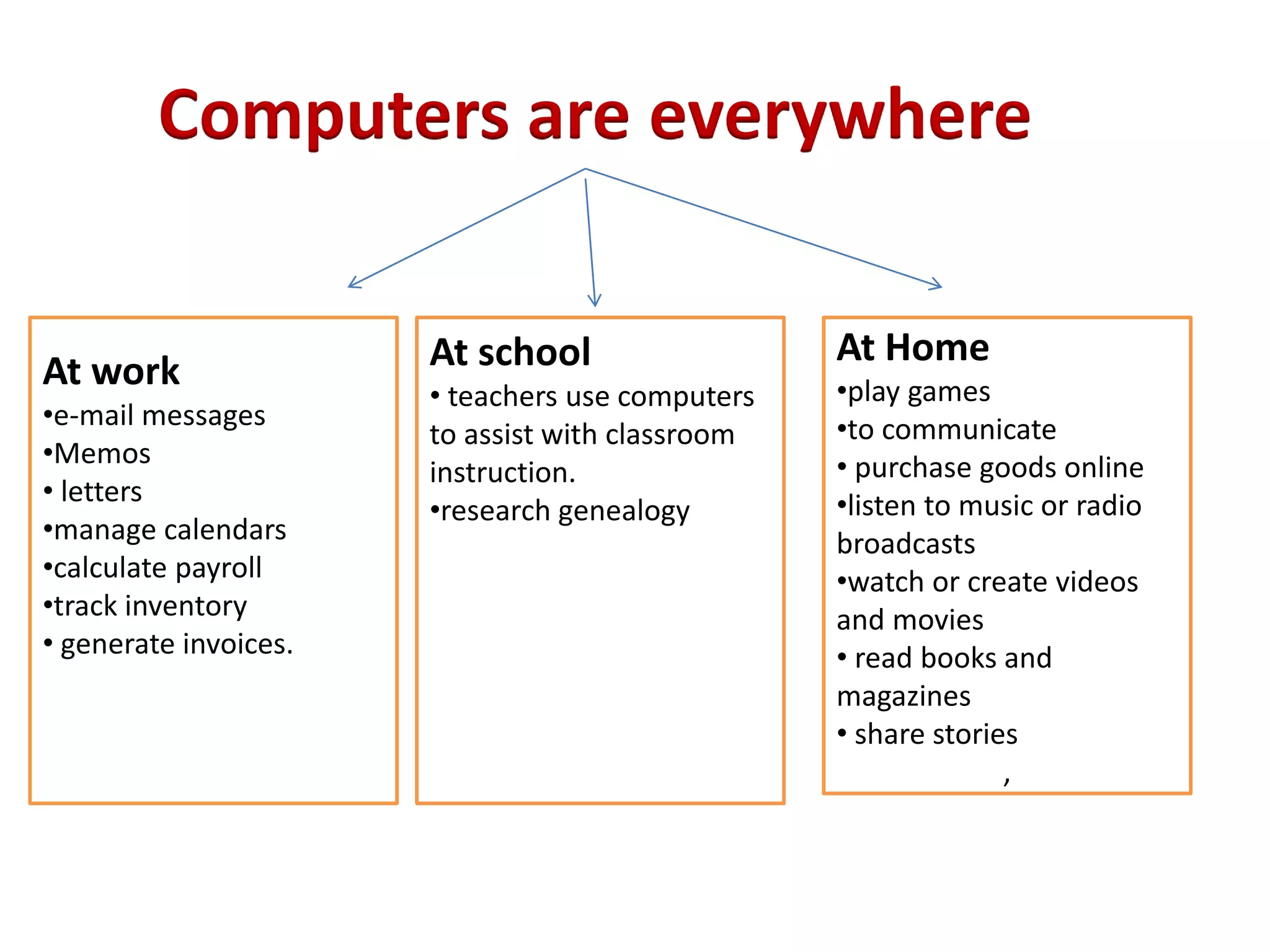
1. Computers are used everywhere at work, school, and home for tasks like email, research, games, communication, and entertainment.
