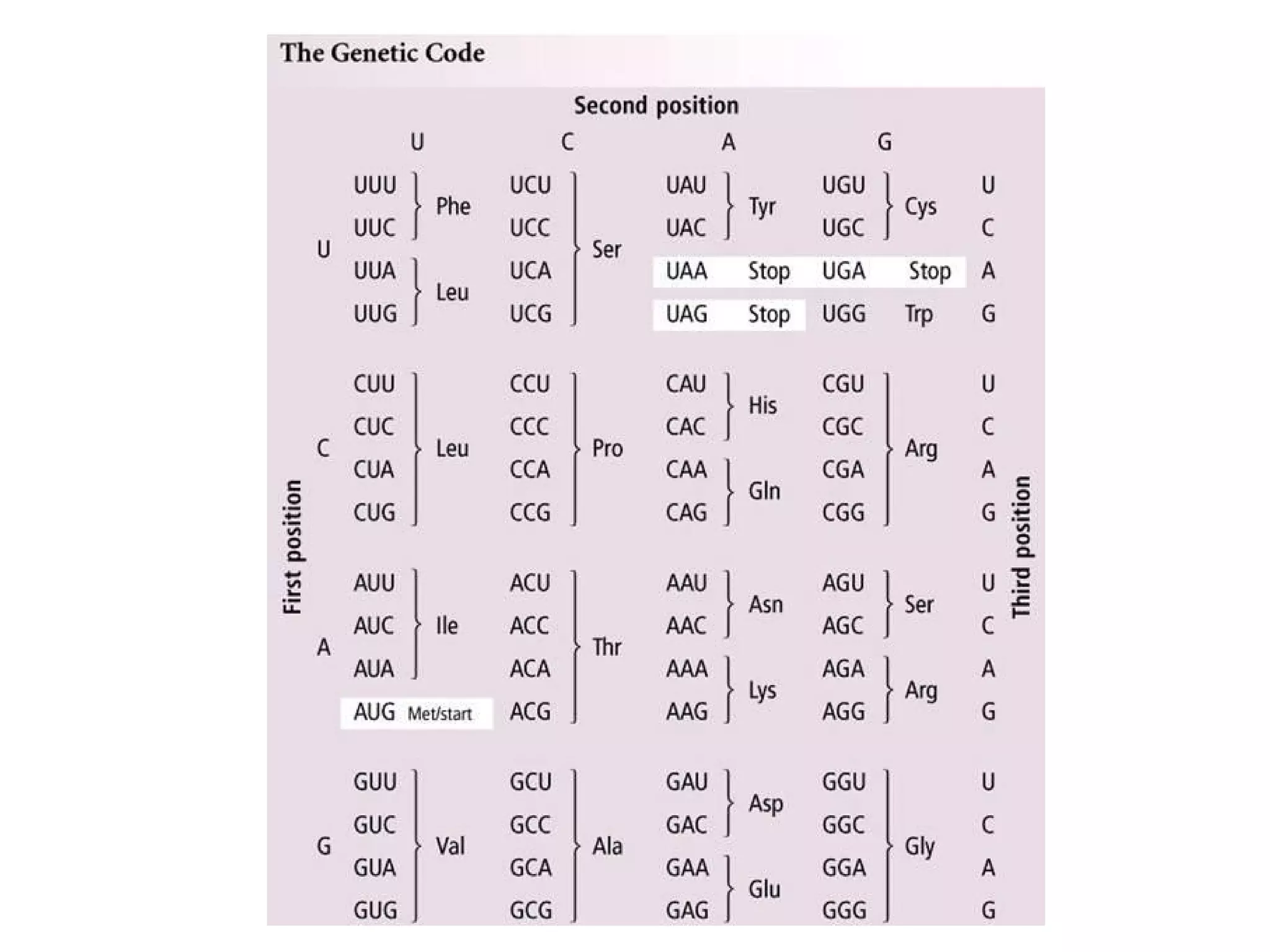
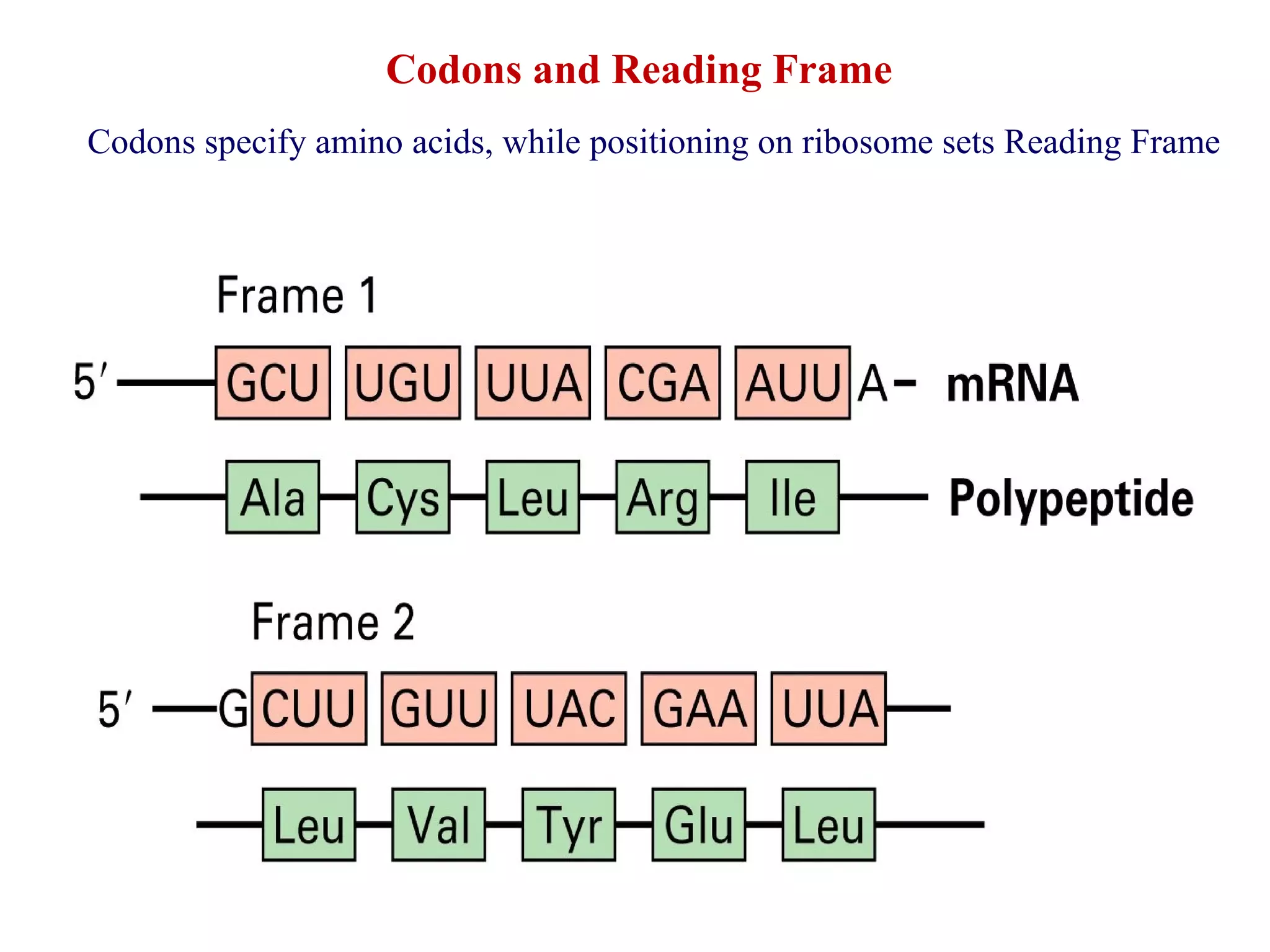
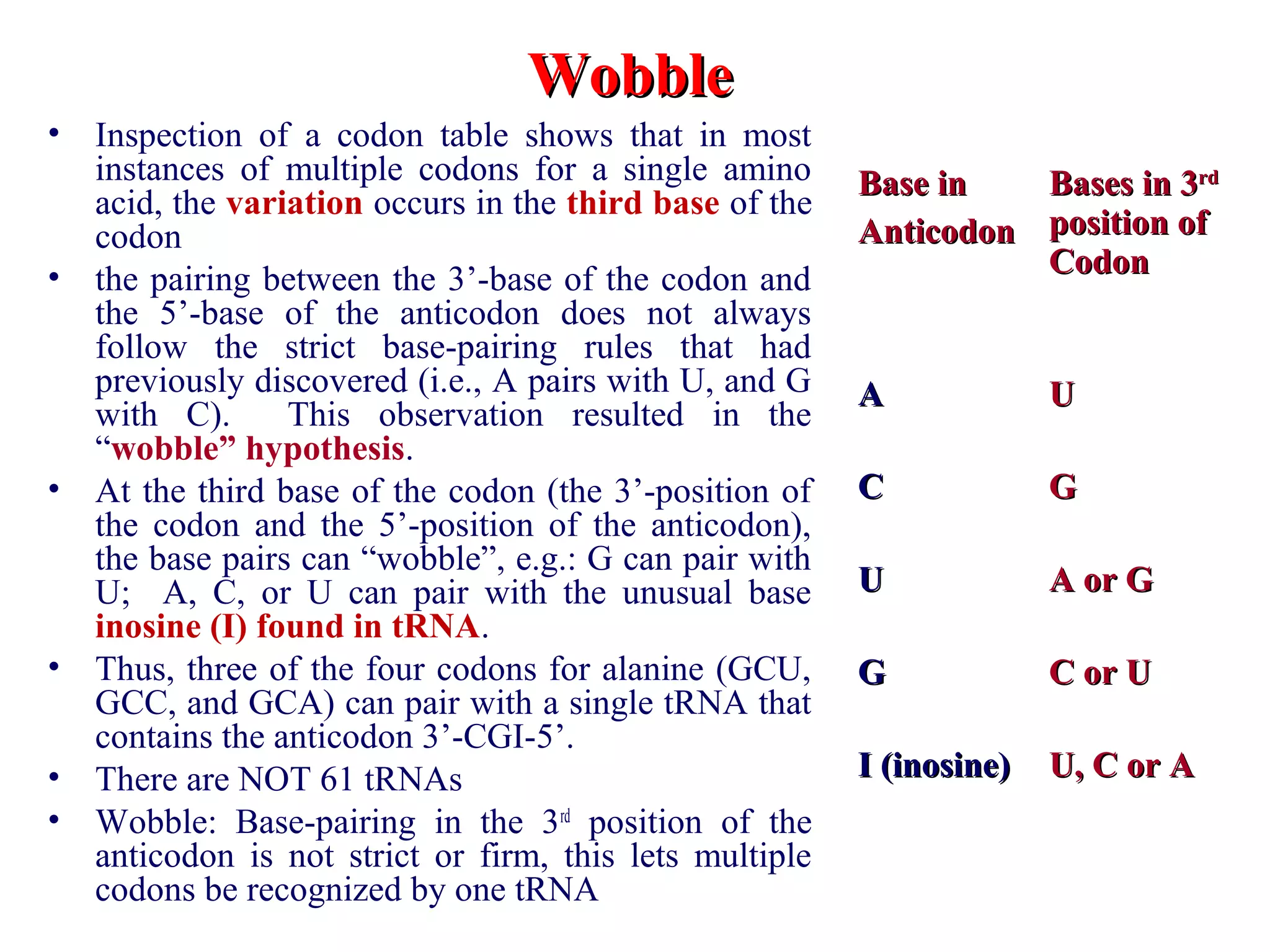
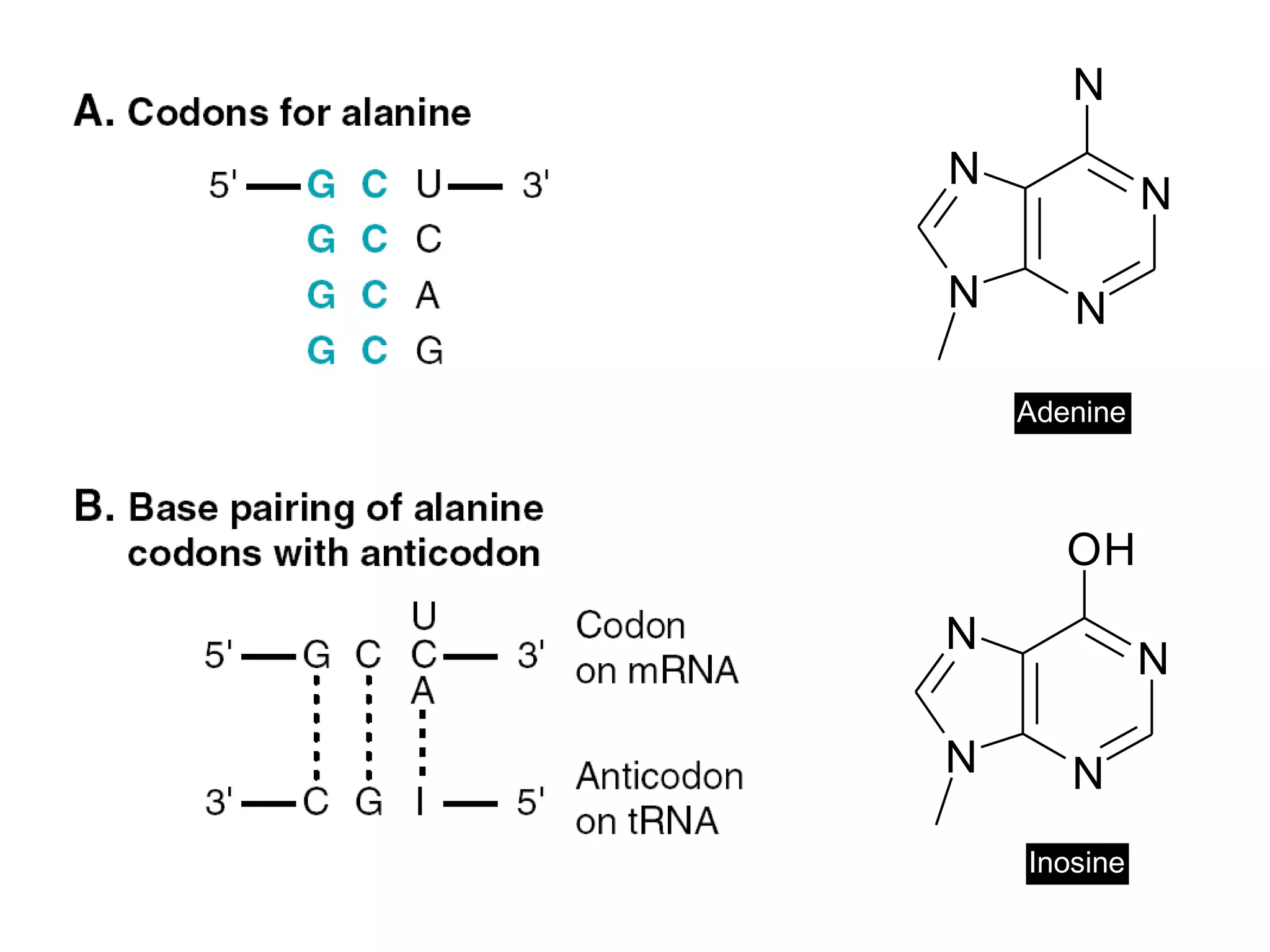
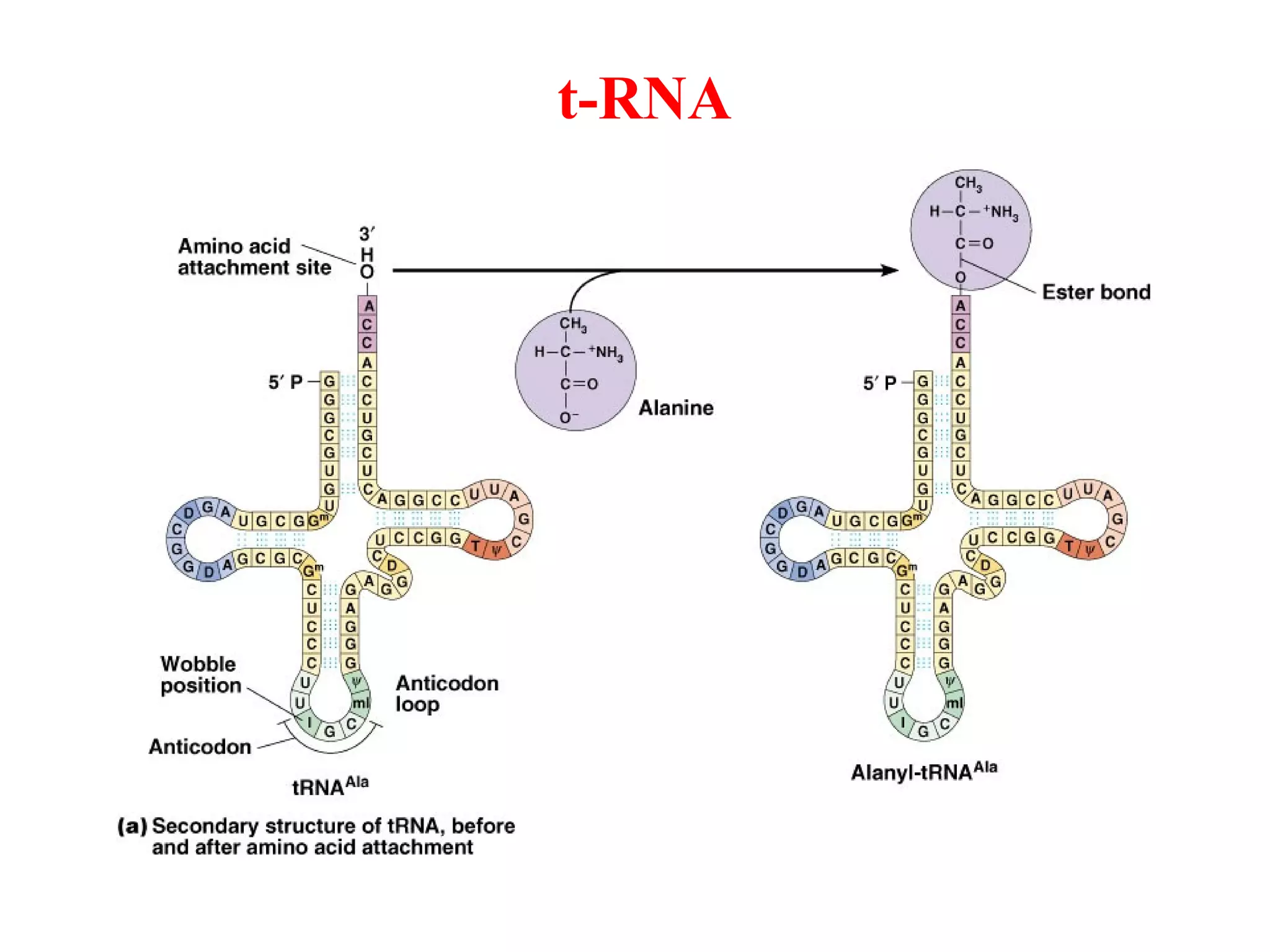
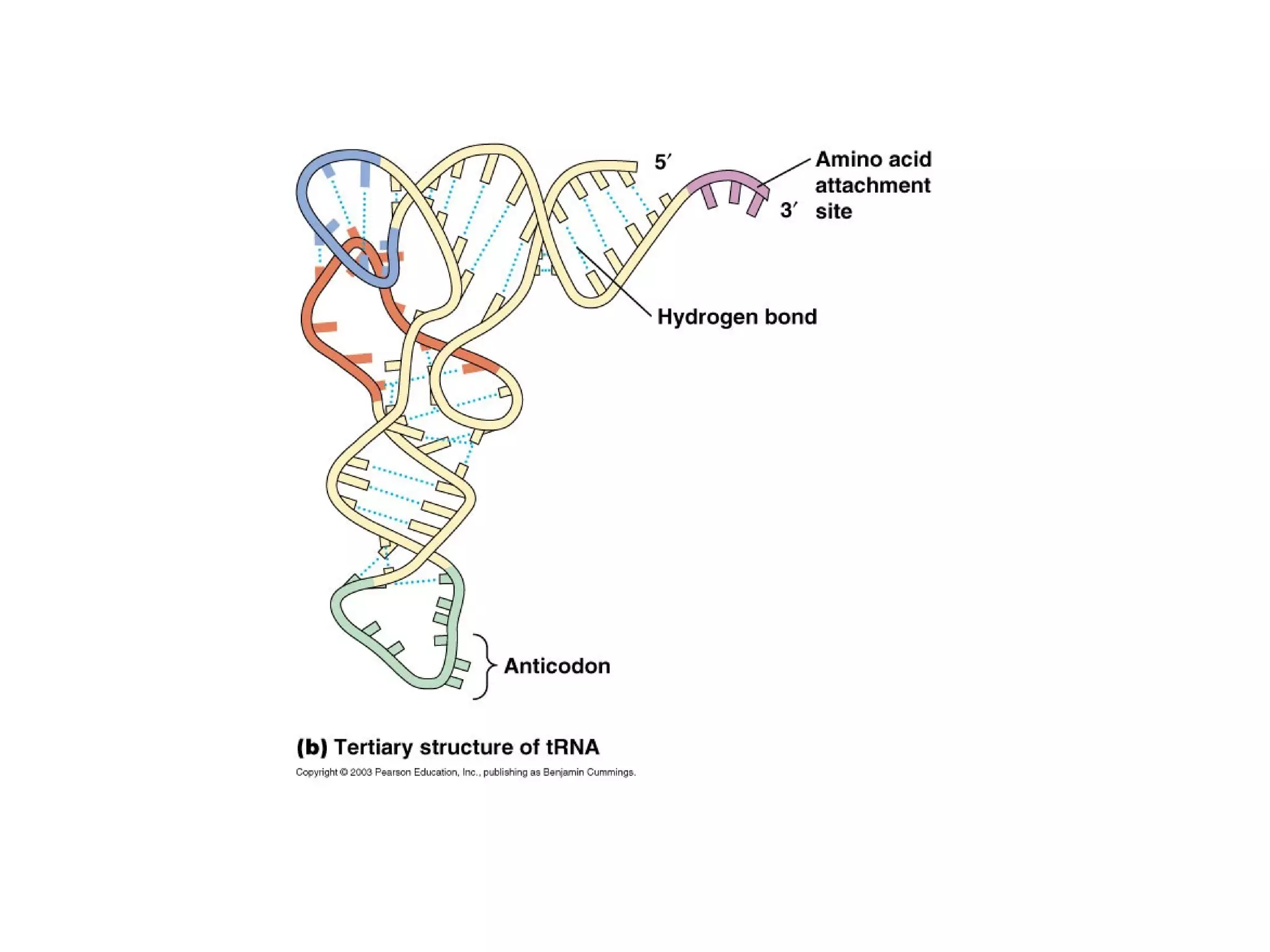
