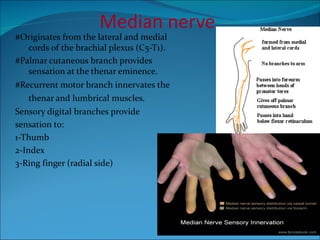
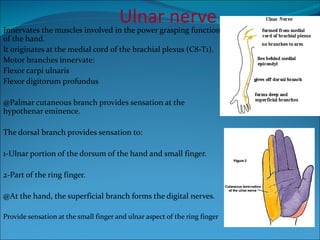
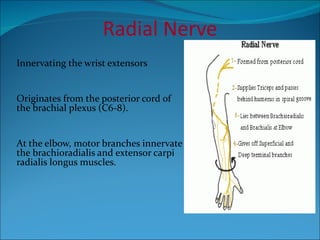
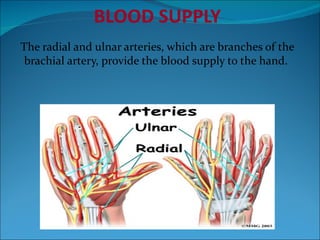
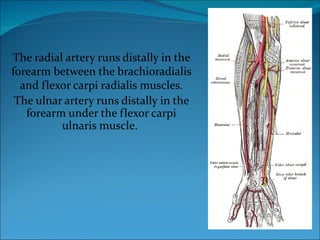
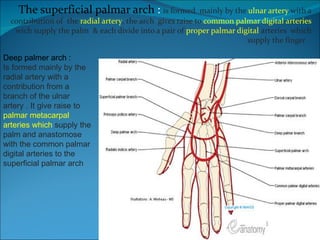
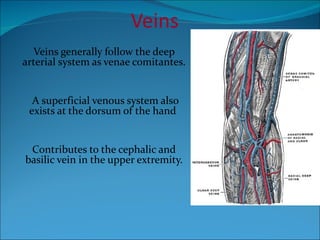
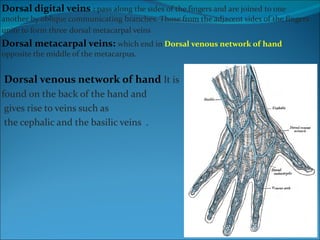
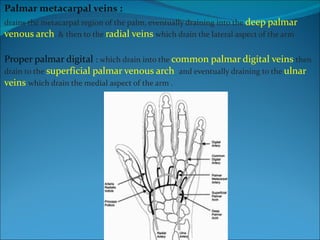
The document summarizes the anatomy of the wrist and hand. It describes the bones that make up the wrist (carpal bones), palm (metacarpal bones), and fingers (phalanges). It then discusses the joints between these bones, including the wrist, intercarpal, carpometacarpal, metacarpophalangeal, and interphalangeal joints. Next, it outlines the muscles of the hand, dividing them into intrinsic and extrinsic muscles. Finally, it briefly reviews the nerves, blood supply, and veins of the hand.