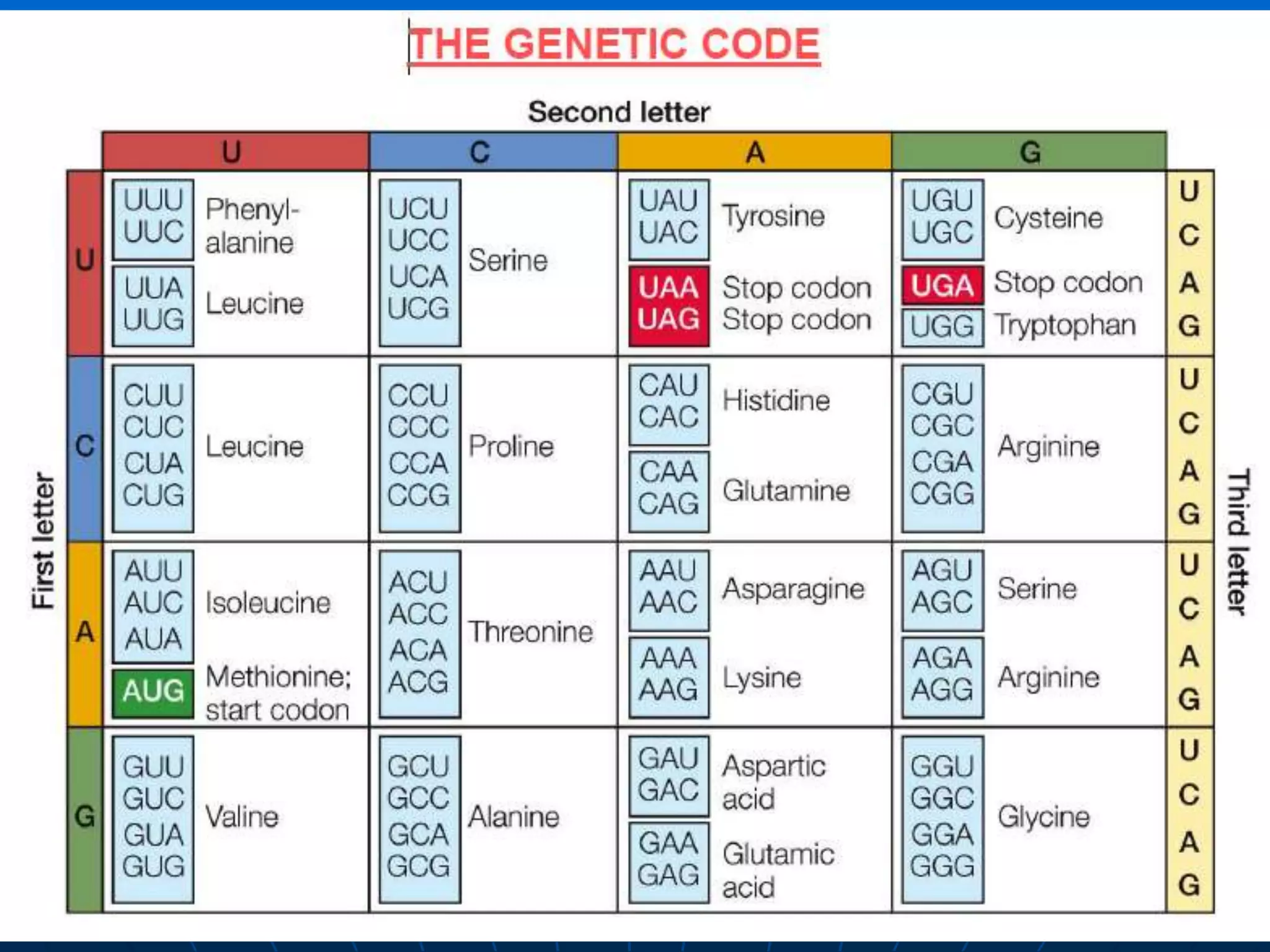
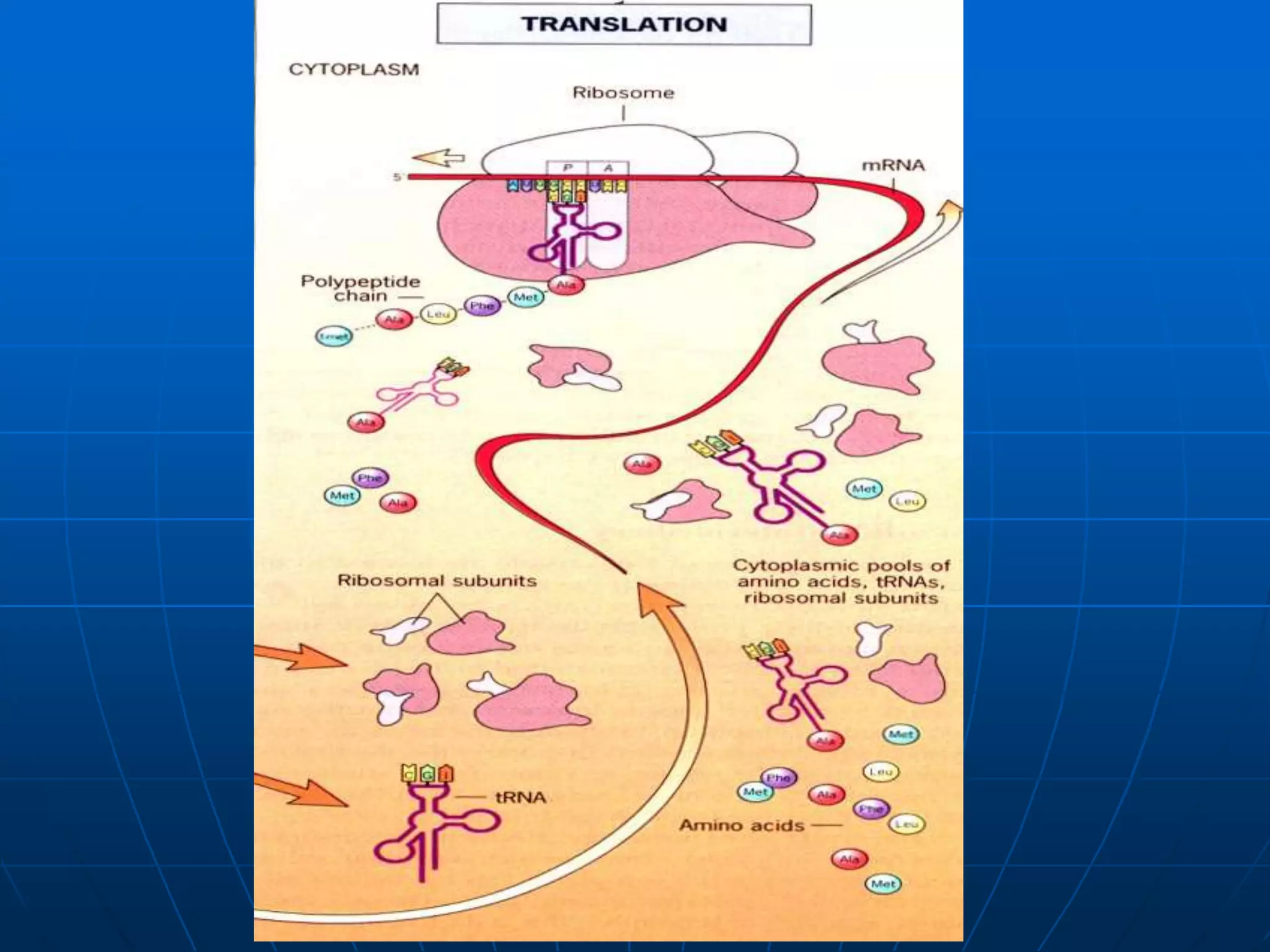
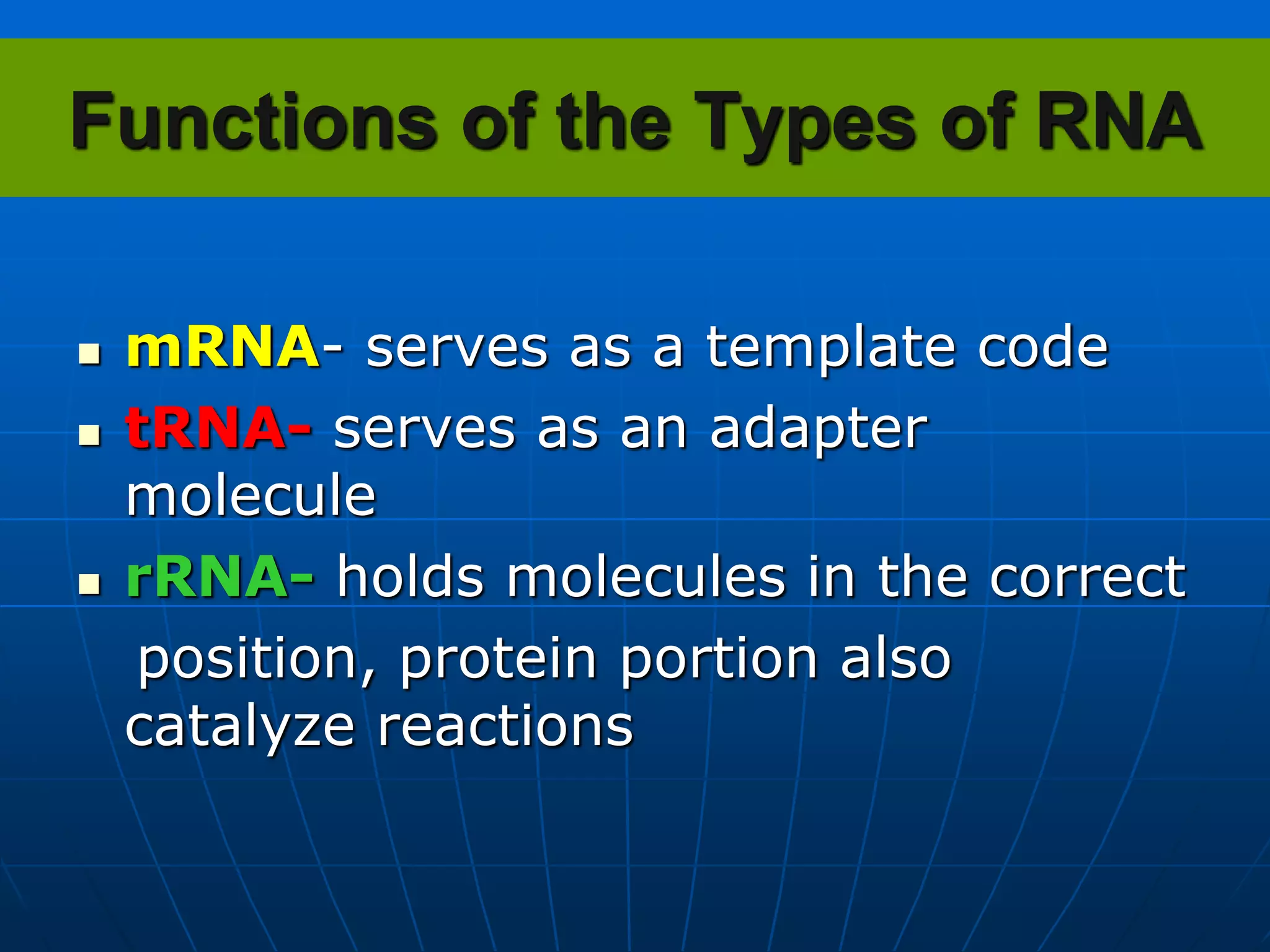
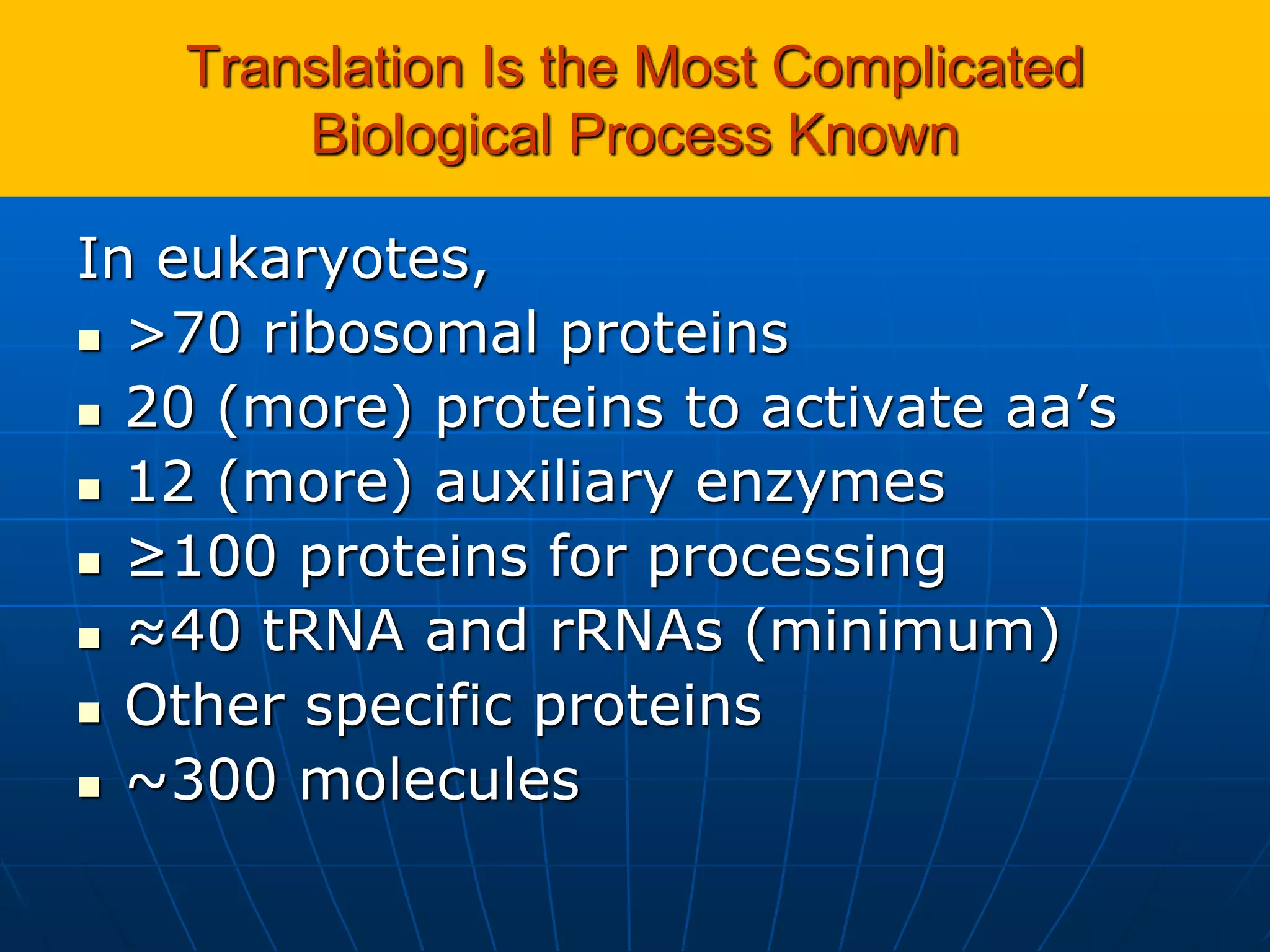
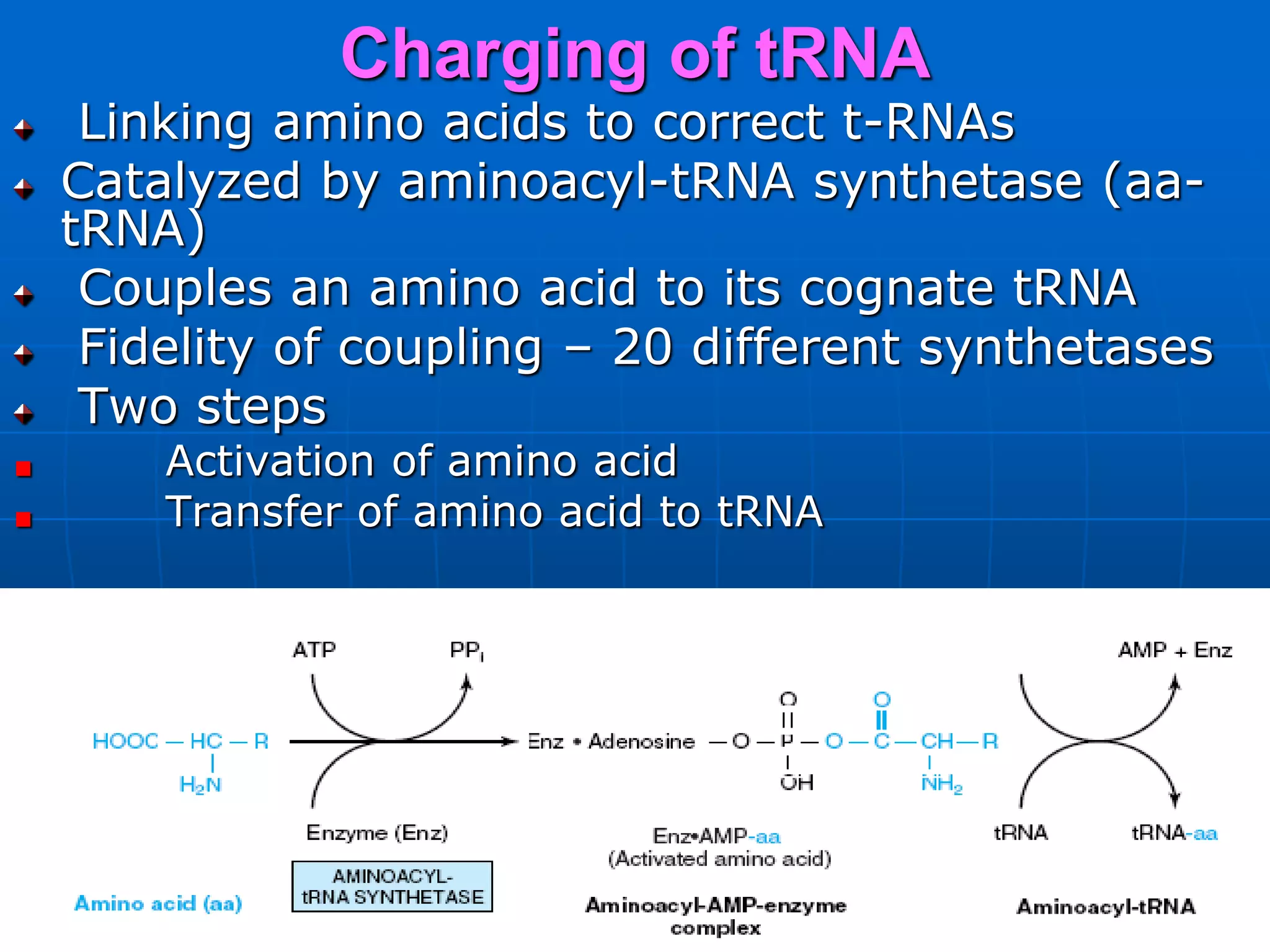