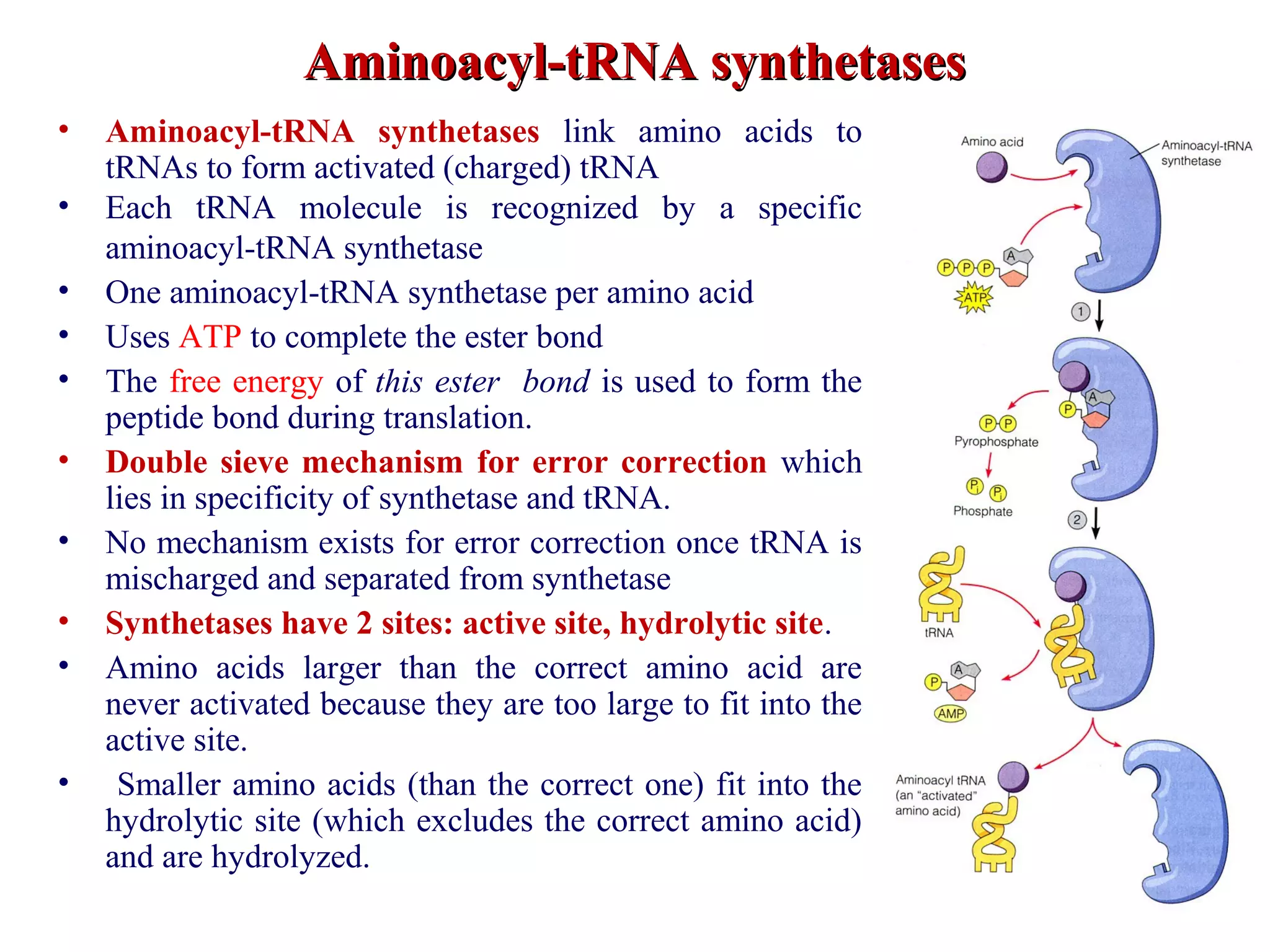
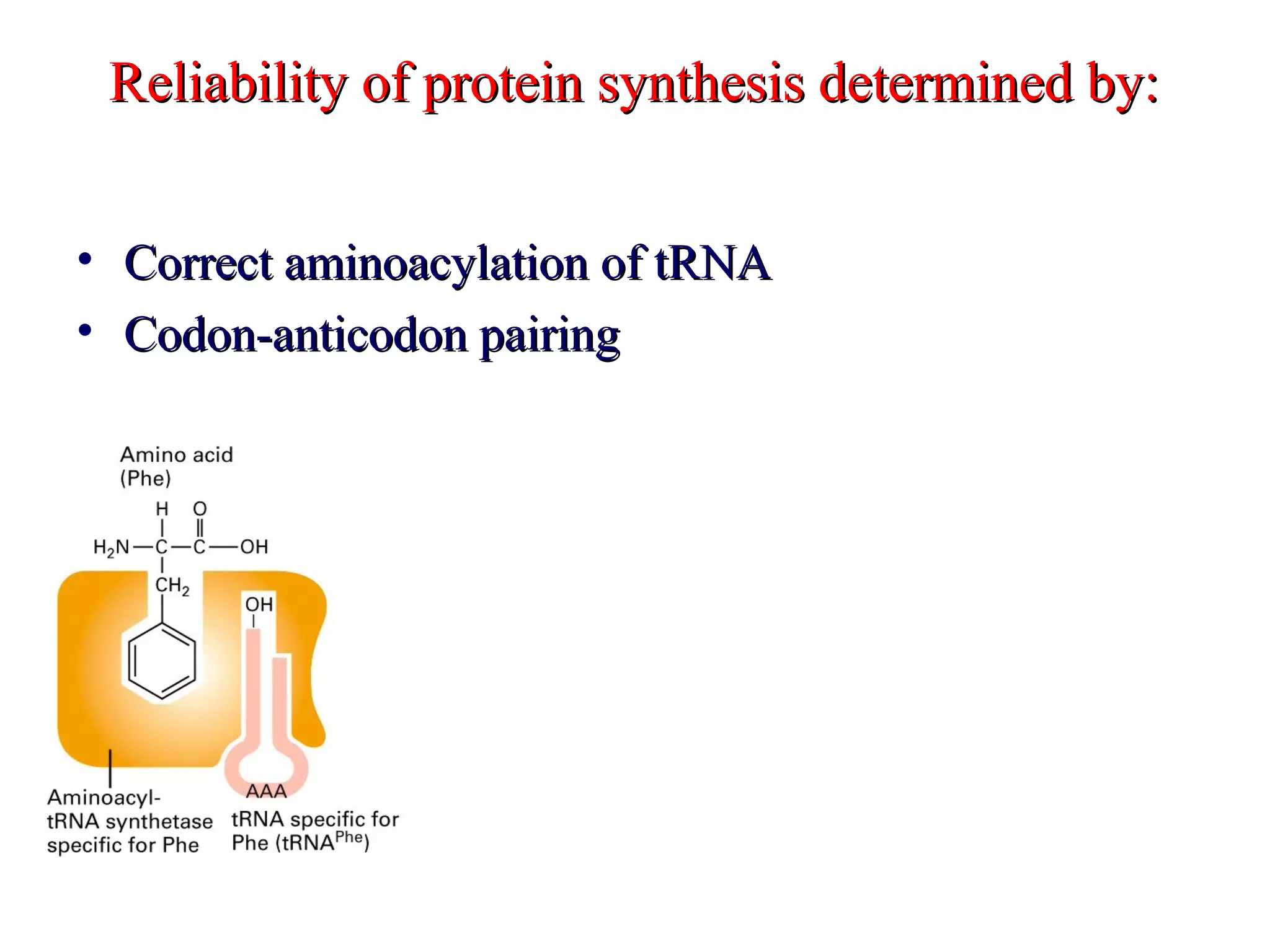
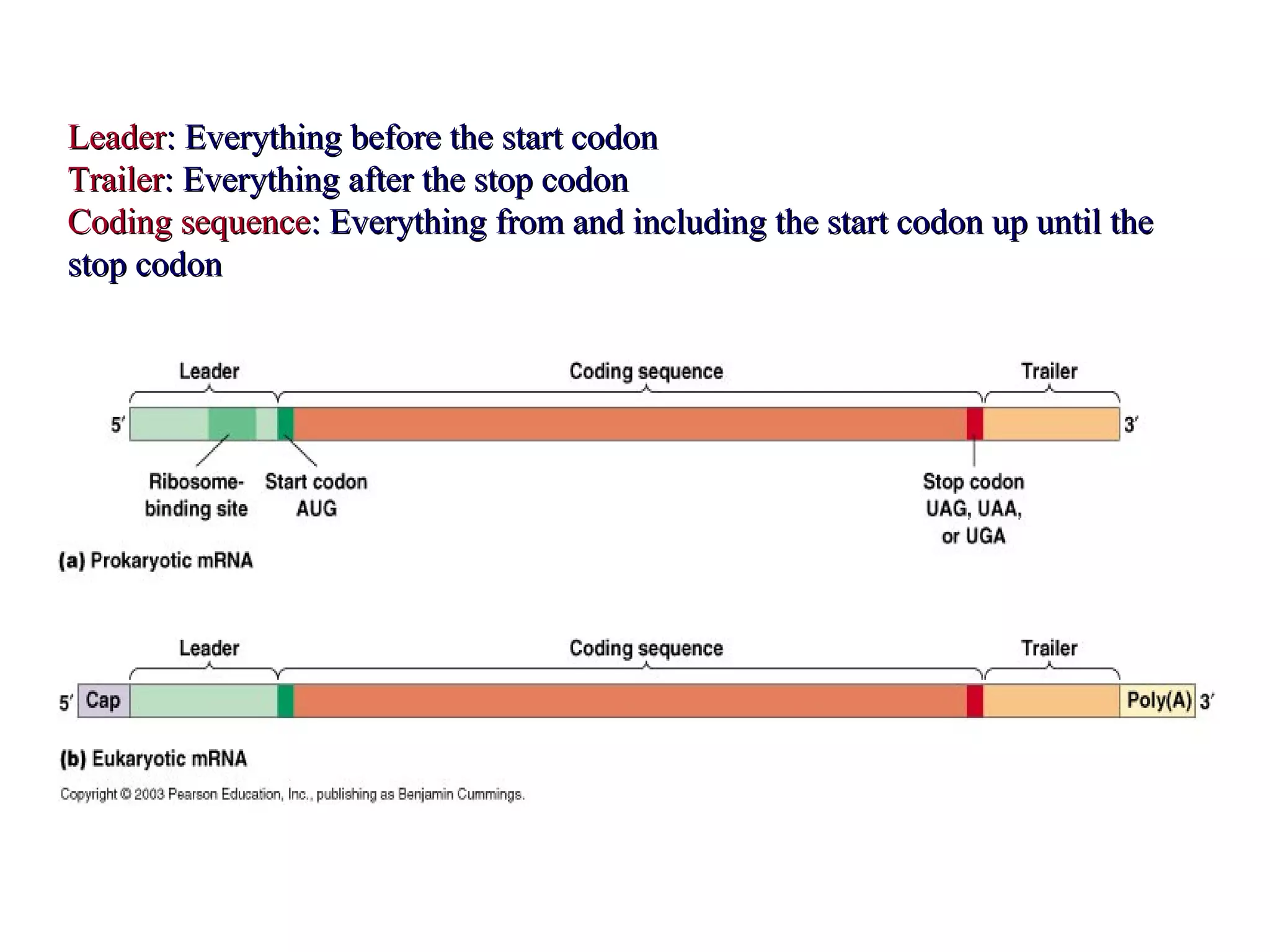
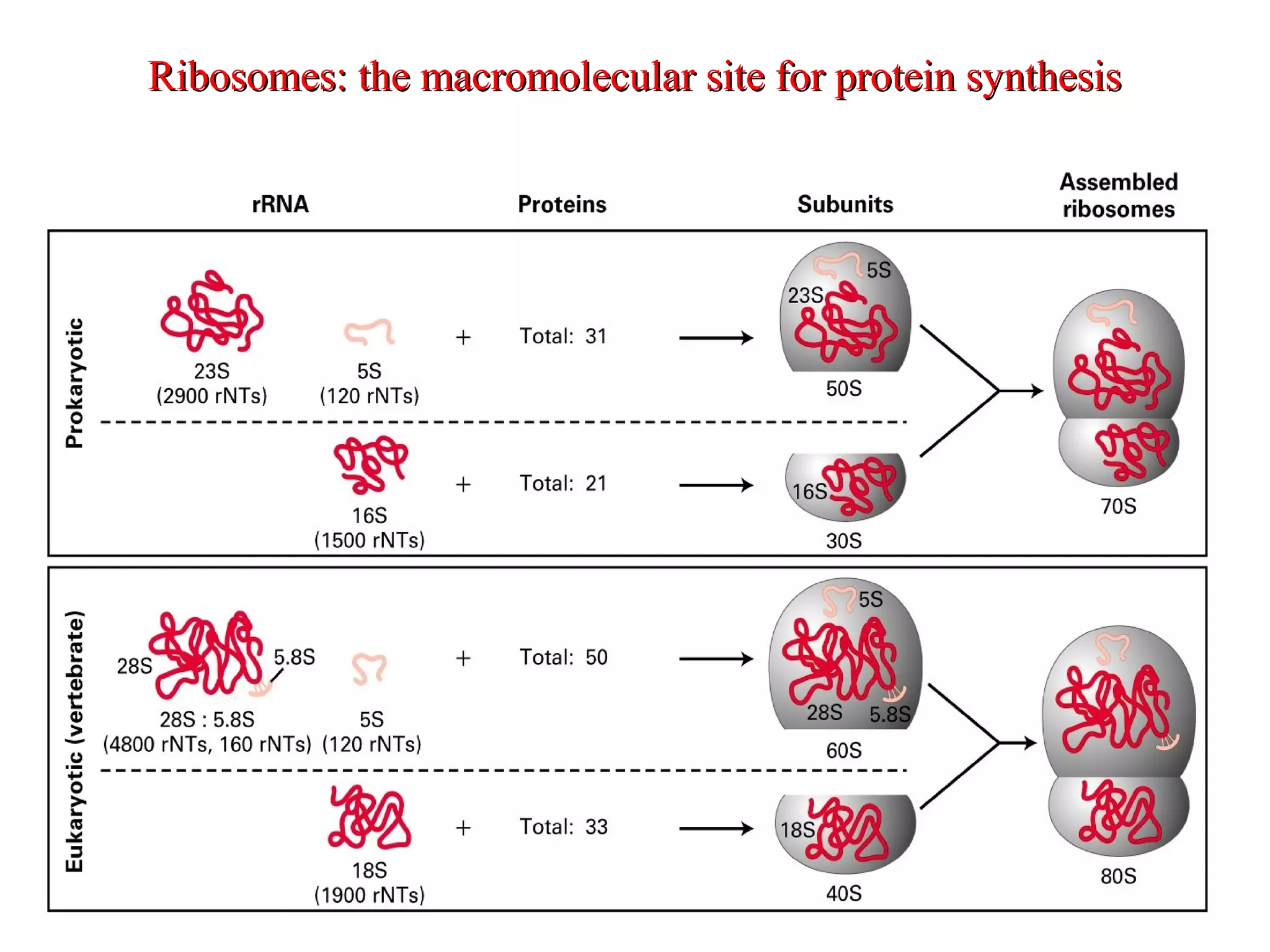
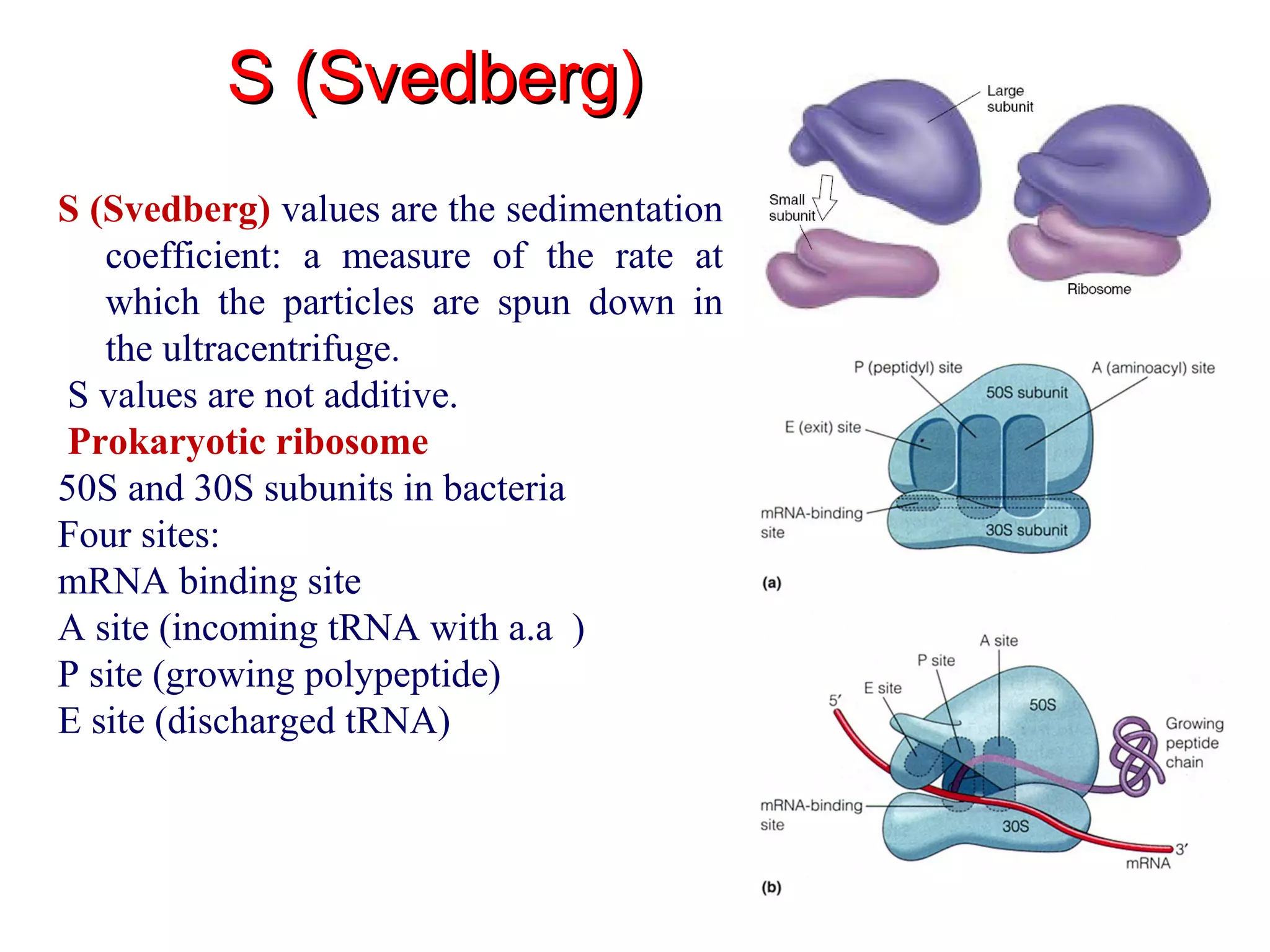
