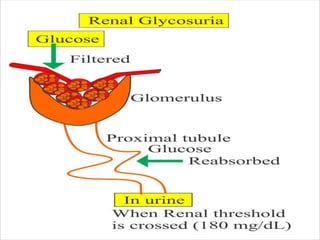
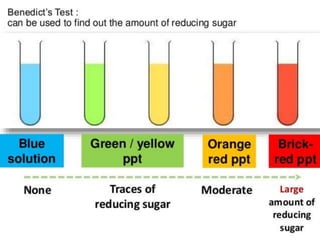
Normally urine contains a small amount of sugar that can't be detected by Benedict's test. Glycosuria refers to detectable amounts of sugar in urine, caused when blood glucose rises above the kidney's threshold. There are three types of glycosuria: 1) Alimentary glycosuria occurs after meals when blood sugar temporarily rises above the threshold, 2) Renal glycosuria is benign and caused by impaired kidney reabsorption despite normal blood sugar, and 3) Diabetic glycosuria is pathological and caused by insulin deficiency in diabetes mellitus.