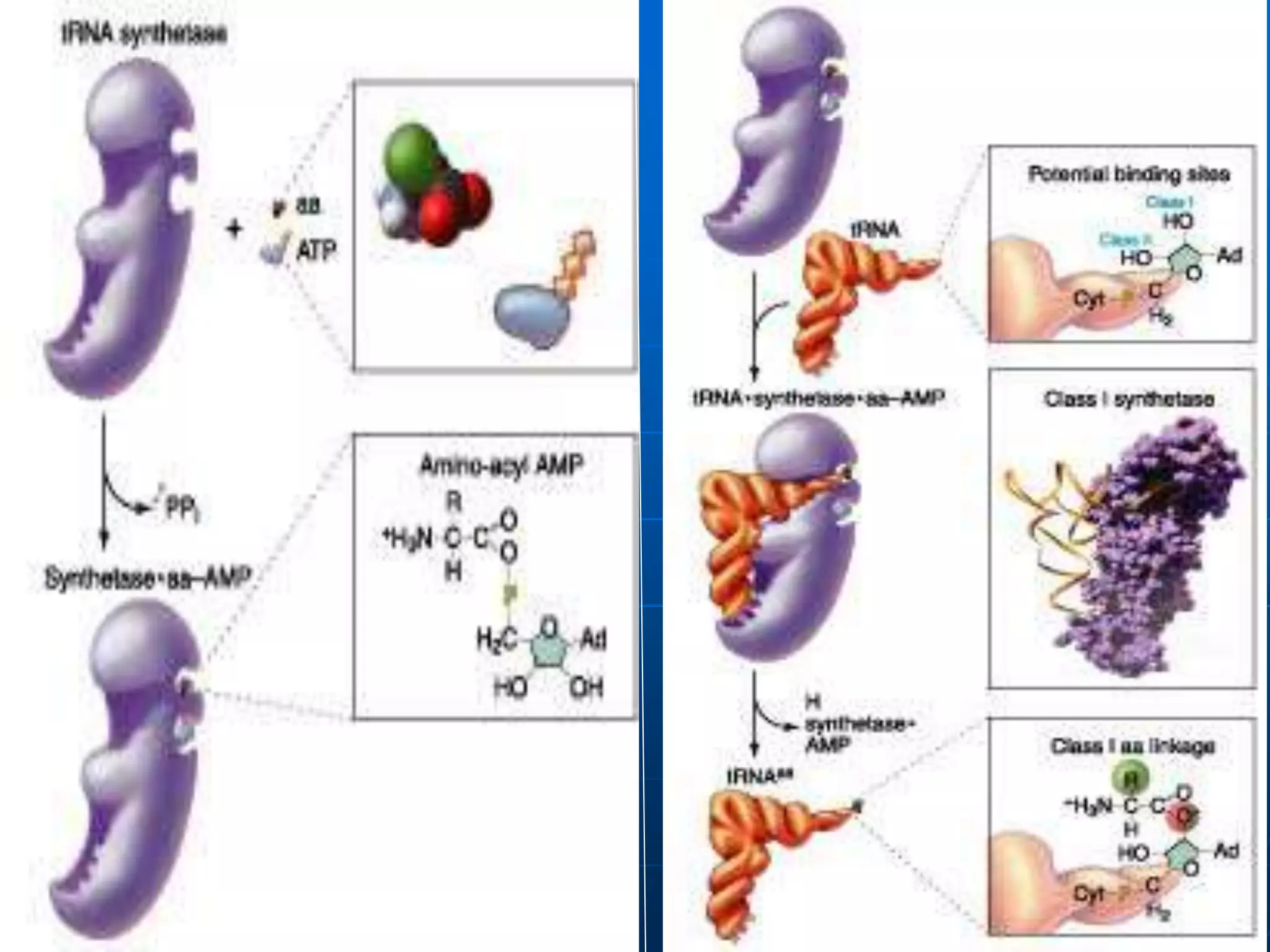
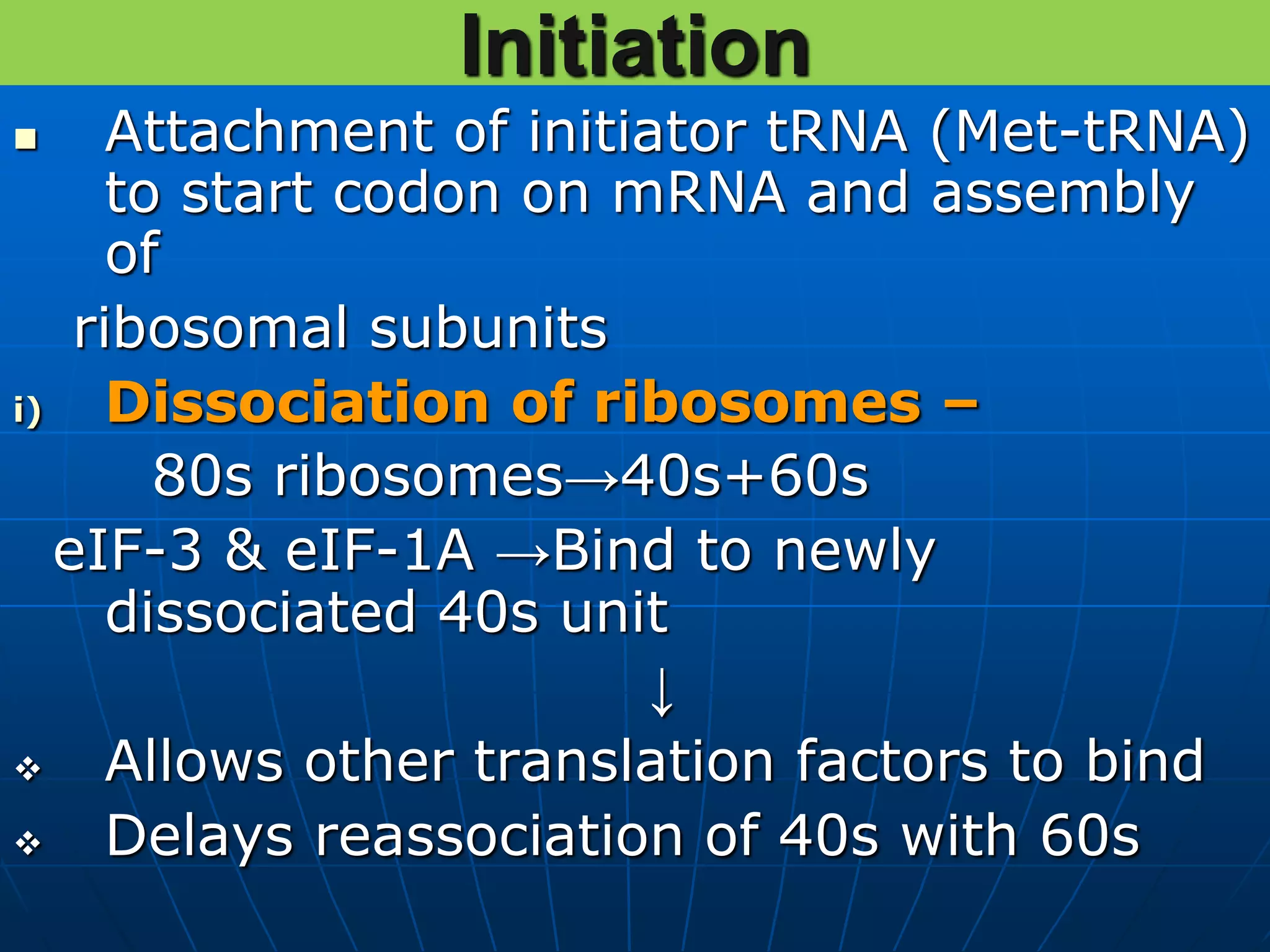
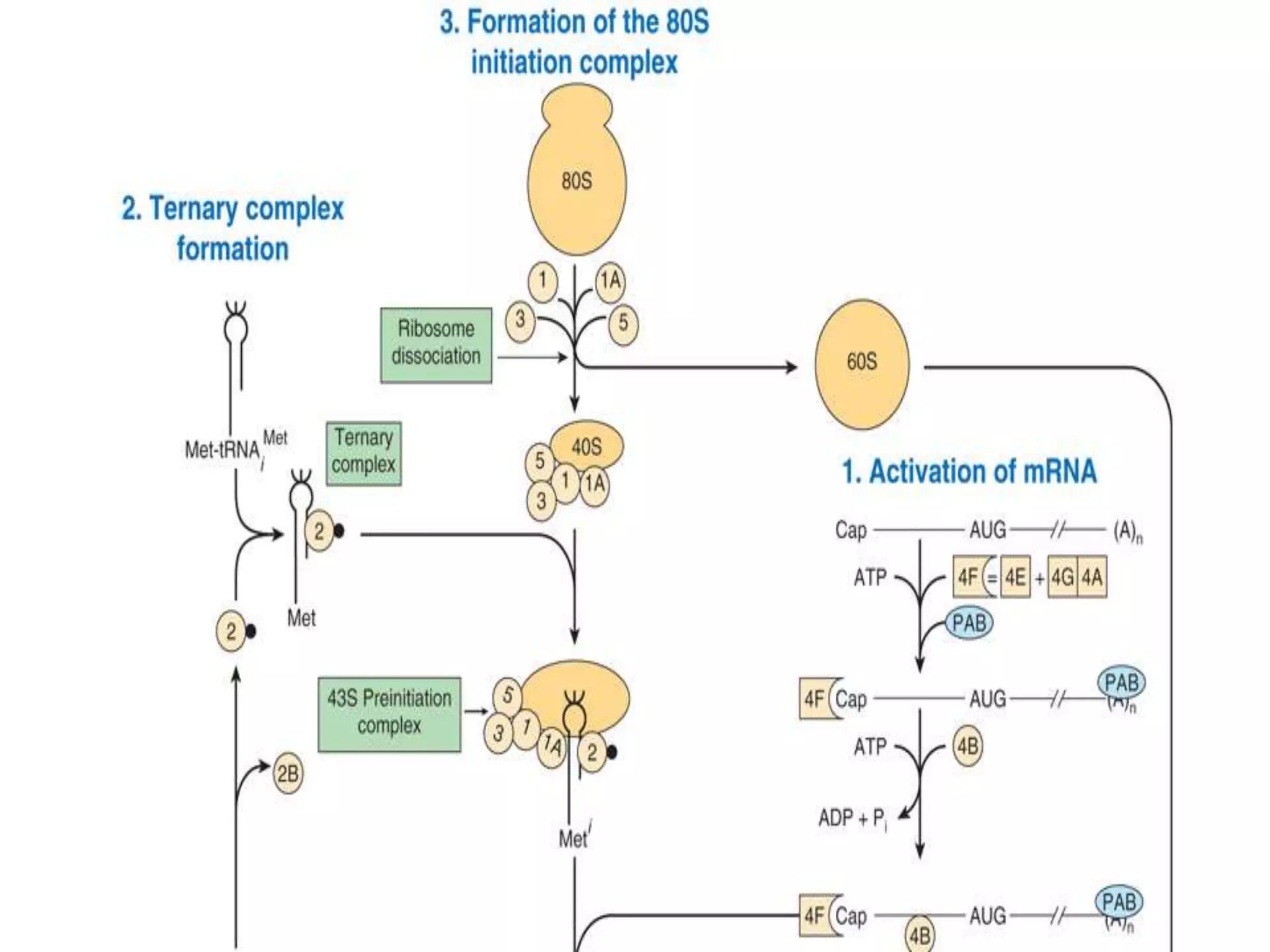
The document provides information on the genetic code and the process of translation. It defines the genetic code as the system of nucleotide sequences that designate amino acid sequences during translation. There are 3 key points:
1. The genetic code is universal, with some minor exceptions, where certain codons code for different amino acids in bacteria and mitochondrial DNA. It uses 64 possible triplet codon combinations of A, C, G, and U nucleotides to specify 20 amino acids.
