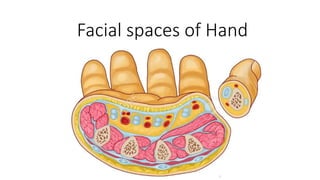
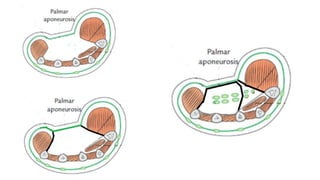
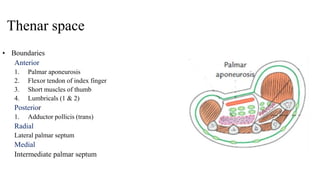
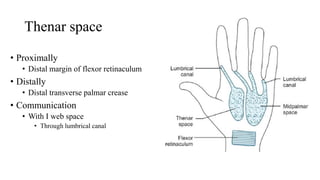
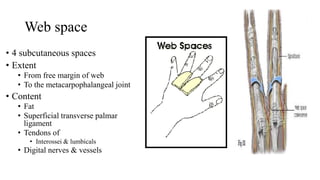
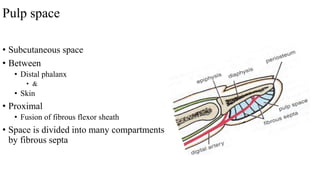
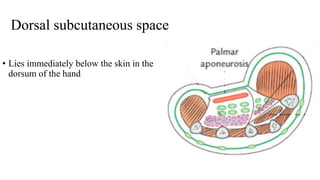
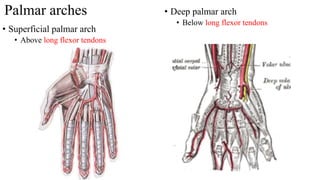
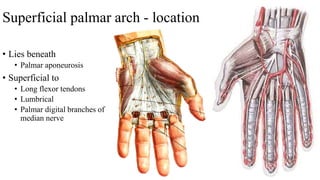
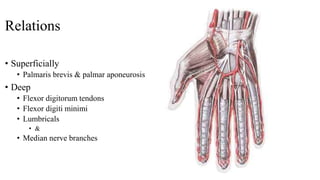
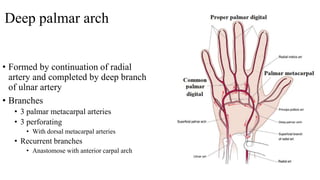
The document describes the spaces and vascular anatomy of the hand. It discusses the thenar, midpalmar, web and pulp spaces. It details the boundaries, contents and communications of these spaces. It also describes the fibrous flexor sheath surrounding the digits and the arterial supply including the superficial and deep palmar arches formed by the ulnar, radial and deep ulnar arteries. Allen's test is explained to test the adequacy of arterial anastomoses in the hand.