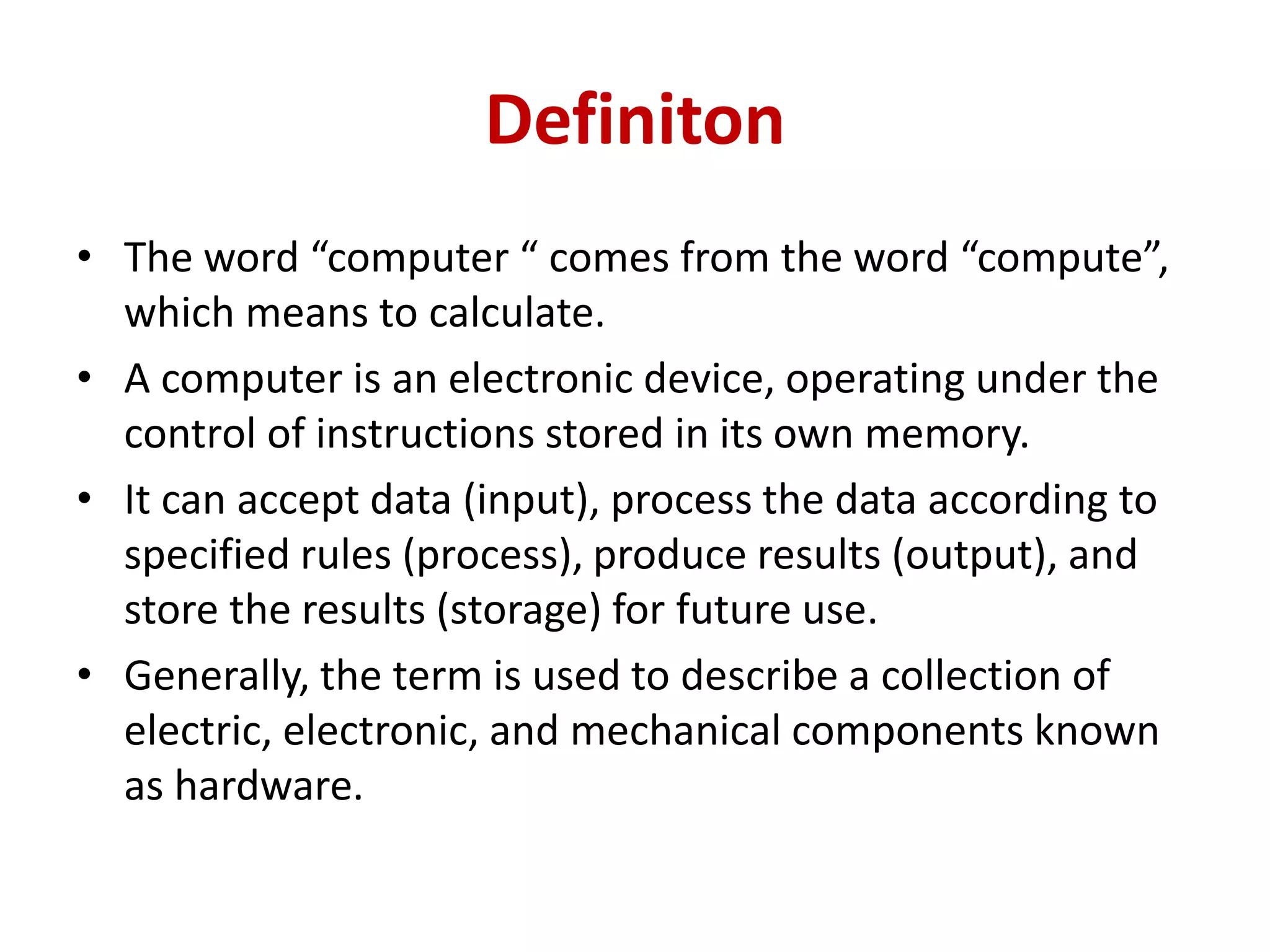
2. A computer is an electronic device that can accept data as input, process it, produce output, and store results. It uses hardware components like a CPU and memory to perform calculations at high speeds and store large amounts of information.
