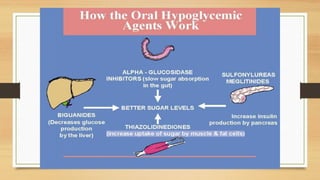
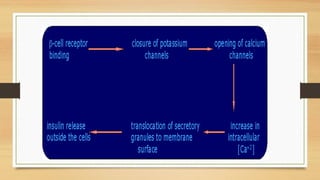
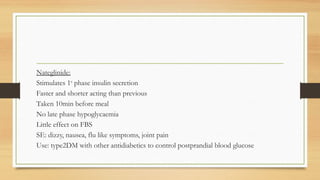
Sulfonylureas are oral hypoglycemic drugs that enhance insulin secretion from the pancreas. They work by blocking ATP-sensitive potassium channels in pancreatic beta cells, which leads to insulin release. Common side effects include hypoglycemia and weight gain. Examples include glibenclamide, glipizide, and glimepiride. Choice of sulfonylurea depends on factors like duration of action, renal function, and patient age. They are generally effective treatments for type 2 diabetes but require caution in elderly patients or those with kidney/liver problems.