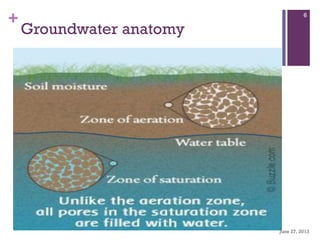
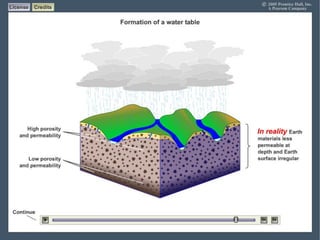
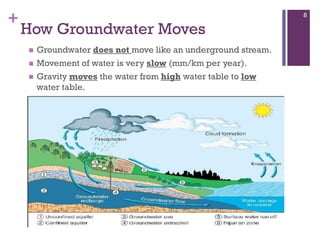
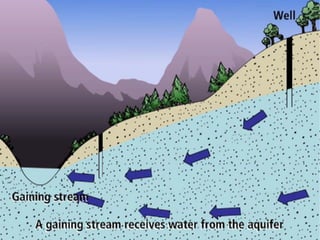
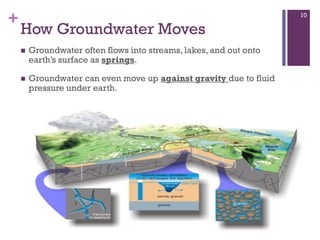
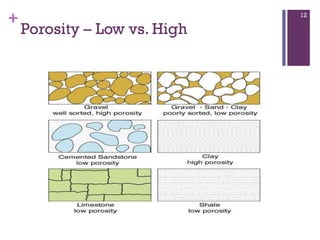
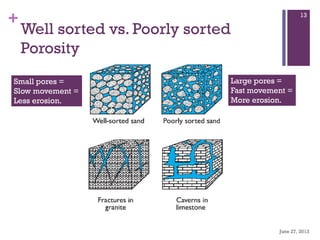
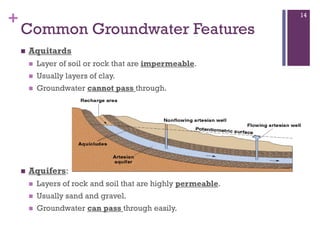
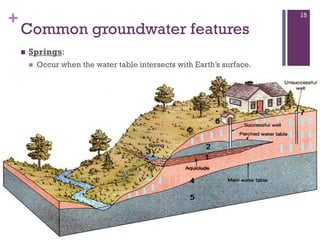
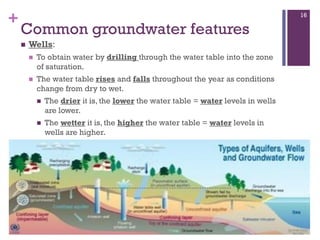
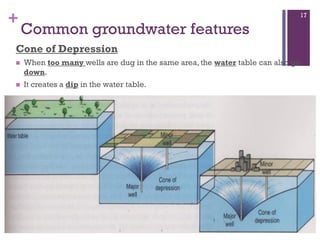
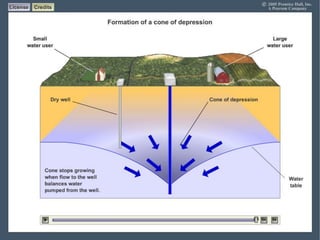
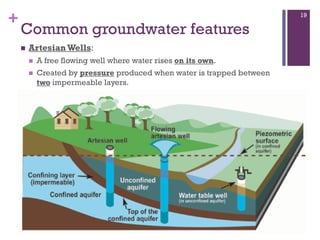
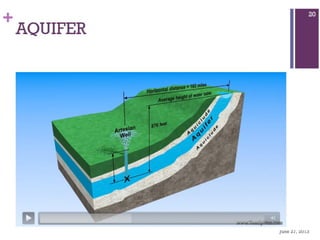
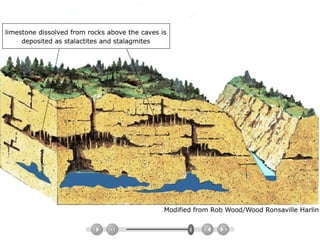
Groundwater forms when water infiltrates the earth's surface and collects underground. It is found in the saturated zone below the water table. Groundwater moves slowly through the pores and cracks in soil, sand, and rock. Over time, groundwater can cause erosion and dissolve limestone bedrock to form caves, sinkholes, and karst topography.