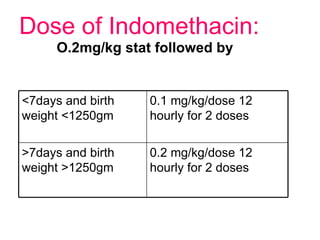
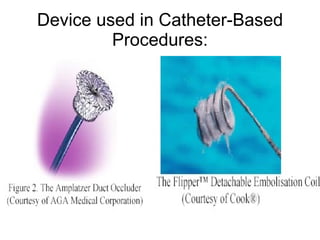
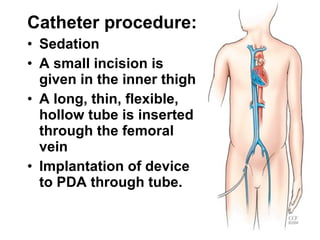
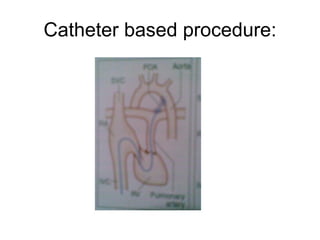
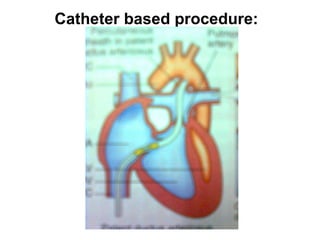
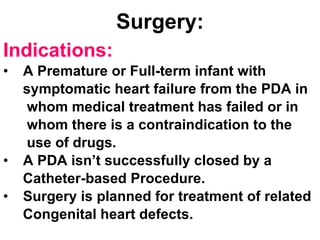
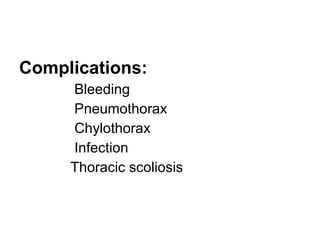
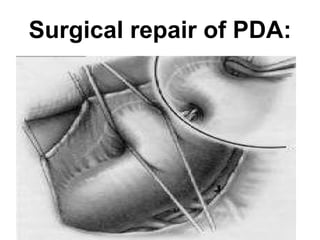
There are three main options to treat a patent ductus arteriosus (PDA): medical management using drugs like indomethacin or ibuprofen, catheter-based procedures to implant occlusion devices, or surgery to ligate and divide the ductus. Medical management aims to treat or prevent heart failure, infective endocarditis, and pulmonary vascular disease. Catheter procedures are usually done after the neonatal period for moderate to large PDAs. Surgery is indicated if medical treatment fails or for treatment of related congenital heart defects, and involves ligating and dividing the ductus via thoracotomy.