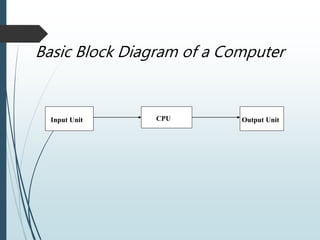
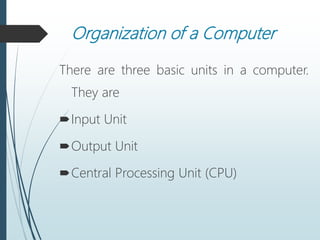
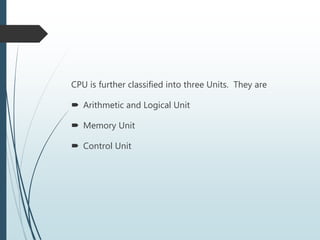
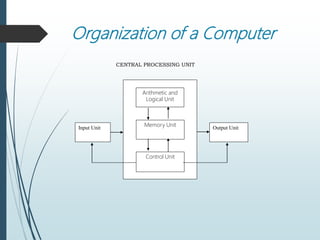
The document provides an overview of the basic organization of a computer, highlighting its three main components: the input unit, output unit, and central processing unit (CPU). It describes the functions of various units within the CPU, including the arithmetic and logical unit, memory unit, and control unit, along with details on main and auxiliary memory types. Key points include the characteristics of volatile (e.g., RAM) and non-volatile memory (e.g., ROM, auxiliary storage) and their roles in data processing.