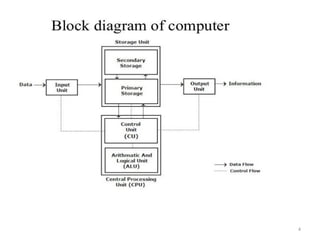
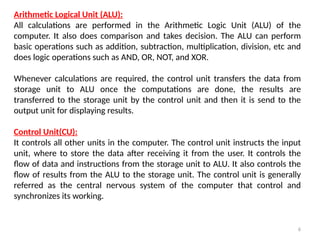
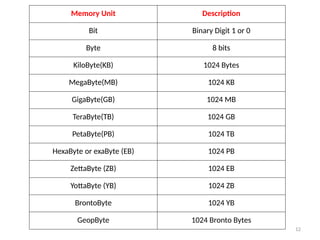
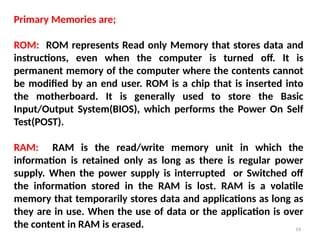
The document provides an overview of computers, defining them as electronic devices that process data and output information. It outlines the characteristics of computers, including speed, storage capacity, accuracy, reliability, versatility, and diligence, as well as detailing the main components such as the CPU, memory units, and input/output devices. Additionally, it discusses different types of memory, including RAM, ROM, and various storage solutions, emphasizing the distinction between data and information.