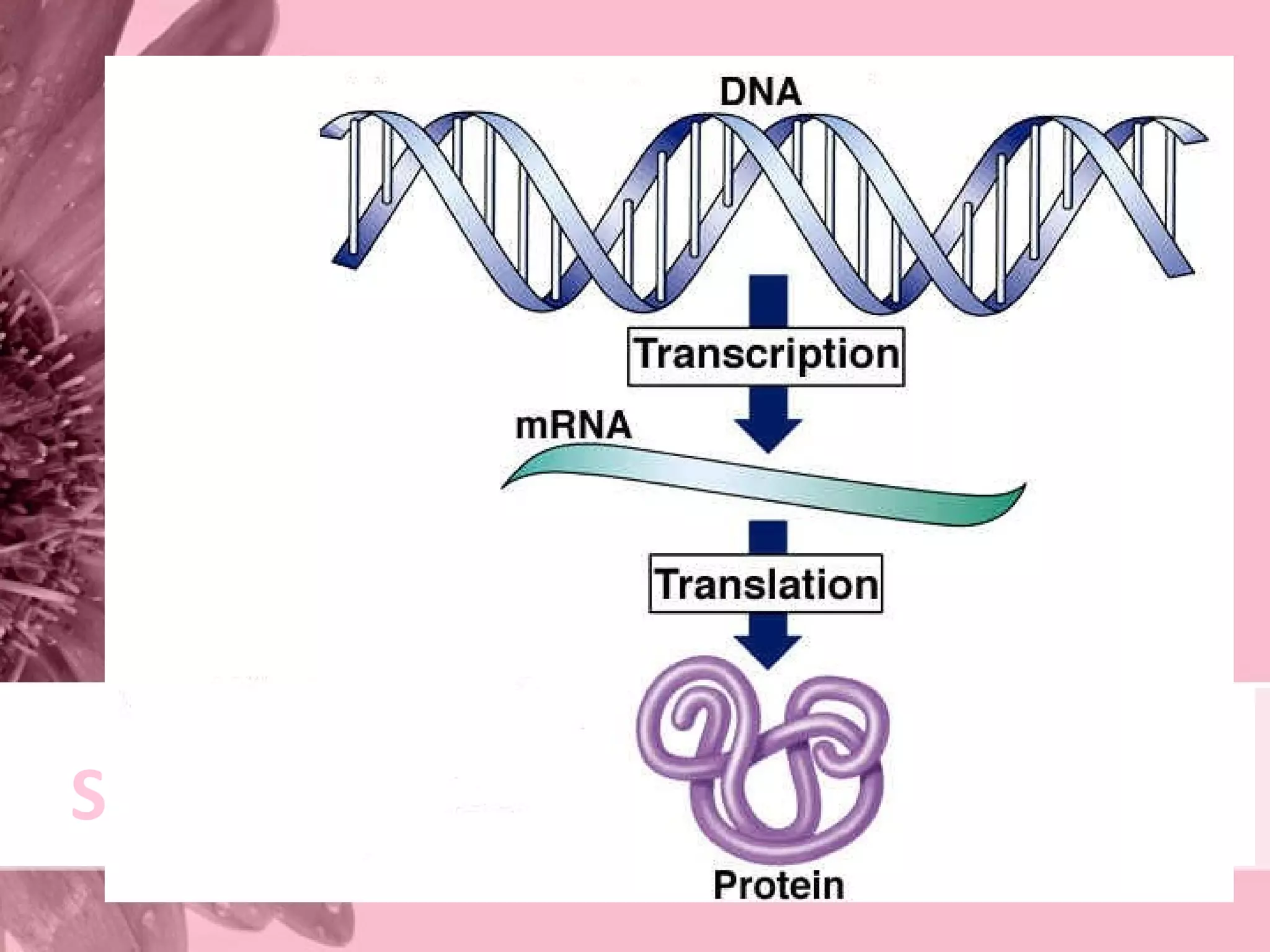
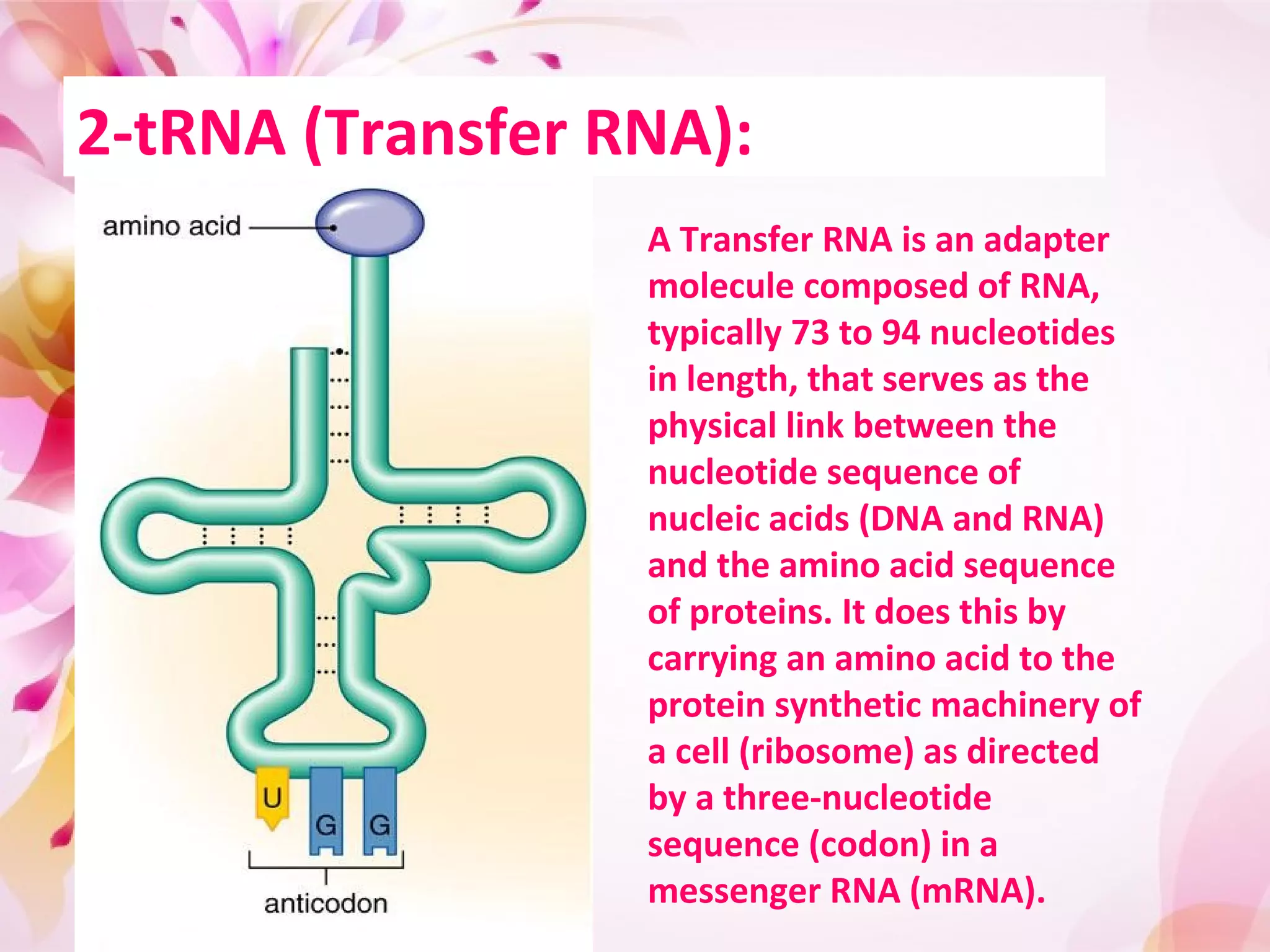
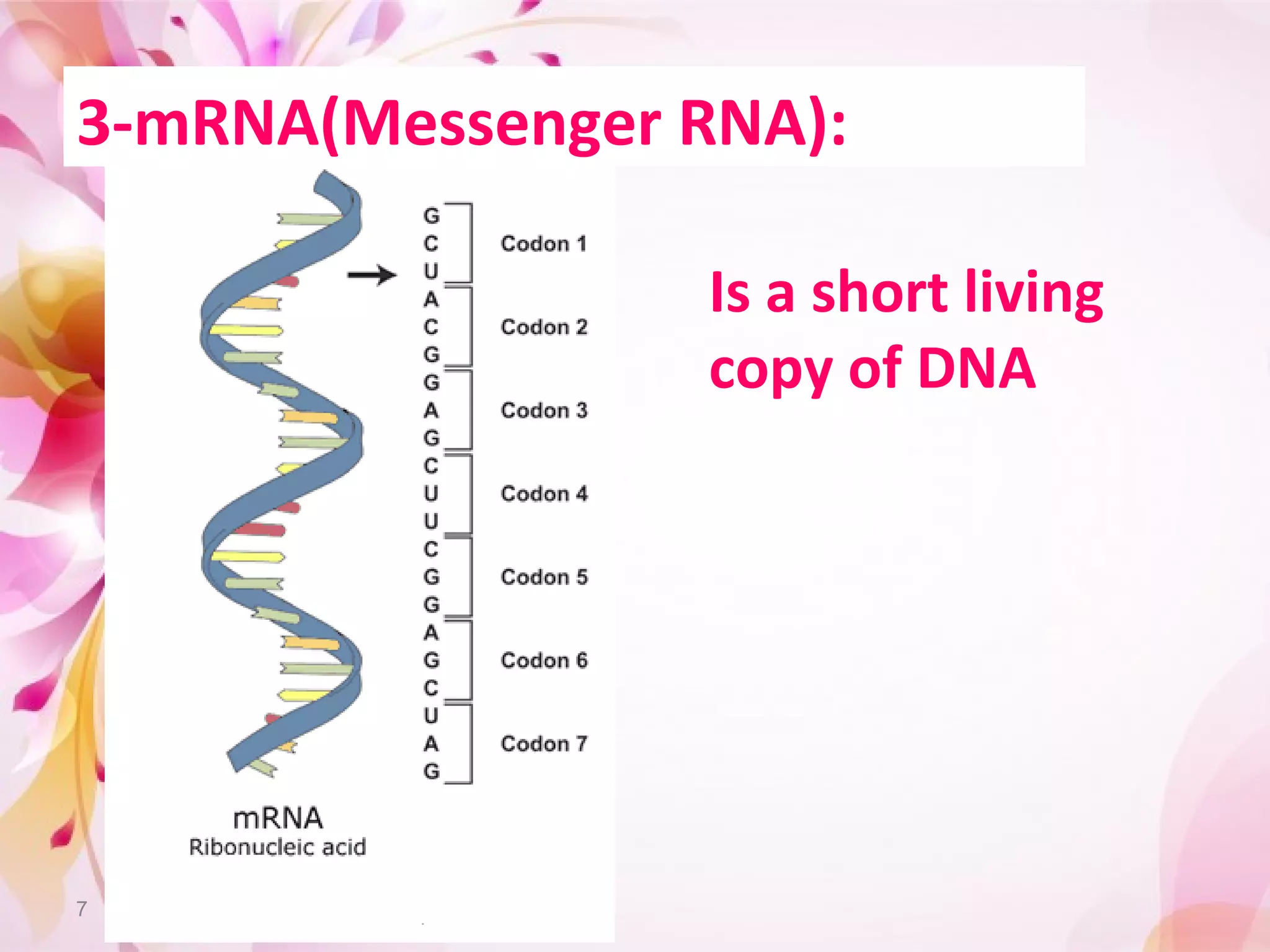
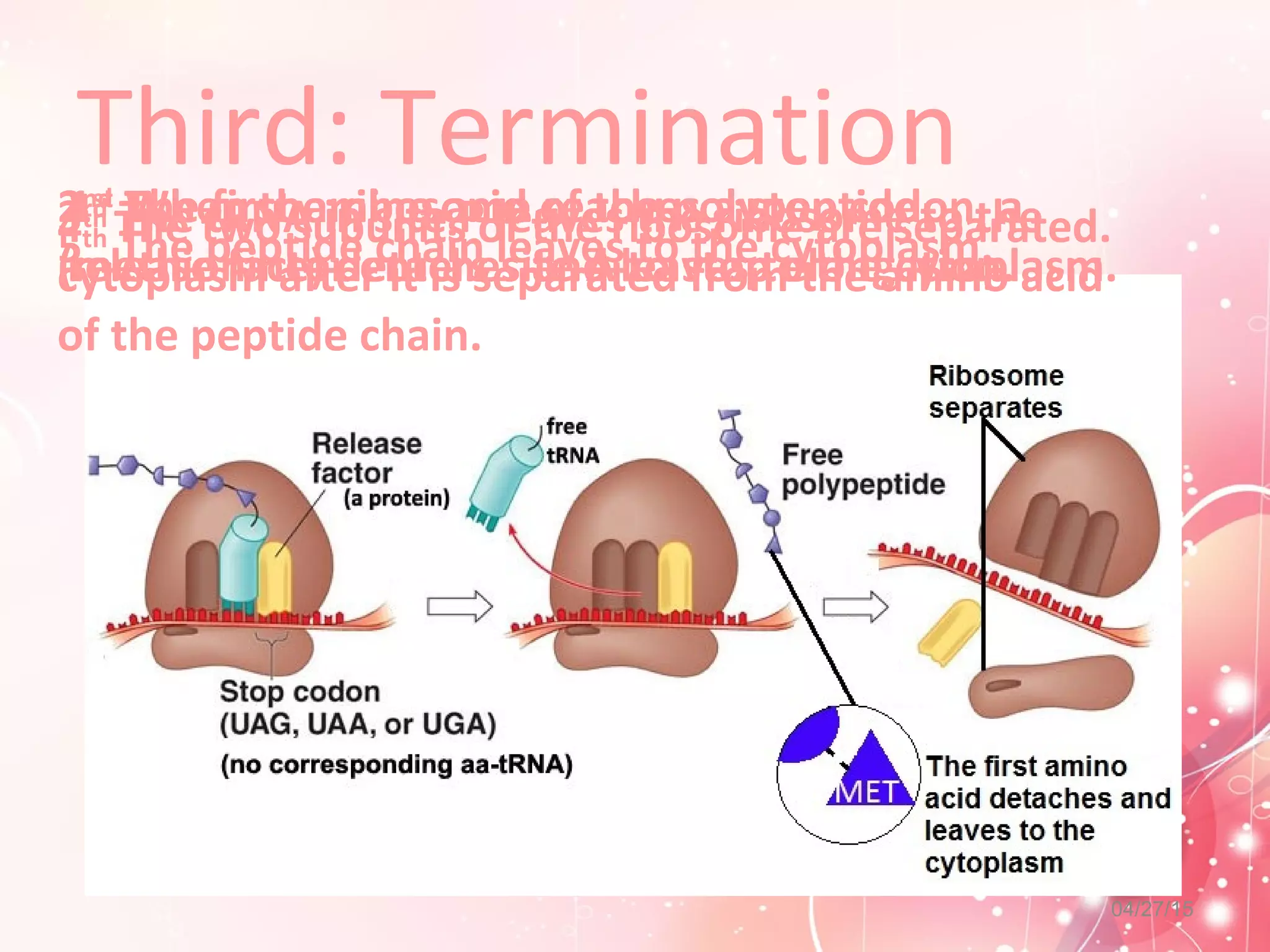
Translation is the process by which ribosomes synthesize proteins using messenger RNA (mRNA) as instructions. It occurs in the cytoplasm and involves transfer RNA (tRNA) carrying amino acids to the ribosome based on mRNA codons. The main steps are initiation, elongation, and termination. Initiation involves a start codon binding to tRNA and methionine. Elongation adds amino acids through peptide bonds between tRNA molecules. Termination releases the full protein when a stop codon is reached. The ribosome, tRNA, mRNA, and ATP provide the tools for translation to convert genetic code into functional proteins.