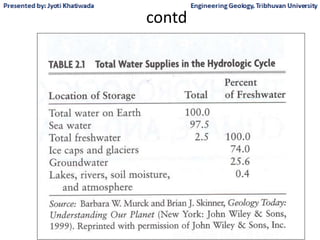
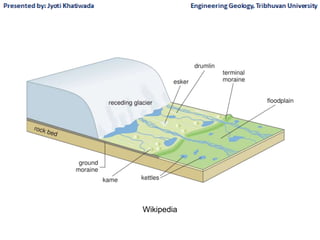
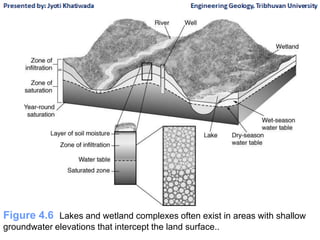
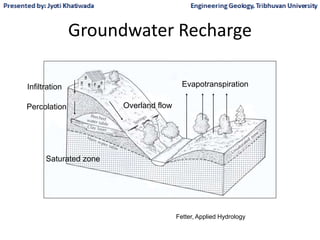
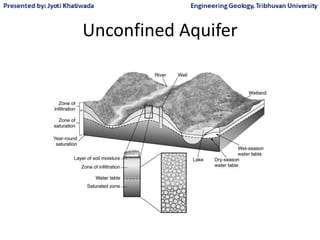
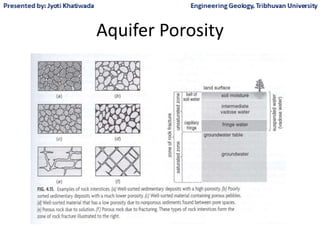
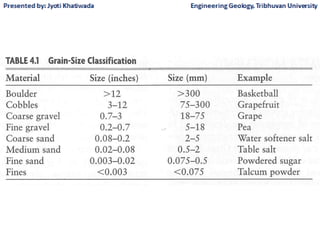
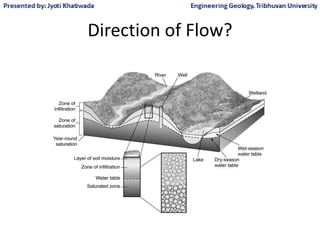
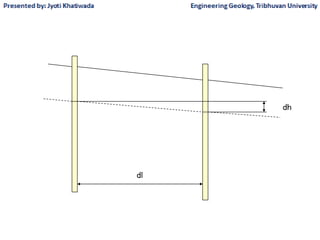
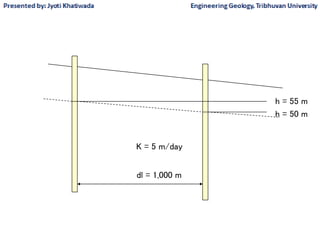
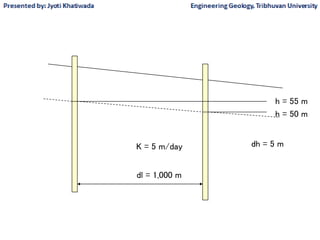
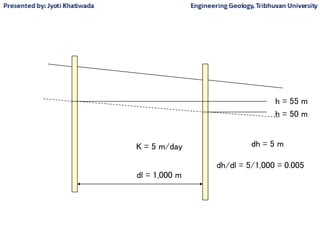
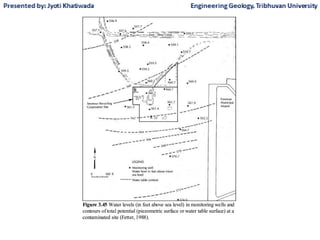
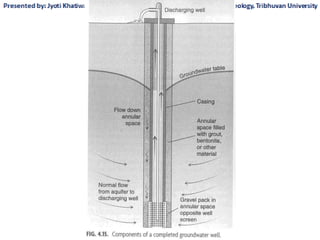
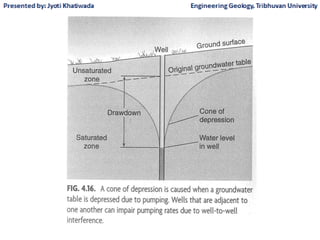
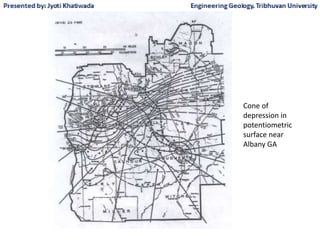
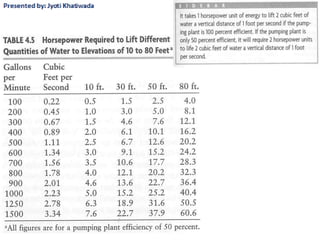
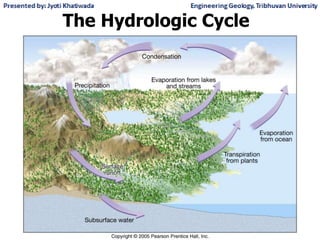
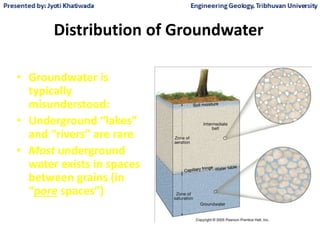
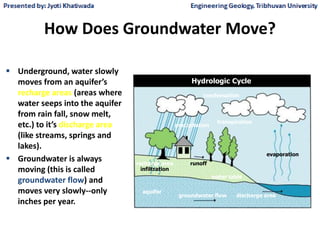
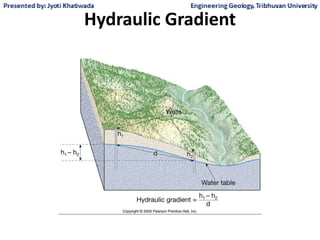
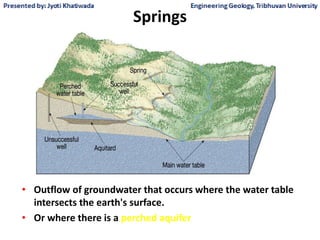