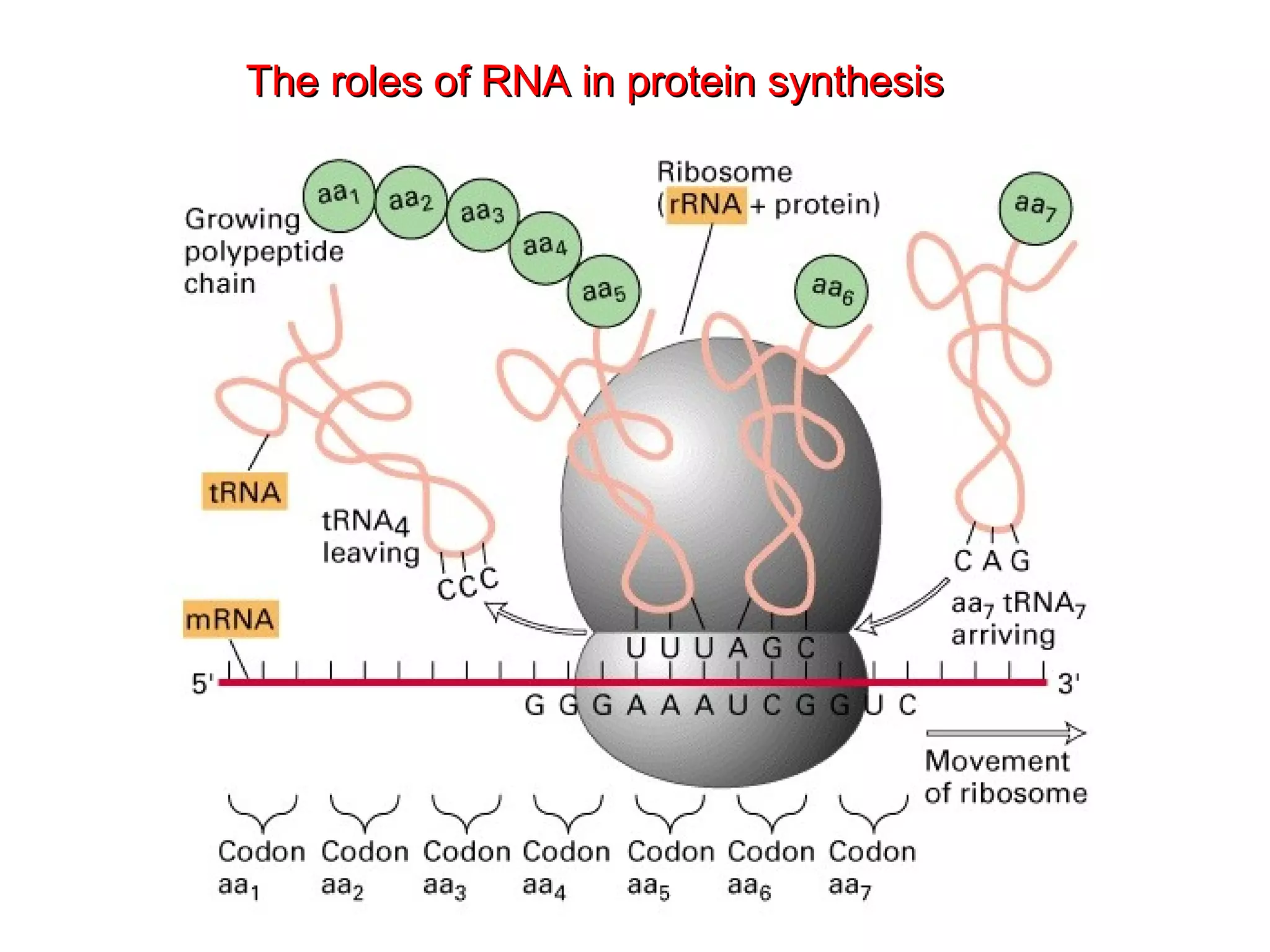
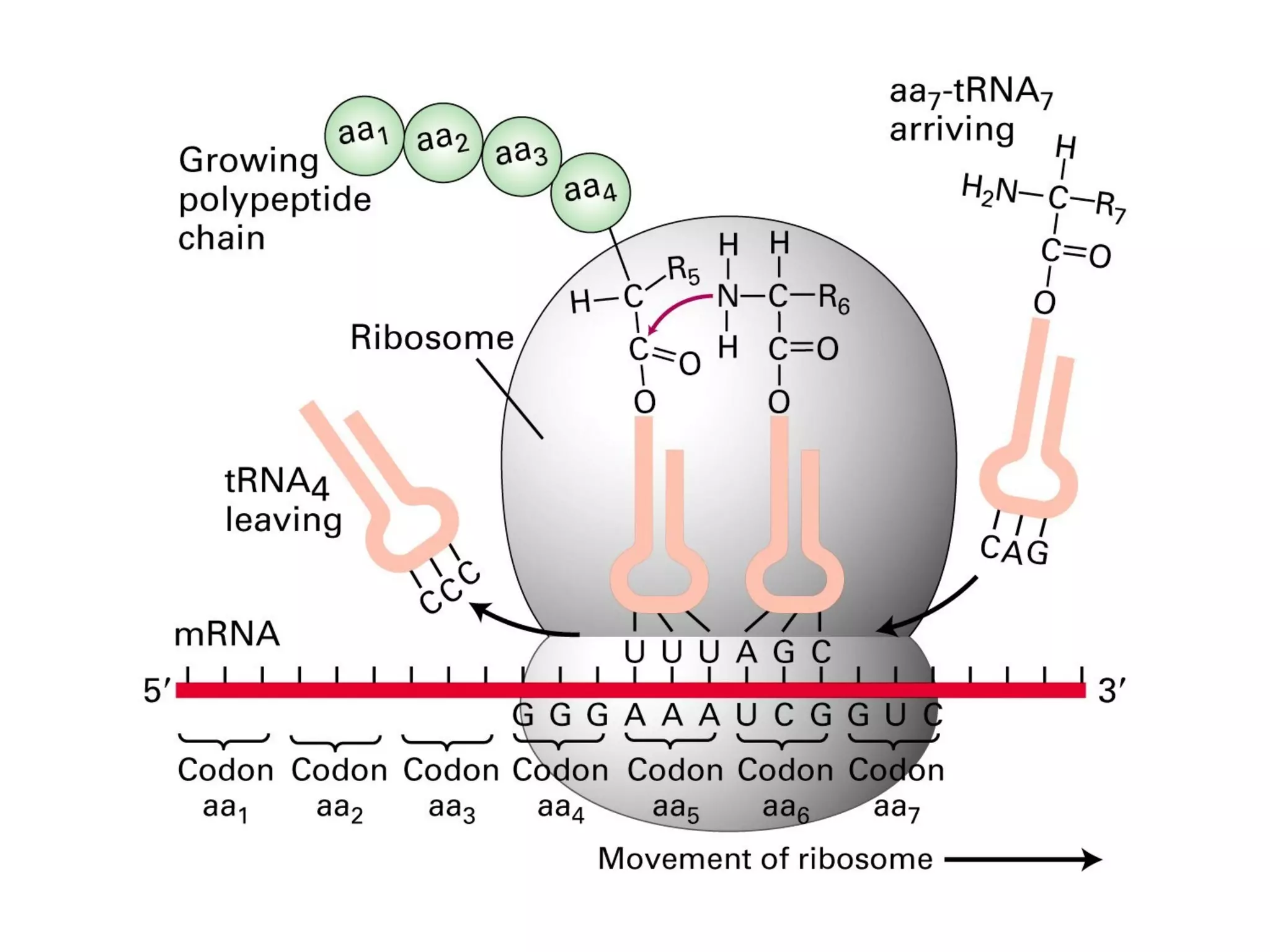
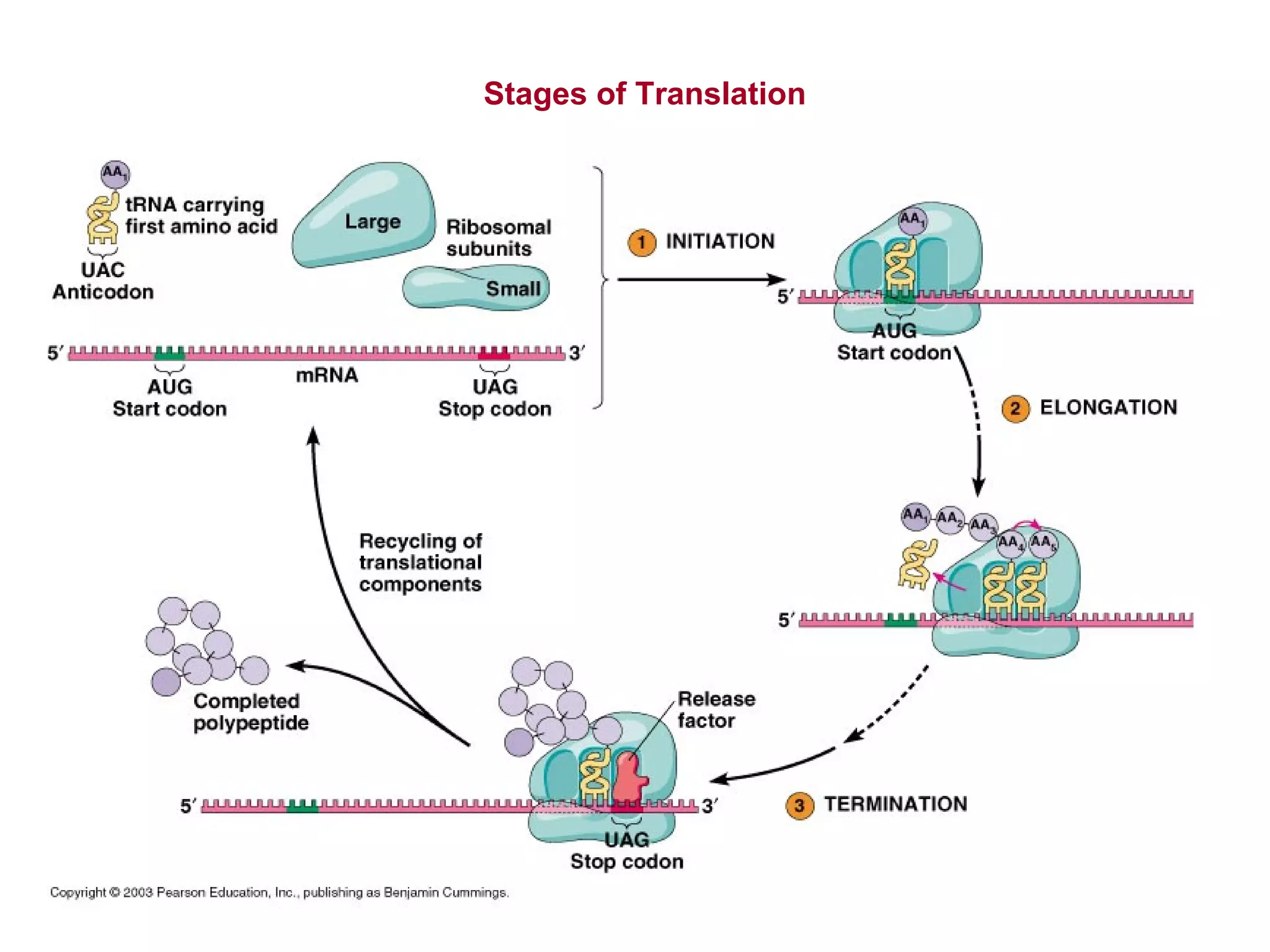
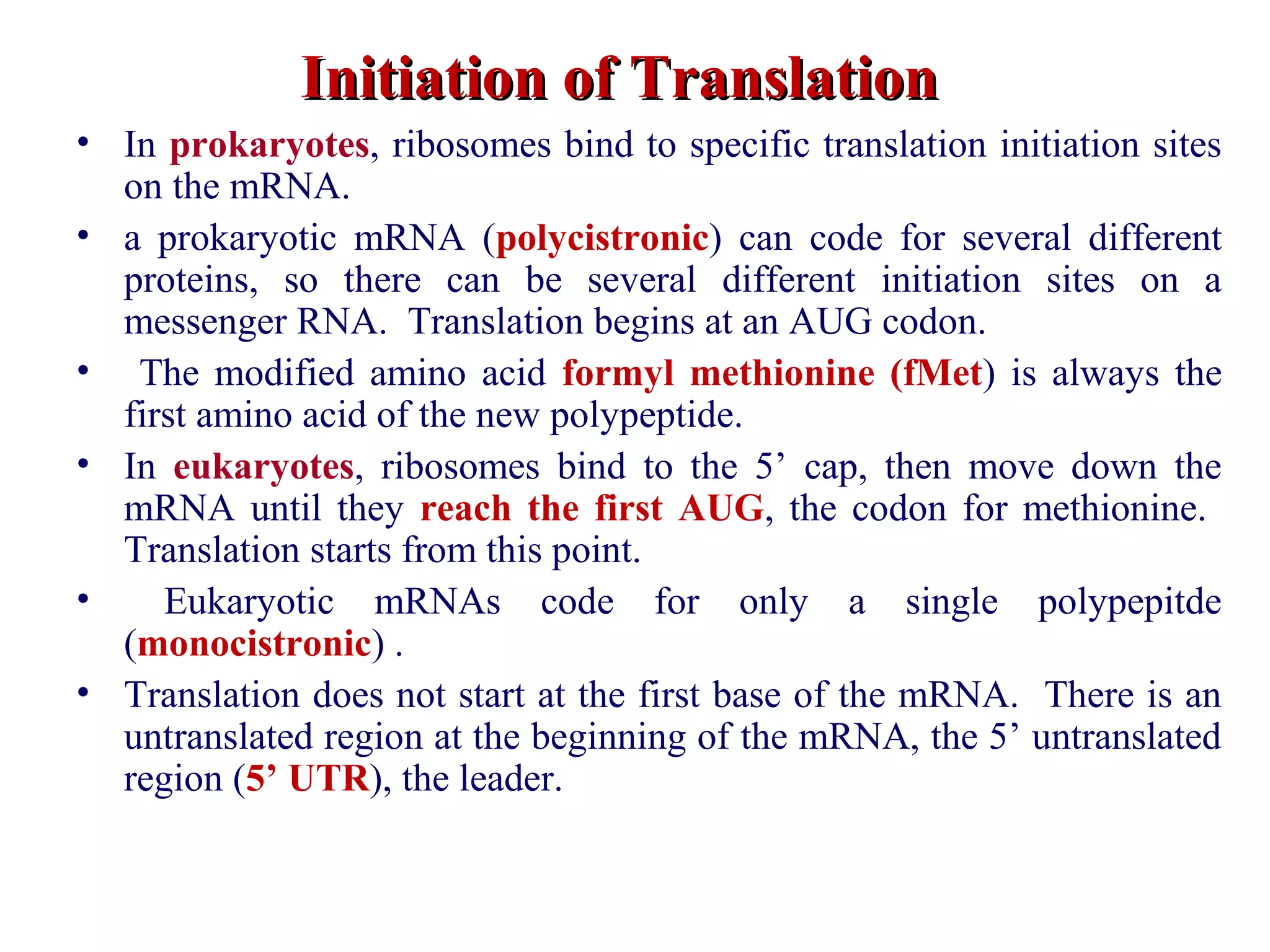
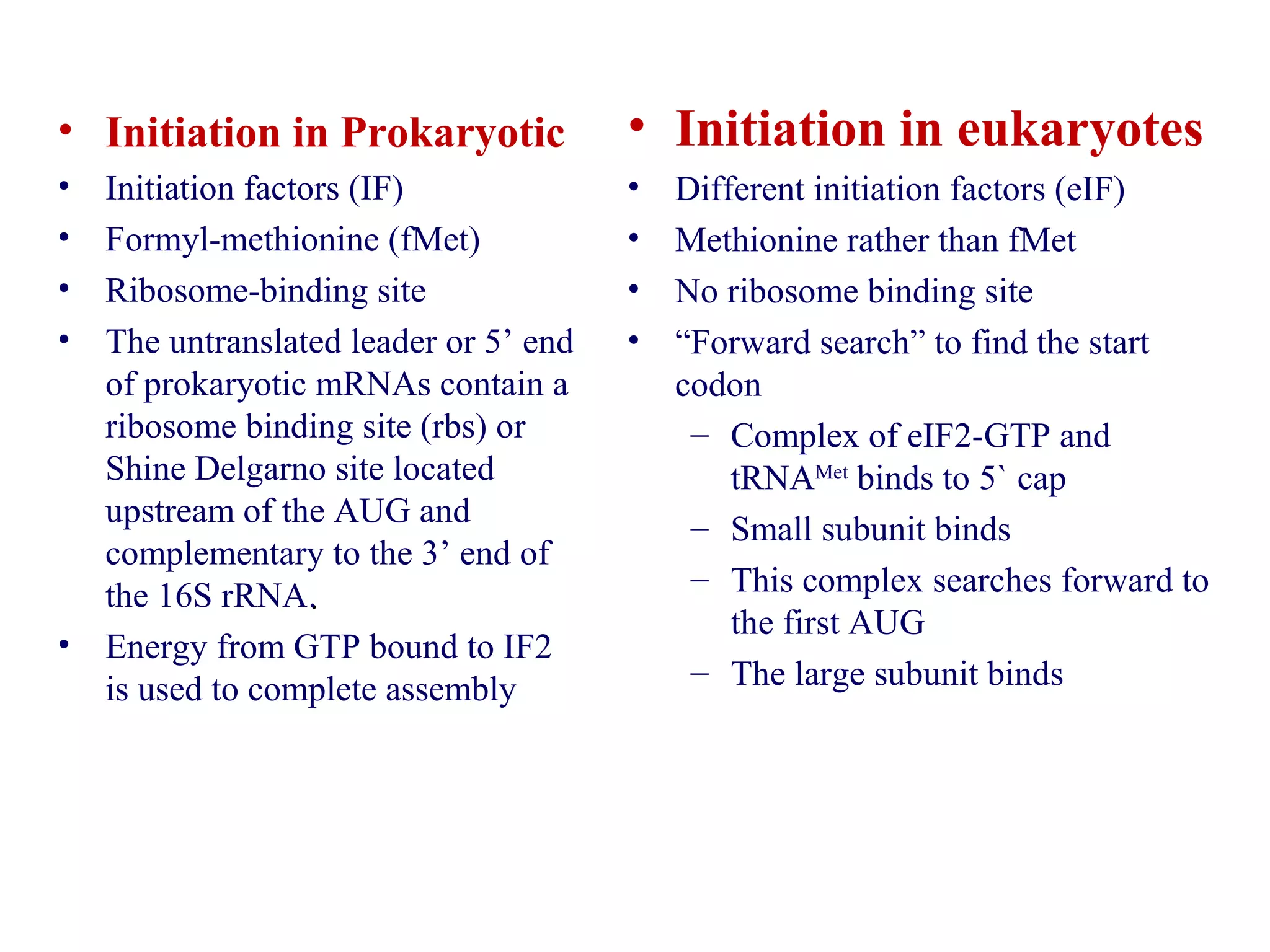
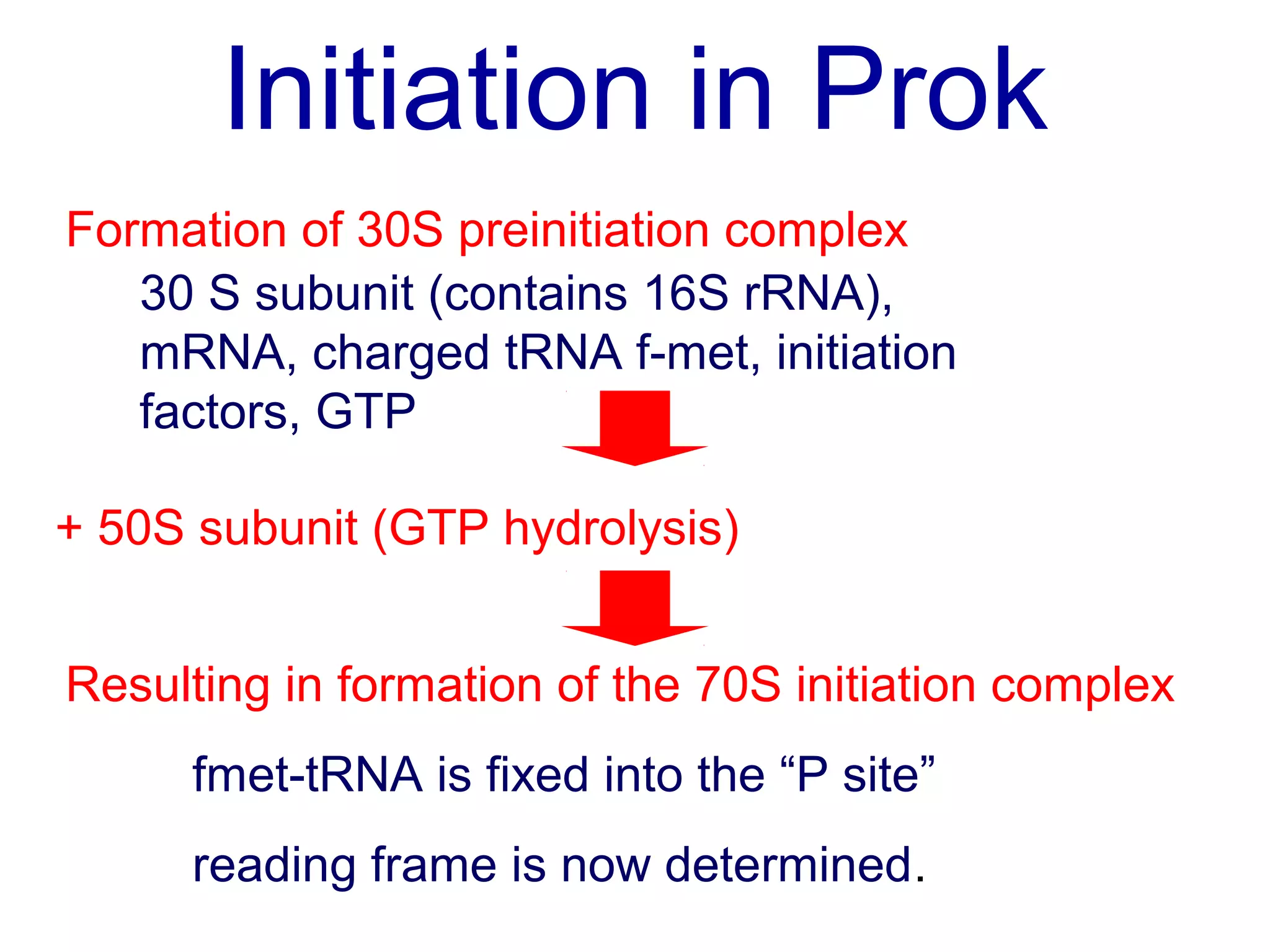
