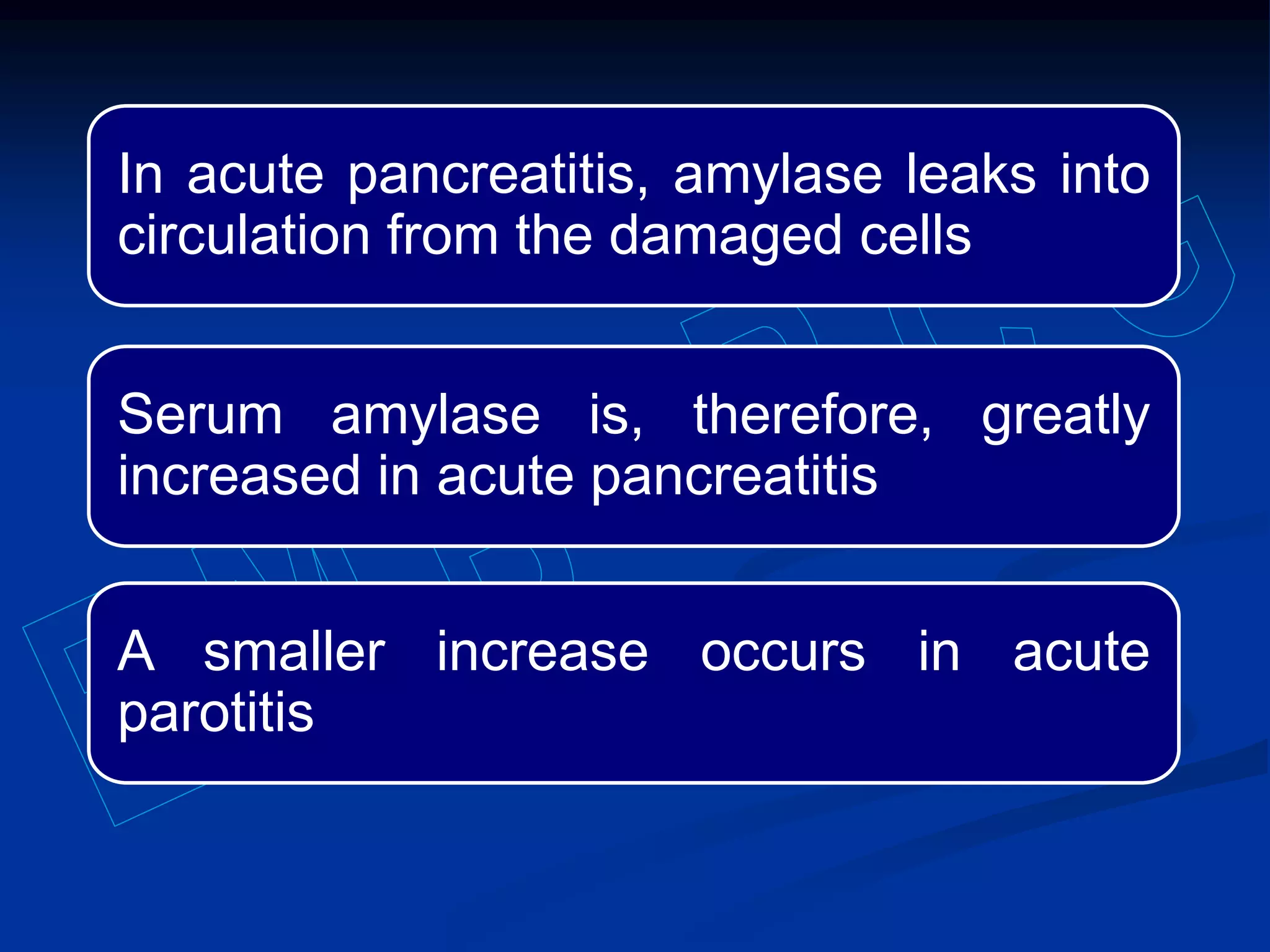
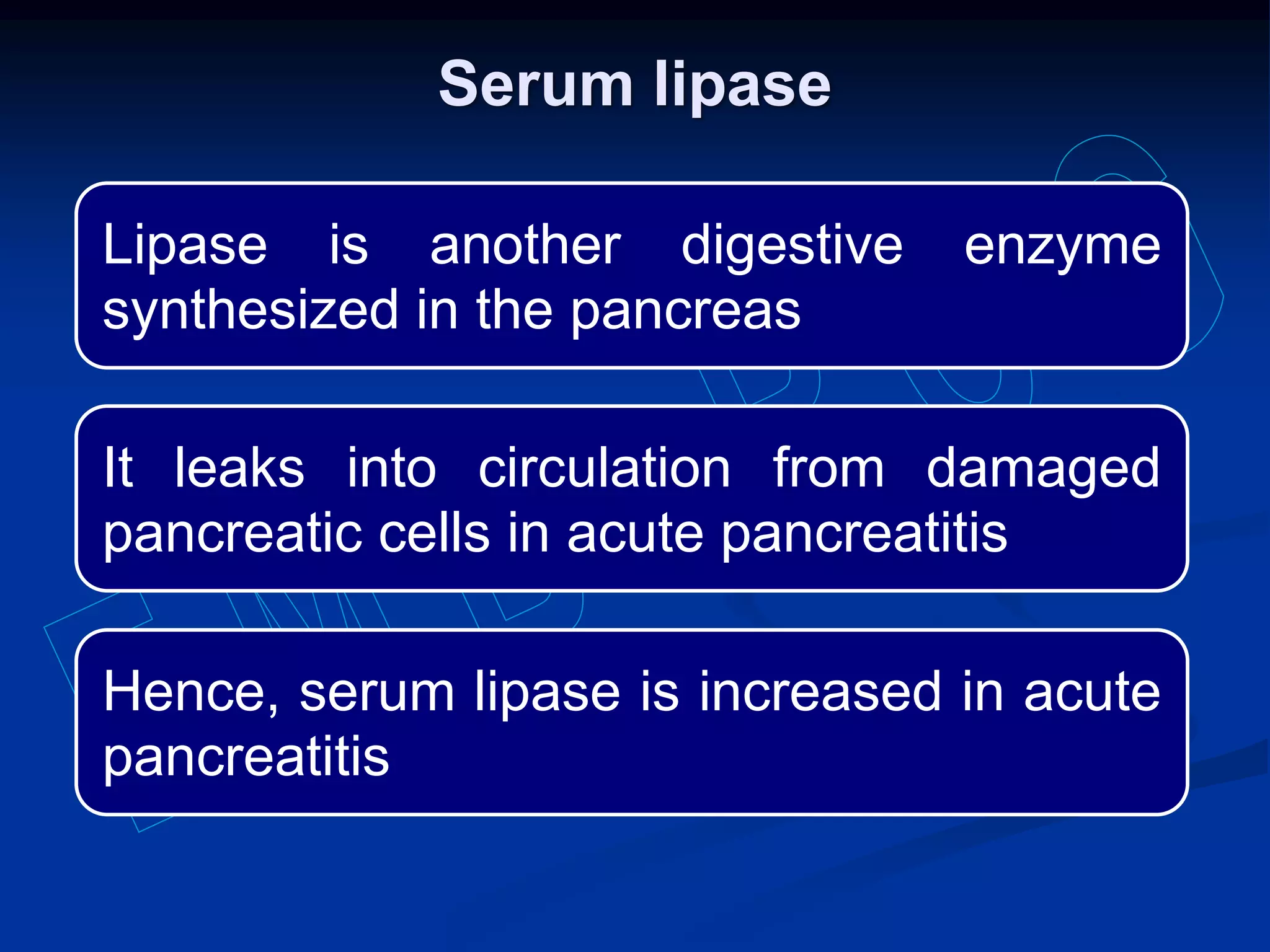
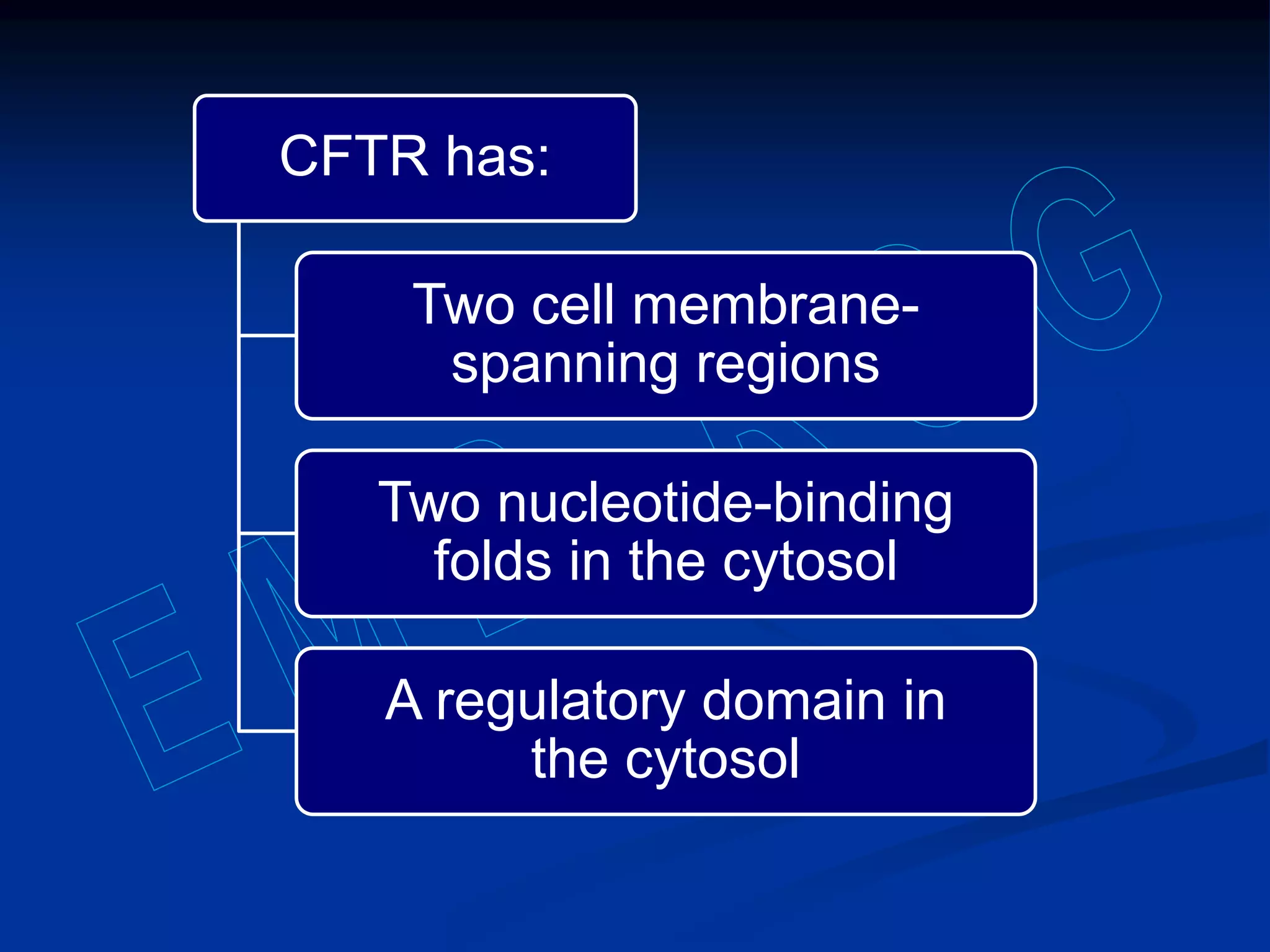
