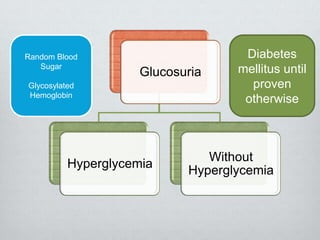
Glucosuria, or glucose in the urine, can occur due to diabetes mellitus resulting in hyperglycemia that exceeds the renal threshold, or due to renal tubular disorders resulting in glycosuria without hyperglycemia. Renal glycosuria is caused by defects in glucose transporters like SGLT2 that normally reabsorb glucose from the glomerular filtrate in the proximal tubule. This leads to glucose appearing in the urine despite normal blood glucose levels. Renal glycosuria is usually benign and inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, though it can also be caused by advanced chronic kidney disease.