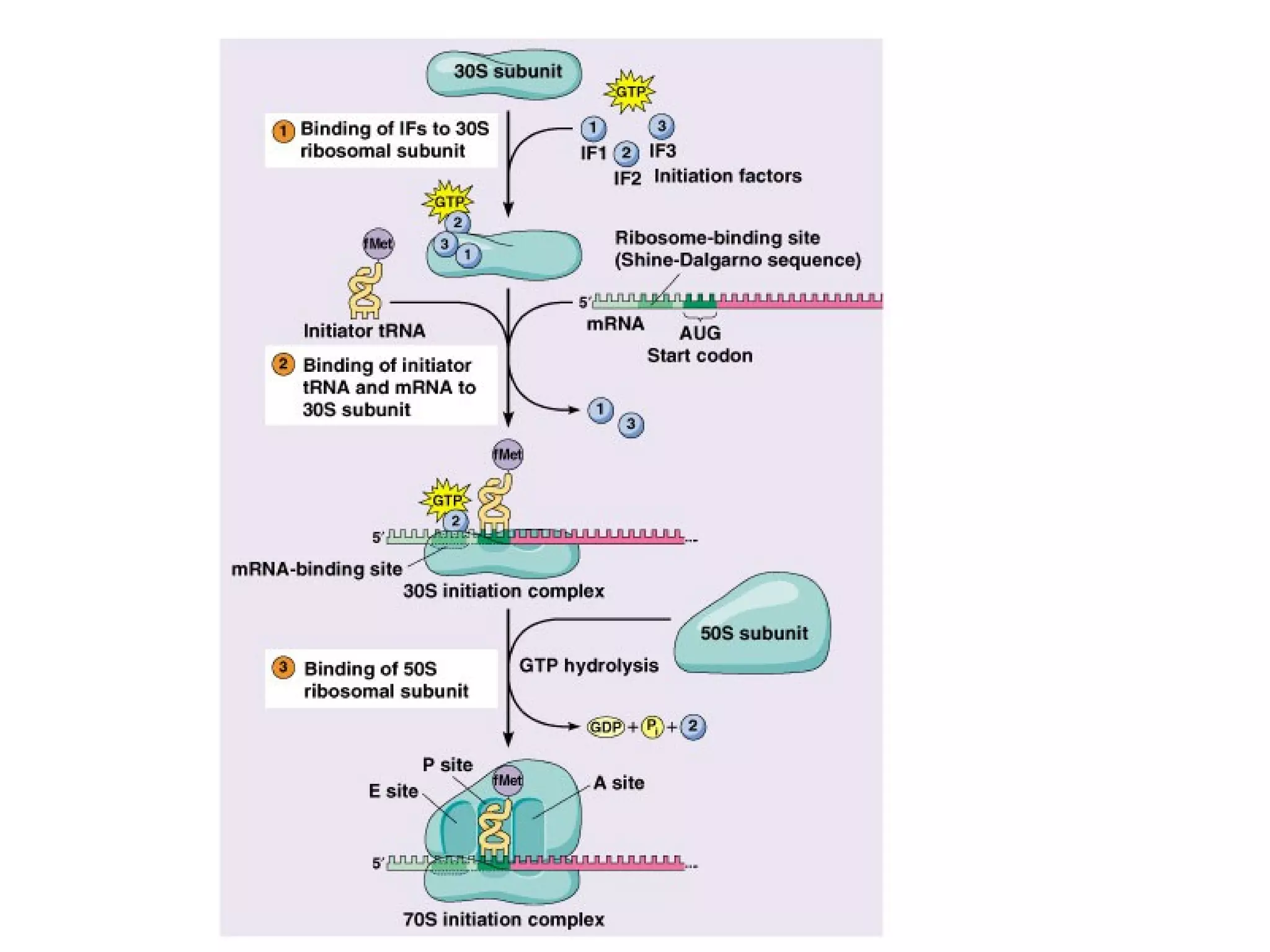
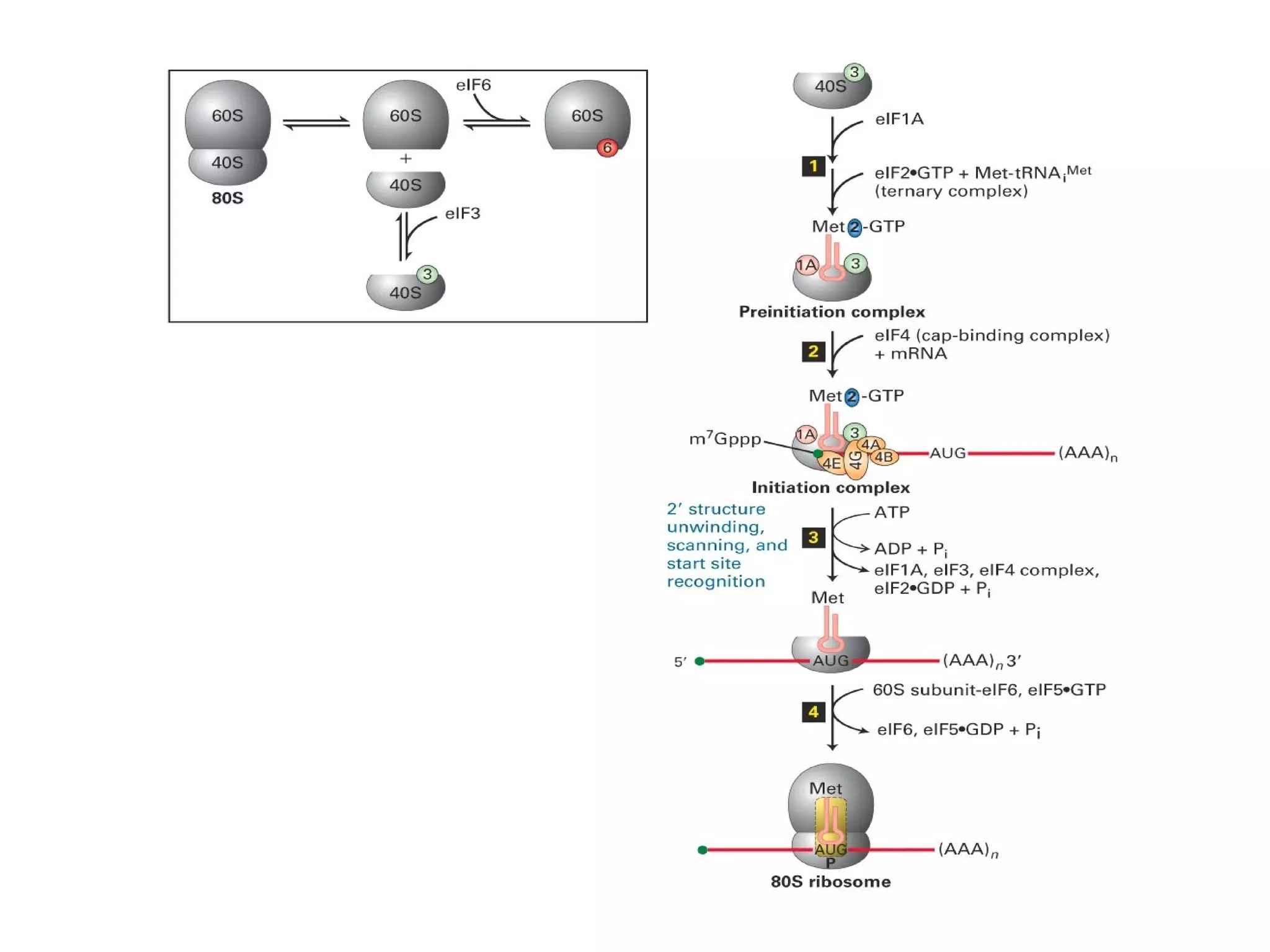
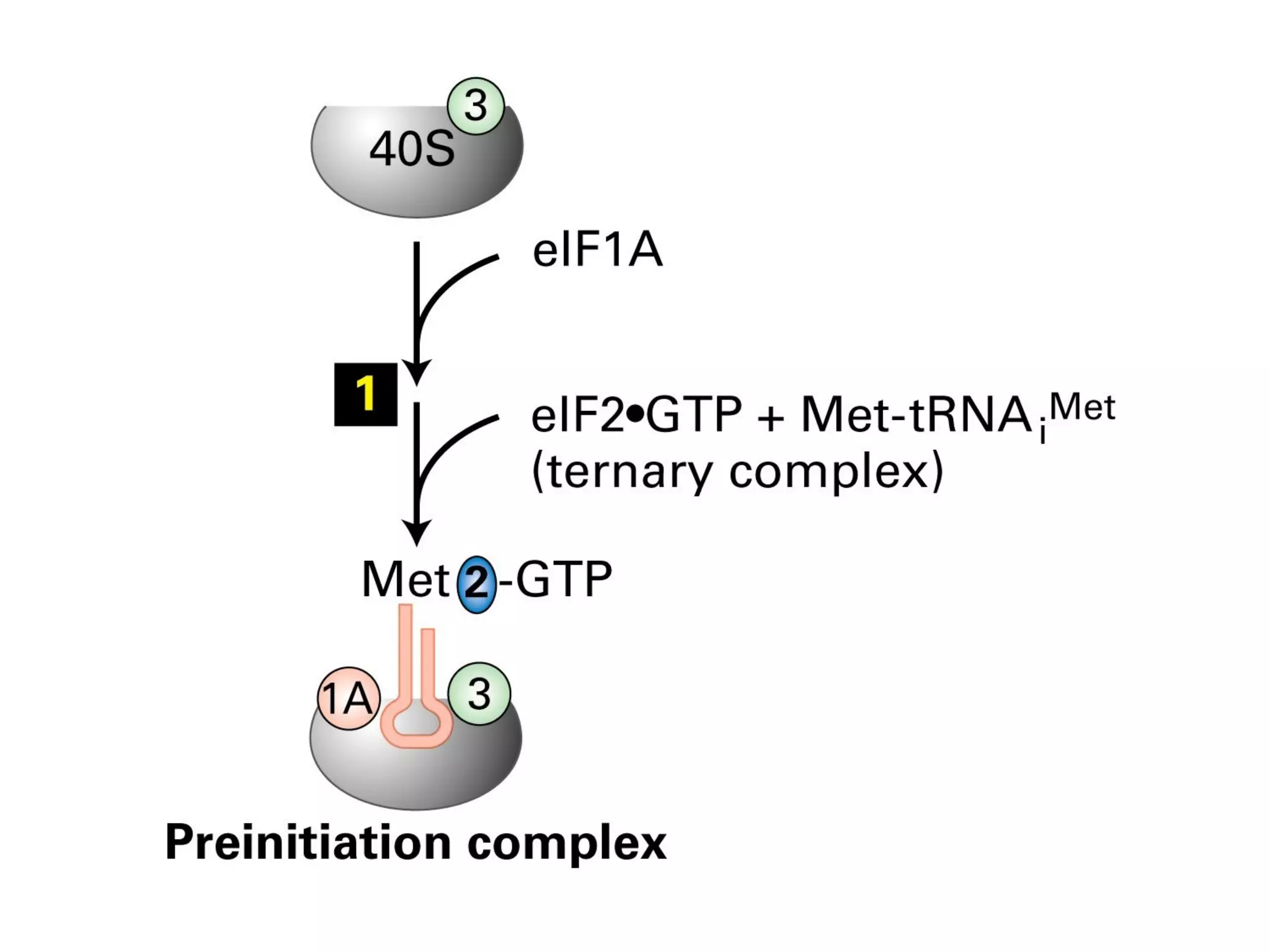
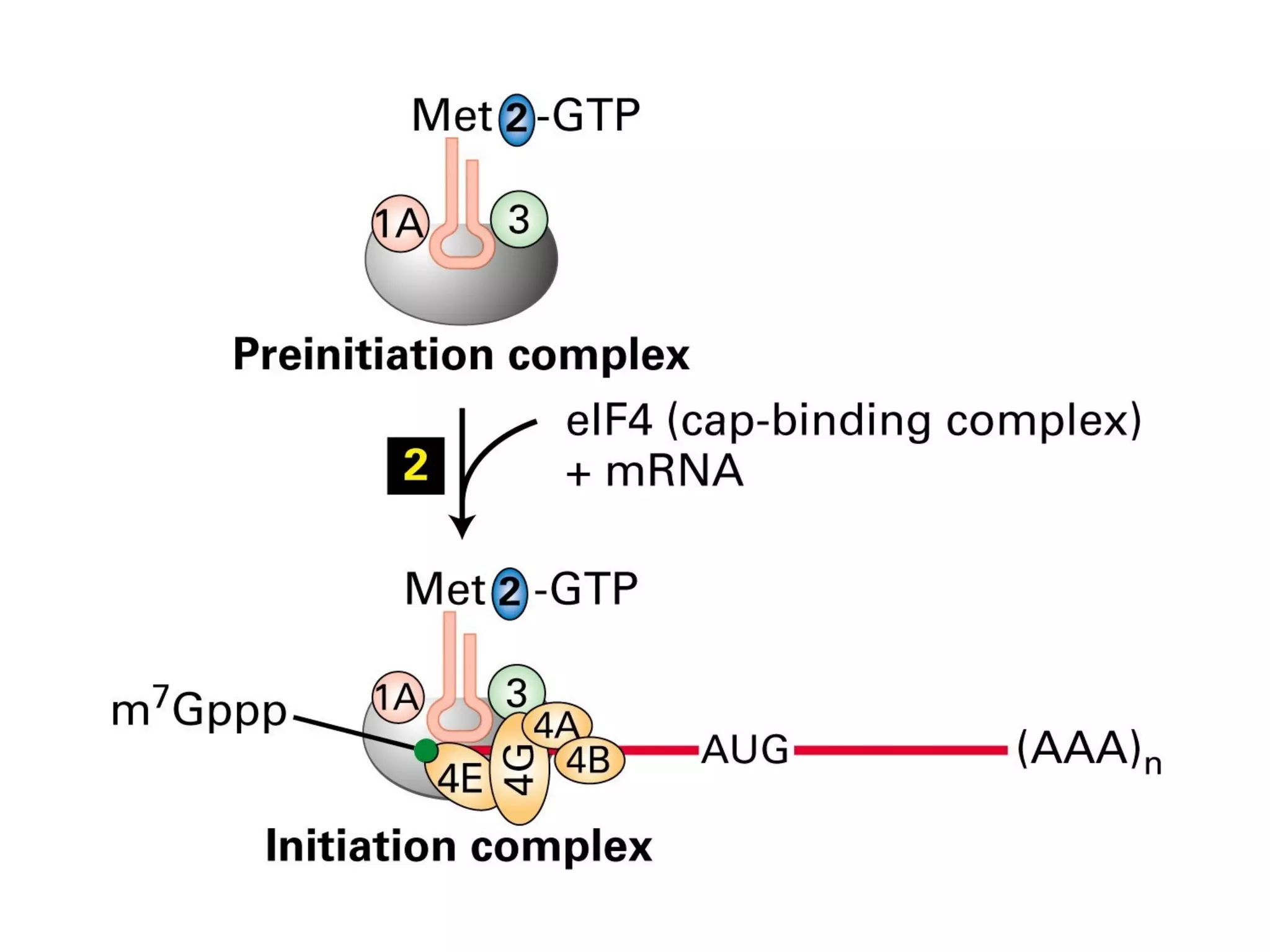
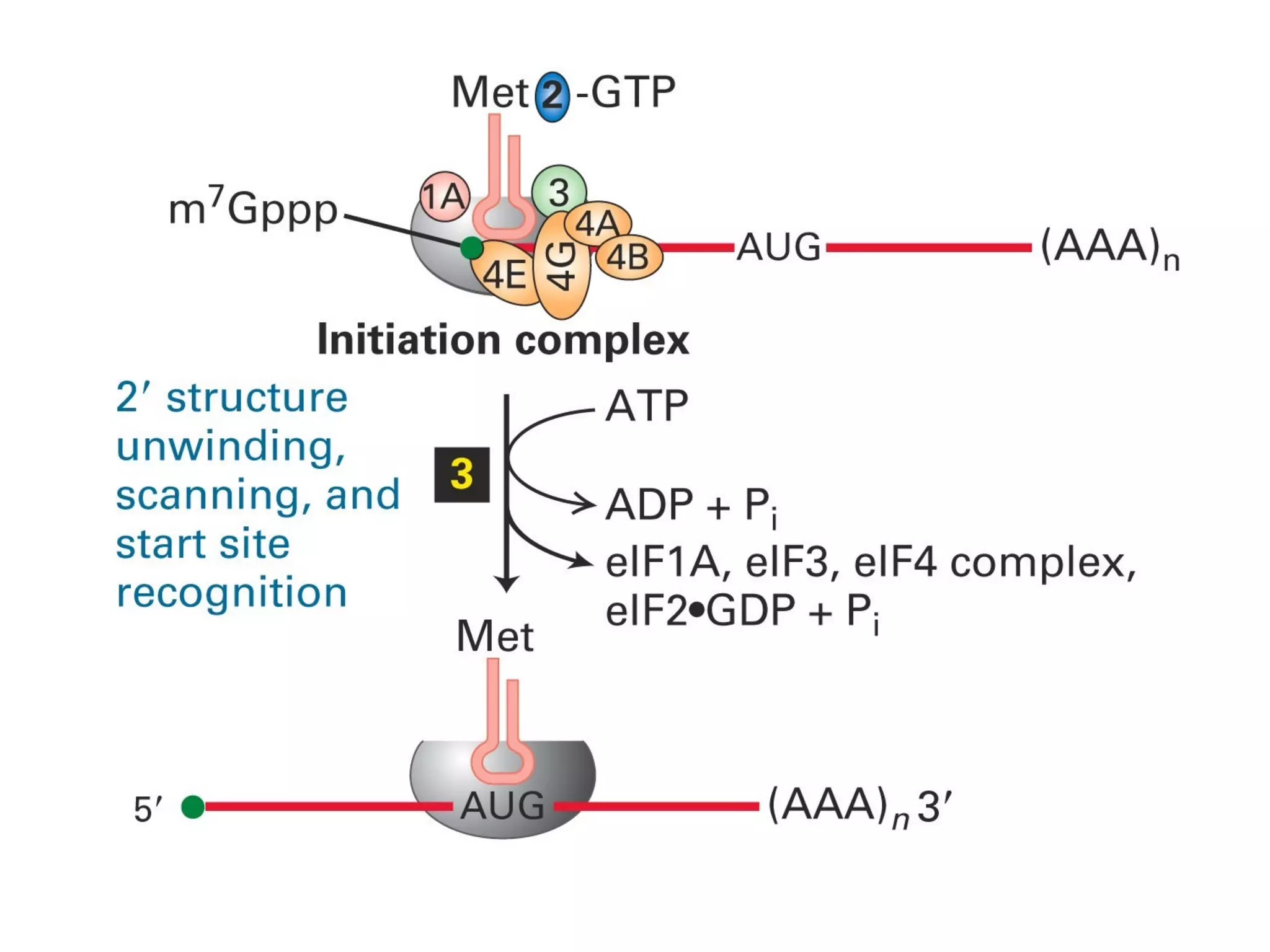