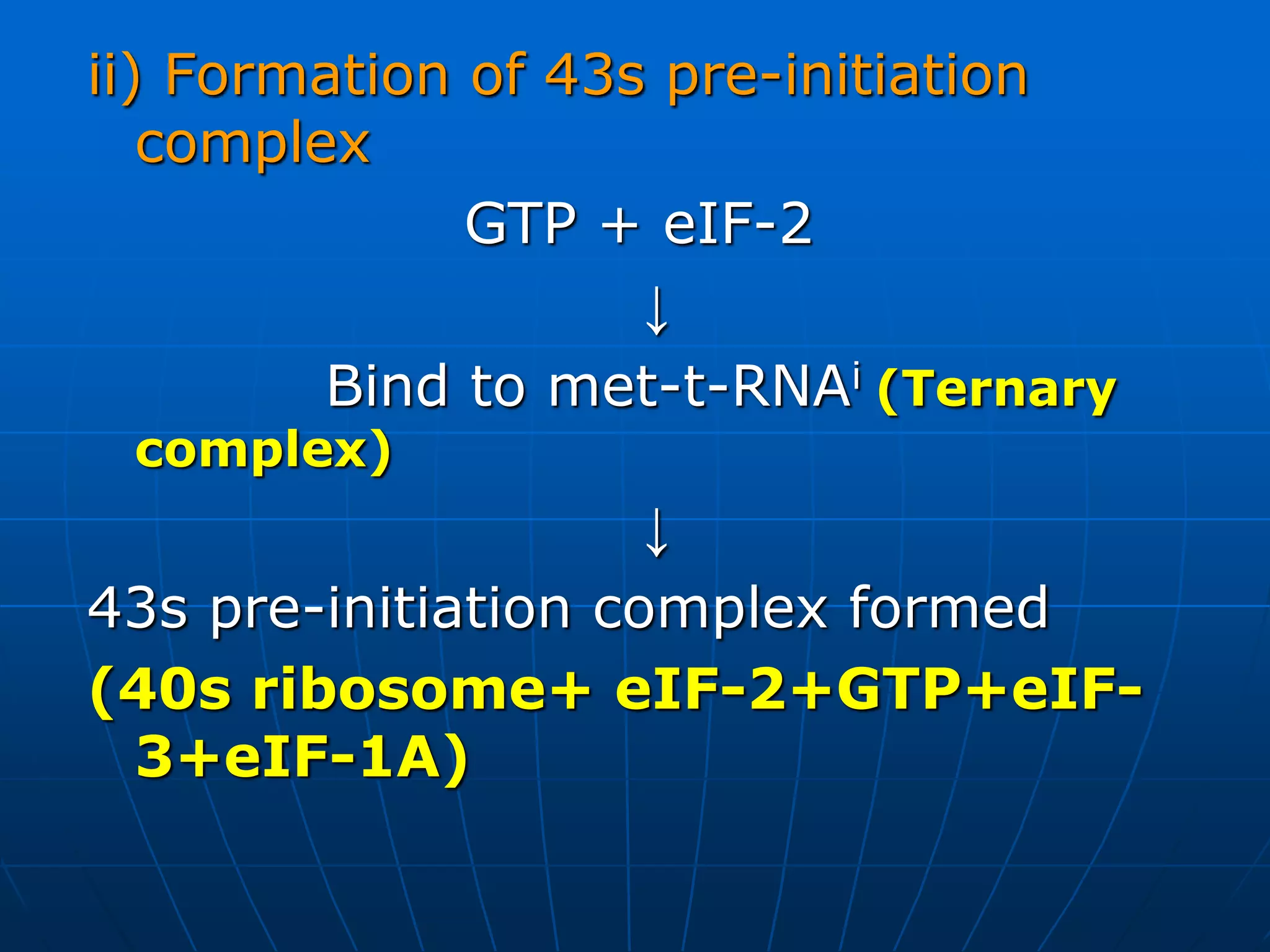
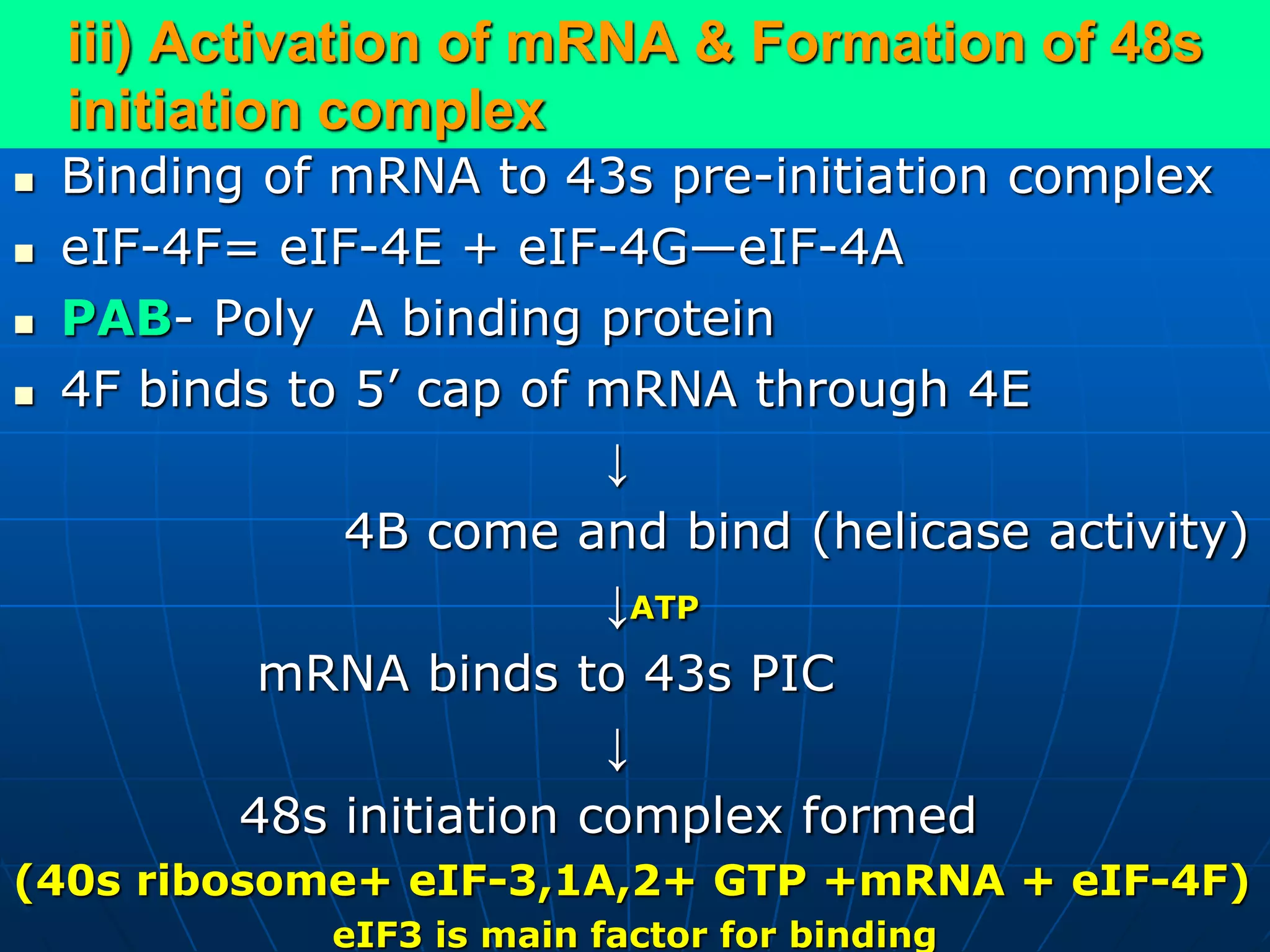
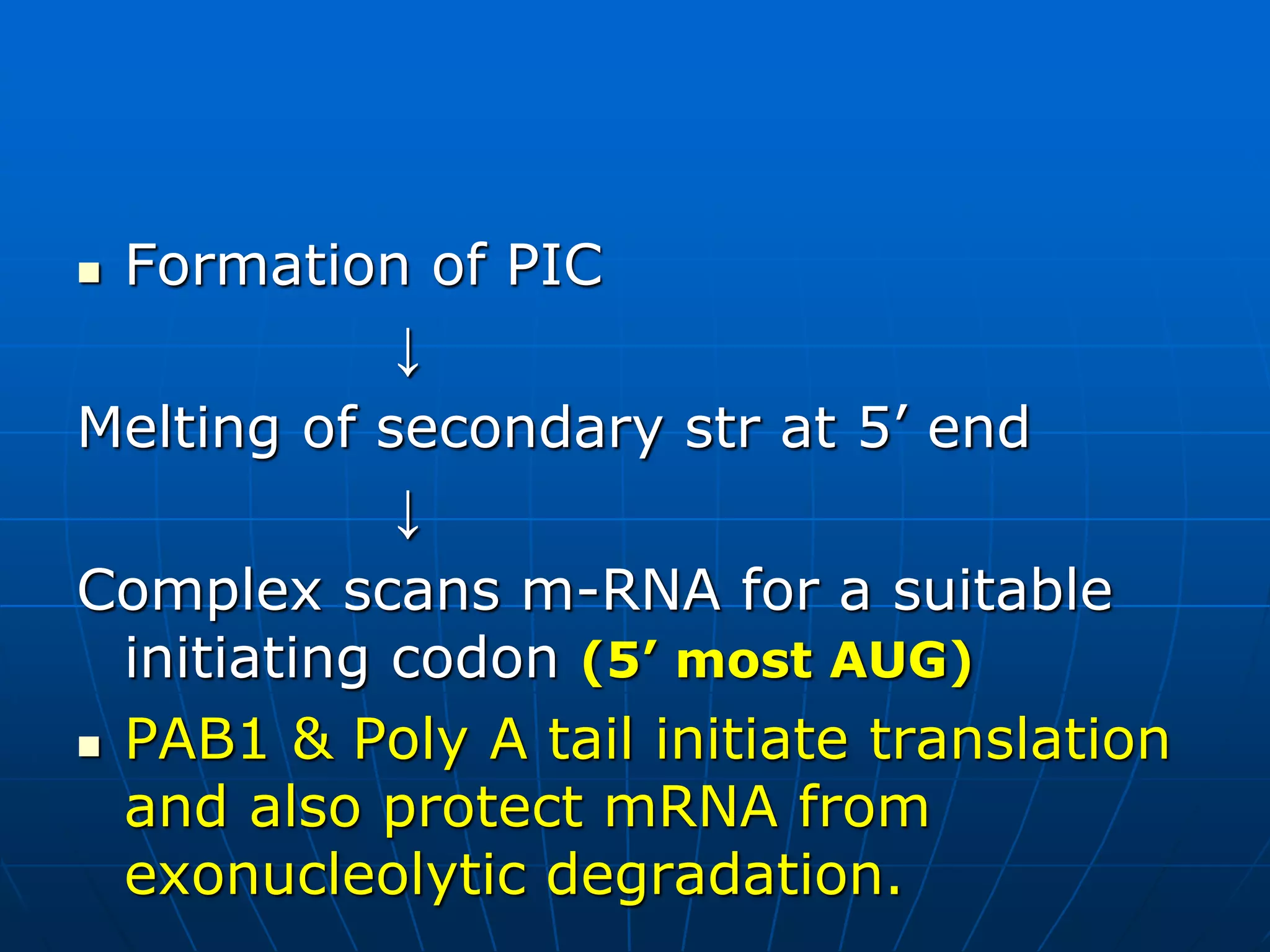
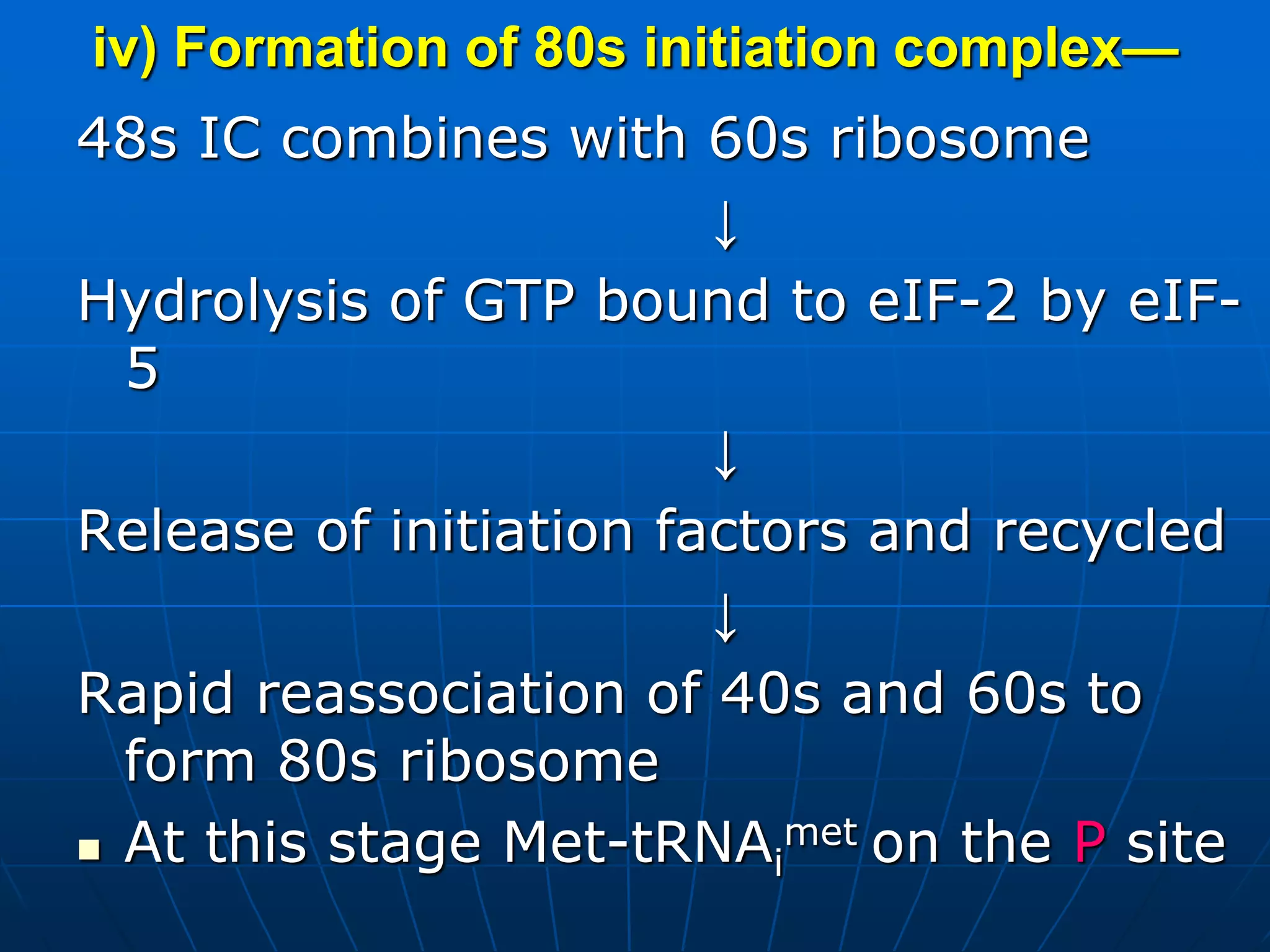
