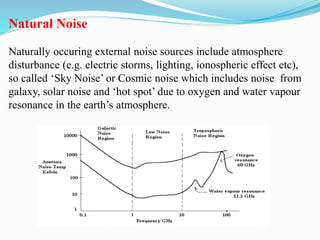
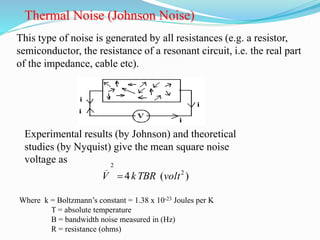
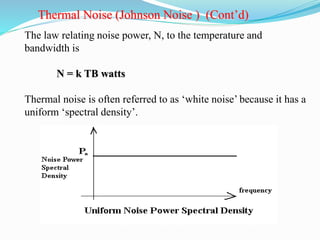
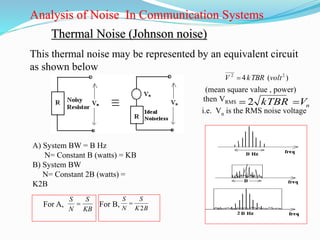
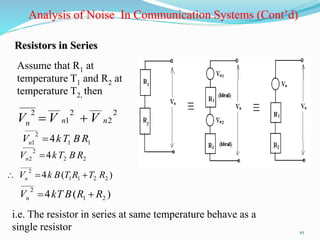
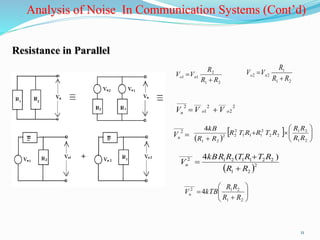
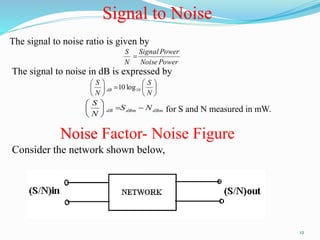
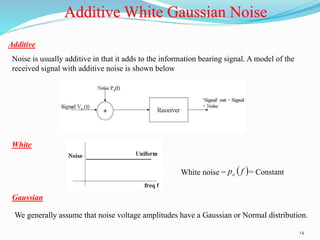
The document discusses different types of noise that affect communication systems, including thermal noise, shot noise, flicker noise, excess resistor noise, and popcorn noise. It provides details on thermal noise generation and its relation to temperature and resistance. The analysis section examines thermal noise in resistors in series and parallel and defines signal-to-noise ratio and noise factor. Additive white Gaussian noise is described as noise that is additive, has a constant spectral density (white), and has a Gaussian amplitude distribution.