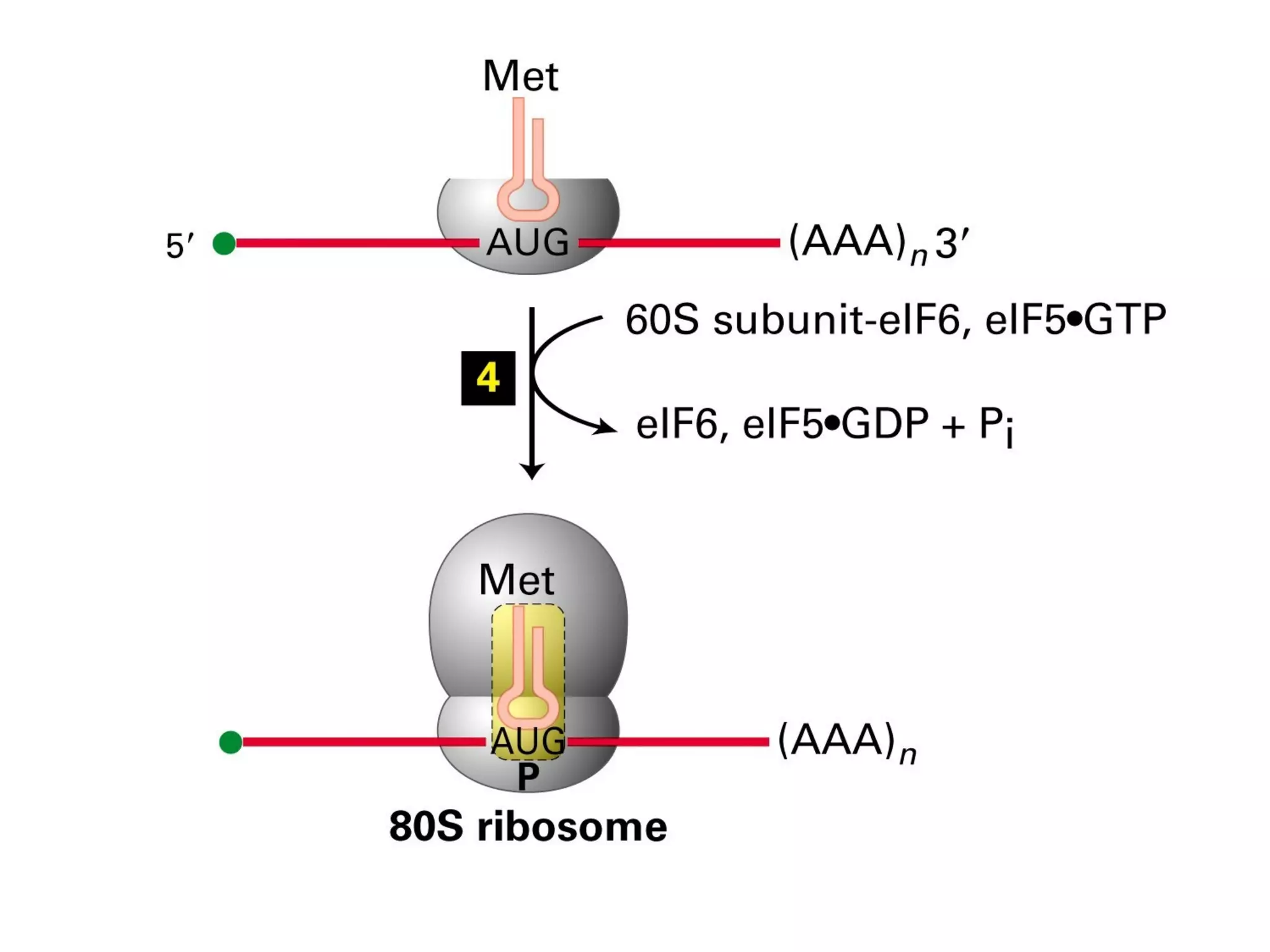
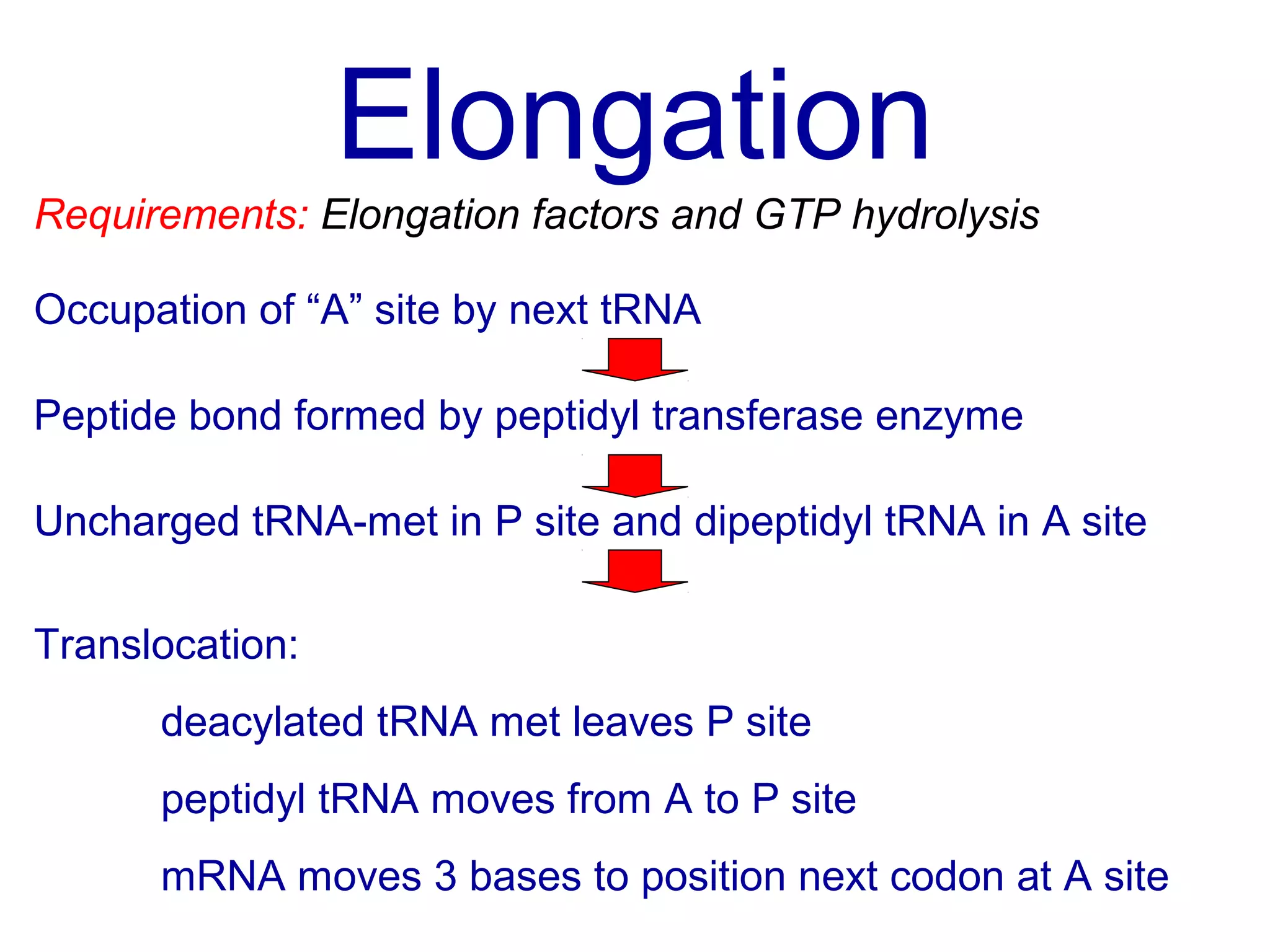
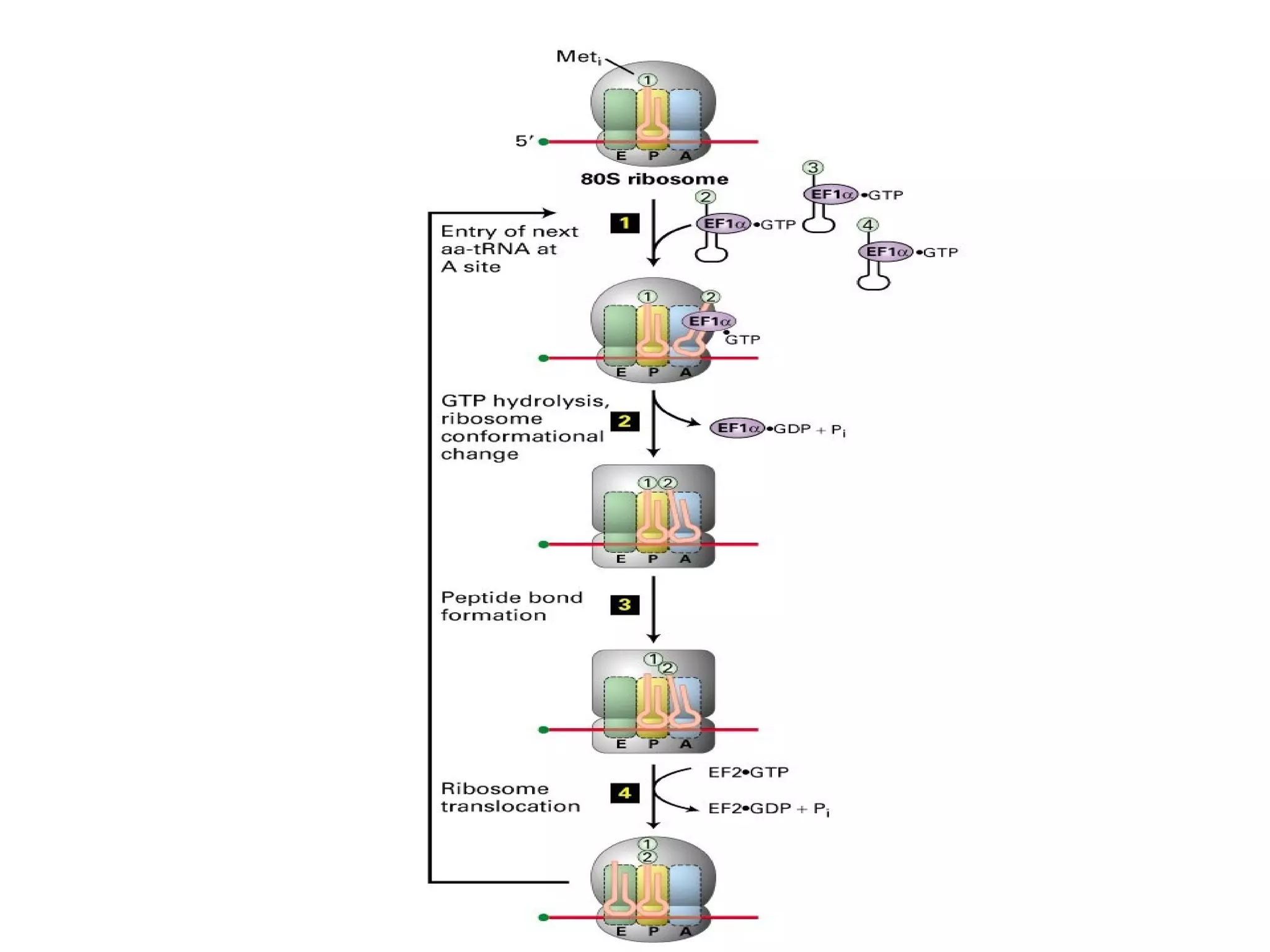
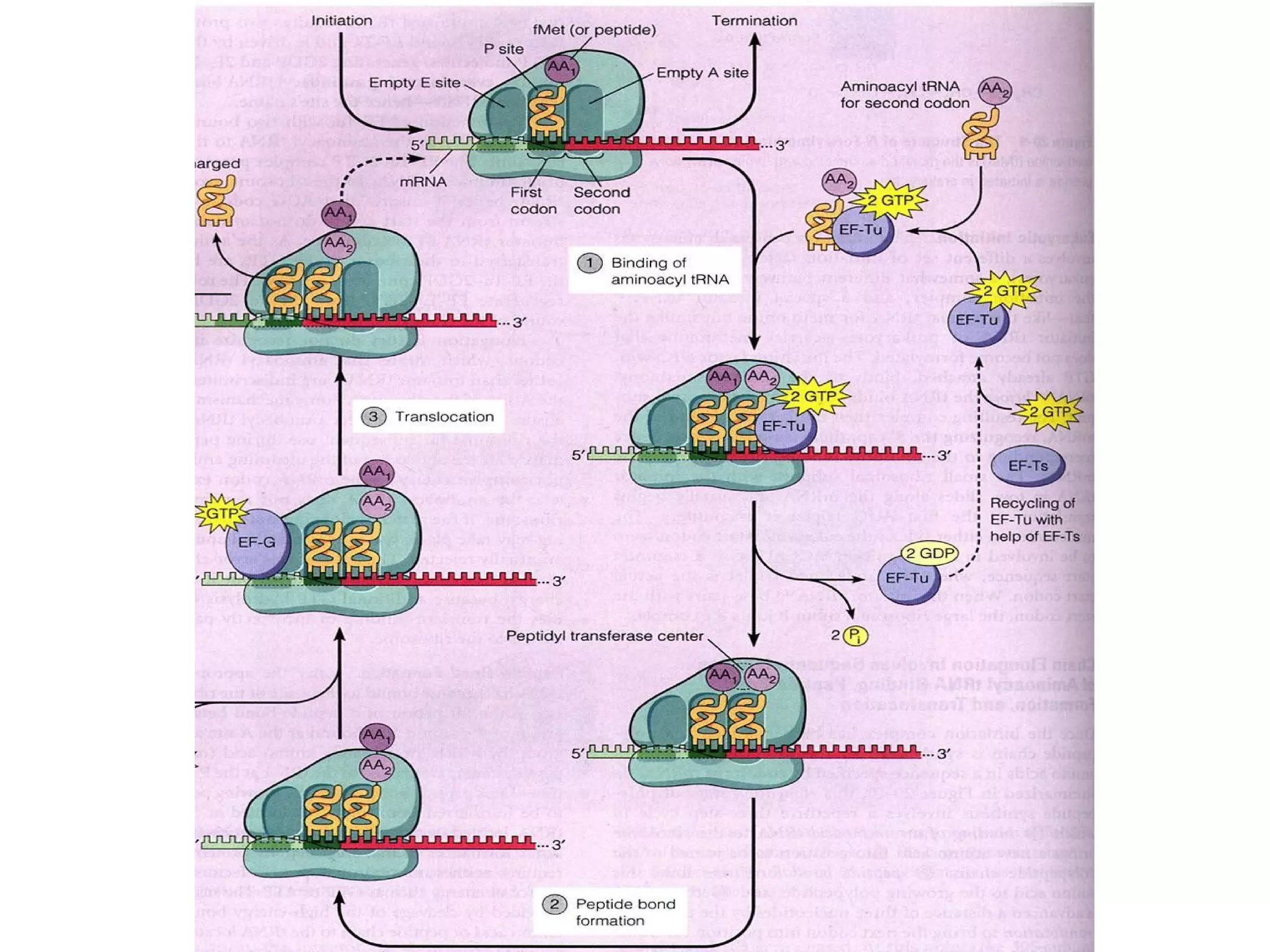
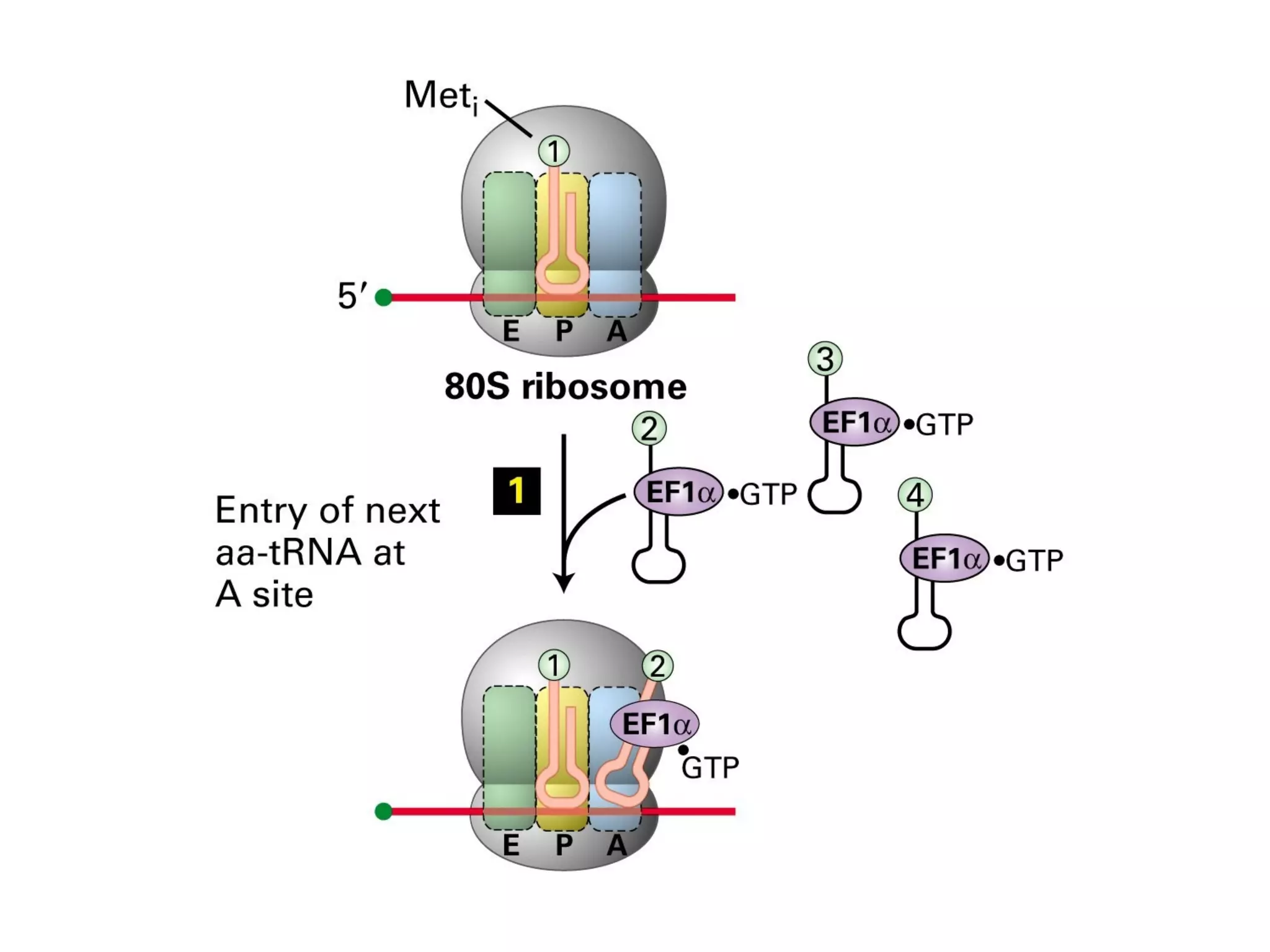
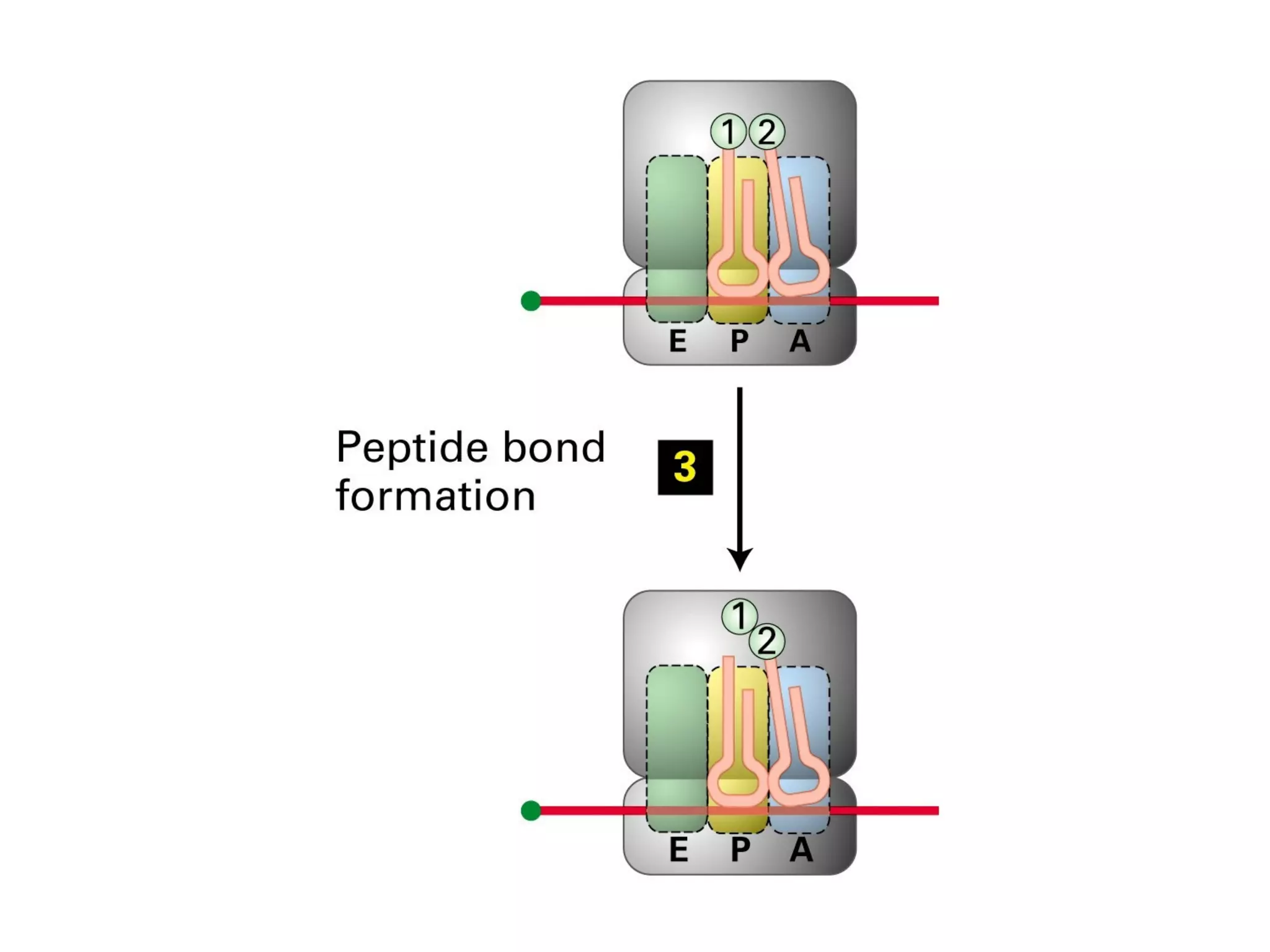