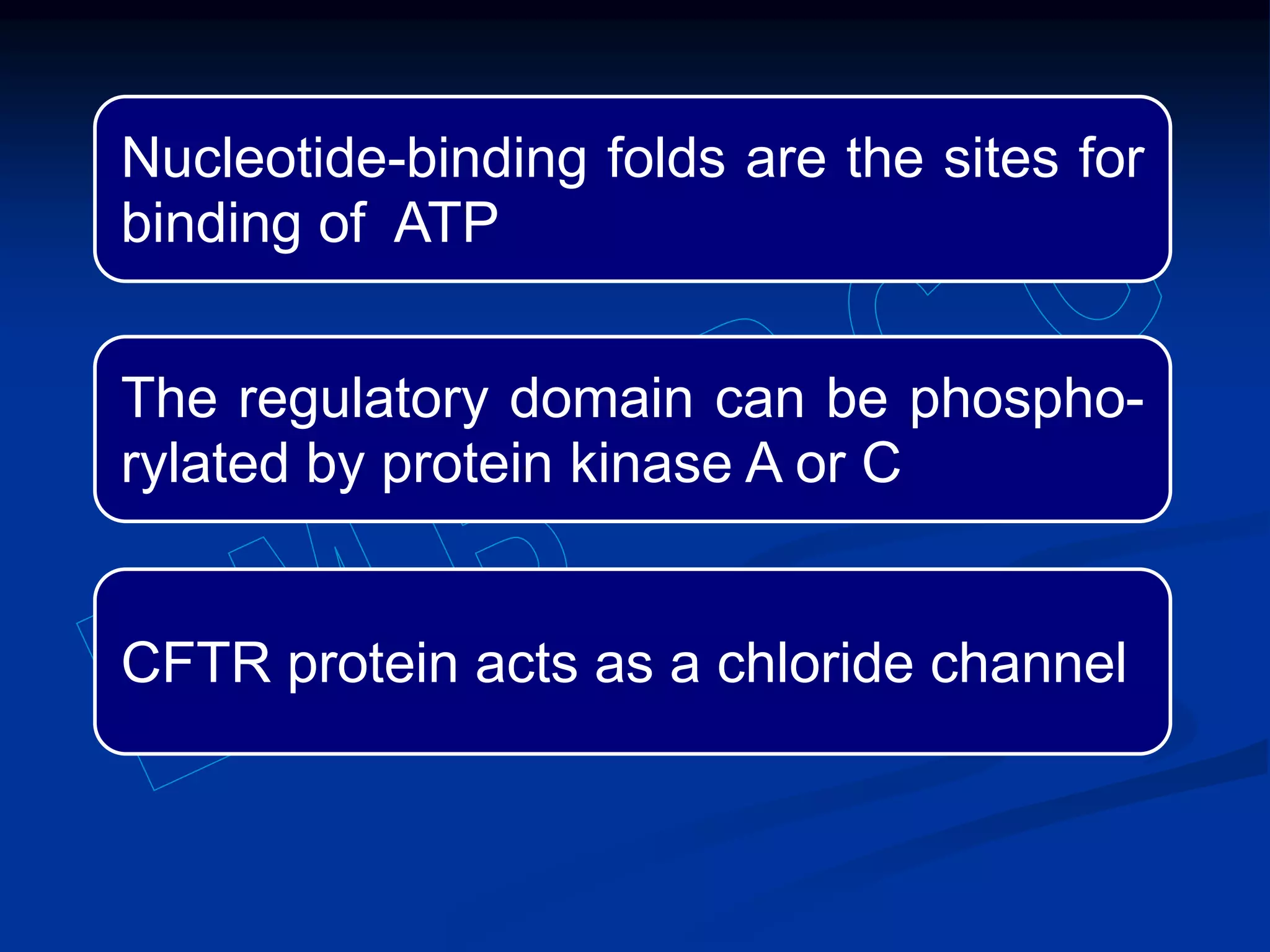
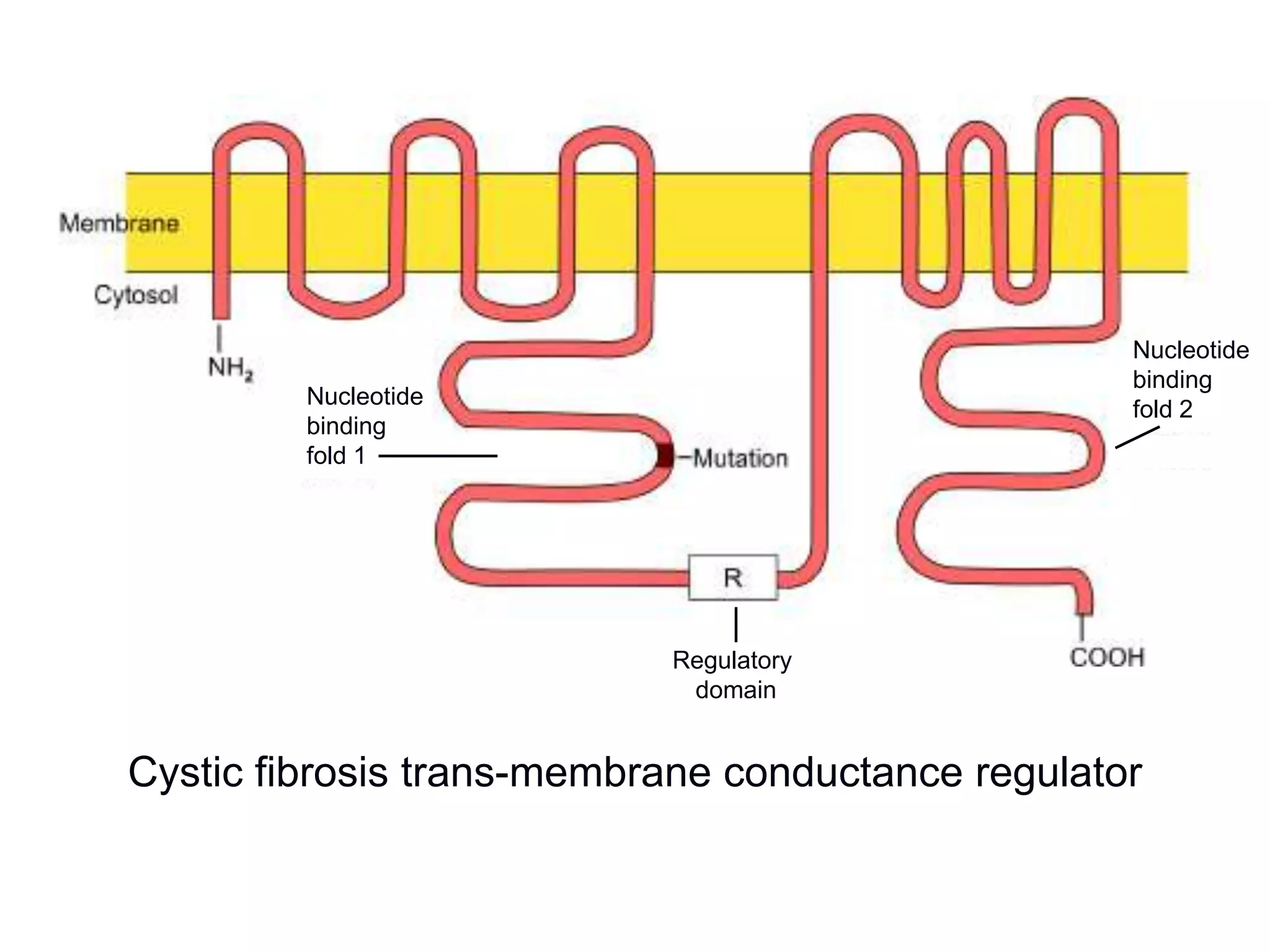
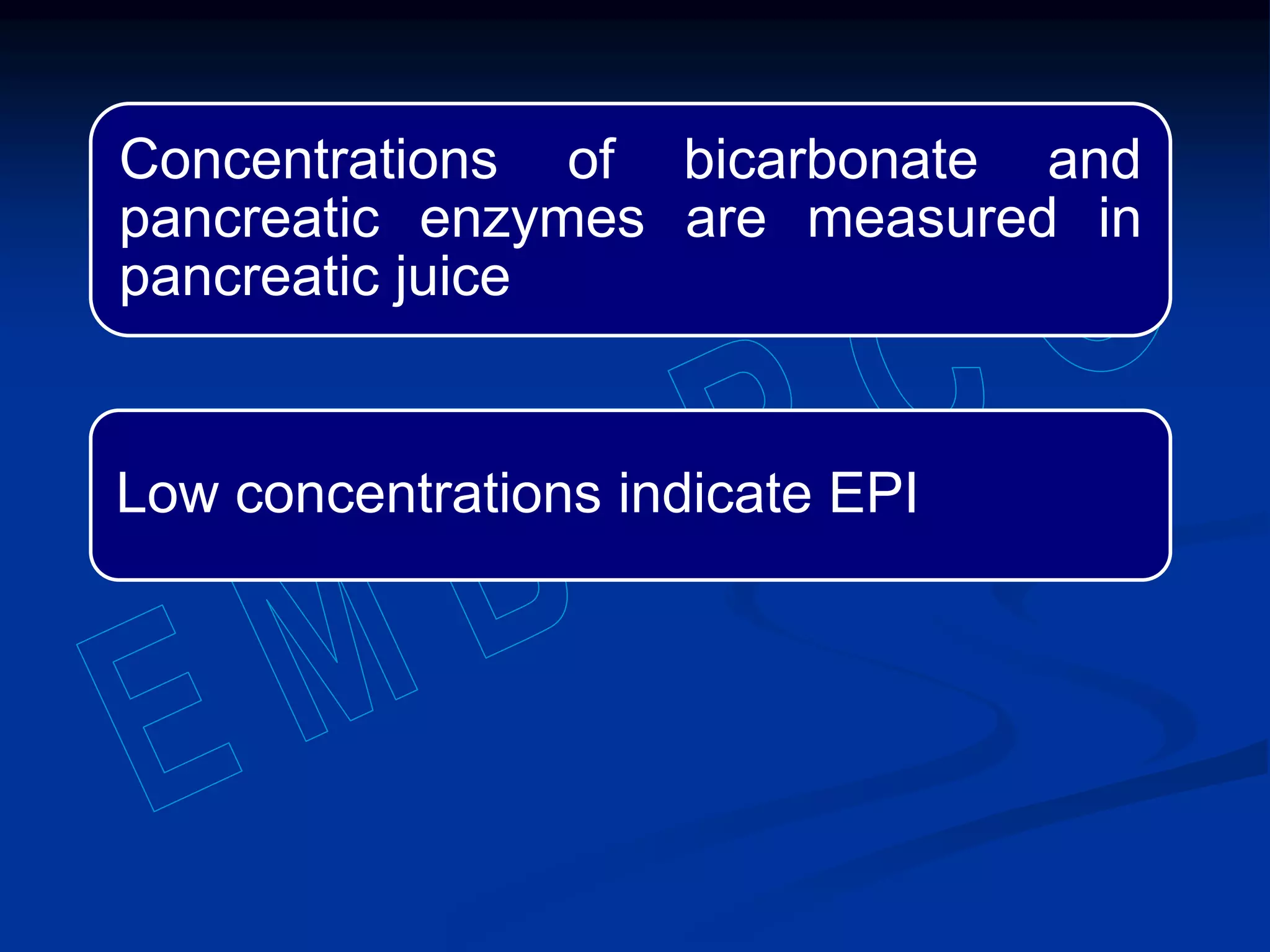
