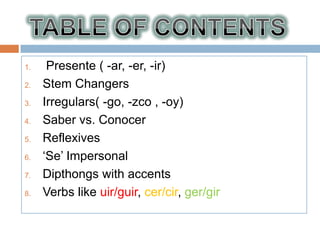
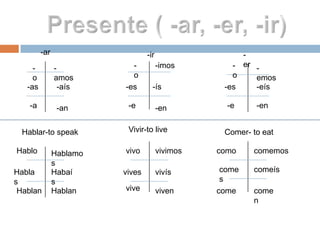
1. The document outlines key grammar points in Spanish including verb conjugations, stem changers, reflexives, impersonal "se", diphthongs, irregular verbs, and tenses like present, preterite, imperfect, and future.
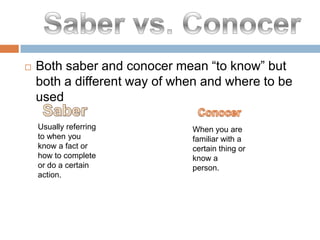
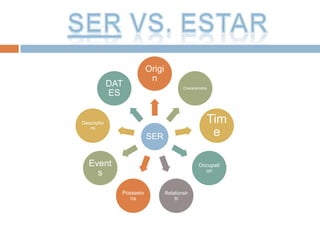
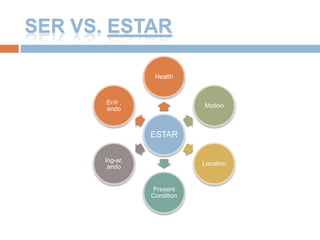
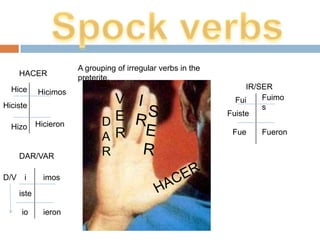
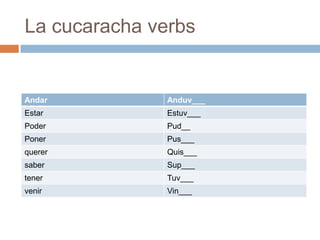
2. It provides examples and explanations of concepts like saber vs conocer, SER vs ESTAR, and irregular verb sets like "La cucaracha" verbs.
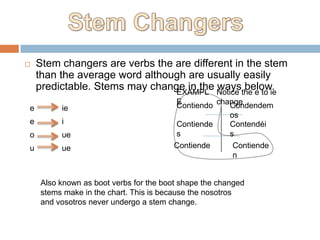
3. Key verb types are defined like stem changers, irregulars with -go, -zco and -oy endings, and "snake" and "snakey" verbs that change roots or add y in the third person.