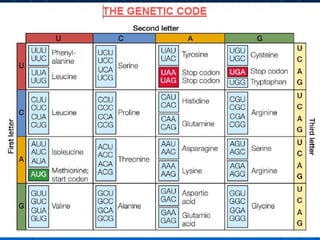
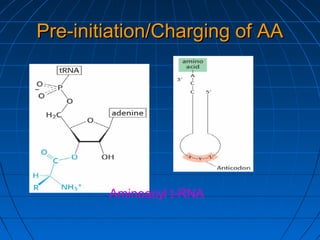
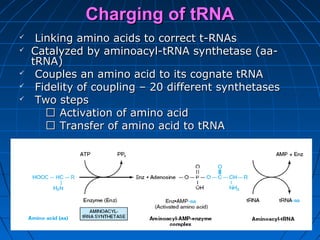
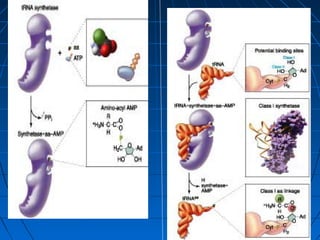
1. The genetic code is the system by which nucleotide sequences in mRNA specify amino acid sequences in proteins during translation. There are 64 possible codon combinations using 3 nucleotides that map to 20 standard amino acids.
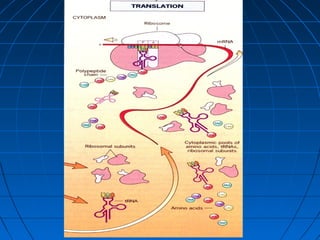
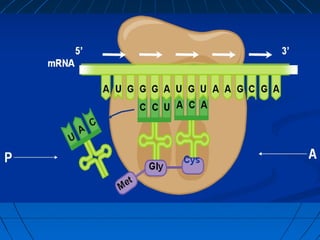
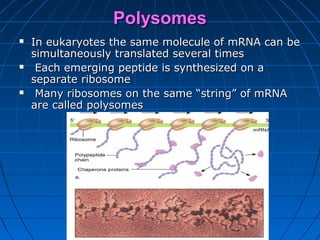
2. Translation is the process by which the sequence of bases in mRNA is used to synthesize a polypeptide chain. It occurs on ribosomes using tRNA molecules to add amino acids specified by mRNA codons.
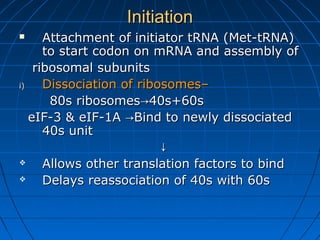
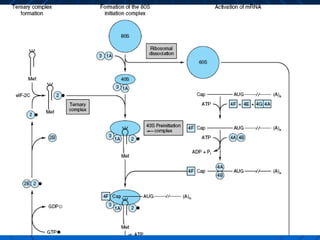
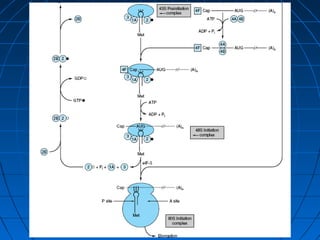
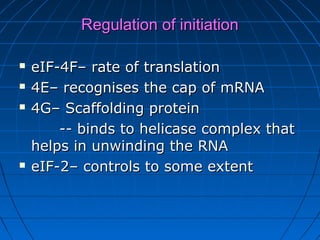
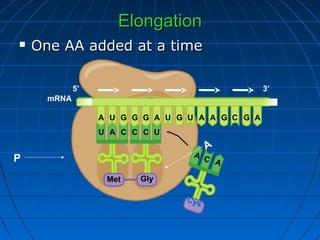
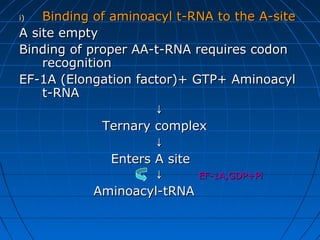
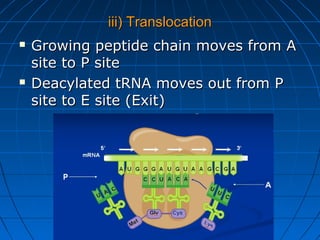
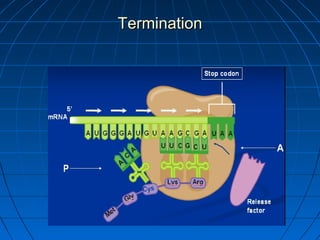
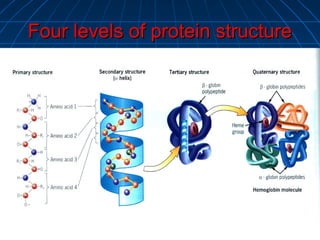
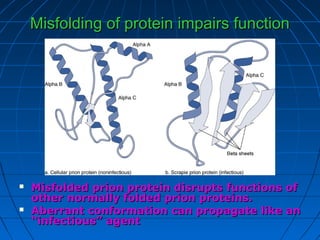
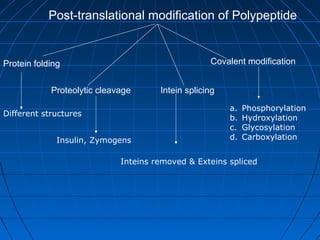
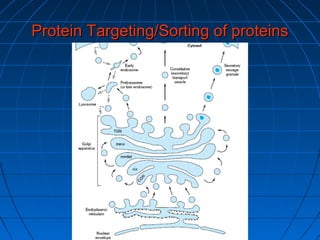
3. The stages of translation are initiation, elongation, termination, and post-translational modification. Initiation involves assembly of the ribosome and initiation factors on the mRNA start codon. Elongation adds one amino acid at a time until a stop codon is reached. Termination releases the pol