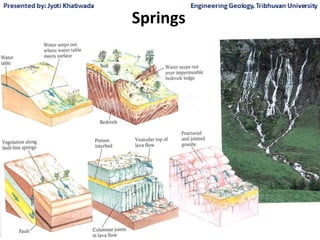
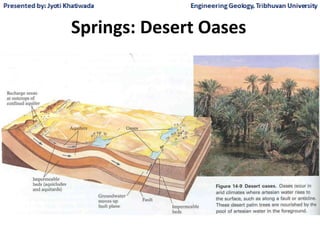
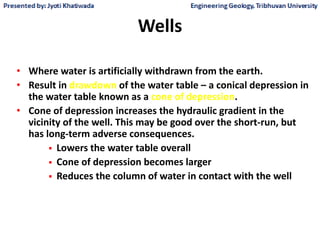
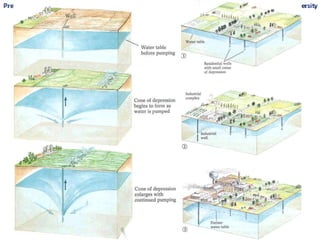
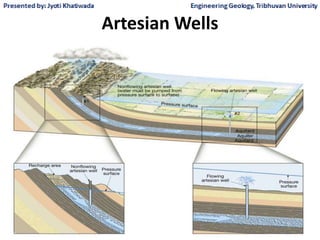
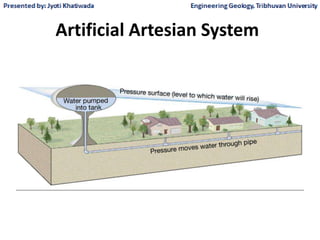
Groundwater, or water located beneath the Earth's surface, is an important source of freshwater. It is found in the pores and cracks of soil, sand, and rock below the water table. Groundwater hydrology is the study of groundwater movement and storage. Key aspects include aquifers, which are geologic formations that can store and transmit water; recharge from precipitation; and groundwater flow through aquifers driven by gravity and the hydraulic gradient. Mapping groundwater involves measuring water levels in wells to determine the piezometric surface and direction of subsurface flow. Sustainable groundwater use requires understanding recharge rates and connections to surface water.