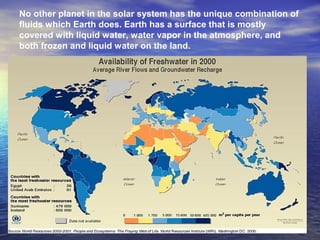
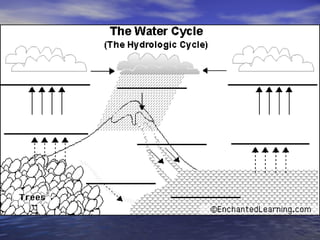
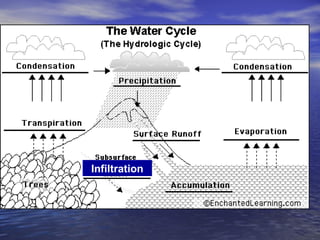
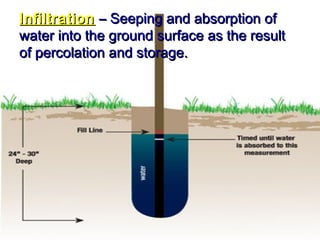
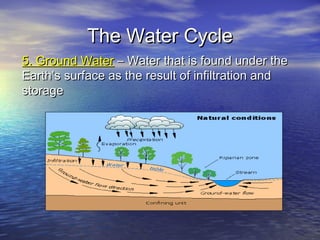
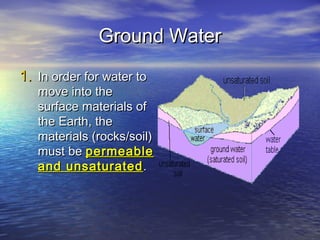
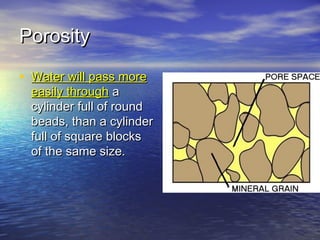
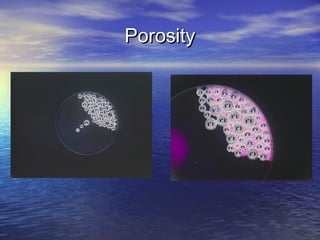
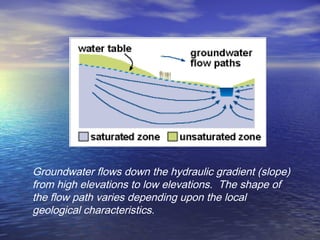
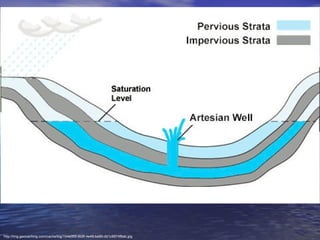
Earth has a unique combination of water in its atmosphere, oceans, and land. The water cycle describes the continuous movement of water on, above, and below the Earth's surface through different states of matter and includes precipitation, infiltration, storage, and evaporation. Below the surface, groundwater flows through zones of saturation and aeration within permeable rocks and soils called aquifers, eventually emerging in springs, streams or being used by humans.