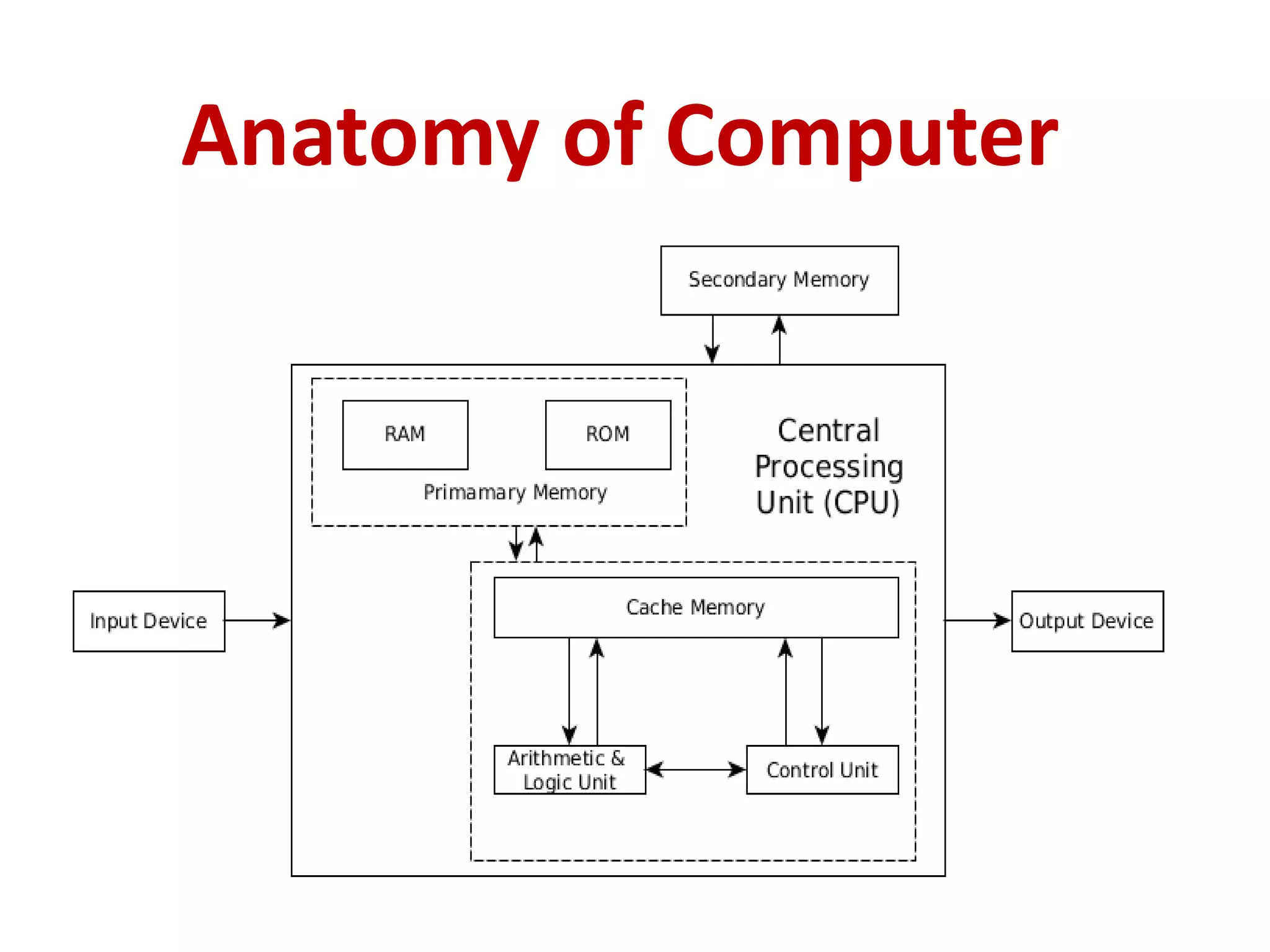
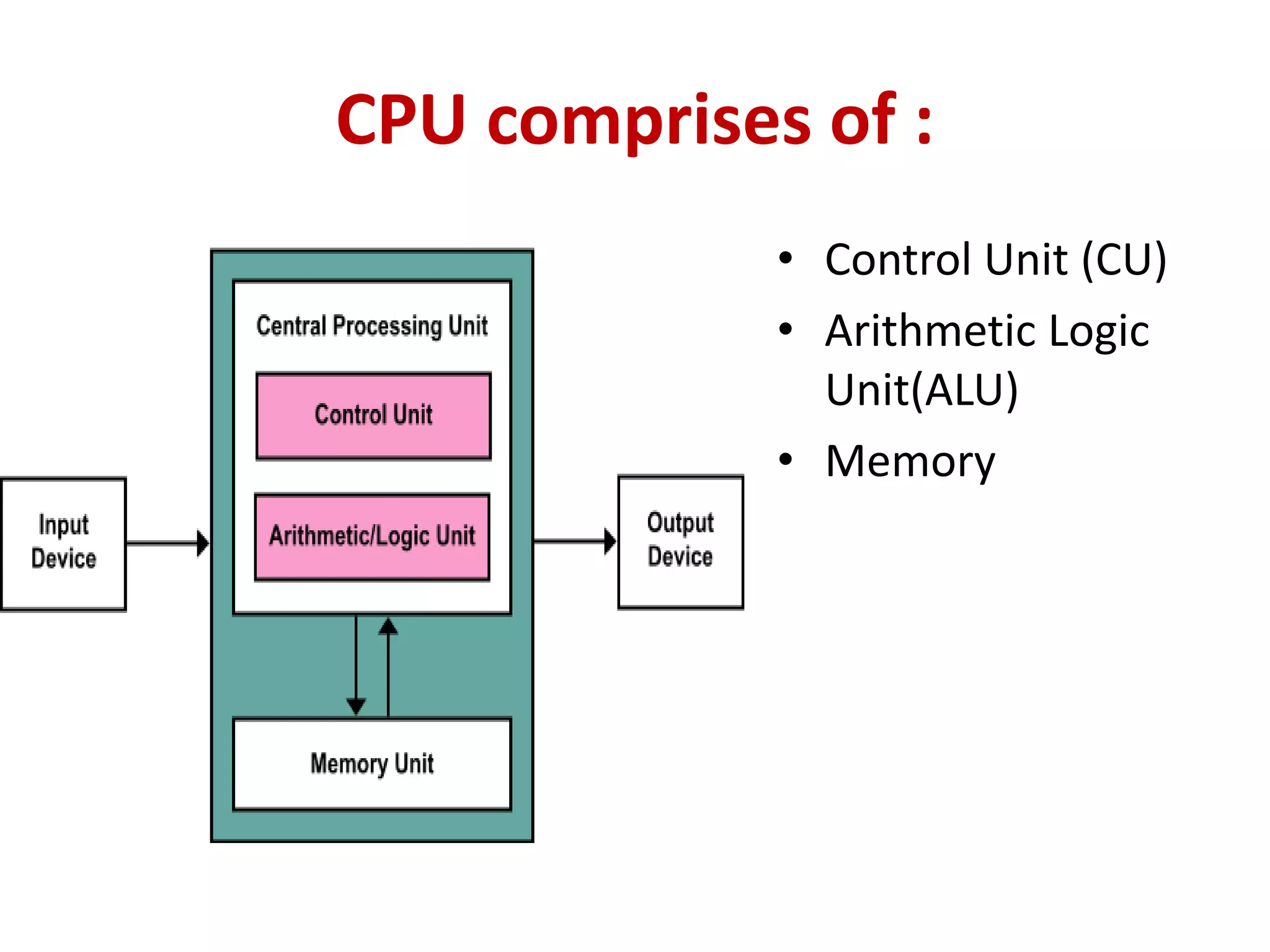
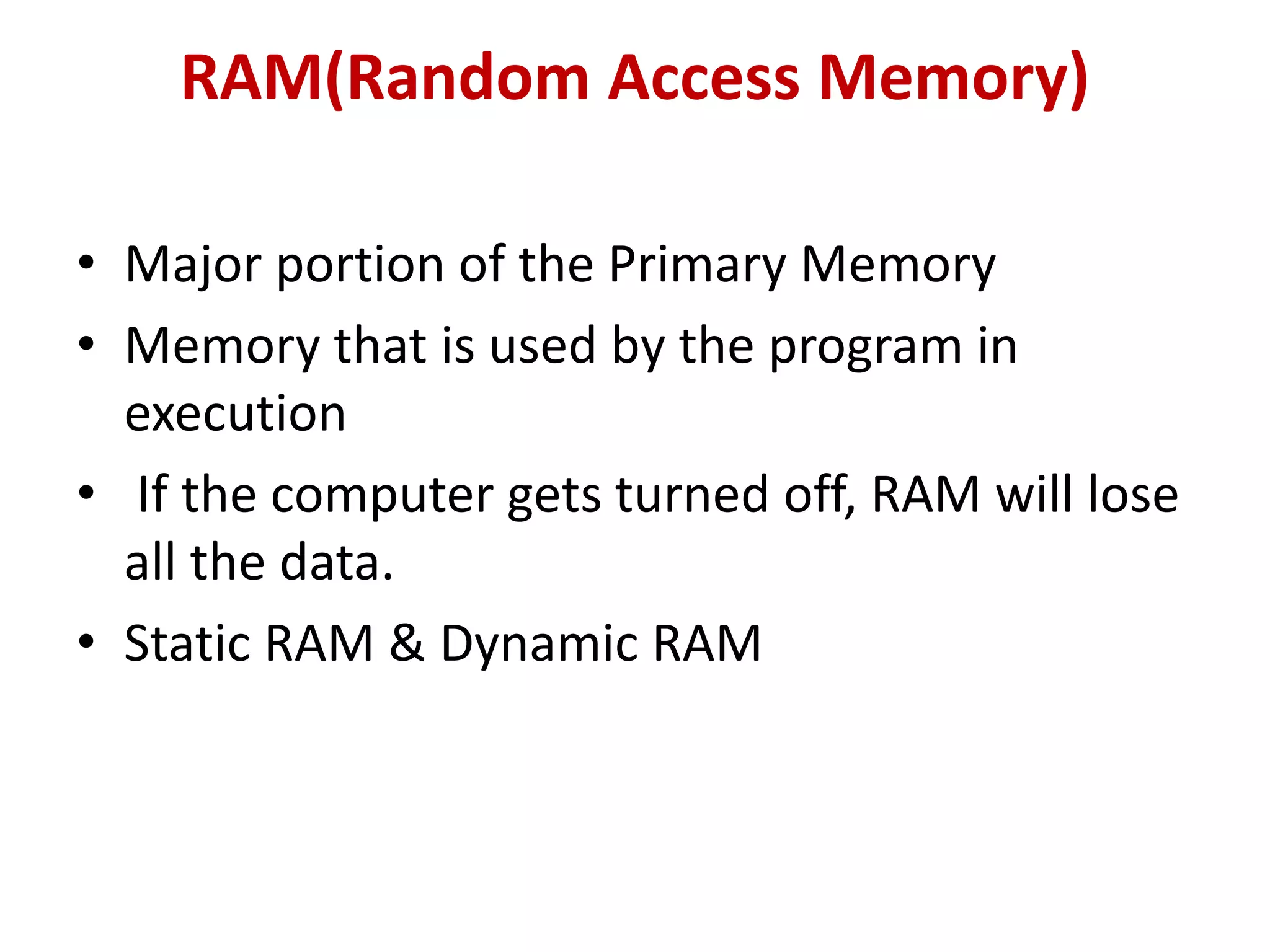