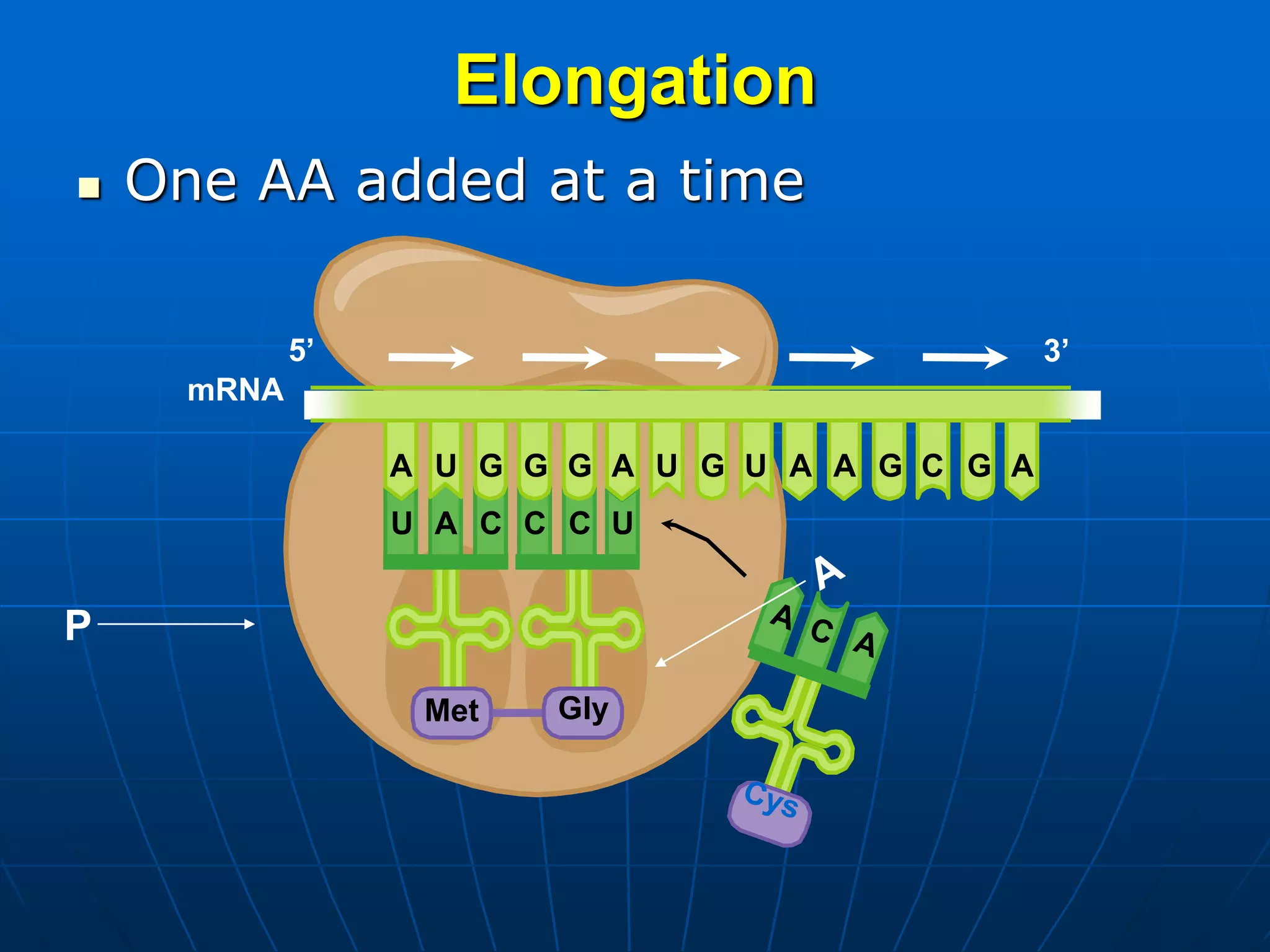
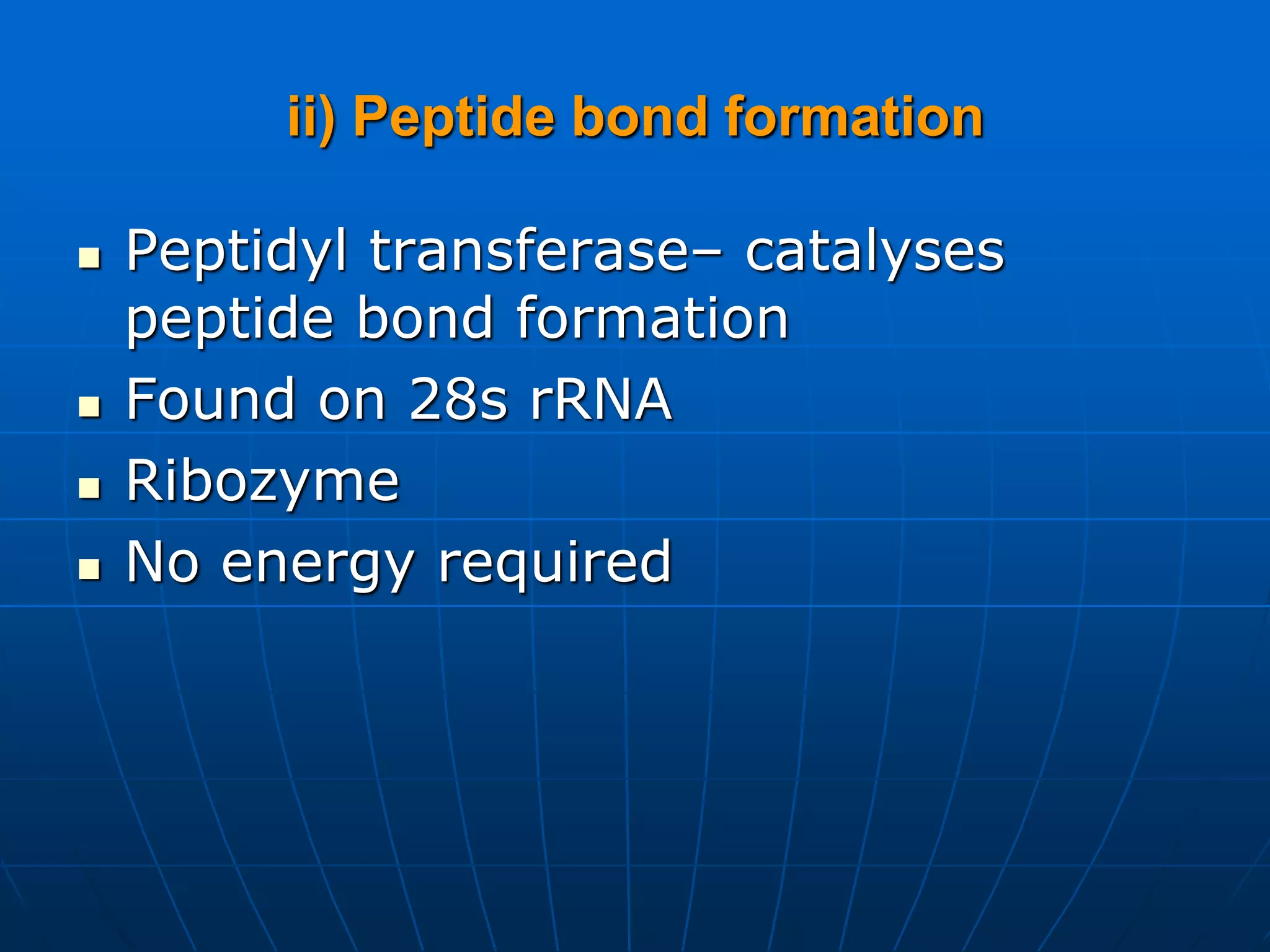
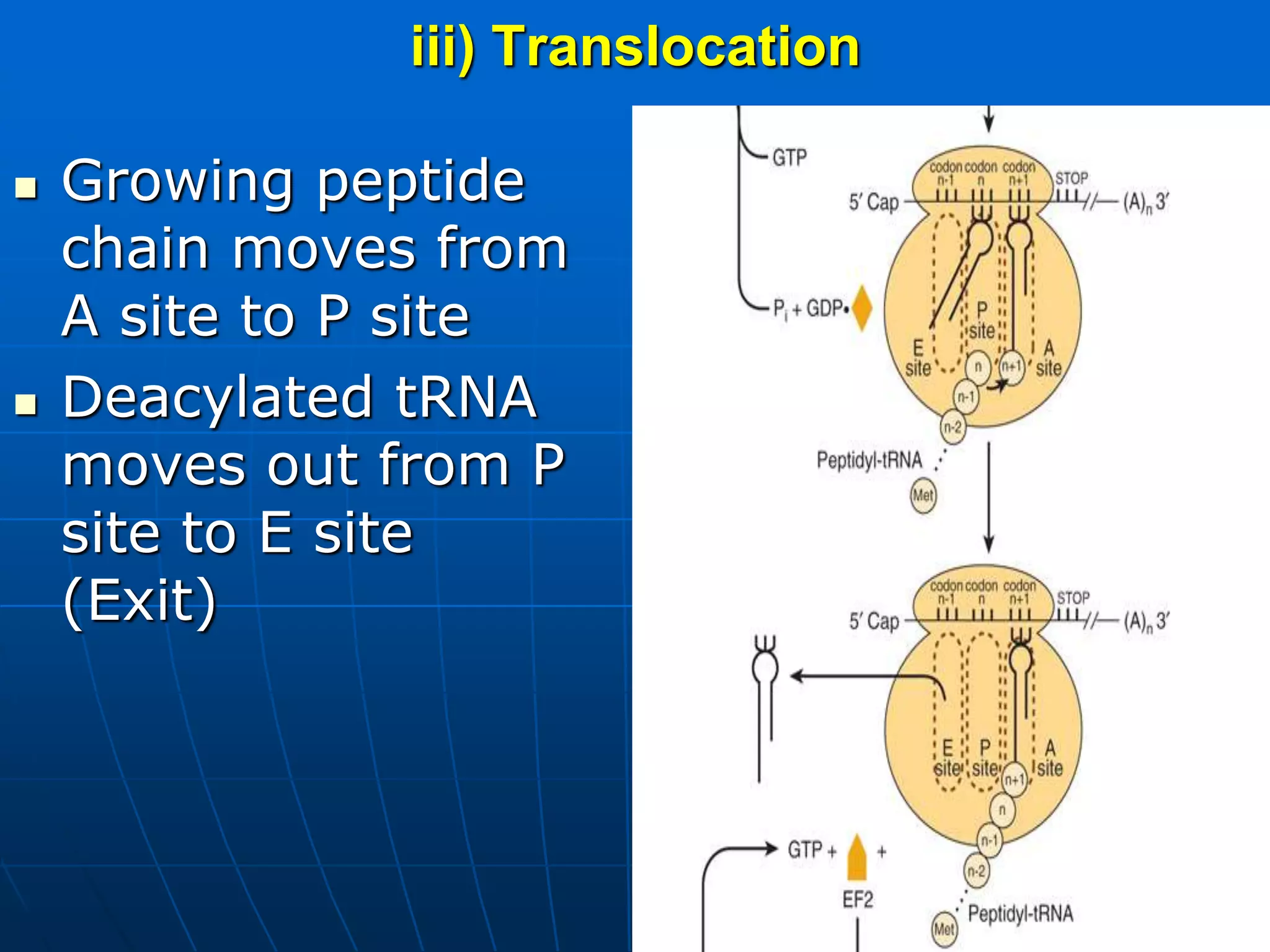
