Here are the answers to the quiz questions:
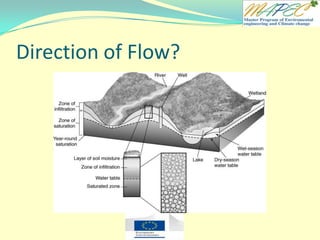
1. Groundwater is flowing from Well A to Well B.
2. The hydraulic gradient is (102 m - 105 m) / 1000 m = 0.003
3. The flux is q = K i = 10 m/day * 0.003 = 0.03 m/day
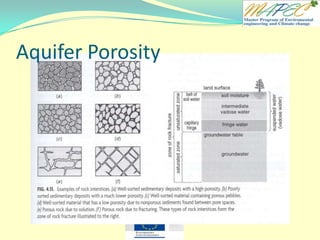
4. The porosity is 250 mL / 1000 mL = 25%
5. The remaining 50 mL of water is held in the material by capillary forces.
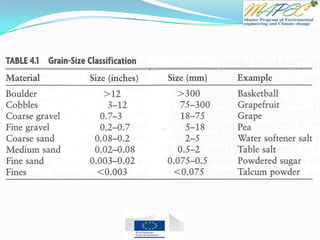
6. The porosity would be less for clay than sand.
7. Less water would pour out if we use clay instead of sand.
8. [T/F] An aquiclude is






















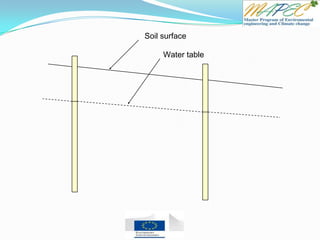
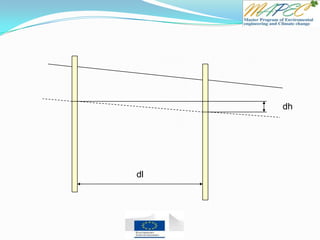
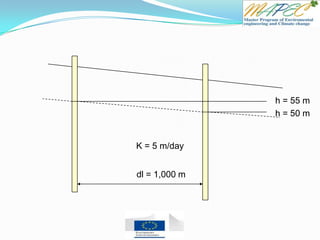
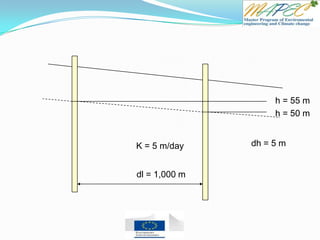
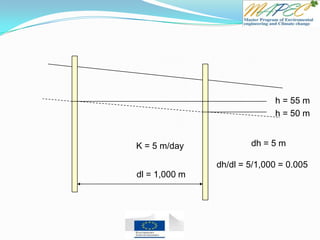
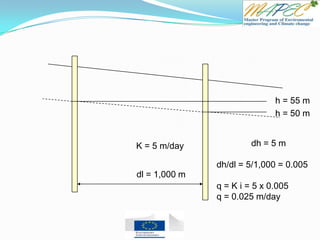









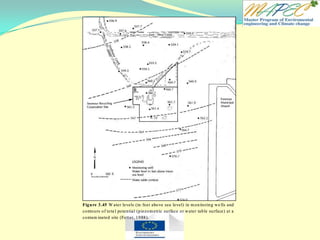




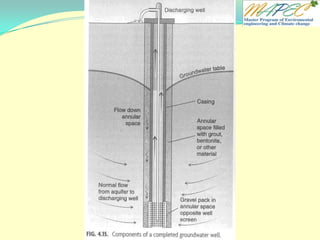
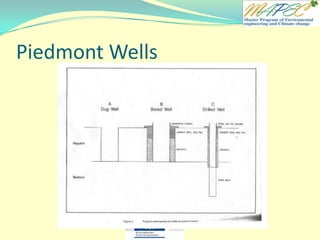
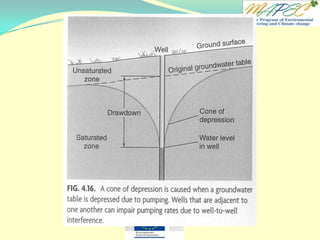



![Quiz 4 Two wells are located 1 km (1,000 meters) apart. Well A has a water level of 105 m
and Well B has a water level of 102 m.
Which direction is the groundwater flowing? From Well ____ to Well ____
What is the hydraulic gradient between the two wells?
What is the flux (flow rate) if the hydraulic conductivity is K = 10 m/day?
A one-liter (1,000 mL) beaker is filled with sand and filled to the top with water.
What is the porosity of the material if 250 mL was required to fill the beaker?
We pour the water out, and 200 mL is collected. What happened to the rest of the water?
What would the porosity be if we use clay instead of sand? (more, less, the same)
How much water would pour out if we use clay instead of sand? (more, less, the same)
True - False Questions
[T / F] An aquiclude is a geologic formation that holds a lot of water.
[T / F] Perched aquifers are a kind of artesian aquifer.
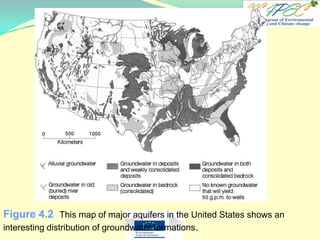
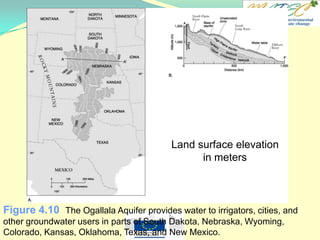
[T / F] The Ogallala aquifer is the major aquifer in the Southeastern U.S.
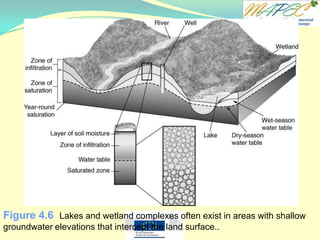
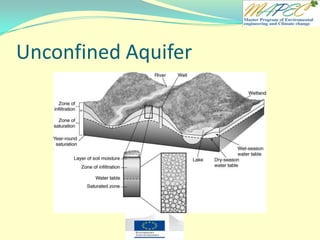
[T / F] The water table is found at the top of the saturated zone.
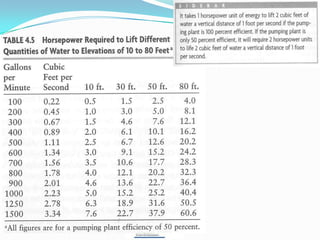
[T / F] The two factors that determine how much horsepower is needed to lift water are
the amount of water that must be lifted and the height that you must lift the water.
Explain what Stream Depletion Factors are used for](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter4groundwaterhydrology-130630055824-phpapp02/85/Chapter-4-groundwater-hydrology-65-320.jpg)