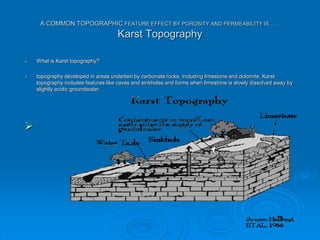
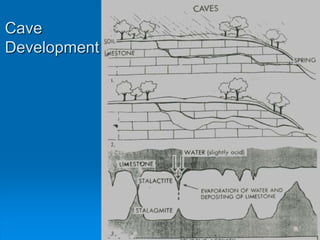
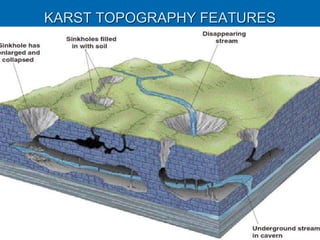
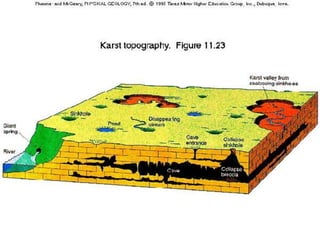
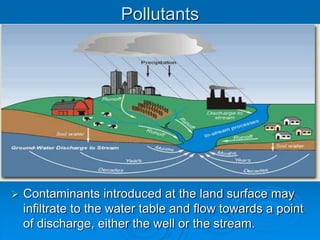
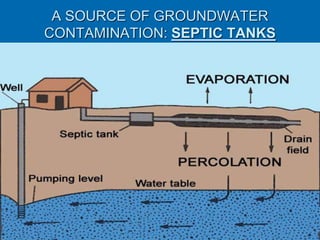
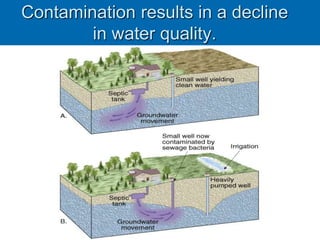
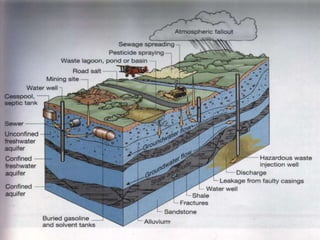
Karst topography develops in areas underlain by carbonate rocks like limestone and dolomite. Groundwater dissolves these rocks by mixing with carbon dioxide to form acidic water, enlarging cracks and creating underground caves and features. Sinkholes can form if underground rock dissolves near the surface or a cave roof collapses. Karst topography is common where sufficient rainfall supplies groundwater that continues dissolving the soluble bedrock over time.