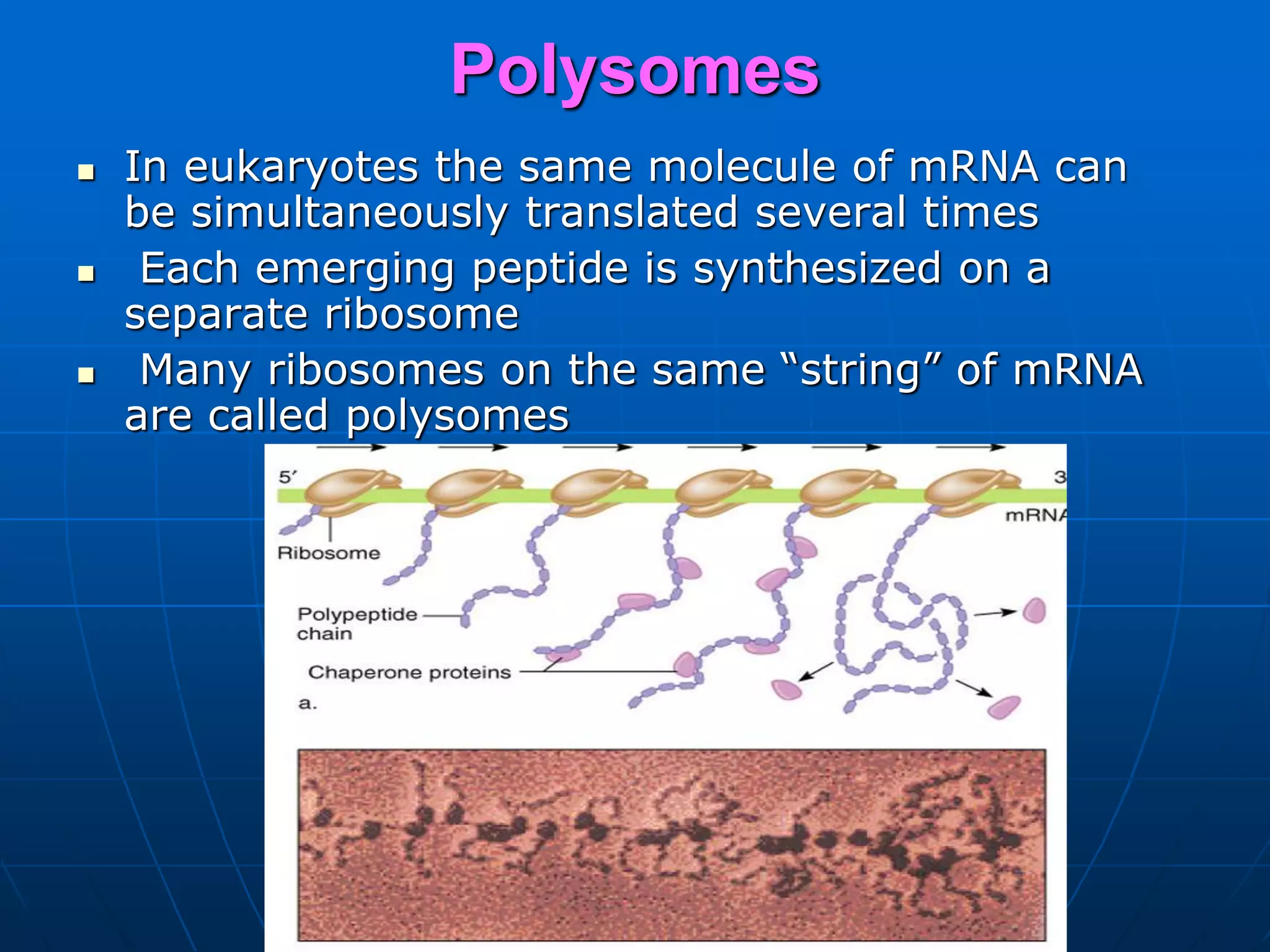
2. Translation is the process by which the genetic code is read to produce proteins. It occurs via five stages - initiation, elongation, termination, and post-translational modification - involving messenger RNA, transfer RNA, ribosomes and other factors.
3