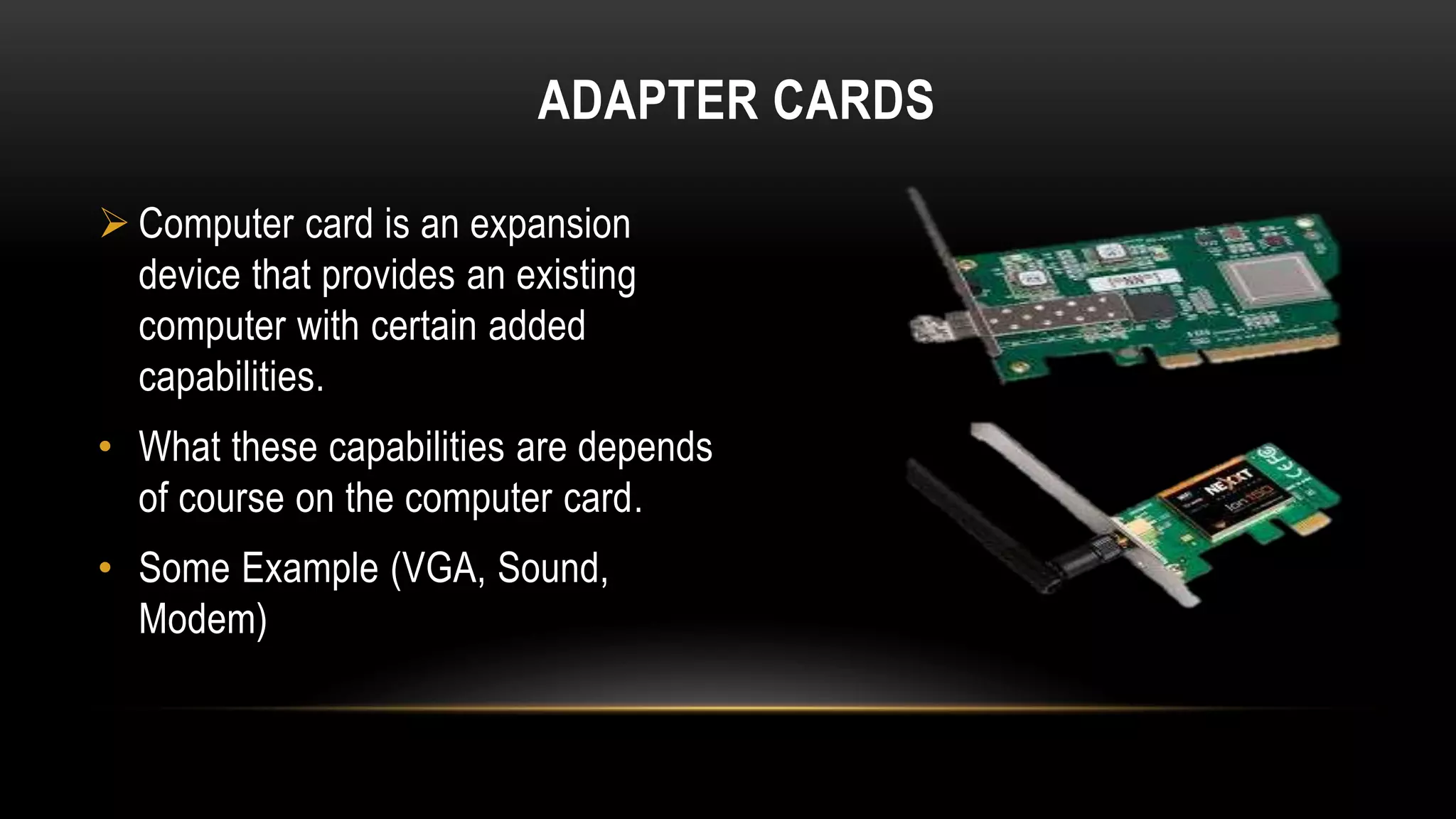
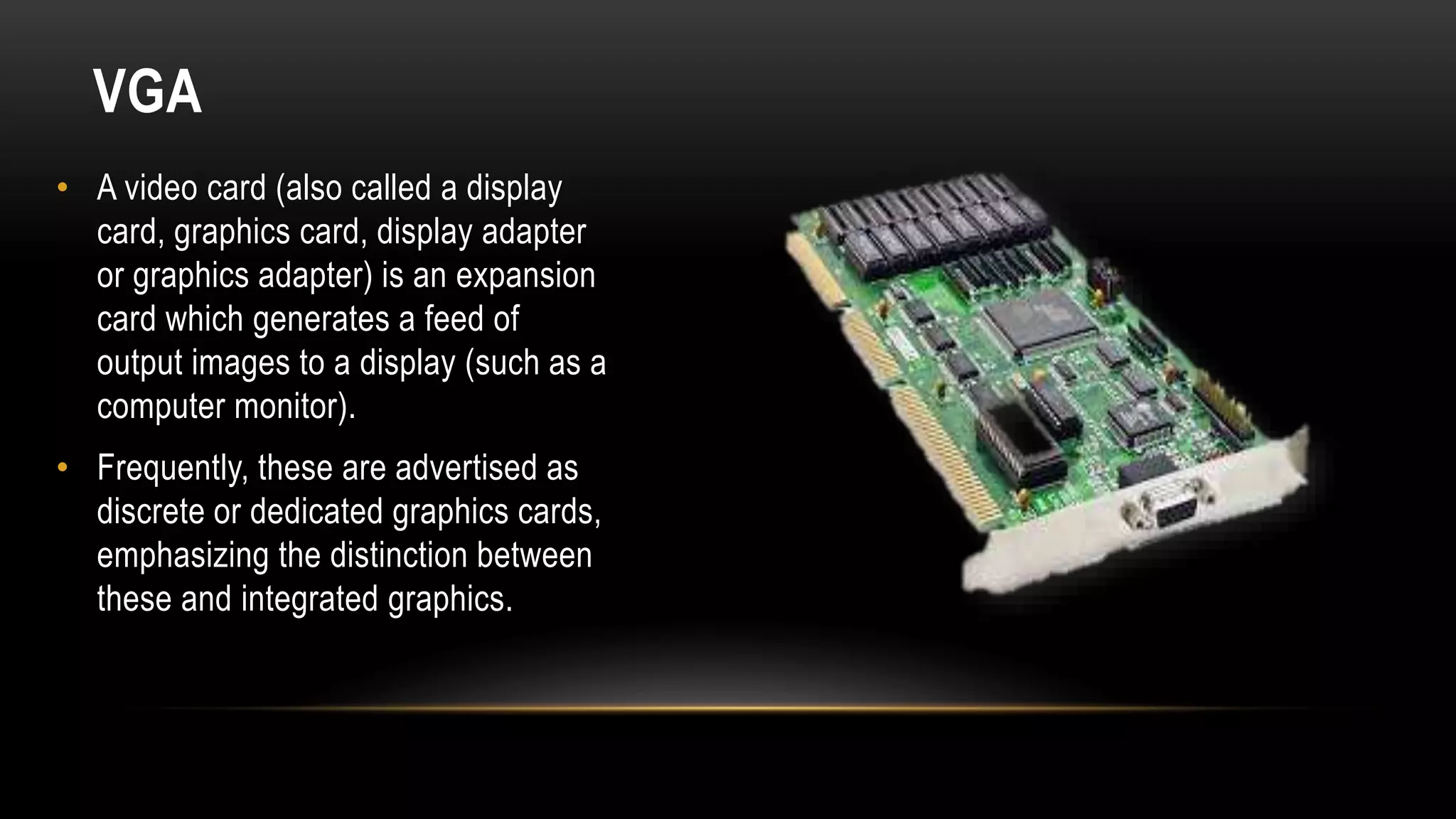
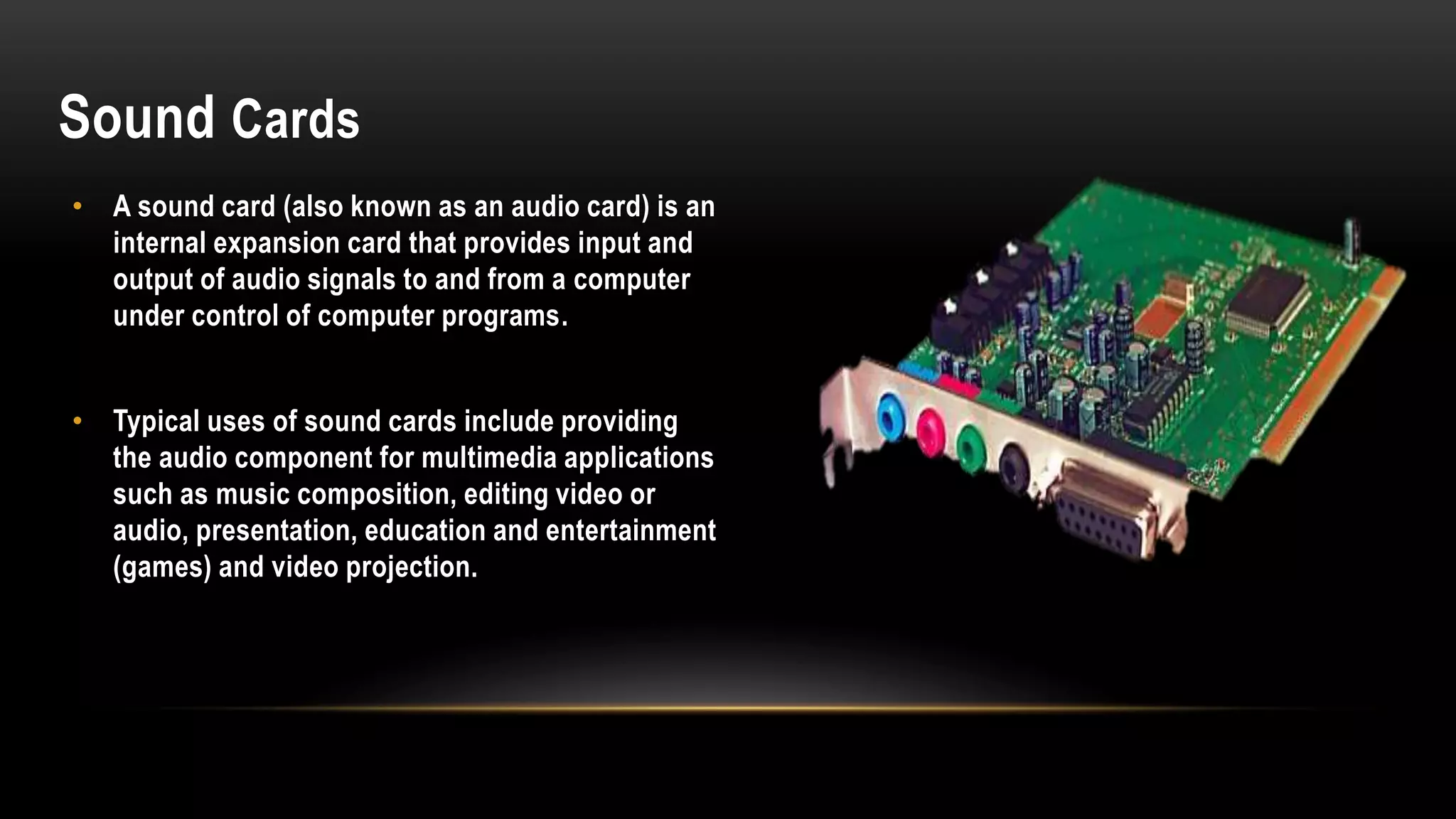
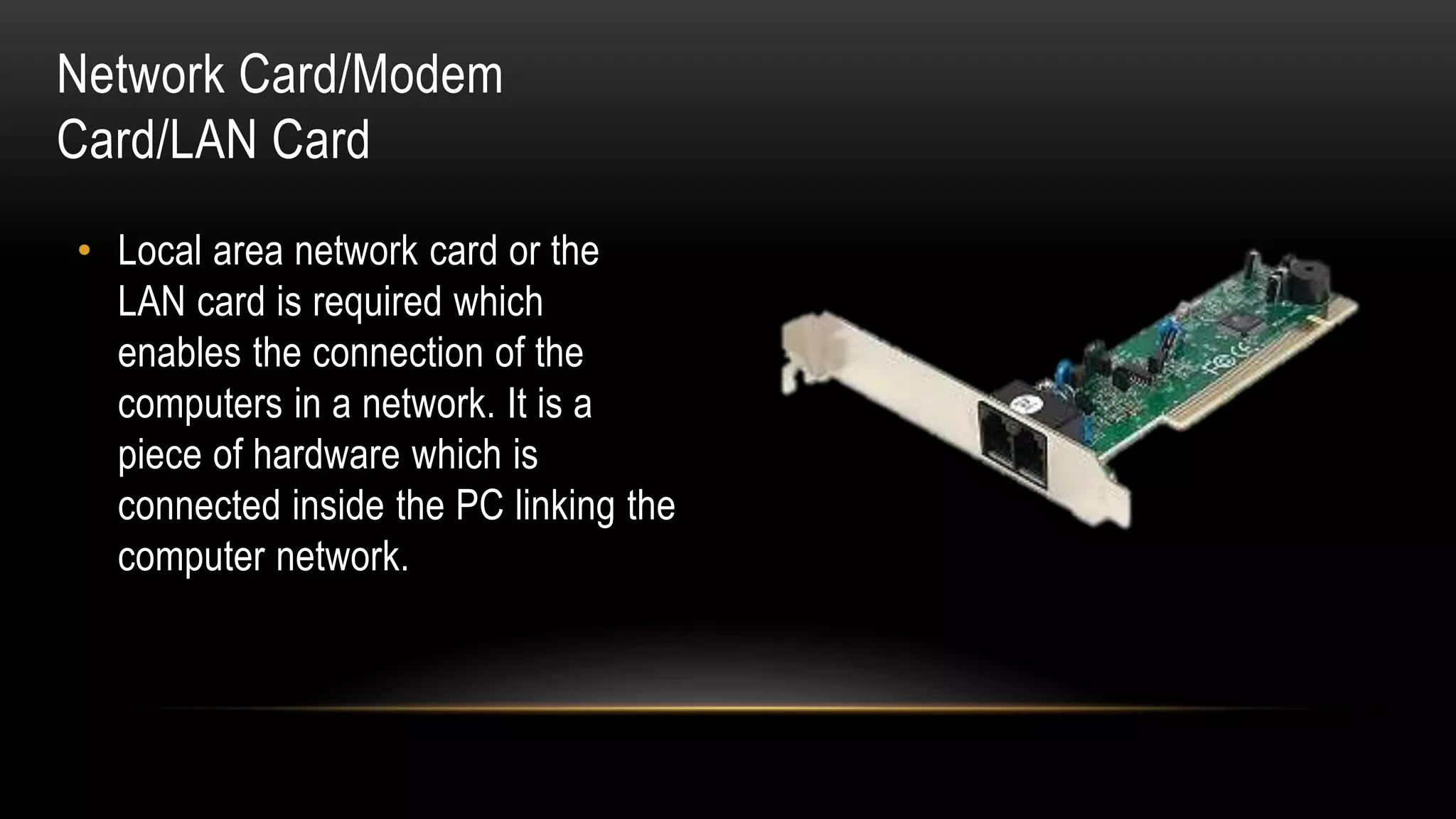
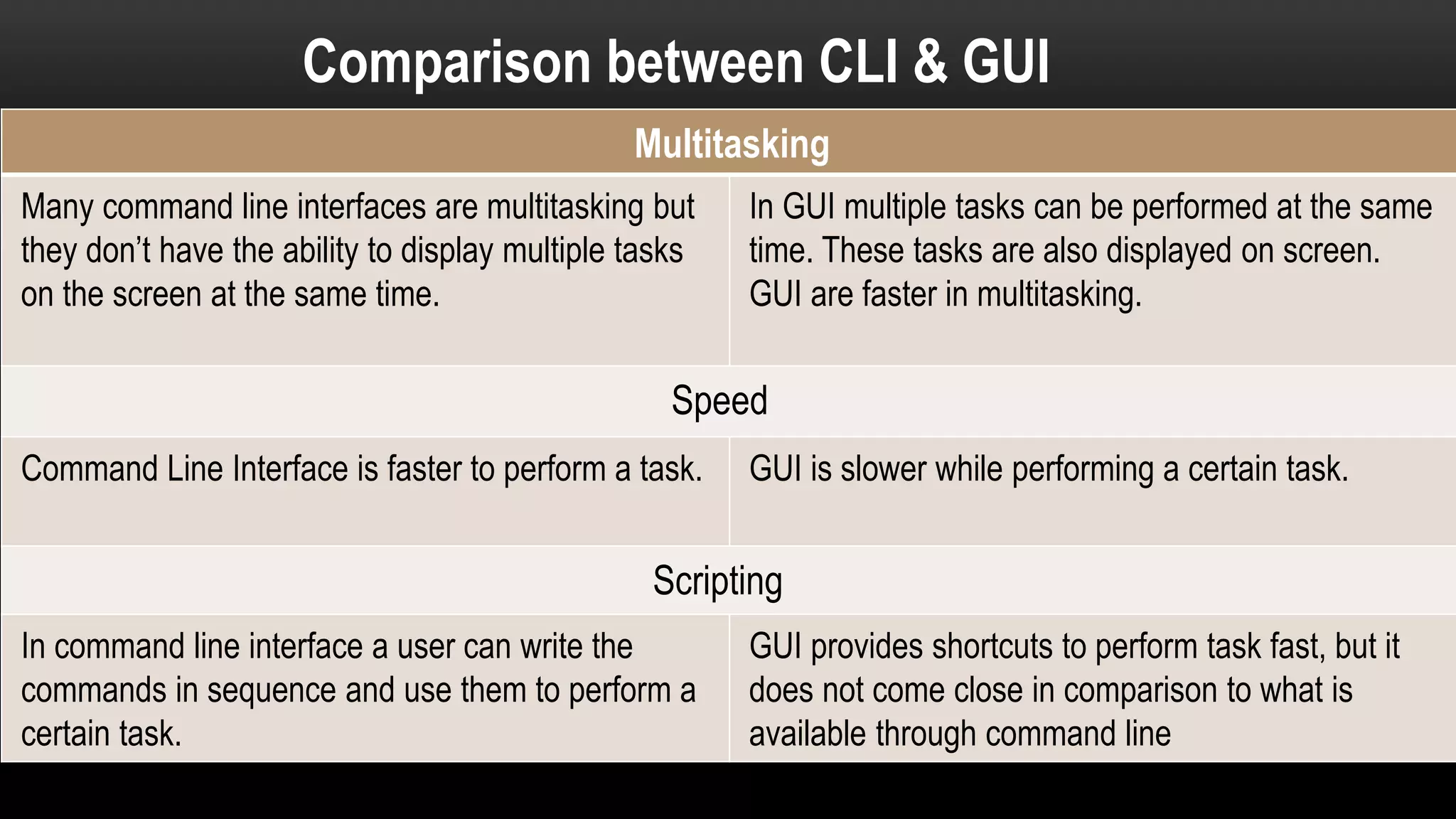
Motherboards connect the various components of a computer system and determine the computer's capabilities. They come in different form factors and have varying components depending on the intended use of the system. Faster motherboards support higher CPU speeds and more memory through wider data buses that transfer information between components. Buses, sockets, and adapter cards are key components that expand the motherboard's capabilities by allowing additional devices to connect and communicate with the CPU and other parts. Common adapter cards include video graphics cards, sound cards, and network interface cards. User interfaces also connect through the motherboard and can be command-line based or graphical user interfaces using icons, windows, and a mouse.