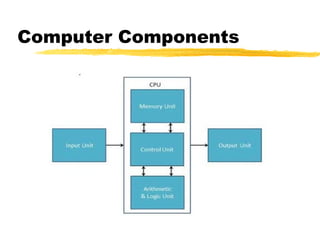
Computer components include the input unit, central processing unit (CPU), memory unit, control unit, and output unit. The CPU contains an arithmetic logic unit and control unit and acts as the brain of the computer by processing data. The memory unit stores instructions, data, and intermediate results to supply to other units. The control unit controls the transfer of data and instructions between units and coordinates the overall operations of the computer without processing data itself.