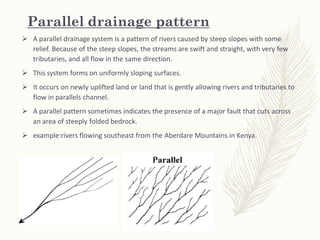
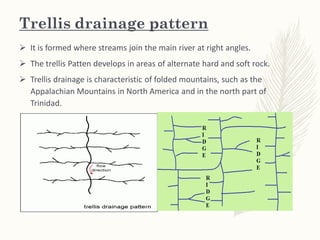
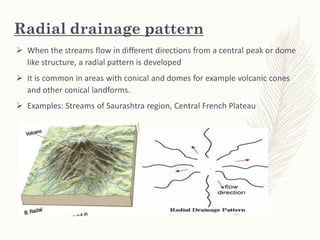
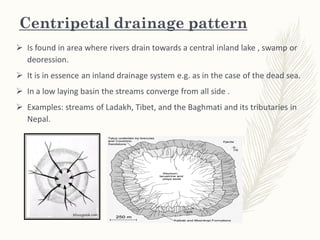
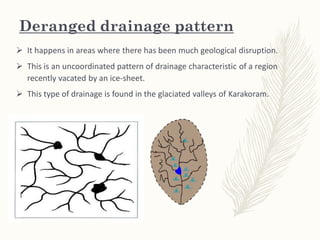
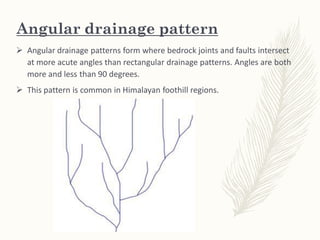
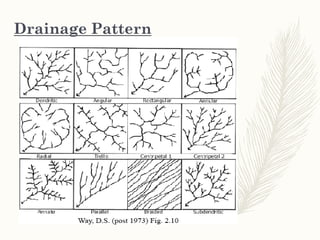
The document discusses various drainage patterns formed by streams, rivers, and lakes in drainage basins, highlighting their dependence on land topography and geology. It categorizes drainage patterns into types including dendritic, parallel, trellis, rectangular, radial, centripetal, deranged, annular, and angular patterns, each characterized by distinct formations and examples. Understanding these patterns is essential for the study of river systems and their interactions with the environment.