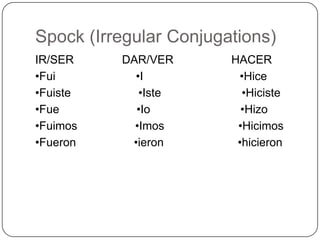
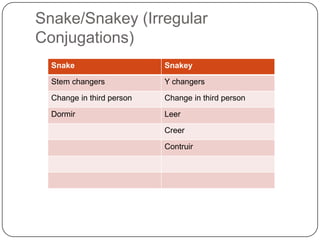
This grammar book covers essential topics of Spanish grammar including: the present tense, stem changers, irregular verbs, saber vs conocer, reflexives, impersonal se, diphthongs, ger/gir and cer/cir verbs, hace + que constructions, the imperfect and preterite tenses, regular and irregular conjugations, comparatives, superlatives, and the future tense. It provides examples and explanations of key grammatical structures in Spanish.