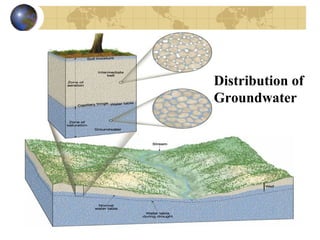
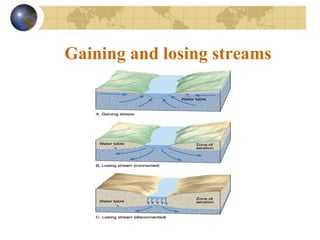
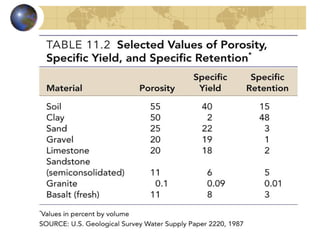
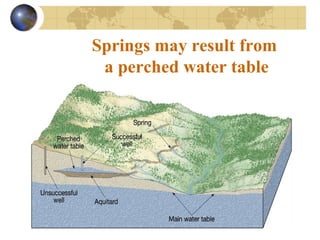
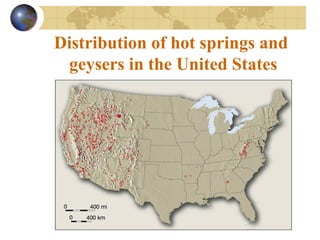
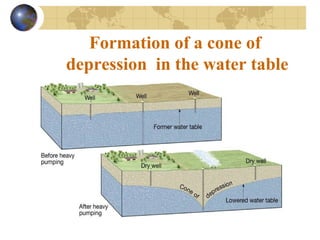
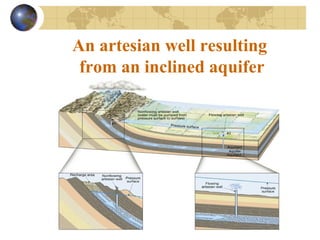
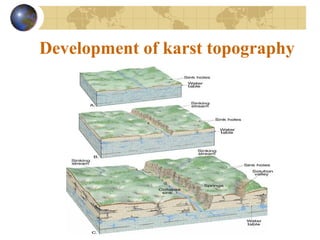
Groundwater is found underground in soil and rock pores and fractures. It is an important source of freshwater. Groundwater exists in three zones: the saturated zone where all pores are full of water, the capillary fringe just above it, and the aeration zone above that. The water table marks the top of the saturated zone. Groundwater interacts with streams, which can gain or lose water from interactions with the water table. Factors like porosity, permeability, and the slope of the water table influence groundwater storage and movement. Groundwater can emerge as springs, hot springs, or geysers, and be accessed via wells. Excessive pumping can cause problems like subsidence and saltwater contamination.