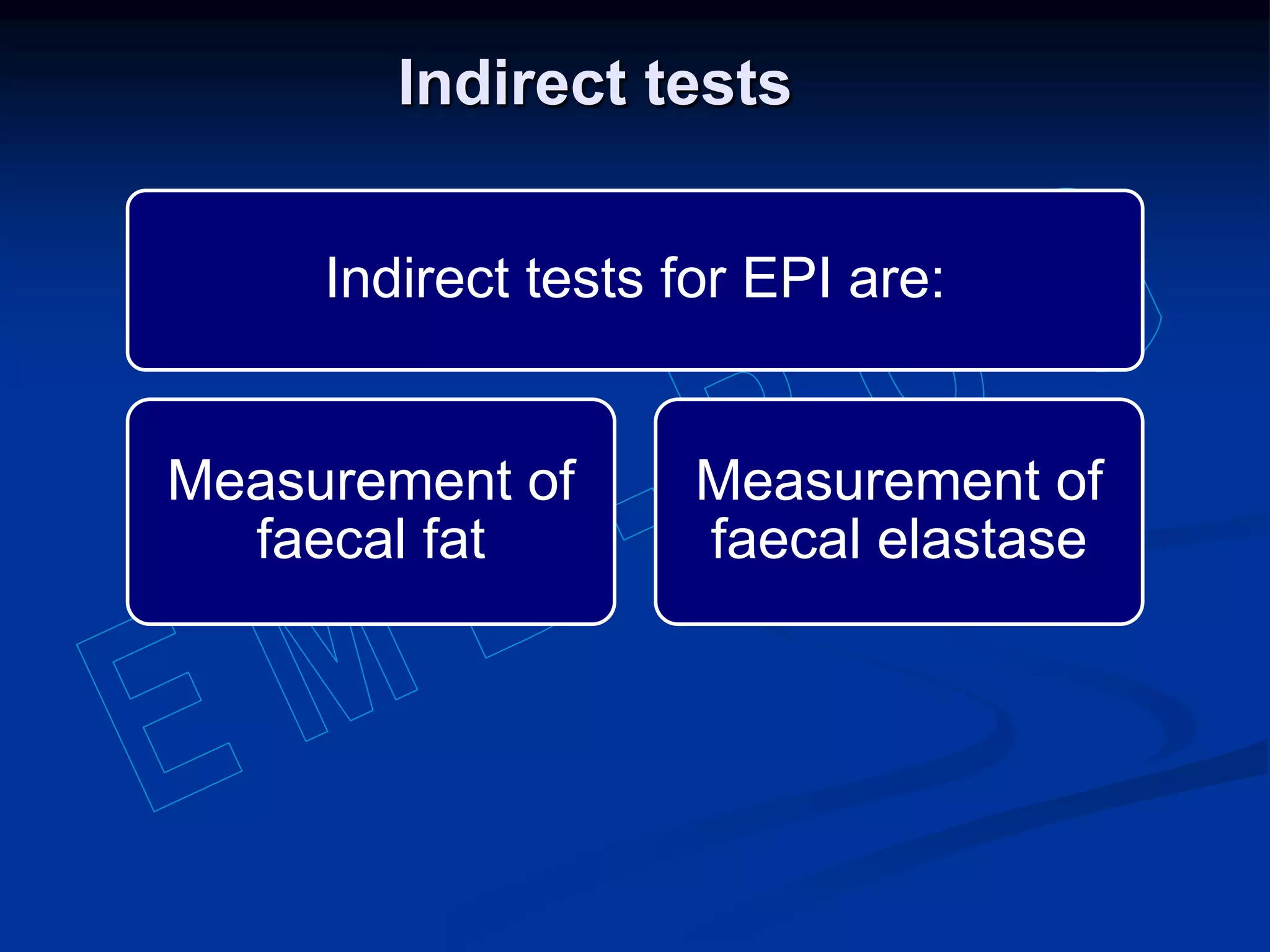
Pancreatic function tests can diagnose diseases of the exocrine pancreas or exocrine pancreatic insufficiency. Tests for diseases include serum amylase, serum lipase, and sweat chloride. Amylase and lipase levels rise in acute pancreatitis as the enzymes leak from damaged pancreatic cells. Sweat chloride testing diagnoses cystic fibrosis by measuring abnormally high chloride levels caused by a genetic mutation. Tests for exocrine pancreatic insufficiency include direct measurement of enzymes in pancreatic juice and indirect tests of fat and elastase levels in stool samples.