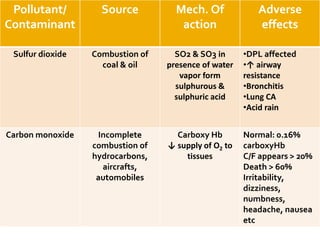
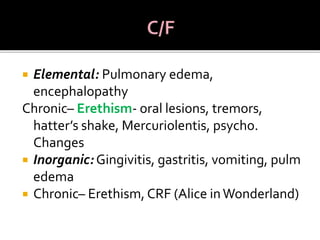
The document outlines various air pollutants and their harmful effects on human health and the environment, including sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen dioxide, detailing their sources and mechanisms of action. It also discusses the impact of heavy metals like lead and mercury, highlighting the health risks associated with exposure and poisoning. Additionally, the document addresses both acute and chronic health issues resulting from exposure to these pollutants.