Embed presentation
Download as ODP, PPTX


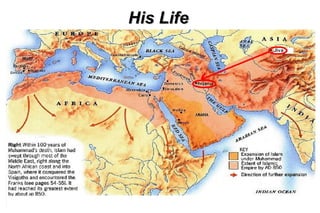

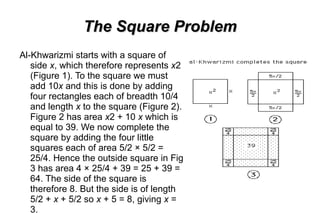



Al-Khwarizmi was an influential Persian mathematician, astronomer and geographer who lived between 780-850 CE. He worked in Baghdad during the time of the Abbasid Caliph al-Mamun and made significant advances in algebra and helped establish the decimal numeral system. In his influential book "Hisāb al-jabr wa-l-muqābala", he introduced the concepts of algebra, algorithms and much of the terminology still used today. He is considered the father of algebra and a pioneer in early Islamic mathematics.