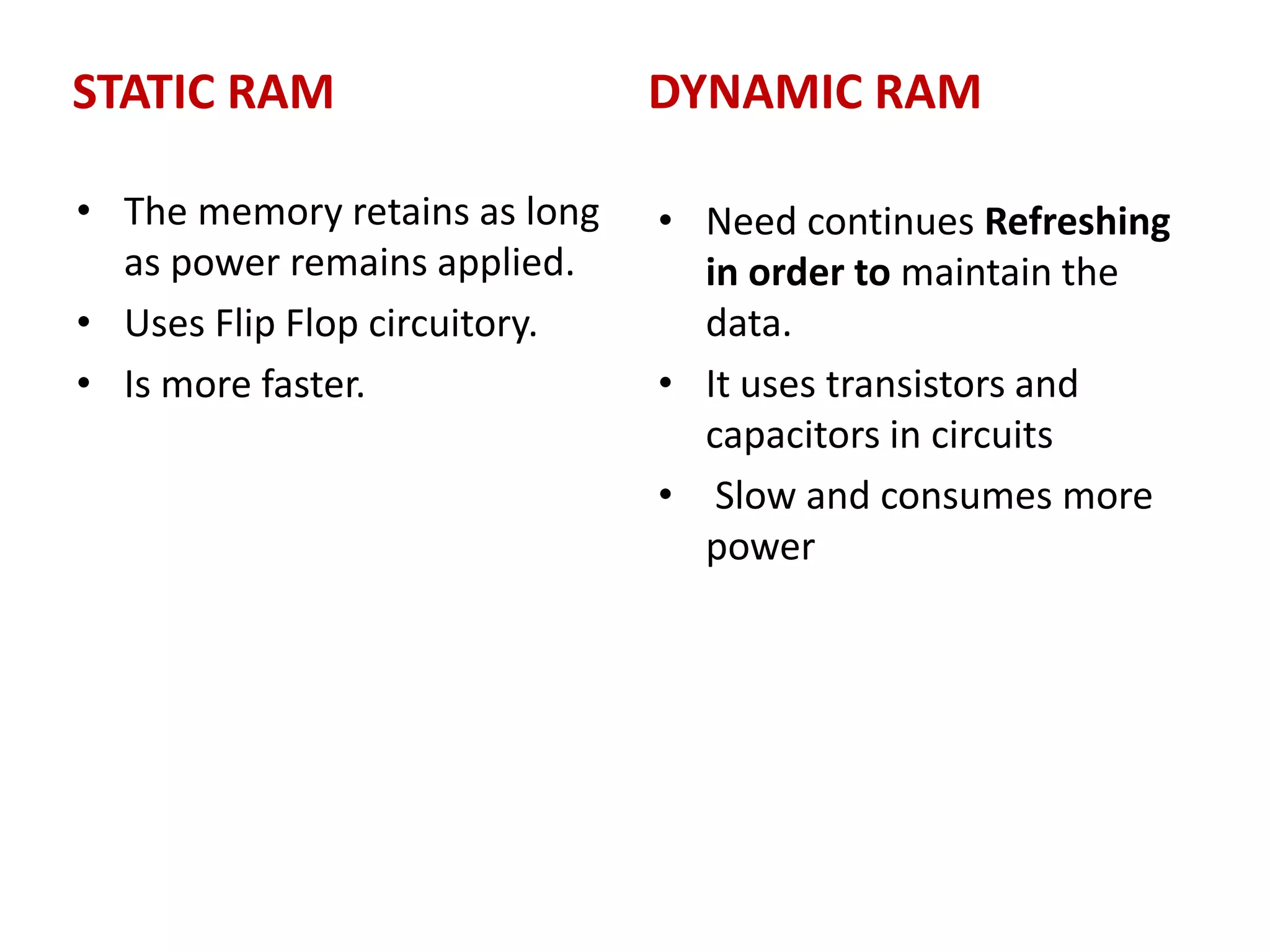
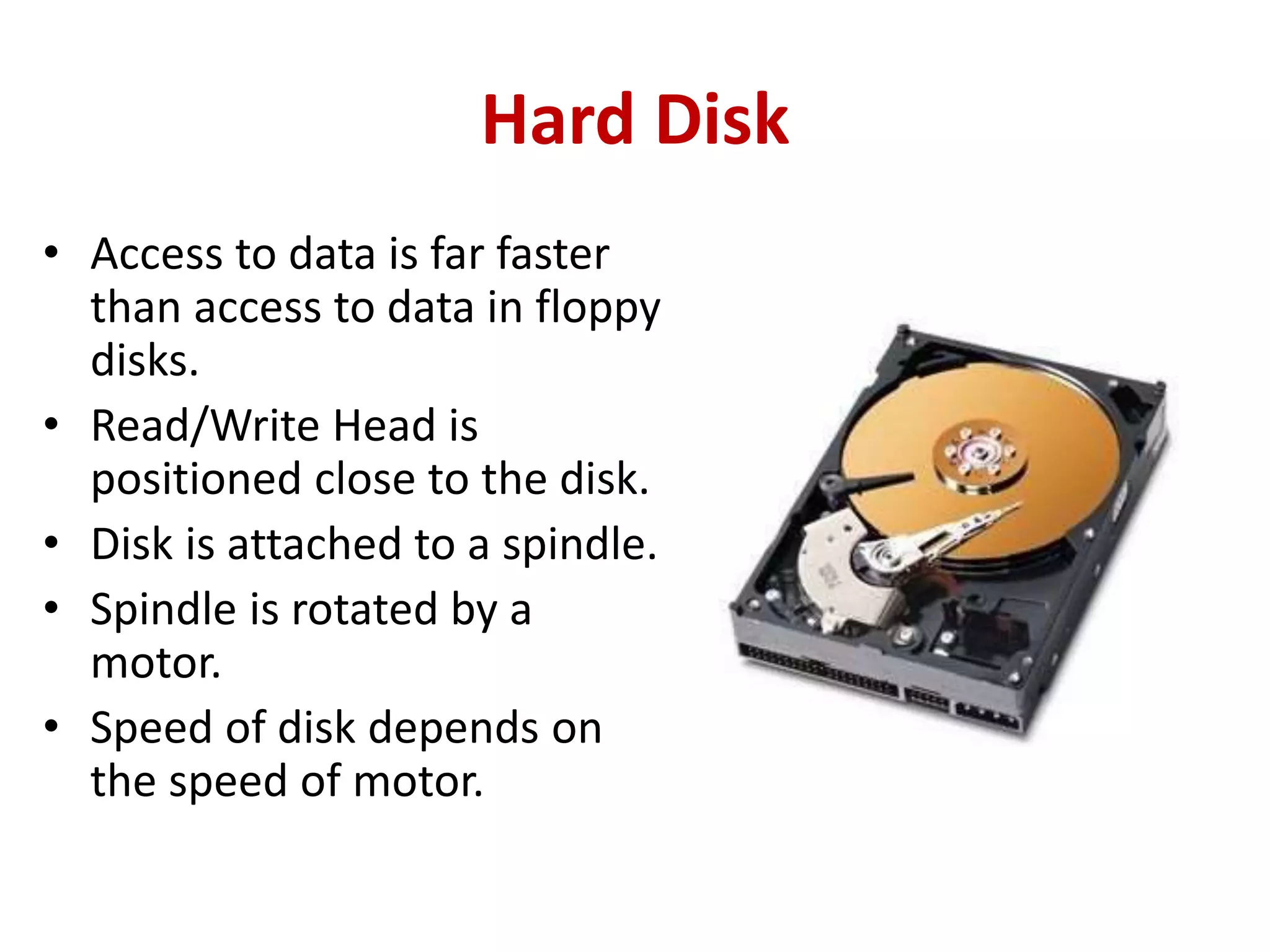
3. Key components of a computer system include input devices like keyboards and mice, a central processing unit (CPU) with an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) and control unit, and primary memory (RAM and ROM) as well as secondary memory like hard disks and optical disks for long-term storage.