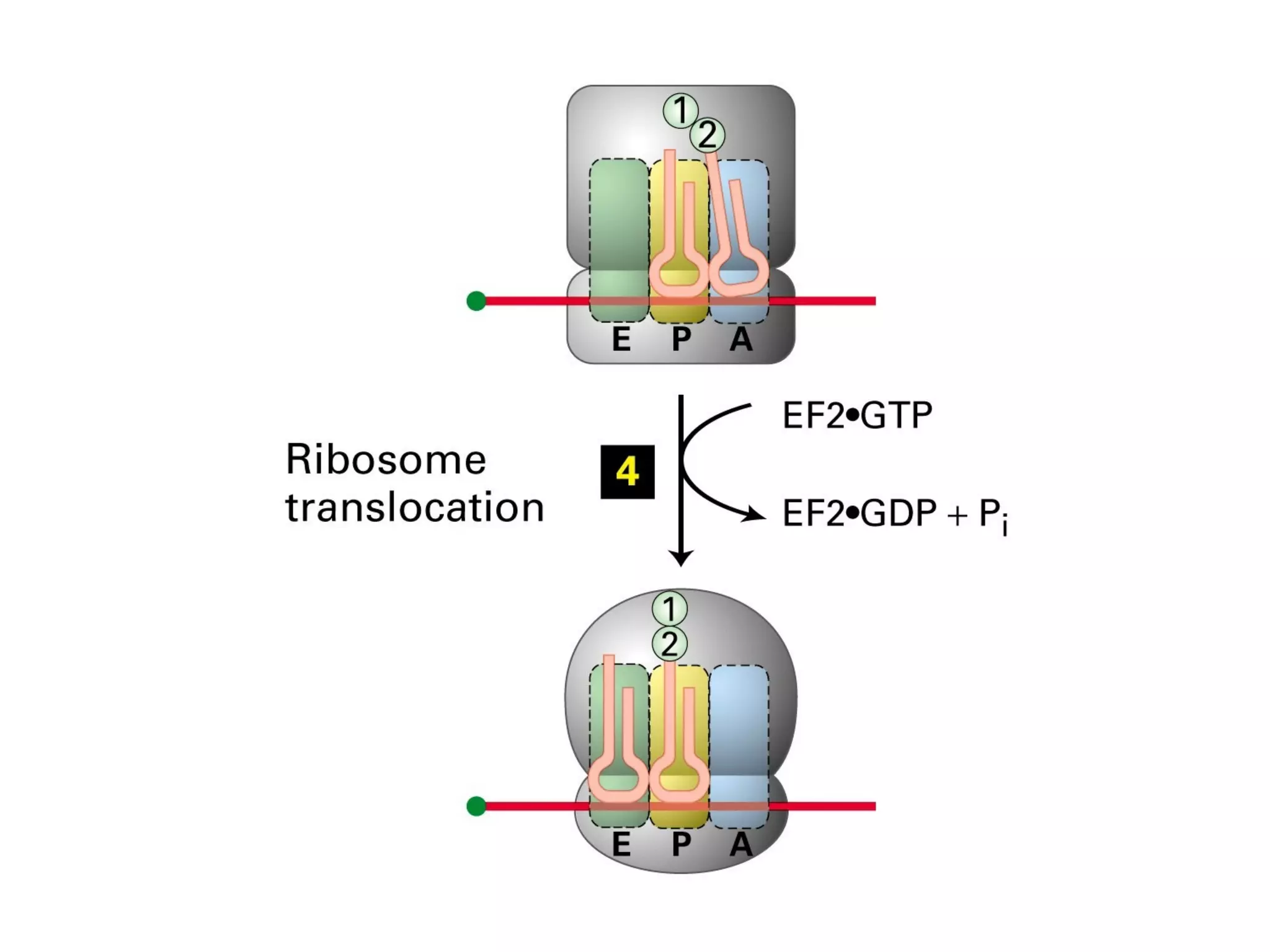
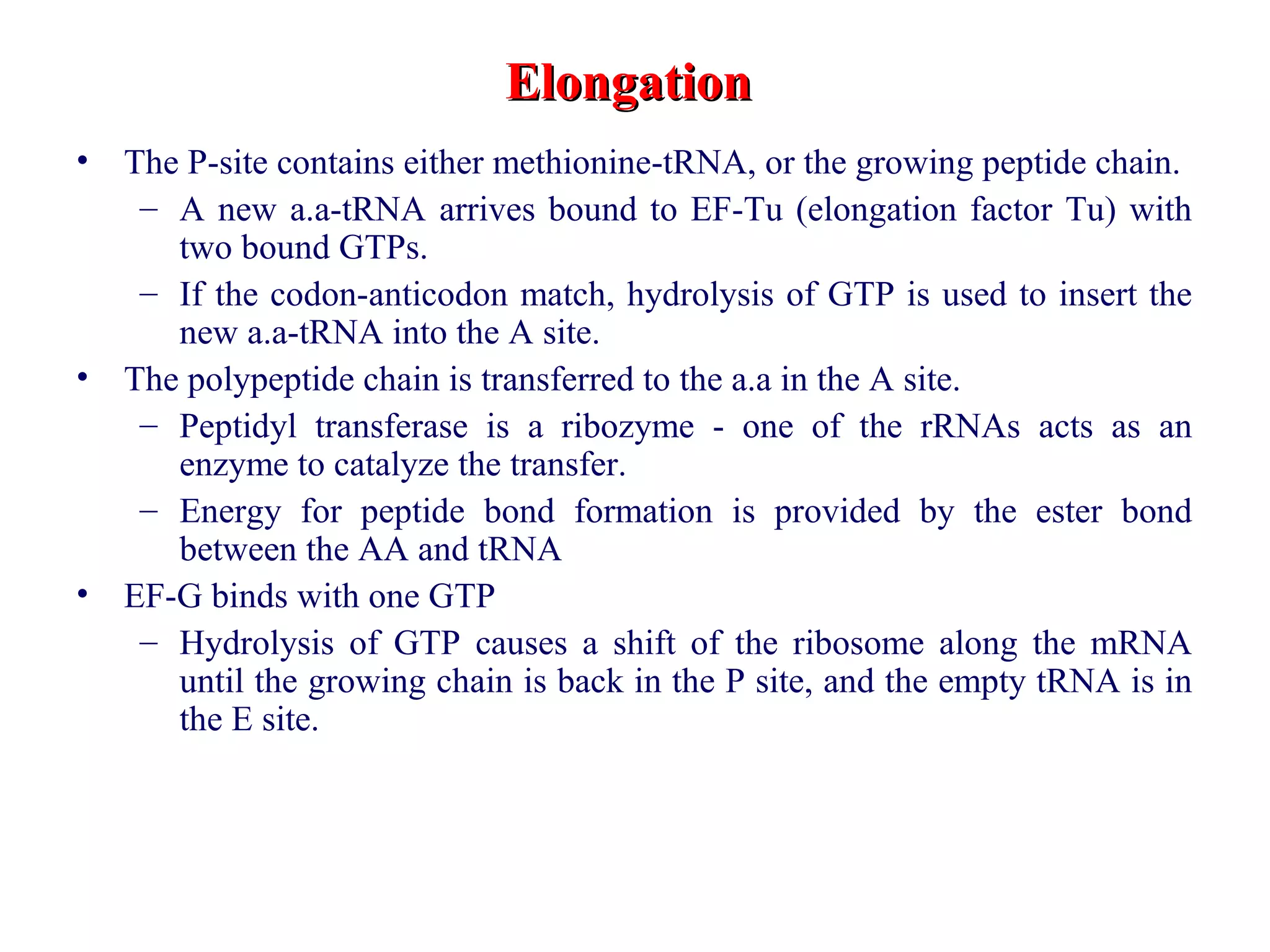
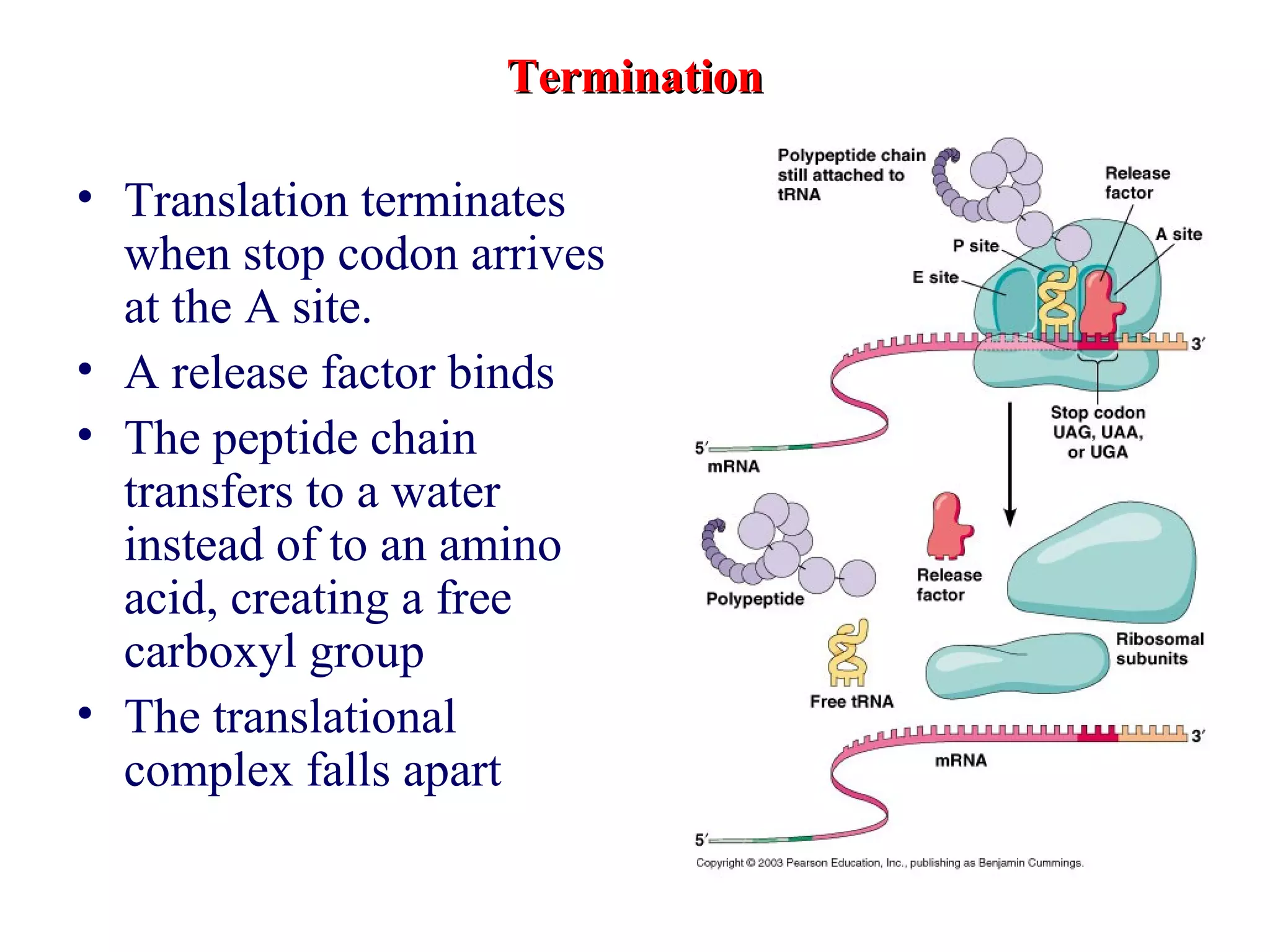
Translation is the process of using mRNA codons to synthesize proteins through ribosomes, utilizing tRNA and aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases to ensure accuracy in attaching the correct amino acids. The genetic code is nearly universal, consisting of 64 codons with specific roles, including 3 stop codons, and features such as redundancy and the wobble hypothesis. Translation occurs in initiation, elongation, and termination stages, with polypeptides often undergoing post-translational modifications for proper functioning.